- Disabling Intel Turbo Boost in ubuntu
- 4 Answers 4
- Prevent overheating by disabling turbo boost
- Motivation
- Solution
- Disable Intel Turbo Boost (on Windows)
- Disable Intel Turbo Boost (on Ubuntu)
- Results
- Включение и отключение Turbo Boost в Linux
- 1. Текущие состояние Turbo Boost и его смена.
- 2. Управление режимом питания процессора, если используется intel_pstate:
- Игорь Горгуль
- Оставить комментарий Отменить комментарий
- Saved searches
- Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
- MarceloSerra/Disable-Turbo-Boost-on-Linux-Based
- Name already in use
- Sign In Required
- Launching GitHub Desktop
- Launching GitHub Desktop
- Launching Xcode
- Launching Visual Studio Code
- Latest commit
- Git stats
- Files
- readme.md
Disabling Intel Turbo Boost in ubuntu
I’m new to Ubuntu and want to disable the turbo boost. I tried with cpufreq but i cant get it to work. is there any other way to do it. In windows it was as easy as changing the CPU speed from 100 to 99.
@Ron: it is Intel(R) Pentium(R) CPU B960 @ 2.20GHz I got the information from the chat they moved to. I think it doesn’t really matter, what matters is which scaling driver is being used. Currently (which is different than the past) it will default to intel_pstate if the processor supports it.
guys, i tried : sudo cpupower frequency-set -g powersave and it says : Setting cpu: 0 Setting cpu: 1 So where to put which core to change ? 🙂
Regardless of which scaling driver you are using, turbo enabled or not is a global setting, one spot covers all CPUs. Myself, I only use primitive commands, never higher level level tools such as cpupower .
4 Answers 4
If your system is using the intel_pstate frequency scaling driver:
$ cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu*/cpufreq/scaling_driver intel_pstate intel_pstate intel_pstate intel_pstate intel_pstate intel_pstate intel_pstate intel_pstate Then you can inquire as to the turbo enabled or disabled status:
$ cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/intel_pstate/no_turbo 0 Where 0 means turbo is enabled and 1 means it is disabled. And you can change it by writting (as sudo) to the same location.
$ echo "1" | sudo tee /sys/devices/system/cpu/intel_pstate/no_turbo 1 I never remember the location or how to do the `tee’ thing properly, so I prefer scripts to be run as sudo:
$ cat set_cpu_turbo_off #! /bin/bash echo "1" > /sys/devices/system/cpu/intel_pstate/no_turbo $ cat set_cpu_turbo_on #! /bin/bash echo "0" > /sys/devices/system/cpu/intel_pstate/no_turbo If you have problems with permissions, try sudo echo «0» | sudo tee /sys/devices/system/cpu/intel_pstate/no_turbo
@Alexey : If you want it to be permanent, then i would suggest to do it in the BIOS instead. Otherwise make the above set_cpu_turbo_off script to run during startup.
@Cirelli94 — even so: sudo echo «1» | sudo tee /sys/devices/system/cpu/intel_pstate/no_turbo 1 tee: /sys/devices/system/cpu/intel_pstate/no_turbo: Operation not permitted
For some reason, this doesn’t have any effect for me in Ubuntu Server 14. sudo wrmsr —all 0x1a0 0x4000850089 does the trick.
To read the current state of the Turbo Boost, we need to install the msr-tools
sudo apt-get install msr-tools To know if the Turbo Boost feature is disabled, run:
rdmsr -pi 0x1a0 -f 38:38 1=disabled 0=enabled Replace i with your cores number
NOte: If you get the following error:
rdmsr:open: No such file or directory then load the “msr” module by the following command:
To disable the Turbo Boost feature, one can set the entire 0x1a0 MSR register to 0x4000850089, as in here:
wrmsr -pC 0x1a0 0x4000850089 Where C refers to a particular core number
ou can get those number by running
cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep processor then once you know your numbers you have to run the command above for each core. in your case numbers would be 0 & 1 so you have to do
wrmsr -p0 0x1a0 0x4000850089 wrmsr -p1 0x1a0 0x4000850089 A script to disable/enable turbo boost
The following script can be used to turn off/on turbo boost:
#!/bin/bash if [[ -z $(which rdmsr) ]]; then echo "msr-tools is not installed. Run 'sudo apt-get install msr-tools' to install it." >&2 exit 1 fi if [[ ! -z $1 && $1 != "enable" && $1 != "disable" ]]; then echo "Invalid argument: $1" >&2 echo "" echo "Usage: $(basename $0) [disable|enable]" exit 1 fi cores=$(cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep processor | awk '') for core in $cores; do if [[ $1 == "disable" ]]; then sudo wrmsr -p$ 0x1a0 0x4000850089 fi if [[ $1 == "enable" ]]; then sudo wrmsr -p$ 0x1a0 0x850089 fi state=$(sudo rdmsr -p$ 0x1a0 -f 38:38) if [[ $state -eq 1 ]]; then echo "core $: disabled" else echo "core $: enabled" fi done save this to a file called turbo-boost.sh
Usage: You can copy the above script and save it into a file named turbo-boost then set it to be executable:
sudo chmod +x turbo-boost.sh you can then use it to disable/enable turbo boost:
./turbo-boost.sh disable ./turbo-boost.sh enable Prevent overheating by disabling turbo boost
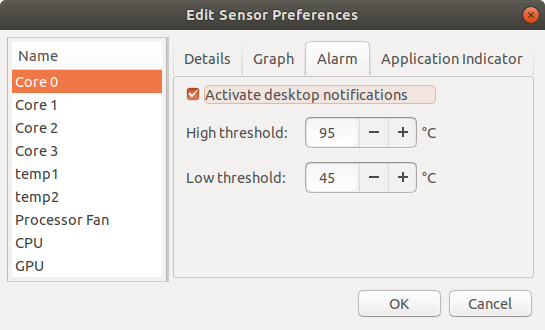
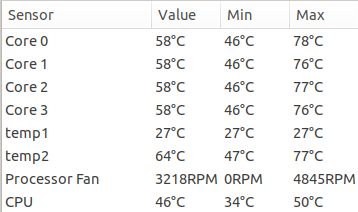
CPU throttling, PC shutting down abruptly, etc. These may be signs of overheating. Disabling Intel turbo boost may help. Screenshot above is the temperature range after disabling turbo boost.
Motivation
My laptop has first generation Intel Core i7 740QM. Its peak CPU core temperature hit a high of 97C (about 207 Fahrenheit) which is very close to its junction temperature of 100C.
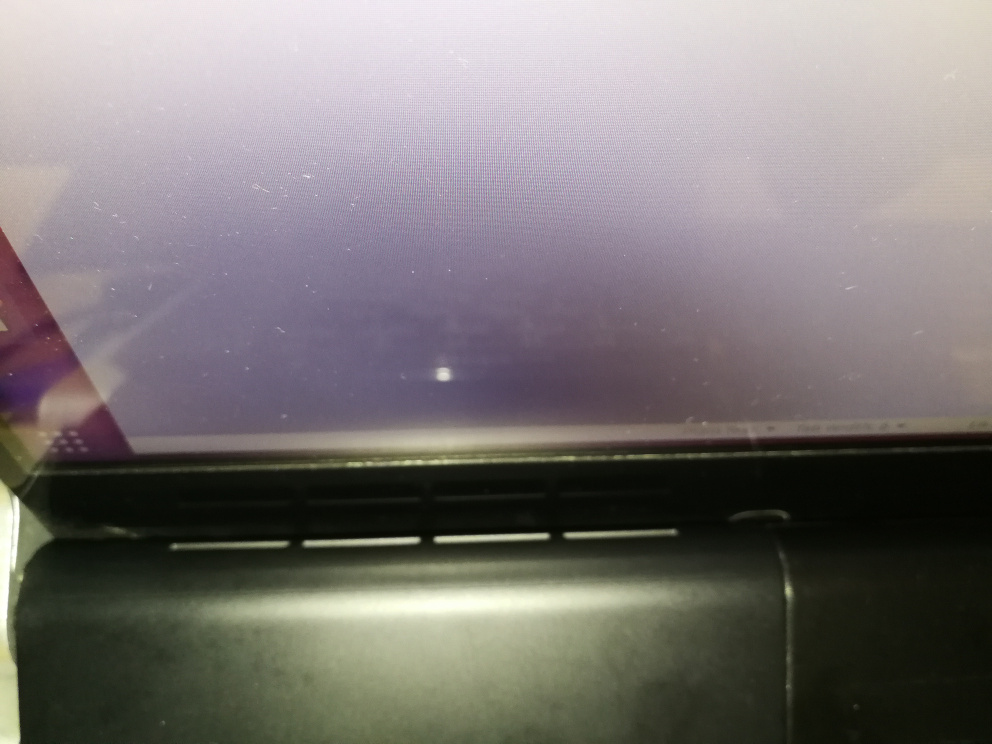
Even if the processor could handle the heat, I was concerned about how the heat would affect interconnected components. One may argue that the brains who designed it ought to have thought about it but I beg to differ. The heat vent of the laptop blows directly onto the screen when the laptop lid is open. Take a look:
When the CPU core temperature hits close to its junction temperature, throttling will begin taking effect and fans will be running at full speed generating loud noise.
Having more stable and predictable performance is what I prefer and disabling Intel Turbo Boost seemed like an easy win.
Solution
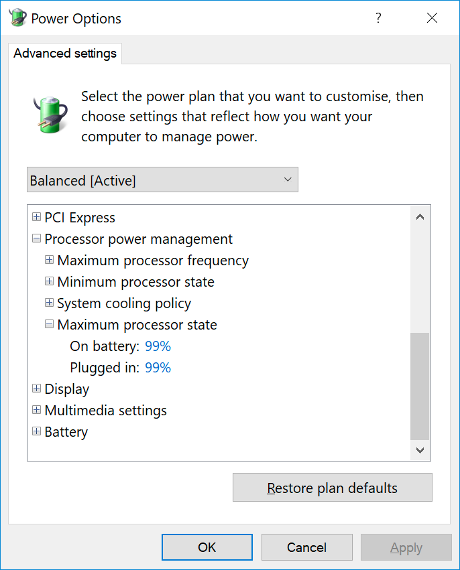
Disable Intel Turbo Boost (on Windows)
Tweak the maximum processor state to 99% via Power Options.
You do lose 1% of non-turbo boost speed as a result but this is likely to be negligible to you.
Disable Intel Turbo Boost (on Ubuntu)
Firstly, identify which frequency scaling driver is used by your Intel CPU.
cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu*/cpufreq/scaling_driver If it is intel_pstate , the command to execute in order to disable turbo boost is:
echo "1" | sudo tee /sys/devices/system/cpu/intel_pstate/no_turbo If it is acpi_cpufreq , the command to execute is:
echo "0" | sudo tee /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpufreq/boost To have this command executed on startup, add it into crontab
Replace with the appropriate one for your machine.
Results
Peak temperatures are now about 20C (68F) lower.
Quite an impressive drop! I did not run benchmarks but real world performance difference is not noticeable to me. Furthermore, throttling does not occur while gaming anymore.
Включение и отключение Turbo Boost в Linux
Бывает нужно отключить Turbo Boost или наоборот включить его, так же узнать текущие состояние. В Linux это можно сделать без перезагрузки в BIOS. Мы рассмотрим с помощью каких команд узнать текущие состояние, так же изменим режим работы процессора с «энергосбережение» на «производительность», что заставит процессор работать более эффективно.
1. Текущие состояние Turbo Boost и его смена.
Установим необходимый пакет
Проверим текущие состоние, где -p0 — номер ядра:
1 = деактивирован
0 = активирован
rdmsr:open: No such file or directory
Нужно загрузить модуль msr в ядро:
Далее можно правя регистры включать или отключать Turbo Boost, но чтобы было проще, я нашел скрипт, который активирует или деактивирует его, без запоминания сложных регистров. Назовем его turbo-boost.sh:
#!/bin/bash if [[ -z $(which rdmsr) ]]; then echo "msr-tools is not installed. Run 'sudo apt-get install msr-tools' to install it." >&2 exit 1 fi if [[ ! -z $1 && $1 != "enable" && $1 != "disable" ]]; then echo "Invalid argument: $1" >&2 echo "" echo "Usage: $(basename $0) [disable|enable]" exit 1 fi cores=$(cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep processor | awk '') for core in $cores; do if [[ $1 == "disable" ]]; then sudo wrmsr -p$ 0x1a0 0x4000850089 fi if [[ $1 == "enable" ]]; then sudo wrmsr -p$ 0x1a0 0x850089 fi state=$(sudo rdmsr -p$ 0x1a0 -f 38:38) if [[ $state -eq 1 ]]; then echo "core $: disabled" else echo "core $: enabled" fi done
Теперь вы можете активировать/деактивировать Turbo Boost:
./turbo-boost.sh disable ./turbo-boost.sh enable
2. Управление режимом питания процессора, если используется intel_pstate:
Установим утилиту cpupower:
apt install linux-cpupower
Узнать текущие состояние 1-го ядра:
cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_governor
Возможные варианты: https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/cpu-freq/governors.txt.
Нас интересует режим performance, так как он дает наибольшую производительность. У вас возможно стоит powersave, как было у меня, поэтому сменим его.
cpupower frequency-set -g performance
На этом все, мы включили Turbo Boost и переключили режим работы процессора на максимальную производительность, так как нам нет смысла экономить электроэнергию на арендованом сервере в Дата Центре.
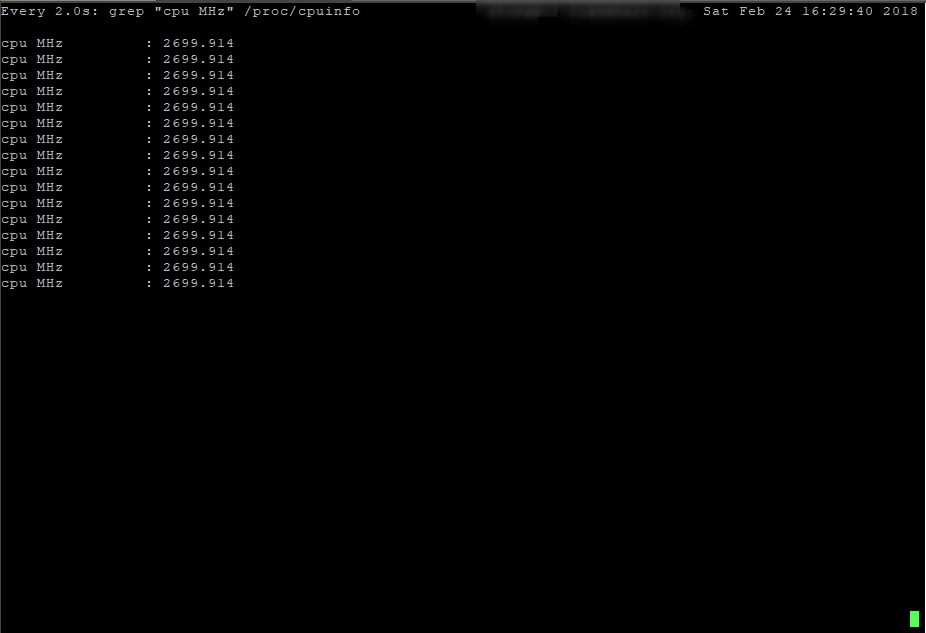
Еще дам команду, с помощью которой можно наблюдать за изменением частоты ядер процессора:
watch grep \"cpu MHz\" /proc/cpuinfo
Игорь Горгуль
Оставить комментарий Отменить комментарий
Этот сайт использует Akismet для борьбы со спамом. Узнайте, как обрабатываются ваши данные комментариев.
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session. You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session. You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.
Just an easy way to disable (and re-enable) Intel Turbo Boost using shell scripts.
MarceloSerra/Disable-Turbo-Boost-on-Linux-Based
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
Name already in use
A tag already exists with the provided branch name. Many Git commands accept both tag and branch names, so creating this branch may cause unexpected behavior. Are you sure you want to create this branch?
Sign In Required
Please sign in to use Codespaces.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching Xcode
If nothing happens, download Xcode and try again.
Launching Visual Studio Code
Your codespace will open once ready.
There was a problem preparing your codespace, please try again.
Latest commit
Git stats
Files
Failed to load latest commit information.
readme.md
git clone https://github.com/MarceloSerra/Disable-Turbo-Boost-on-Linux
Go to the folder, extract and execute chmod inside to give permissions (* will give permissions to all files in the folder, but you can set to one file just changing * by file name):
Now it’s necessary to verify if you’ve got an intel scaling driver (intel_pstate) output:
If the output was (intel_pstate), you can continue and execute:
You can check the status by executing (0 output = ENABLED and 1 output = DISABLED):
You can also re-enable the Turbo Boost by executing: