- Create VMs with KVM on Oracle Linux
- Objectives
- Prerequisites
- Validate Environment Supports Virtualization
- Install and Start KVM
- Setup Cockpit Web Console to manage KVM on Oracle Linux
- Create Virtual Machine from an ISO
- Create Virtual Machine using Oracle Cloud Images
- [Optional] View VM from Cockpit Dashboard
- For More Information:
- More Learning Resources
- Oracle linux виртуальная машина
- Pre-Built Developer VMs (for Oracle VM VirtualBox)
- Updated Oracle Linux Vagrant Boxes
- Prerequisites for Oracle Linux Vagrant Boxes
- Further Development VMs based on Vagrant/VirtualBox
- Further Virtual Machines, available on this page:
Create VMs with KVM on Oracle Linux
Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) is an open-source type-1 (bare-metal) hypervisor. This functionality permits a host system, such as Oracle Linux 8, to host multiple virtual machines (VMs) or guests when running on supported hardware.
This tutorial will deploy Oracle Linux Kernel Virtualization Manager (KVM) to create a virtual machine.
Objectives
- Deploy KVM
- Deploy Cockpit for Virtual Machines
- Create Virtual Machine from an ISO
- Create Virtual Machine using Oracle Cloud Images
Prerequisites
Any Oracle Linux 8 or later system with the following configurations:
Validate Environment Supports Virtualization
Note: When using the free lab environment, see Oracle Linux Lab Basics for connection and other usage instructions.
grep -e 'vendor_id' /proc/cpuinfo [oracle@ol-node01 ~]$ grep -e 'vendor_id' /proc/cpuinfo vendor_id : GenuineIntel vendor_id : GenuineIntel vendor_id : GenuineIntel vendor_id : GenuineIntel vendor_id : GenuineIntel vendor_id : GenuineIntel [oracle@ol-node01 ~]$ lsmod |grep kvm kvm_intel 262144 0 kvm 696320 1 kvm_intel irqbypass 16384 1 kvm Install and Start KVM
sudo dnf module install virt -y sudo dnf install virt-install virt-viewer -y [oracle@ol-node01 ~]$ virt-host-validate QEMU: Checking for hardware virtualization : PASS QEMU: Checking if device /dev/kvm exists : PASS QEMU: Checking if device /dev/kvm is accessible : PASS QEMU: Checking if device /dev/vhost-net exists : PASS QEMU: Checking if device /dev/net/tun exists : PASS QEMU: Checking for cgroup 'cpu' controller support : PASS QEMU: Checking for cgroup 'cpuacct' controller support : PASS QEMU: Checking for cgroup 'cpuset' controller support : PASS QEMU: Checking for cgroup 'memory' controller support : PASS QEMU: Checking for cgroup 'devices' controller support : PASS QEMU: Checking for cgroup 'blkio' controller support : PASS QEMU: Checking for device assignment IOMMU support : WARN (No ACPI DMAR table found, IOMMU either disabled in BIOS or not supported by this hardware platform) QEMU: Checking for secure guest support : WARN (Unknown if this platform has Secure Guest support) sudo systemctl enable --now libvirtd.service sudo systemctl status libvirtd.service [oracle@ol-node01 ~]$ sudo systemctl enable --now libvirtd.service [oracle@ol-node01 ~]$ sudo systemctl status libvirtd.service * libvirtd.service - Virtualization daemon Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/libvirtd.service; enabled; vendor pr> Active: active (running) since Mon 2022-06-13 21:28:19 GMT; 8s ago Docs: man:libvirtd(8) https://libvirt.org . Setup Cockpit Web Console to manage KVM on Oracle Linux
sudo dnf install cockpit cockpit-machines –y sudo systemctl enable --now cockpit.socket sudo systemctl status cockpit.socket [oracle@ol-node01 ~]$ sudo systemctl enable --now cockpit.socket Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/sockets.target.wants/cockpit.socket -> /usr/lib/systemd/system/cockpit.socket. [oracle@ol-node01 ~]$ sudo systemctl status cockpit.socket * cockpit.socket - Cockpit Web Service Socket Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/cockpit.socket; enabled; vendor pres> Active: active (listening) since Mon 2022-06-13 21:39:24 GMT; 10s ago Docs: man:cockpit-ws(8) Listen: [::]:9090 (Stream) . sudo firewall-cmd --add-service=cockpit --permanent sudo firewall-cmd --reload ssh -L 9090:localhost:9090 oracle@  Click Advanced and accept the connection when you get a warning from the browser.
Click Advanced and accept the connection when you get a warning from the browser.

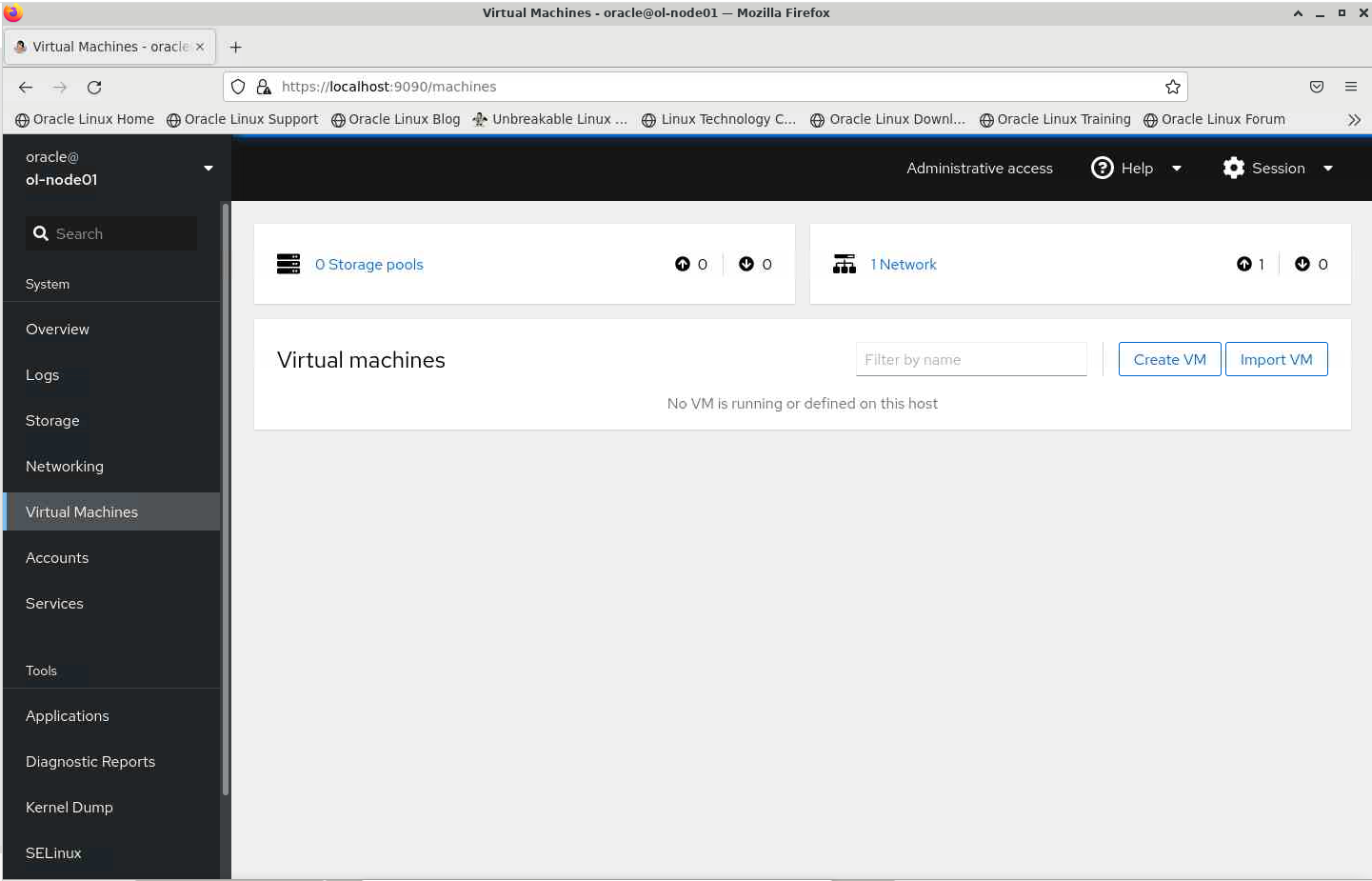
Create Virtual Machine from an ISO
- Click the “Virtual Machines” option in the navigation panel on the left.
- Click the “Create VM” button.
- Provide the following information:
Name: OL-demo Connection: System Installation type: URL (ISO image or distro install tree) Installation source: https://yum.oracle.com/ISOS/OracleLinux/OL8/u8/x86_64/OracleLinux-R8-U8-x86_64-dvd.iso Operating system: Oracle Linux 8.8 Storage: Create new volume Size: 20 GiB Memory: 16 GiB 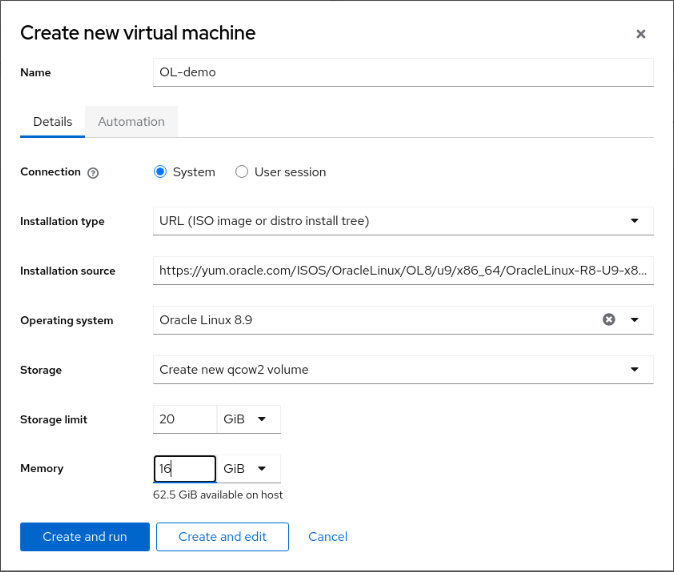
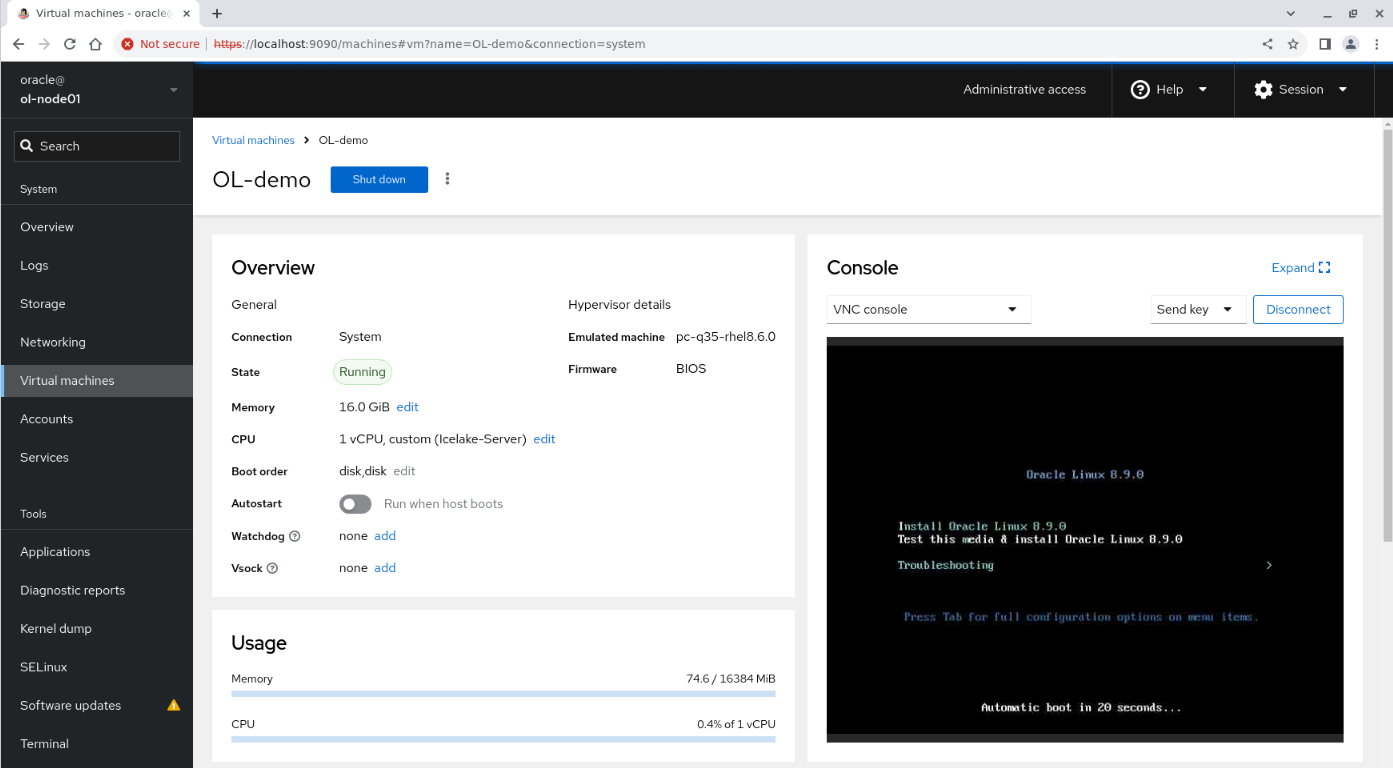
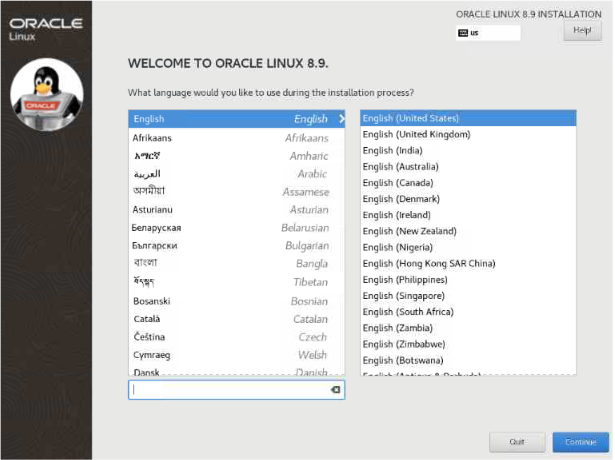 This lab does not continue with the installation process.
This lab does not continue with the installation process. Note: You can watch a free video demonstrating the Oracle Linux installation process at this video link: Installing Oracle Linux 8
Create Virtual Machine using Oracle Cloud Images
Note: Ensure you enter the following commands from your cloud instance (ol-node01) terminal window.
sudo curl -O https://yum.oracle.com/templates/OracleLinux/OL8/u8/x86_64/OL8U8_x86_64-kvm-b198.qcow cat 'EOF' | sudo tee ~/meta-data > /dev/null instance-id: iid-local01 local-hostname: vm-01 EOF cat 'EOF' | sudo tee ~/user-data > /dev/null #cloud-config system_info: default_user: name: opc ssh_authorized_keys: - EOF SSHKEY=$(cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub) sed -i "s||$SSHKEY>|g" ~/user-data sudo genisoimage -output /var/lib/libvirt/images/vm-01.iso -volid cidata -joliet -rock ~/user-data ~/meta-data sudo cp /var/lib/libvirt/images/OL8U8_x86_64-kvm-b198.qcow /var/lib/libvirt/images/vm-01.qcow sudo virt-install --name vm-01 \ --memory 2048 \ --vcpus 2 \ --disk /var/lib/libvirt/images/vm-01.qcow,device=disk,bus=virtio \ --disk /var/lib/libvirt/images/vm-01.iso,device=cdrom \ --os-type linux --os-variant ol8.6 \ --virt-type kvm --graphics none \ --network network=default,model=virtio \ --noautoconsole \ --import sudo virsh net-dhcp-leases --network default Note: Depending on how quickly the virtual machine starts, you may need to run the command again to display the IP address.
sudo virsh domiflist vm-01 sudo virsh net-dhcp-leases --network default --mac
[oracle@ol-node01 images]$ ssh opc@192.168.122.46 The authenticity of host '192.168.122.46 (192.168.122.46)' can't be established. ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:xcuVfQdoFDCC72i7plD0OfqDTSBG6QWhOm5ti4HIKEs. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? yes Warning: Permanently added '192.168.122.46' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts. [opc@vm-01 ~]$ uname -a Linux ol-node01 5.15.0-101.103.2.1.el8uek.x86_64 #2 SMP Mon May 1 20:11:30 PDT 2023 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux [Optional] View VM from Cockpit Dashboard
Note: Run this next command from a terminal on the lunabox Desktop.
- Enter the following command from your lunabox Desktop terminal window to create a local port forward for Cockpit using ssh.
ssh -L 9090:localhost:9090 oracle@ Note: The console is not active within Cockpit as the vm-01 virtual machine was created using the —graphical none option with virt-install .
For More Information:
More Learning Resources
Explore other labs on docs.oracle.com/learn or access more free learning content on the Oracle Learning YouTube channel. Additionally, visit education.oracle.com/learning-explorer to become an Oracle Learning Explorer.
For product documentation, visit Oracle Help Center.
Create VMs with KVM on Oracle Linux
Copyright © 2022, Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Oracle linux виртуальная машина
Pre-Built Developer VMs (for Oracle VM VirtualBox)
Learning your way around a new software stack is challenging enough without having to spend multiple cycles on the install process. Instead, we have packaged such stacks into pre-built Oracle VM VirtualBox appliances that you can download, install, and experience as a single unit. Just downloaded/assemble the files, import into VirtualBox (available for free), import, and go (but not for production use or redistribution)!
Some of these VMs are designed to support Developer Day workshops, and have specific hands on labs embedded in them, but they’re available to all.) Be sure to install VirtualBox first.
Updated Oracle Linux Vagrant Boxes
Vagrant is a tool to manage virtual machine-based development environments. Vagrant Boxes are pre-built base images that can be imported into Vagrant as a starting point. Read more about Vagrant here. On Linux Yum Server website Oracle publishes Vagrant boxes based on latest Oracle Linux Releases.
Prerequisites for Oracle Linux Vagrant Boxes
You will need the following software installed on your machine. Check the minimum required versions in the Vagrant Box description.
Further Development VMs based on Vagrant/VirtualBox
On GitHub Oracle created an official Vagrant Project repository dedicated to Oracle Products running on top of Oracle Linux. Between them you can find ready-to-run VMs with Kubernetes, Oracle Database, Oracle APEX and more.
Further Virtual Machines, available on this page:
- Oracle Database 12c R1 Enterprise Edition Release 12.1.0.2.0
- Oracle WebLogic Server 12.2.1
- Oracle Fusion Middleware Web Tier Utilities 12.2.1
- Oracle WebCenter Content 12.2.1
- Oracle WebCenter Portal 12.2.1
- Oracle JDeveloper 12.2.1
- WebCenter Extensions for JDeveloper 12.2.1
- Oracle Linux
- Oracle Database 12c Release 1 Enterprise Edition
- Cloudera’s Distribution including Apache Hadoop
- Cloudera Manager
- Oracle Big Data Connectors
- Oracle NoSQL Database Enterprise Edition 12cR1
- Oracle Data Integrator 12cR1
- . and more
- Oracle Linux 7
- Oracle Database 19.3 Linux x86-64
- Oracle XML DB
- Oracle SQL Developer
- Oracle SQL Developer Data Modeler
- Oracle Application Express
- Hands-On-Labs (accessed via the Toolbar Menu in Firefox)
- A default desktop installation of Oracle Solaris 11.4
- A default desktop installation of Oracle Solaris 10 1/13