- Простые методы освобождения места в Linux Mint 21
- Простые методы освобождения места в Linux Mint 21
- 1: очистить корзину для мусора
- 2: очистить кэш обновлений
- 3: очистить кэш эскизов
- 4. Сделайте так, чтобы Firefox очищался автоматически
- 5: Работа с Flatpak и инфраструктурой Flatpak
- 6. Удалите старые и ненужные пакеты/ядра и кэш APT
- 7: Удалите ненужные шрифты
- Заключение
- How to Clean Up Disk Space on Linux Mint Distro
- How to Clean Up Disk Space on Linux Mint Distro?
- Clean up Disk Space Using Linux Terminal
- Remove the Redundant Applications
- Clean APT Cache
- Remove the Snap Packages
- Clean up Disk Space Using GUI Tools
- BleachBit
- Stacer
- Ubuntu Cleaner
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Prateek Jangid
Простые методы освобождения места в Linux Mint 21
Основная проблема нехватки места для хранения в Linux Mint снижает производительность Linux Mint. Он также не позволяет устанавливать новые приложения. Эта статья посвящена тому, как удалить неиспользуемые данные, чтобы освободить место в Linux Mint.
Простые методы освобождения места в Linux Mint 21
Чтобы освободить место в Linux Mint, вы можете использовать методы, указанные ниже:
- Пустой мусорный бак
- Очистите кэш обновлений
- Очистить кеш эскизов
- Заставить Firefox очистить себя
- Работа с Flatpak и инфраструктурой Flatpak
- Удалите старые и ненужные пакеты/ядра и кеш APT
- Удалить ненужные шрифты
1: очистить корзину для мусора
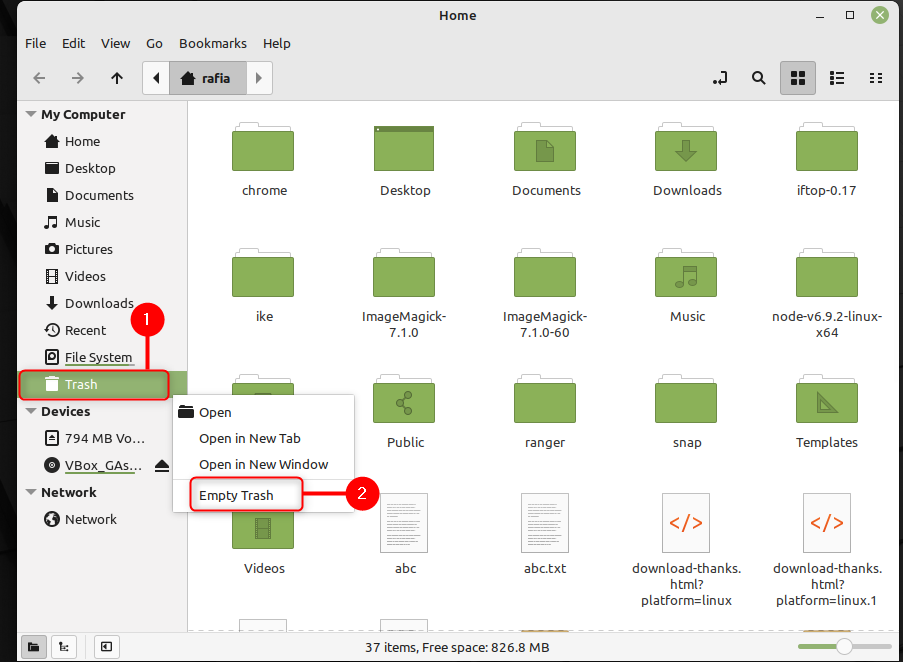
Всякий раз, когда вы собираетесь очистить свою систему, удалив файлы или программы, сначала очистите корзину. Для этого сначала щелкните правой кнопкой мыши на Дом а потом нажмите при открытии:
Теперь перейдите к Мусор, щелкните правой кнопкой мыши на нем, а затем нажмите Очистить корзину:
2: очистить кэш обновлений
Один из способов освободить место в Linux Mint — очистить кеш обновлений. Для этого выполните следующие шаги:
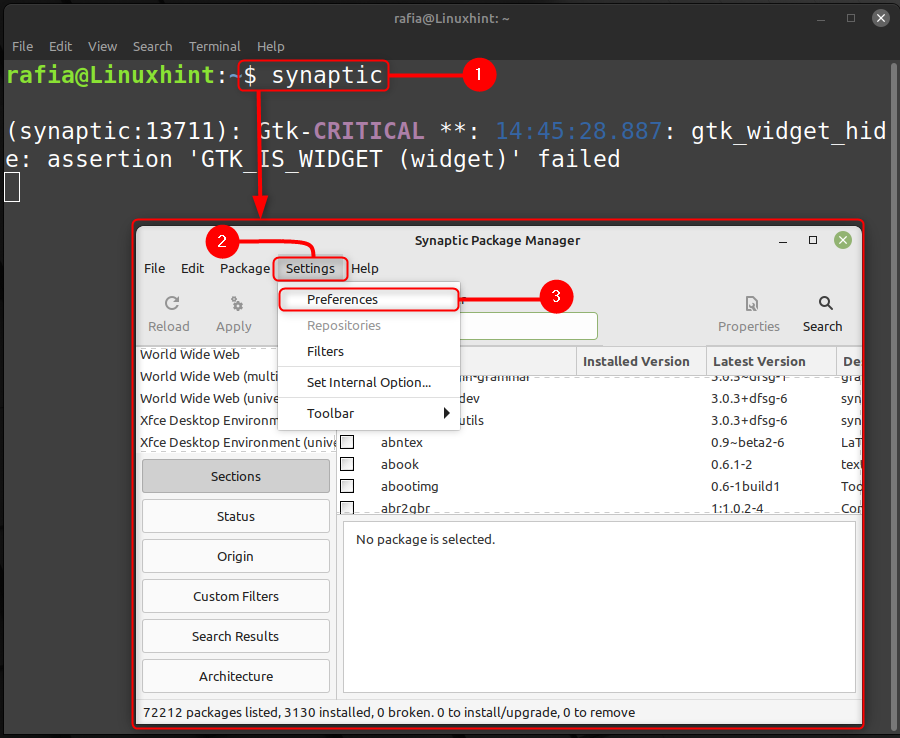
Шаг 1: Введите указанную ниже команду, чтобы запустить Синаптический менеджер пакетов, нажмите на Настройки и Настройки:
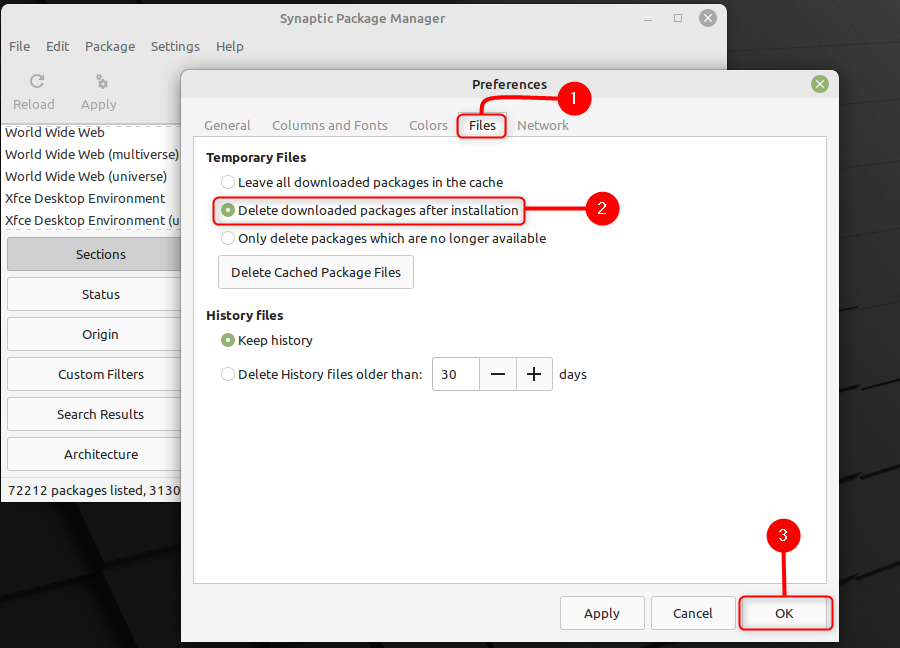
Шаг 2: В Настройки идти к Файлы и выберите Удалить пакеты загрузки после установки, а затем щелкните Хорошо.
3: очистить кэш эскизов
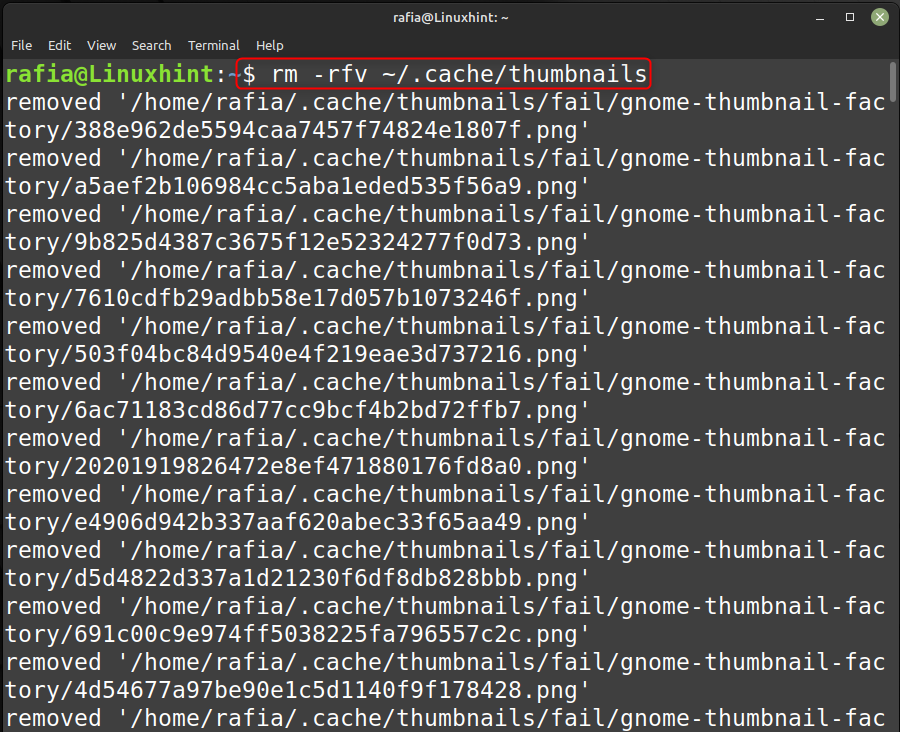
Вы также можете очистить кеш эскизов, выполнив шаги, указанные ниже:
Выполните указанную ниже команду, чтобы очистить весь кеш эскизов в системе Linux Mint:
4. Сделайте так, чтобы Firefox очищался автоматически
Для этого выполните шаги, указанные ниже:
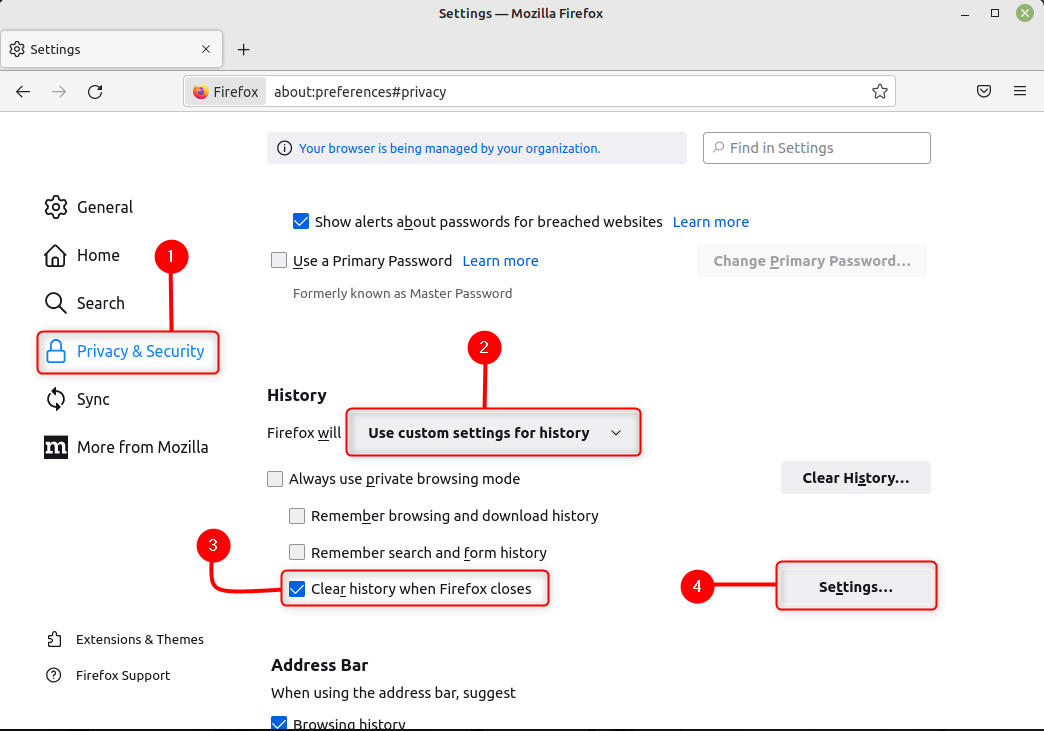
Шаг 1: Откройте браузер, щелкните значок меню браузера (значок гамбургера), затем нажмите Настройки:
Шаг 2: Теперь нажмите на Конфиденциальность и безопасность, прокрутите вниз и перейдите к истории, выберите Использовать пользовательские настройки для истории, отметьте Очистить историю при закрытии Firefox а затем, наконец, нажмите на Настройки перед ней:
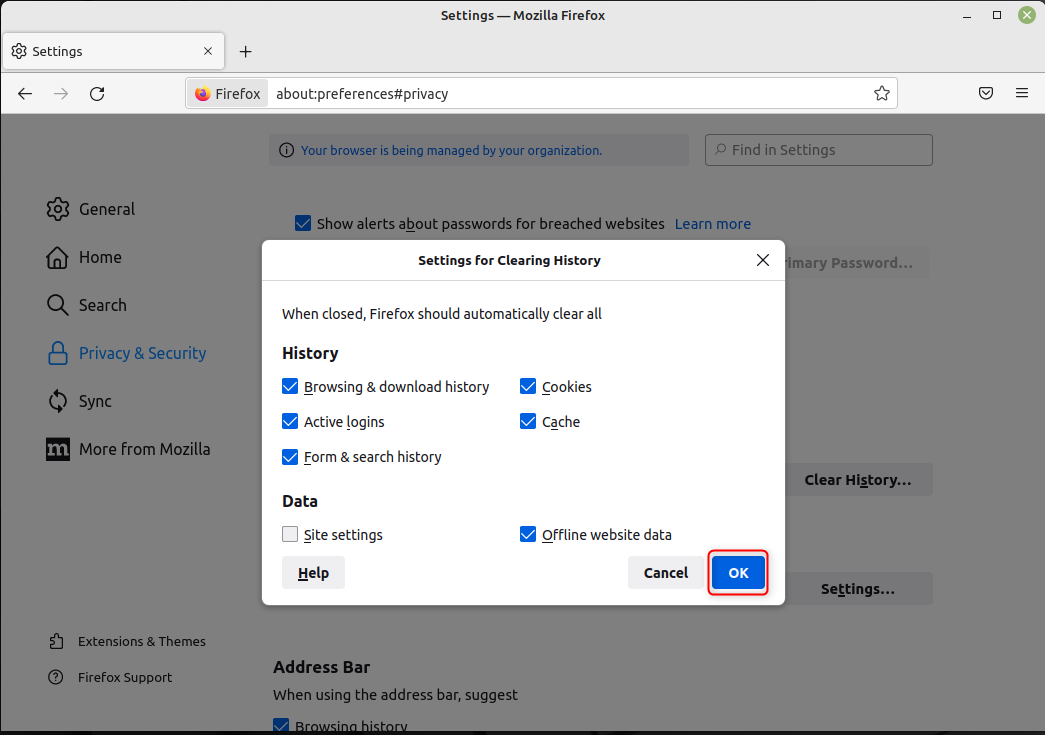
Шаг 3: В этих настройках отметьте все, кроме Настройки сайта и нажмите на ХОРОШО:
После этого закройте браузер и перезагрузите систему, чтобы изменения вступили в силу.
5: Работа с Flatpak и инфраструктурой Flatpak
Вы можете установить последнюю версию некоторых приложений с помощью Flatpak. Но это занимает больше места на диске, чем приложения, установленные с помощью других программ. Вы можете ограничить объем дискового пространства, используемого приложением, установленным с помощью Flatpak, выполнив шаги, указанные ниже:
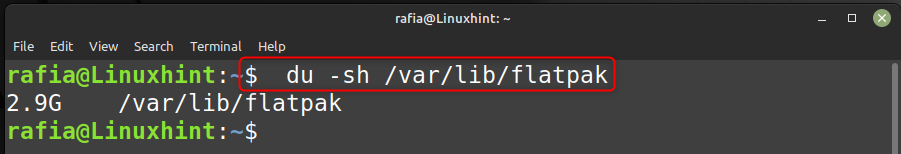
Шаг 1: выполните следующую команду, чтобы показать пространство, используемое Flatpak:
дю -ш / вар / библиотека / плоский пакет
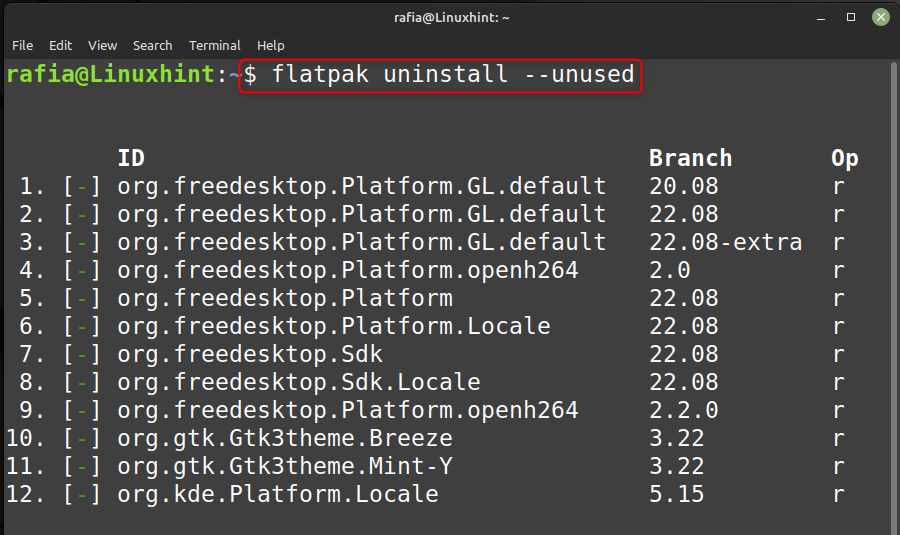
Шаг 2: Чтобы удалить приложение, которое не используется, выполните команду, указанную ниже:
удаление плоского пакета —неиспользованный
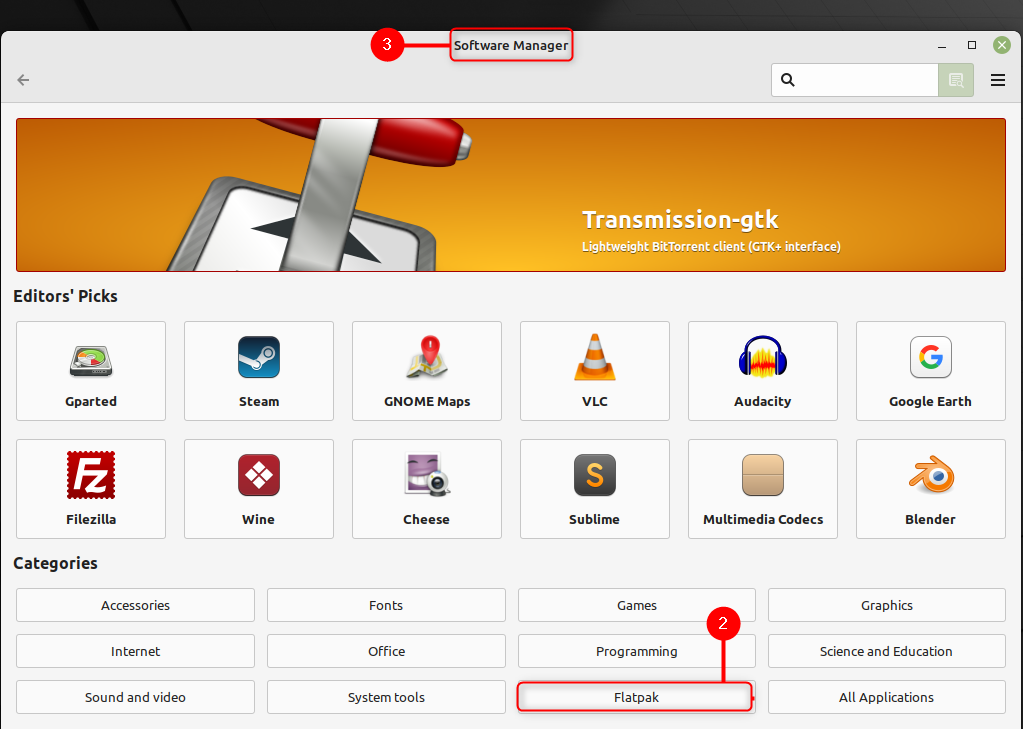
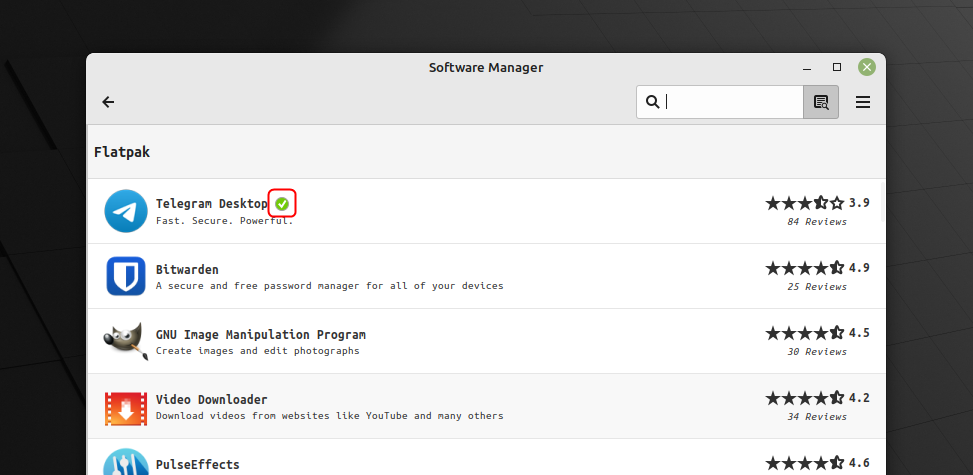
Шаг 3: Открой Программный менеджер нажмите на Плоский пакет:
Затем удалите все приложения, которые вы больше не используете, установленные приложения будут иметь зеленый значок с галочкой внутри, чтобы освободить место в вашей системе:
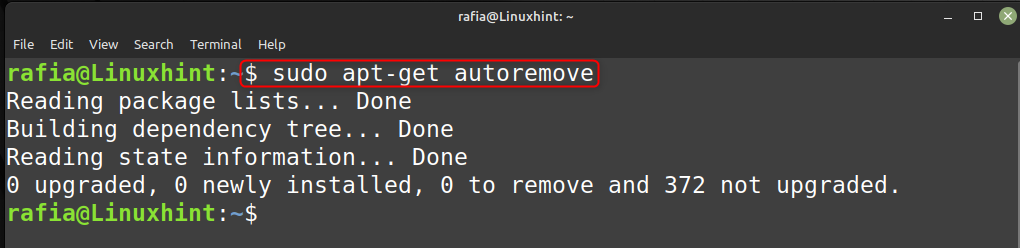
6. Удалите старые и ненужные пакеты/ядра и кэш APT
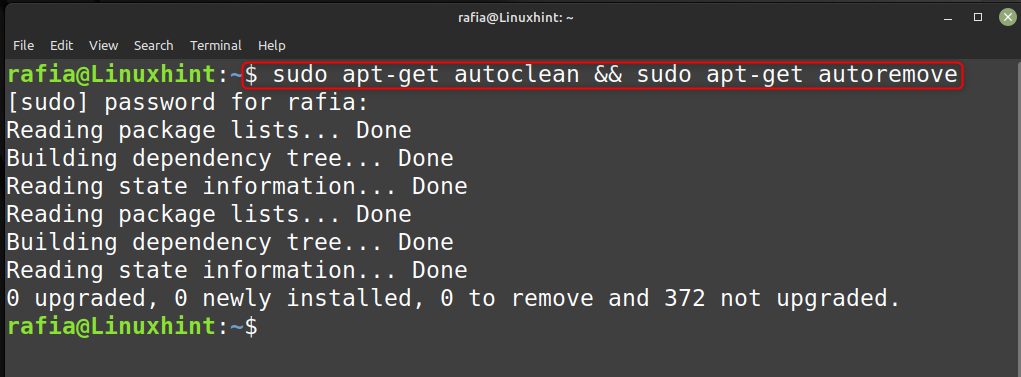
Чтобы удалить старые и ненужные пакеты/ядра и кэш Apt, вы можете выполнить команду, указанную ниже:
судо apt-получить автоочистку && судо apt-получить автоматическое удаление
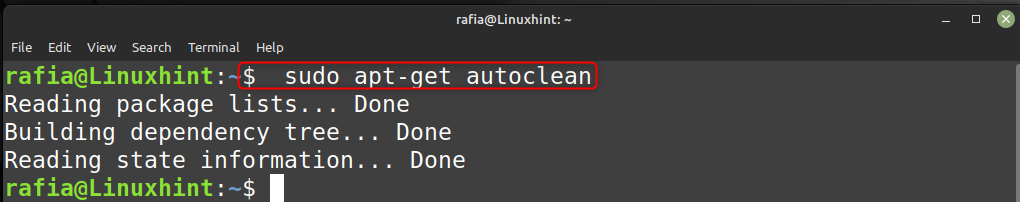
Чтобы очистить кеш apt, выполните команду, приведенную ниже:
судо apt-получить автоочистку
Чтобы удалить старые пакеты, выполните следующую команду:
судо apt-получить автоматическое удаление
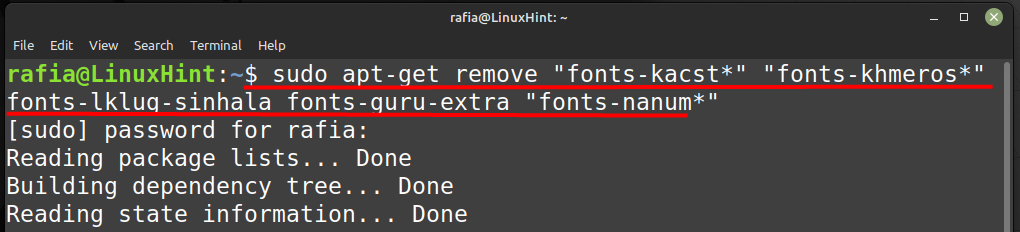
7: Удалите ненужные шрифты
Вы можете удалить неиспользуемые шрифты, для этого выполните шаги, указанные ниже:
Шаг 1: выполните указанную ниже команду, чтобы удалить шрифты:
судо удалить «шрифты-kacst*» «шрифты-хмерос*» шрифты-lklug-сингальские шрифты-гуру-дополнительно «шрифты-нанум*»
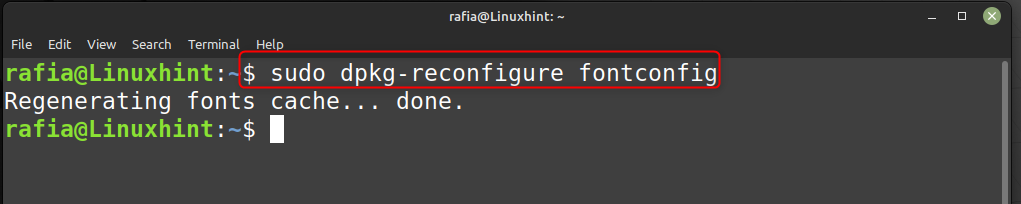
Шаг 2: теперь перенастройте кеш шрифтов, выполнив команду, указанную ниже:
судо dpkg-переконфигурировать fontconfig
Заключение
Вы можете освободить место на вашем Linux Mint, используя различные методы. Вы можете попробовать все методы, упомянутые в статье, чтобы освободить место на диске, включая очистку корзины, работа с Flatpak и инфраструктурами Flatpak, удаление неиспользуемых шрифтов, очистка истории посещенных страниц, кеша и более.
How to Clean Up Disk Space on Linux Mint Distro
It is no secret that junk files from installing new programs and updates can cause an operating system to slow down. These junk files can affect the performance and slow down the speed. Besides that, it can also seriously affect the performance of a system if there are unnecessary system files.
Operating systems such as Linux Mint and Ubuntu-based systems can have many clutter and logs. If your computer is old and space is not analyzed regularly, then it is required to declutter the system.
In case you’re also facing the same issues, here are a few easy ways to clean up disk space on Linux Mint Distro.
How to Clean Up Disk Space on Linux Mint Distro?
We will use two different ways to clean up disk space on Linux Mint Distro. First, we will use terminal and then GUI tools for clearing the disk space.
Clean up Disk Space Using Linux Terminal
You can launch the terminal using CTRL+ALT+T or search for “terminal” from dash (it’s like Ubuntu’s start menu).
In case you want to see the current disk space, use the command below:
You will get an output like this:
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use % Mounted on
udev 5G 0G 1G 0 % / dev
tmpfs 1G 0G 1G 1 % / run
/ dev / sda1 30G 0G 6.3G 60 % /
And you will get an output like this:
Remove the Redundant Applications
Now, execute the following command for listing the installed packages in the system:
After that, run the command below and replace the package_name with the name of the package you want to remove:
In case you want to remove multiple packages at once, type the following command and replace package_name1, package_name2 with the name of the packages you want to remove:
This way, you can remove multiple packages straight away.
In case you run out of storage capacity, remove unnecessary applications to free up space. We all have some applications that we rarely use and various system left-over files of deleted applications, so it is better to uninstall and remove them.
Execute the command below to perform the package file remove procedure:
The package name is the name of the application you want to delete. This removes the programs along with the configuration files created at the time of installation.
The major difference between apt remove and apt purge is that apt remove removes the package’s binaries by leaving reside configuration files. On the other hand, apt purge works to remove every package file, including all configuration files.
In case you use apt remove to delete a specific package and install it again, then that package will work on the same configuration files. The system will ask you to overwrite the configuration files while reinstalling the package.
Using an apt purge can remove everything regarding a specific package and the package will create new configuration files during re-installation.
You can also use the following command to remove all of the package and dependencies which are not required:
In case you want to clear the APT cache only, then execute this command:
You can use sudo apt-get autoremove to remove and clean all of the old packages.
Clean APT Cache
APT is the acronym of Advanced Package Tool present in UBUNTU systems which is used to install, remove and upgrade the software on the system.
In simple words, it is used to manage applications. Installing and uninstalling software keeps the generated cache within itself even after uninstalling apps, resulting in cluttering the space with unnecessary cache files that may increase in size with time.
The du command helps you know the disk usage information which you can use to determine how much cache file is present on the system.
Use the command below to gain cache information:
The above code will remove the content of the /var/cache/apt/archives directory.
If you don’t have enough storage and cache files are large, you can clean the apt-cache with this dedicated command:
Remove the Snap Packages
Snap packages are big packages containing some dependencies. It is one of the major downsides of snap packages. By uninstalling such bulky packages, you can reclaim a lot of free space being taken up by these packages. There’s a simple way to delete snaps to free a large amount of storage used by snap packages.
Use the command below to list snap packages:
Remove the snap by typing the following command:
To remove snapd, use the command below:
Now you have successfully removed the snap packages you didn’t want to be on the system. Also, you can use the working scripts to perform the same task.
Clean up Disk Space Using GUI Tools
Graphical User Interface saves you from writing dull commands and offers an aesthetically pleasing interface with plenty of options to perform the task you do with the command-line interface. It is easy to use especially for those who are not comfortable with command-line utility.
BleachBit
With plenty of good features to free up space quickly, BleachBit comes in handy when your system runs out of space. You can delete cache, cookies, logs, junks and remove temporary files.
You can use it by following the steps given below:
- Download the latest version of BleachBit from here.
- Launch the app, and you will see two options: preview and clean.
- It will show you files like caches, cookies, apps’ data, junks, etc.
- Select the files and tap and clean.
- This way, you can free up space and remove unnecessary files quickly.
Stacer
Stacer is one of the great tools that comes up with rich features to optimize the system. The dashboard shows your system’s information (like CPU usage, disk space, memory) and the other system cleaner and uninstaller features.
System cleaner removes the junk files that includes app cache, apt-cache, system logs, and other unnecessary files. On the other hand, the uninstaller lets you delete all the applications installed on your system. You can use it by following the steps below:
- Start the app using the command $ stacer.
- Head to the dashboard to declutter space and remove redundant files through its appealing graphical user interface.
Ubuntu Cleaner
Ubuntu Cleaner is another GUI tool that helps you free up the disk space and wipe out unnecessary files like caches, unneeded packages, old kernels, etc.
It is an amazing tool. So, if you want to use it then follow the steps given below:
- Search for the “Ubuntu cleaner” in the app directory.
- Open app to clean up the system.
- It offers you a clean dashboard to quickly get rid of unnecessary files.
Conclusion
The operating system should be neat and clean. Junks, system logs, cache application leftovers can make a system slow thus affecting the performance badly and eventually putting a system to potential threats.
Often, we get a lot of mess on the system because we are not aware on how to organize the system by removing unnecessary and duplicate files, making the system slow. You can regain the used space by unnecessary files with command line terminal or the use of GUI apps, which we have already mentioned in this article.
We hope that this article will help you declutter the disk space to enhance the performance of your operating system. Do let us know if you have any further queries or tips.
About the author
Prateek Jangid
A passionate Linux user for personal and professional reasons, always exploring what is new in the world of Linux and sharing with my readers.