- Introduction to the 1-wire (w1) subsystem¶
- What does the w1 subsystem do?¶
- W1 device families¶
- What does a w1 master driver need to implement?¶
- w1 master sysfs interface¶
- w1 slave sysfs interface¶
- Introduction to the 1-wire (w1) subsystem¶
- What does the w1 subsystem do?¶
- W1 device families¶
- What does a w1 master driver need to implement?¶
- w1 master sysfs interface¶
- w1 slave sysfs interface¶
- How to use the 1-WIRE bus
- Dallas/Maxim DS18B20 thermal sensor
- Pinout of 1-wire
- Enable the Linux Kernel 1-wire driver
- Configure the device tree
- Arietta G25 wirings
- Read the temperature
- Reading the temperature in Python
- Links
Introduction to the 1-wire (w1) subsystem¶
The 1-wire bus is a simple master-slave bus that communicates via a single signal wire (plus ground, so two wires).
Devices communicate on the bus by pulling the signal to ground via an open drain output and by sampling the logic level of the signal line.
The w1 subsystem provides the framework for managing w1 masters and communication with slaves.
All w1 slave devices must be connected to a w1 bus master device.
Example w1 master devices:
- DS9490 usb device
- W1-over-GPIO
- DS2482 (i2c to w1 bridge)
- Emulated devices, such as a RS232 converter, parallel port adapter, etc
What does the w1 subsystem do?¶
When a w1 master driver registers with the w1 subsystem, the following occurs:
- sysfs entries for that w1 master are created
- the w1 bus is periodically searched for new slave devices
When a device is found on the bus, w1 core tries to load the driver for its family and check if it is loaded. If so, the family driver is attached to the slave. If there is no driver for the family, default one is assigned, which allows to perform almost any kind of operations. Each logical operation is a transaction in nature, which can contain several (two or one) low-level operations. Let’s see how one can read EEPROM context: 1. one must write control buffer, i.e. buffer containing command byte and two byte address. At this step bus is reset and appropriate device is selected using either W1_SKIP_ROM or W1_MATCH_ROM command. Then provided control buffer is being written to the wire. 2. reading. This will issue reading eeprom response.
It is possible that between 1. and 2. w1 master thread will reset bus for searching and slave device will be even removed, but in this case 0xff will be read, since no device was selected.
W1 device families¶
Slave devices are handled by a driver written for a family of w1 devices.
A family driver populates a struct w1_family_ops (see w1_family.h) and registers with the w1 subsystem.
- (ds18?20 thermal sensor family driver) provides temperature reading function which is bound to ->rbin() method of the above w1_family_ops structure.
- driver for simple 64bit memory cell provides ID reading method.
You can call above methods by reading appropriate sysfs files.
What does a w1 master driver need to implement?¶
The driver for w1 bus master must provide at minimum two functions.
Emulated devices must provide the ability to set the output signal level (write_bit) and sample the signal level (read_bit).
Devices that support the 1-wire natively must provide the ability to write and sample a bit (touch_bit) and reset the bus (reset_bus).
Most hardware provides higher-level functions that offload w1 handling. See struct w1_bus_master definition in w1.h for details.
w1 master sysfs interface¶
A directory for a found device. The format is family-serial
(standard) symlink to the w1 bus
(standard) symlink to the w1 driver
(rw) manually register a slave device
(ro) the number of times a search was attempted
(rw) maximum number of slaves to search for at a time
(ro) the name of the device (w1_bus_masterX)
(rw) 5V strong pullup 0 enabled, 1 disabled
(rw) manually remove a slave device
(rw) the number of searches left to do, -1=continual (default)
(ro) the number of slaves found
(ro) the names of the slaves, one per line
(ro) the delay in seconds between searches
(ro) the delay in microseconds beetwen searches
If you have a w1 bus that never changes (you don’t add or remove devices), you can set the module parameter search_count to a small positive number for an initially small number of bus searches. Alternatively it could be set to zero, then manually add the slave device serial numbers by w1_master_add device file. The w1_master_add and w1_master_remove files generally only make sense when searching is disabled, as a search will redetect manually removed devices that are present and timeout manually added devices that aren’t on the bus.
Bus searches occur at an interval, specified as a sum of timeout and timeout_us module parameters (either of which may be 0) for as long as w1_master_search remains greater than 0 or is -1. Each search attempt decrements w1_master_search by 1 (down to 0) and increments w1_master_attempts by 1.
w1 slave sysfs interface¶
(standard) symlink to the w1 bus
(standard) symlink to the w1 driver
the device name, usually the same as the directory name
(optional) a binary file whose meaning depends on the family driver
(optional) created for slave devices which do not have appropriate family driver. Allows to read/write binary data.
Introduction to the 1-wire (w1) subsystem¶
The 1-wire bus is a simple master-slave bus that communicates via a single signal wire (plus ground, so two wires).
Devices communicate on the bus by pulling the signal to ground via an open drain output and by sampling the logic level of the signal line.
The w1 subsystem provides the framework for managing w1 masters and communication with slaves.
All w1 slave devices must be connected to a w1 bus master device.
Example w1 master devices:
- DS9490 usb device
- W1-over-GPIO
- DS2482 (i2c to w1 bridge)
- Emulated devices, such as a RS232 converter, parallel port adapter, etc
What does the w1 subsystem do?¶
When a w1 master driver registers with the w1 subsystem, the following occurs:
- sysfs entries for that w1 master are created
- the w1 bus is periodically searched for new slave devices
When a device is found on the bus, w1 core tries to load the driver for its family and check if it is loaded. If so, the family driver is attached to the slave. If there is no driver for the family, default one is assigned, which allows to perform almost any kind of operations. Each logical operation is a transaction in nature, which can contain several (two or one) low-level operations. Let’s see how one can read EEPROM context: 1. one must write control buffer, i.e. buffer containing command byte and two byte address. At this step bus is reset and appropriate device is selected using either W1_SKIP_ROM or W1_MATCH_ROM command. Then provided control buffer is being written to the wire. 2. reading. This will issue reading eeprom response.
It is possible that between 1. and 2. w1 master thread will reset bus for searching and slave device will be even removed, but in this case 0xff will be read, since no device was selected.
W1 device families¶
Slave devices are handled by a driver written for a family of w1 devices.
A family driver populates a struct w1_family_ops (see w1_family.h) and registers with the w1 subsystem.
- (ds18?20 thermal sensor family driver) provides temperature reading function which is bound to ->rbin() method of the above w1_family_ops structure.
- driver for simple 64bit memory cell provides ID reading method.
You can call above methods by reading appropriate sysfs files.
What does a w1 master driver need to implement?¶
The driver for w1 bus master must provide at minimum two functions.
Emulated devices must provide the ability to set the output signal level (write_bit) and sample the signal level (read_bit).
Devices that support the 1-wire natively must provide the ability to write and sample a bit (touch_bit) and reset the bus (reset_bus).
Most hardware provides higher-level functions that offload w1 handling. See struct w1_bus_master definition in w1.h for details.
w1 master sysfs interface¶
A directory for a found device. The format is family-serial
(standard) symlink to the w1 bus
(standard) symlink to the w1 driver
(rw) manually register a slave device
(ro) the number of times a search was attempted
(rw) maximum number of slaves to search for at a time
(ro) the name of the device (w1_bus_masterX)
(rw) 5V strong pullup 0 enabled, 1 disabled
(rw) manually remove a slave device
(rw) the number of searches left to do, -1=continual (default)
(ro) the number of slaves found
(ro) the names of the slaves, one per line
(ro) the delay in seconds between searches
(ro) the delay in microseconds beetwen searches
If you have a w1 bus that never changes (you don’t add or remove devices), you can set the module parameter search_count to a small positive number for an initially small number of bus searches. Alternatively it could be set to zero, then manually add the slave device serial numbers by w1_master_add device file. The w1_master_add and w1_master_remove files generally only make sense when searching is disabled, as a search will redetect manually removed devices that are present and timeout manually added devices that aren’t on the bus.
Bus searches occur at an interval, specified as a sum of timeout and timeout_us module parameters (either of which may be 0) for as long as w1_master_search remains greater than 0 or is -1. Each search attempt decrements w1_master_search by 1 (down to 0) and increments w1_master_attempts by 1.
w1 slave sysfs interface¶
(standard) symlink to the w1 bus
(standard) symlink to the w1 driver
the device name, usually the same as the directory name
(optional) a binary file whose meaning depends on the family driver
(optional) created for slave devices which do not have appropriate family driver. Allows to read/write binary data.
How to use the 1-WIRE bus
1-Wire is a device communications bus system designed by Dallas Semiconductor that provides low-speed data, signaling, and power over a single signal. 1-Wire is similar in concept to I2C, but with lower data rates and longer range. It is typically used to communicate with small inexpensive devices such as digital thermometers and weather instruments.
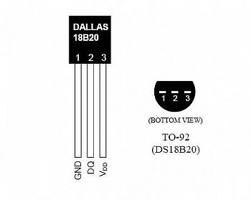
Dallas/Maxim DS18B20 thermal sensor
The DS18B20 digital thermometer provides 9-bit to 12-bit Celsius temperature measurements. It communicates over a 1-Wire bus that by definition requires only one data line (and ground) for communication with a central microprocessor.
It has an operating temperature range of -55°C to +125°C and is accurate to ±0.5°C over the range of °10°C to +85°C. (read more on datasheet).
Pinout of 1-wire
The 1-wire bus is managed in bit banging so anu GPIO can be used as 1-wire bus. The pin used depends from the device tree definition
Enable the Linux Kernel 1-wire driver
Follow this tutorial: to know how to cross compile the Linux Kernel and how to configure the drivers to enable inside it.
Enable the Dallas’s 1-wire support and the Thermal family implementation as shown below:
Device Drivers ---> Dallas's 1-wire support 1-wire Bus Masters ---> GPIO 1-wire busmaster 1-wire Slaves ---> Thermal family implementation Configure the device tree
Edit the device tree source of your board adding these lines:
onewire@0 < compatible = "w1-gpio"; gpios = ; pinctrl-names = "default"; pinctrl-0 = ; >; Changing the gpio parameter you can chaneg the GPIO to use as 1-wire bus
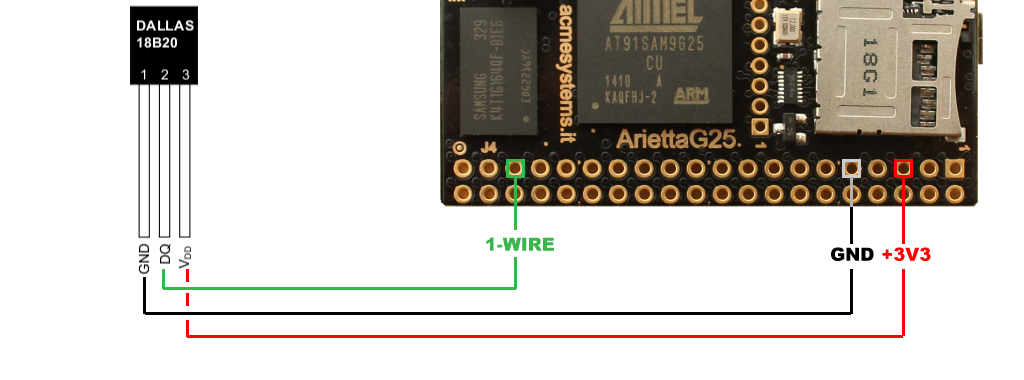
Arietta G25 wirings
Following is an example on how to wire a Dallas 1-wire sensor to the Arietta G25 using the port PC2 (J4.35). It is possible to wire more sensors on the same lines. Don’t forget to enable the 1-wire bus on the device tree file using this utility: Arietta pinout.
Read the temperature
The 1-wire driver automatically scans every 10 seconds if new sensors are plugged on the 1-wire bus.
For each 1-wire device detected a new directory is created on /sys/bus/w1/devices/w1 bus master.
cd "/sys/bus/w1/devices/w1 bus master" ls 28-0000028f6667 w1_master_add w1_master_remove 28-0000028fa89c w1_master_attempts w1_master_search driver w1_master_max_slave_count w1_master_slave_count power w1_master_name w1_master_slaves subsystem w1_master_pointer w1_master_timeout uevent w1_master_pullup The two directories 28-xxxx indicate that two thermal sensors are probed on the bus (28 is the family ID) and their unique IDs are 0000028f6667 and 0000028fa89c.
The file w1_master_slaves contains an updated list:
ls cat w1_master_slaves 28-0000028fa89c 28-0000028f6667 To read the temperature for each sensor type:
cat 28-0000028f6667/w1_slave 49 01 4b 46 7f ff 07 10 f6 : crc=f6 YES 49 01 4b 46 7f ff 07 10 f6 t=20562 t=20562 indicates that the temperature read is 20.562 °C Reading the temperature in Python
These simple programs in Python scan the 1-wire bus to detect the thermal sensors available:
Download this example from playground then launch it by typing:
python scan1w.py Scan for the available thermal sensors Sensor >This other example reads the temperature from a specific sensor.
Change the sensor ID in the source and try it: