- How to Start/Stop and Enable/Disable FirewallD and Iptables Firewall in Linux
- What is FirewallD
- What is Iptables
- How to Start/Stop and Enable/Disable FirewallD Service
- How to Start/Stop and Enable/Disable IPtables Service
- Conclusion
- How to fully disable the Firewall on Linux Mint
- How to disable a firewall port on Linux Mint using a terminal
- How to disable a firewall on Linux Mint using a GUFW utility
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Taimoor Mohsin
- Как полностью отключить брандмауэр в Linux Mint
- Как отключить порт брандмауэра в Linux Mint с помощью терминала
- Как отключить брандмауэр на Linux Mint с помощью утилиты GUFW
- Заключение
How to Start/Stop and Enable/Disable FirewallD and Iptables Firewall in Linux
Firewall is a software that acts as a shield between user’s system and external network allowing some packets to pass while discarding other’s. Firewall commonly operates on network layer i.e. on IP packets both Ipv4 and Ipv6.
Whether a packet will pass or will be bocked, depends on the rules against such type of packets in the firewall. These rules can be built-in or user-defined ones. Each packet which enters the network has to pass through this shield which verifies it against rules defined in it for such type of packets.
Each rule has a target action which is to be applied in case the packet fails to satisfy it. On Linux systems, firewall as a service is provided by many softwares, most common which are: firewalld and iptables.
In Linux there are many different types of firewalls used, but most standard ones are Iptables and Firewalld, which is going to discuss in this article.
What is FirewallD
FirewallD is the Dynamic Firewall Manager of Linux systems. This service is used to configure the network connections, thus deciding which external network or internal packets to allow traversing the network and which to block.
It allows two types of configurations, permanent and runtime. Runtime configurations will get lost ones the service is restarted while the permanent ones get retained across the system boot so that they are followed every time the service gets active.
Corresponding to these configurations, firewallD has two directories, default/fallback one (/usr/lib/firewall) which is lost ones system is updated and the system configuration (/etc/firewall) which remains permanent and overrides the default one if given. This is found as a default service in RHEL/CentOS 7 and Fedora 18.
What is Iptables
Iptables is another service which decides to allow, drop or return IP packets. Iptables service manages Ipv4 packets while Ip6tables manages Ipv6 packets. This service manages a list of tables where each table is maintained for different purpose like: ‘filter‘ table is for firewall rules, ‘nat‘ table is consulted in case of new connection, ‘mangle‘ in case of packet alterations and so on.
Each table further has chains which can be built-in or user-defined where a chain signifies a set of rules which are applies to a packet, thus deciding what the target action for that packet should be i.e. it must be ALLOWED, BLOCKED or RETURNED. This service is a default service on systems like: RHEL/CentOS 6/5 and Fedora, ArchLinux, Ubuntu etc.
To learn more about firewalls, follow the following links:
In this article we will explain how to start, stop or restart Iptables and FirewallD services in Linux.
How to Start/Stop and Enable/Disable FirewallD Service
If you’re using CentOS/RHEL 7 or Fedora 18+ versions, you should follow below instructions to manage FirewallD service.
Start FirewallD Service
# systemctl start firewalld
Stop FirewallD Service
Check the Status of FirewallD
# systemctl status firewalld
Check the State of FirewallD
As an alternative, you can disable the firewalld service so that it doesn’t apply rules to packets and enable ones needed again.
Disable FirewallD Service
# systemctl disable firewalld
Enable FirewallD Service
# systemctl enable firewalld
Mask FirewallD Service
Also, you can mask the firewall service which creates a symbolic link of the firewall.service to /dev/null , thus disabling the service.
Unmask FirewallD Service
# systemctl unmask firewalld
This is reverse of masking the service. This removes the symlink of the service created during masking, thus re-enabling the service.
How to Start/Stop and Enable/Disable IPtables Service
On RHEL/CentOS 6/5/4 and Fedora 12-18 iptables firewall comes as pre and later, the iptables service can be installed via:
# yum install iptables-services
Then, the service can be started, stopped or restarted via following commands:
Start Iptables Service
# systemctl start iptables OR # service iptables start
Stop Iptables Service
# systemctl stop iptables OR # service iptables stop
Disable Iptables Service
# systemctl disable iptables Or # service iptables save # service iptables stop
Enable Iptables Service
# systemctl enable iptables Or # service iptables start
Check Status of Iptables Service
# systemctl status iptables OR # service iptables status
On Ubuntu and some other Linux distributions however, ufw is the command which is used to manage the iptables firewall service. Ufw provides an easy interface for the user to handle the iptables firewall service.
Enable Ufw Iptables Firewall
Disable Ufw Iptables Firewall
Check Status of Ufw Iptables Firewall
However, if you want to list chains in iptables which contains all the rules following command can help you achieve the same:
Conclusion
These are the techniques which can help you start, stop, disable and enable the packet management services in Linux Based Systems. Different Linux distros can have different services as default, like: Ubuntu can have iptables as the default and pre-installed service, while CentOS can have firewalld as the default configured service for managing incoming and outgoing of IP packets.
Presented in this article are the most common tricks to manage these services on almost all Linux Distros, however, if you find something and would like to add on to this article, your comments are always welcome.
How to fully disable the Firewall on Linux Mint
A firewall is a network security system built into an operating system that monitors and manages network traffic according to preset rules. The firewall also aids in the monitoring of networks to determine whether they are trustworthy or not. They also protect your PC from hackers by filtering dangerous network traffic.
The uncomplicated firewall (UFW) in Linux Mint provides a user-friendly interface for managing firewall rules. Its main goal is to make firewall rule management as simple as possible, as the name suggests. Although it is recommended that you keep the firewall turned on, there may be times when you need to disable it, such as when troubleshooting or testing. So this article will provide you the details on how you can disable a firewall on Linux Mint.
There are two main ways to disable a firewall port which are as follows.
How to disable a firewall port on Linux Mint using a terminal
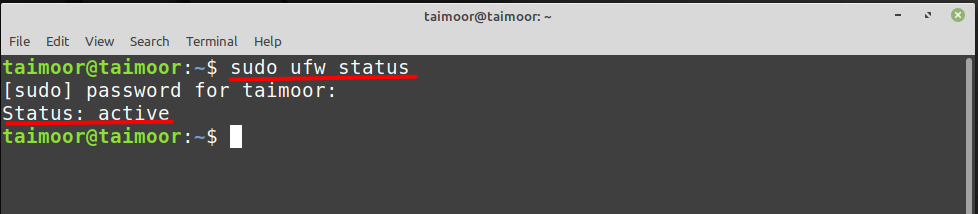
Before doing anything you first need to verify if the firewall status is currently disabled or not and you can do that by typing.
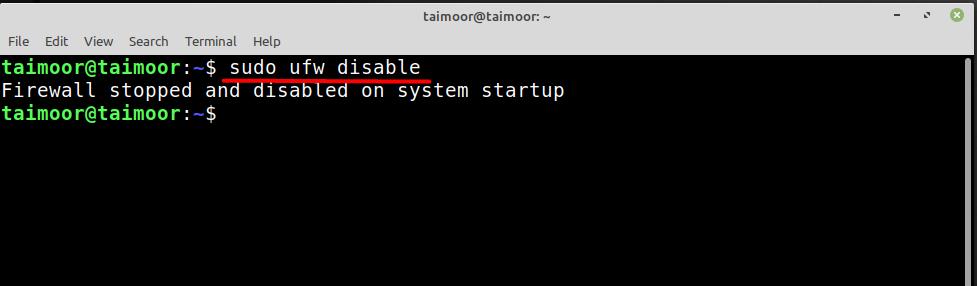
As you can see that currently, the firewall is working and active, so to disable it you can type.
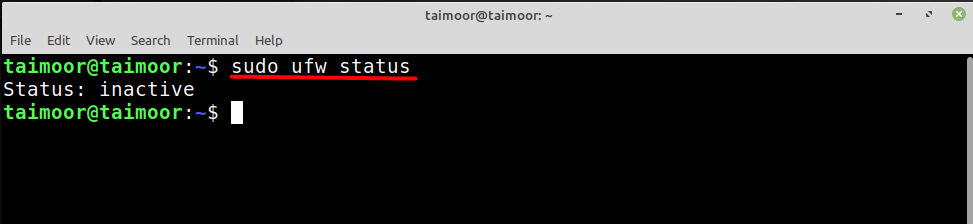
Now as you can see from the above image that the firewall has been stopped and disabled and you can also verify that by checking the status again.
How to disable a firewall on Linux Mint using a GUFW utility
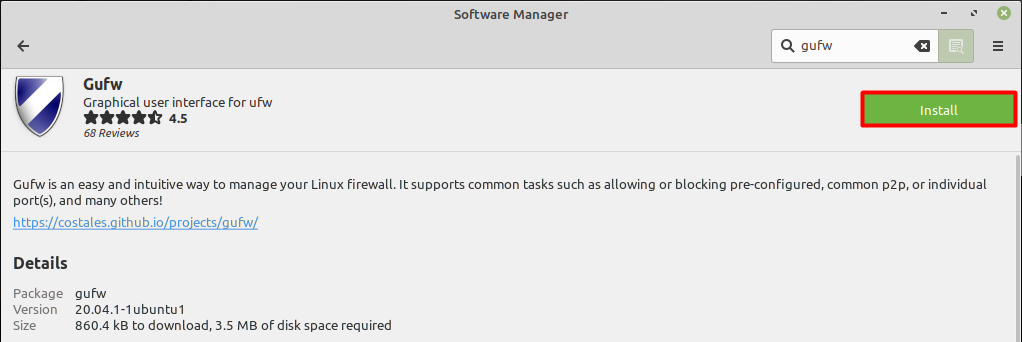
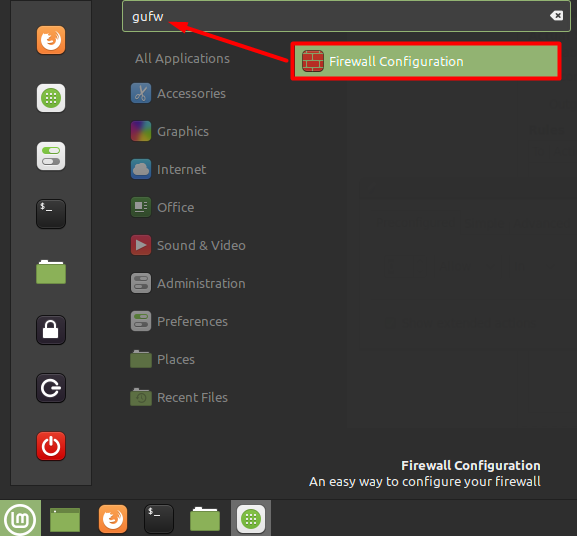
The working of Graphical Uncomplicated Firewall (GUFW) utility is the same as the UFW that’s been discussed above but it is Graphical user interface (GUI) based utility as the name suggests. To install it you need to open the software manager and search for a “gufw” utility.
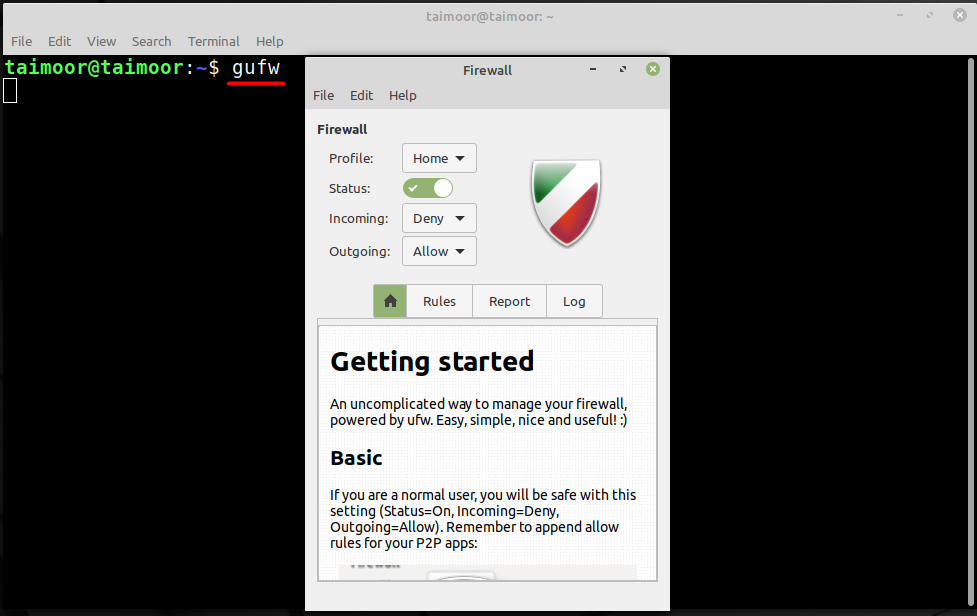
After its installation, you can either open it by using the software manager, from the menu bar or by a terminal. Opening it using a terminal is quite a simple task, all you need to do is to type.
You can also open GUFW by finding this utility from the Linux Mint menu as shown below.
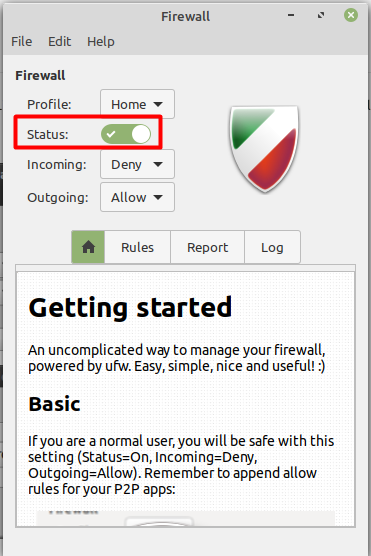
You will see multiple options after opening it such as profile, status, internet traffic, and rule management.
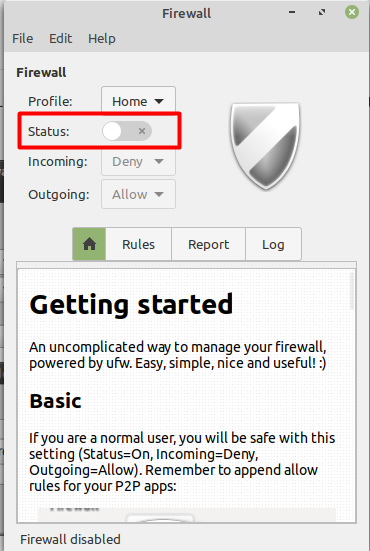
As you can see from the above image that currently the firewall is working from its status tab where you can see the green tick. To disable it you need to uncheck this tab as shown below.
Conclusion
Disabling the firewall is not recommended as it monitors your incoming and outgoing traffic and can protect your system from external attacks. But sometimes it is necessary to turn off the firewall for troubleshooting purposes otherwise it won’t allow it. So, in this article, we have taught you how you can disable your system’s firewall on Linux Mint. Two methods have been discussed; the first one uses a terminal and the second one is by using a graphical utility known as a graphical uncomplicated firewall (GUFW)
About the author
Taimoor Mohsin
Hi there! I’m an avid writer who loves to help others in finding solutions by writing high-quality content about technology and gaming. In my spare time, I enjoy reading books and watching movies.
Как полностью отключить брандмауэр в Linux Mint
Брандмауэр — это система сетевой безопасности, встроенная в операционную систему, которая отслеживает и управляет сетевым трафиком в соответствии с заданными правилами. Брандмауэр также помогает в мониторинге сетей, чтобы определить, заслуживают ли они доверия. Они также защищают ваш компьютер от хакеров, фильтруя опасный сетевой трафик.
Несложный межсетевой экран (UFW) в Linux Mint предоставляет удобный интерфейс для управления правилами межсетевого экрана. Его основная цель — максимально упростить управление правилами брандмауэра, как следует из названия. Хотя рекомендуется держать брандмауэр включенным, в некоторых случаях его необходимо отключить, например, при устранении неполадок или тестировании. В этой статье вы узнаете, как отключить брандмауэр в Linux Mint.
Есть два основных способа отключить порт брандмауэра:
Как отключить порт брандмауэра в Linux Mint с помощью терминала
Прежде чем что-либо делать, вам сначала нужно проверить, отключен ли в настоящее время статус брандмауэра, и вы можете сделать это, набрав.
Как видите, в настоящее время брандмауэр работает и активен, поэтому, чтобы отключить его, вы можете ввести.
Теперь, как вы можете видеть на изображении выше, брандмауэр был остановлен и отключен, и вы также можете проверить это, снова проверив статус.
Как отключить брандмауэр на Linux Mint с помощью утилиты GUFW
Утилита Graphical Uncomplicated Firewall (GUFW) работает так же, как UFW, о которой говорилось выше, но, как следует из названия, это утилита на основе графического пользовательского интерфейса (GUI). Чтобы установить его, вам нужно открыть диспетчер программного обеспечения и найти утилиту «gufw».
После установки вы можете открыть его с помощью диспетчера программного обеспечения, из строки меню или с помощью терминала. Открыть его с помощью терминала — довольно простая задача, все, что вам нужно сделать, это ввести.
Вы также можете открыть GUFW, найдя эту утилиту в меню Linux Mint, как показано ниже.
После открытия вы увидите несколько опций, таких как профиль, статус, интернет-трафик и управление правилами.
Как видно из приведенного выше изображения, в настоящее время брандмауэр работает на вкладке состояния, где вы можете видеть зеленую галочку. Чтобы отключить его, вам нужно снять отметку с этой вкладки, как показано ниже.
Заключение
Отключение брандмауэра не рекомендуется, поскольку он контролирует ваш входящий и исходящий трафик и может защитить вашу систему от внешних атак. Но иногда необходимо отключить брандмауэр для устранения неполадок, иначе он не позволит. Итак, в этой статье мы научили вас, как отключить брандмауэр вашей системы в Linux Mint. Обсуждались два метода; первый использует терминал, а второй — графическую утилиту, известную как графический несложный брандмауэр (GUFW).
Насколько публикация полезна?
Нажмите на звезду, чтобы оценить!
Средняя оценка / 5. Количество оценок:
Оценок пока нет. Поставьте оценку первым.