- How to Run a Program from the Command Line on Linux
- Running a Program From the Terminal
- Running a Program Outside the $PATH Variable
- Adding a Directory to your $PATH Variable
- Installing and Uninstalling a Program in the Terminal
- Expert Q&A
- Tips
- You Might Also Like
- How to open a particular file from a terminal?
- 3 Answers 3
- How do I Open a Text File in Linux Terminal?
- Method 1: Using the cat Command
- Method 2: Using the more Command
- Method 3: Using the nl Command
- Method 4: Using the xdg-open Command
- Method 5: Using the Text Editors
- Method 6: Using the less Command
- Alternate Methods
- tail Command
- head Command
- Conclusion
How to Run a Program from the Command Line on Linux
This article was co-authored by wikiHow staff writer, Travis Boylls. Travis Boylls is a Technology Writer and Editor for wikiHow. Travis has experience writing technology-related articles, providing software customer service, and in graphic design. He specializes in Windows, macOS, Android, iOS, and Linux platforms. He studied graphic design at Pikes Peak Community College.
The wikiHow Tech Team also followed the article’s instructions and verified that they work.
This article has been viewed 278,602 times.
Most Linux distributions have a graphical user interface that allows you to open programs by just clicking on the program’s icon in the Apps menu. However, there are situations where you may want to run a program from the Terminal. The Terminal is a powerful tool that allows you to run programs and manage your Linux system using keyboard commands. This wikiHow teaches you how to run a program from the Terminal in Linux.
Running a Program From the Terminal
Press Ctrl + Alt + T to open the Terminal. You can open the Terminal using the keyboard shortcut on most Linux distributions. The keyboard shortcut is Ctrl + Alt + T. You can also click the Terminal icon in your Apps menu. It generally has an icon that resembles a black screen with a white text cursor.
- For example, if you want to run Firefox from the Terminal, you would simply type firefox and press Enter.
- Type -h or —help after the program name to display the help menu for that program. Many programs have additional command modifiers you can use to launch the program in a specific way. For example, you can launch a website in a web browser by typing the web browser name followed by the web address and press Enter to launch that website in the web browser (i.e. firefox www.wikihow.com .
- If you receive a message that says you don’t have permission to run a program or access is denied, type sudo before the program name and press Enter. The «sudo» command allows regular users to run Terminal commands with administrative privileges or root access.
- If you want to run a C or C++ program from the Terminal, you will first need to complie the program before you can launch it from the Terminal.
Running a Program Outside the $PATH Variable
Press Ctrl + Alt + T to open the Terminal. You can open the Terminal using the keyboard shortcut on most Linux distributions. The keyboard shortcut is Ctrl + Alt + T. You can also click the Terminal icon in your Apps menu. It generally has an icon that resembles a black screen with a white text cursor.
Type cd followed by a space and the location the program file is saved to. If the program launch file is saved to a location that is not in your $PATH variable, then you will need to navigate to that location inside the Terminal. You can do so using the «cd» command. For example, if you have folder for Python programs saved in your «Documents» folder, you can navigate to it in the Terminal by typing cd ~/Documents/Python or something similar, and then press Enter.
Type chmod a+x [filename] and press ↵ Enter . Replace «filename» with the actual launch file of the program. The «chmod a+x» command tells Linux the file is an executable file. [1] X Research source
Type «./» followed by the launch filename and press ↵ Enter . This launches the program. For example, if you have a Python file called «Helloworld.py», you would type ./helloworld.py to launch the file. [2] X Research source
Adding a Directory to your $PATH Variable
Press Ctrl + Alt + T to open the Terminal. If you cannot run a program by simply typing the program’s name, you may need to add the directory that the program is installed in to your $PATH variable. You can do this from the Terminal as well. Use the keyboard shortcut to open the Terminal if you haven’t already done so.
- For example, if you have a program installed in the «bin» directory of your «Home» folder, you would type export PATH=$PATH:$Home/bin and press Enter. This will temporarily add the «$Home/bin» directory to your $PATH variable.
- You can see which directories are currently added to your $PATH variable by typing the command echo $PATH and pressing Enter.
Type nano ~/.bashrc and press ↵ Enter . This opens the «.bashrc» file in a text editor that is based in the Terminal. You can use this file to permanently add the directory to your $PATH variable.
Add the «export PATH» command to the file. To do so, scroll down to the bottom of the file using the mouse wheel and type export PATH=$PATH:[path/to/program] at the bottom. Replace «[path/to/program]» with the actual directory tree the program is installed in. [3] X Research source
Press Y and press ↵ Enter . This confirms that you want to save and exit the text editor. You will be returned to the standard command prompt in the Terminal.
Type source ~/.bashrc and press ↵ Enter . This loads the updated $PATH variable into your current session. [4] X Research source
Type the name of the program and press ↵ Enter . With the program’s directory now added to your $PATH variable, you should be able to launch the program by simply typing the program name and pressing Enter.
Installing and Uninstalling a Program in the Terminal
Press Ctrl + Alt + T to open the Terminal. In addition to launching programs from within the Terminal, you can also install and uninstall programs from within the Terminal. Use the keyboard shortcut to open the Terminal if you haven’t already done so.
Type sudo apt install [app_name] and press ↵ Enter (Debian). Replace «[app_name]» with the actual name of the program you want to install. This command works in Debian-based Linux distributions, such as Ubuntu, and Mint.
Type sudo apt remove [app_name] and press ↵ Enter (Debian). Replace «[app_name]» with the name of the app you want to uninstall. This command works in Debian-based Linux distributions, such as Ubuntu, and Mint.
Type sudo dnf install [app_name] and press ↵ Enter (Red Hat). Replace «[app_name]» with the actual name of the program you want to install. This command works for Red Hat Linux distributions such as RHEL, Fedora, and CentOS.
Type sudo dnf remove [app_name] and press ↵ Enter (Red Hat). Replace «[app_name]» with the name of the app you want to uninstall. This command works for Red Hat Linux distributions such as RHEL, Fedora, and CentOS. [5] X Research source
Type the name of the program and press ↵ Enter . Once the program is installed, you can launch the program by simply typing the program’s name and pressing Enter in the Terminal.
Expert Q&A
Tips
You Might Also Like
How to Change 4-Digit User Codes on Schlage Locks
How to Delay a Batch File: Timeout, Pause, Ping, Choice & Sleep
How to Factory Reset a Schlage Lock & Restore the Default Programming Code
Learn to Write Pseudocode: What It Is and Why You Need It
How to Start Coding: The Beginner’s Guide to Programming
3 Ways to Download GitHub Directories and Repositories
How to open a particular file from a terminal?
Sounds like you’re coming from a Mac, where open does the same as double-clicking would in the Desktop.
3 Answers 3
You can use xdg-open to open files in a terminal.
From the man-page of xdg-open :
xdg-open — opens a file or URL in the user’s preferred application
The command xdg-open _b2rR6eU9jJ.txt will open the text file in a text editor that is set to handle text files. The command will also work with other common file extensions, opening the file with the relevant application.
If you struggle to remember xdg-open like I often do, add alias open=xdg-open to your ~/.bashrc file. Then, run source ~/.bashrc and now you can use open instead of xdg-open .
You must use an editor to open a text file:
- vi _b2rR6eU9jJ.txt - vim _b2rR6eU9jJ.txt - emacs _b2rR6eU9jJ.txt - nano _b2rR6eU9jJ.txt - gedit _b2rR6eU9jJ.txt (gnome's default editor) - leafpad _b2rR6eU9jJ.txt (lxde's default editor) - kedit _b2rR6eU9jJ.txt (KDE's default editor) Or if you wanted to just view the file without modifying its contents: cat _b2rR6eU9jJ.txt
EDIT #1: I just noticed that the question is tagged fedora, which up until now is using gnome as its core graphical user interface, which comes with gedit preinstalled. So this is guaranteed to work: gedit _b2rR6eU9jJ.txt
How do I Open a Text File in Linux Terminal?
In Linux, the text files are created by different text editors such as nano and vim text editors. The touch command line utility can also be used to create the file. Similarly, various commands can be used to open a text file in Linux.
In this tutorial, different command line utilities have been discussed to open the text files in Linux using the terminal by covering the below-mentioned topics:
Method 1: Using the cat Command
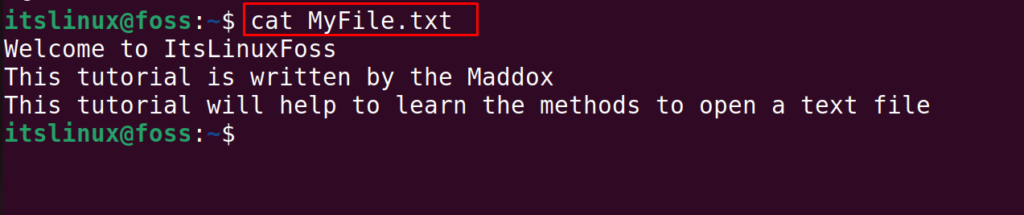
To view the content of the text file, the most convenient and recommended command utility is the “cat” command utility which can be used:
To understand the usage of the above command, we will display the contents of the “MyFile.txt” using the cat command:
The contents of the file have been displayed.
Method 2: Using the more Command
The “more” command utility is similar to the less command utility. The only difference between both the commands is that more command leaves their output displayed on the screen without clearing it. Due to this reason, it is recommended to use the less command utility for opening files compared to the more command. The general syntax of using the more command in the Linux terminal is
For example, we will open the file “MyFile.txt” using the more command:
The output has been displayed on the screen of Linux.
Method 3: Using the nl Command
The “nl” command utility can also be used to open the text file, and its usage syntax of the command is:
The “nl” command is used to open the “MyFile.txt” using the command:
We can see in the above output, the lines have been displayed of the file with the line numbers.
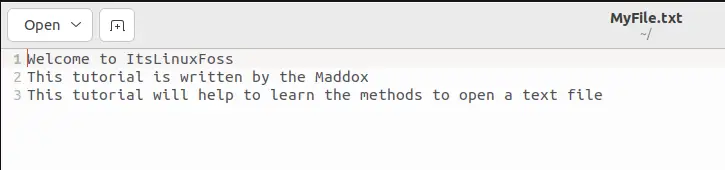
Method 4: Using the xdg-open Command
The last command which can be used to open the text file in Linux is by using the “xdg-open” command utility. The general syntax of using the “xdg-open” command:
For example, we will understand its usage by opening the file:
The file has been opened in Linux.
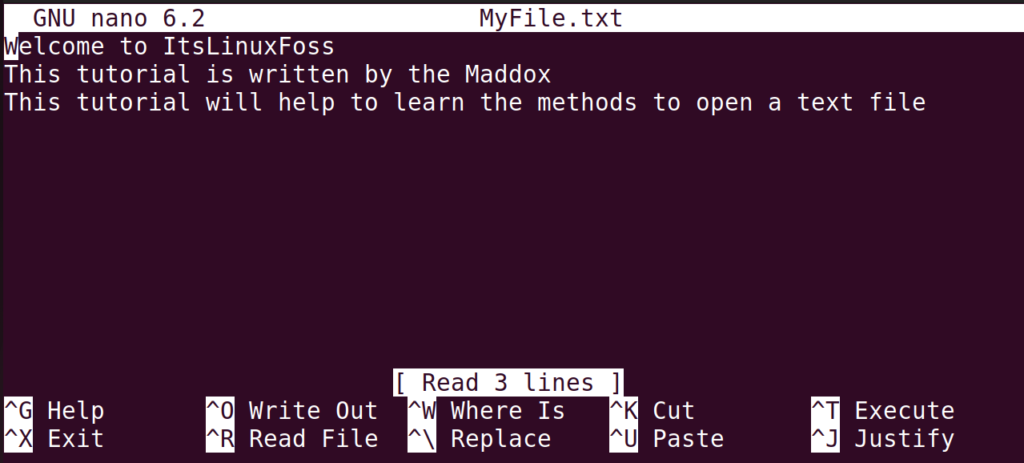
Method 5: Using the Text Editors
The text editors can also open and edit the text file. There are different text editors, such as “nano” and “vim”, but we will use the nano text editor as it comes pre-installed on most Linux distributions. The syntax of this command to open the text file is described below:
For example, we will open our text file using the nano text editor:
Interestingly, you can view as well as edit the content of the file.
Note: To learn about the “vim‘ editor, click here to read our detailed article on “vim” commands.
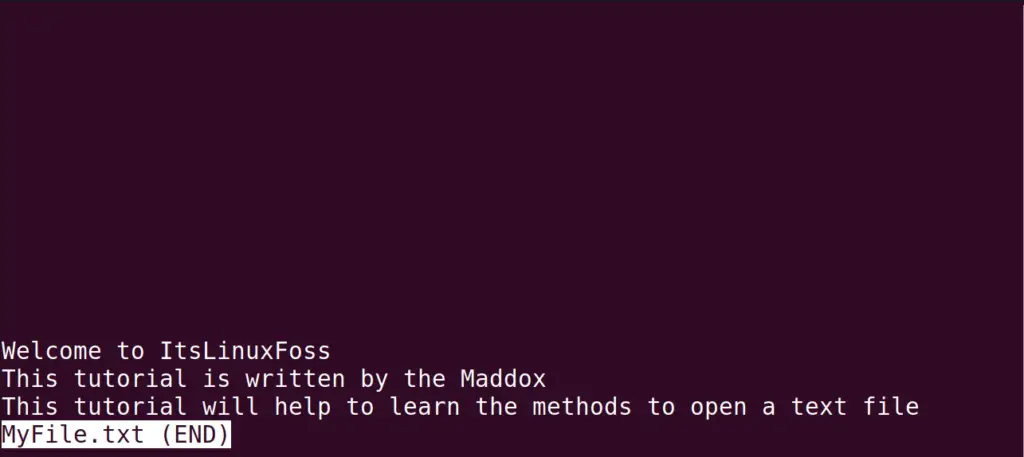
Method 6: Using the less Command
We can also use the “less” command utility, which opens the text file by displaying its one page at a time and the general syntax of using the less command:
For example, we will open the “MyFile.txt” using the less command utility:
After one page’s content, you must press the “Enter” key to view more content.
Moreover, you can exit the output by pressing the “q” key on the keyboard.
Alternate Methods
The methods listed in this section are also used to open up a text file with limited content. The “head” and “tail” command utilities are used to display only the first ten lines and the last ten lines, respectively.
tail Command
The “tail” command can also be used to serve the above-said purpose using the syntax provided below:
To understand the usage of the tail command, we will open the “MyFile.txt” using the command:
The contents of the file have been displayed.
head Command
The “head” utility can be used following the below-stated syntax:
Following the above syntax of the head command, we will open the “MyFile.txt” using the command:
The file has been opened in the terminal.
That’s all about this tutorial!
Conclusion
To open a text file in a Linux terminal, we can use the “cat”, “more”, “less”, “nl”, and “xdg-open” commands with different text editors. Moreover, the “head” and “tail” commands can also open a file with limited content. This method is super beneficial to get the content on the terminal. However, if you open it via text editors, you can edit the content as well. This blog has briefly explained all the possible methods to open a text file in Linux.