How can I execute PHP code from the command line?
I would like to execute a single PHP statement like if(function_exists(«my_func»)) echo ‘function exists’; directly with the command line without having to use a separate PHP file. How is it possible?
doing function_exists() without using any other files containing user defined function isn’t going to be much good, except for testing the PHP version, which you can find out in other ways. What function do you want to test for?
6 Answers 6
If you’re going to do PHP in the command line, I recommend you install phpsh, a decent PHP shell. It’s a lot more fun.
Anyway, the php command offers two switches to execute code from the command line:
-r Run PHP without using script tags -R Run PHP for every input line You can use php 's -r switch as such:
php -r 'echo function_exists("foo") ? "yes" : "no";' The above PHP command above should output no and returns 0 as you can see:
>>> php -r 'echo function_exists("foo") ? "yes" : "no";' no >>> echo $? # print the return value of the previous command 0 Another funny switch is php -a:
-a Run as interactive shell It's sort of lame compared to phpsh, but if you don't want to install the awesome interactive shell for PHP made by Facebook to get tab completion, history, and so on, then use -a as such:
>>> php -a Interactive shell php > echo function_exists("foo") ? "yes" : "no"; no php > If it doesn't work on your box like on my boxes (tested on Ubuntu and Arch Linux), then probably your PHP setup is fuzzy or broken. If you run this command:
You should see:
Server API => Command Line Interface If you don't, this means that maybe another command will provides the CLI SAPI. Try php-cli; maybe it's a package or a command available in your OS.
If you do see that your php command uses the CLI (command-line interface) SAPI (Server API), then run php -h | grep code to find out which crazy switch - as this hasn't changed for year- allows to run code in your version/setup.
Another couple of examples, just to make sure it works on my boxes:
>>> php -r 'echo function_exists("sg_load") ? "yes" : "no";' no >>> php -r 'echo function_exists("print_r") ? "yes" : "no";' yes Also, note that it is possible that an extension is loaded in the CLI and not in the CGI or Apache SAPI. It is likely that several PHP SAPIs use different php.ini files, e.g., /etc/php/cli/php.ini vs. /etc/php/cgi/php.ini vs. /etc/php/apache/php.ini on a Gentoo Linux box. Find out which ini file is used with php -i | grep ini .
How to Use and Execute PHP Codes in Linux Command Line – Part 1
PHP is an open source server side scripting Language which originally stood for ‘Personal Home Page‘ now stands for ‘PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor‘, which is a recursive acronym. It is a cross platform scripting language which is highly influenced by C, C++ and Java.
A PHP Syntax is very similar to Syntax in C, Java and Perl Programming Language with a few PHP-specific feature. PHP is used by some 260 Million websites, as of now. The current stable release is PHP Version 5.6.10.
PHP is HTML embedded script which facilitates developers to write dynamically generated pages quickly. PHP is primarily used on Server-side (and JavaScript on Client Side) to generate dynamic web pages over HTTP, however you will be surprised to know that you can execute a PHP in a Linux Terminal without the need of a web browser.
This article aims at throwing light on the command-line aspect of PHP scripting Language.
1. After PHP and Apache2 installation, we need to install PHP command Line Interpreter.
# apt-get install php5-cli [Debian and alike System) # yum install php-cli [CentOS and alike System)
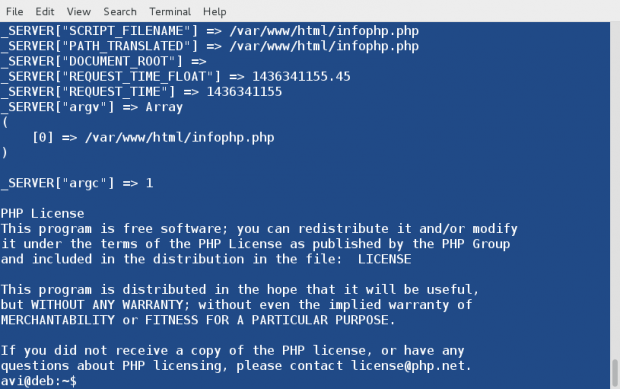
Next thing, we do is to test a php (if installed correctly or not) commonly as by creating a file infophp.php at location ‘/var/www/html‘ (Apache2 working directory in most of the distros), with the content , simply by running the below command.
# echo '' > /var/www/html/infophp.php
and then point your browser to http://127.0.0.1/infophp.php which opens this file in web browser.
Same results can be obtained from the Linux terminal without the need of any browser. Run the PHP file located at ‘/var/www/html/infophp.php‘ in Linux Command Line as:
# php -f /var/www/html/infophp.php
Since the output is too big we can pipeline the above output with ‘less‘ command to get one screen output at a time, simply as:
# php -f /var/www/html/infophp.php | less
Here Option ‘-f‘ parse and execute the file that follows the command.
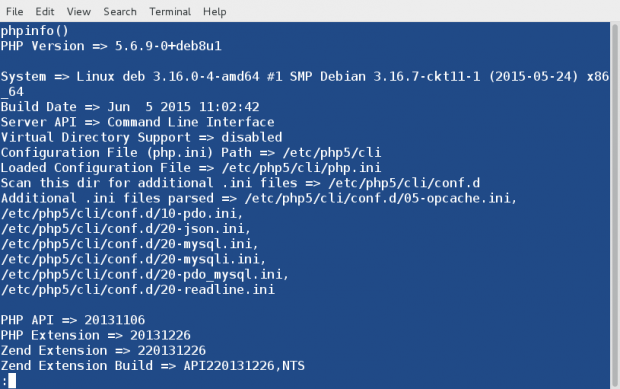
2. We can use phpinfo() which is a very valuable debugging tool directly on the Linux command-line without the need of calling it from a file, simply as:
Here the option ‘-r‘ run the PHP Code in the Linux Terminal directly without tags < and >.
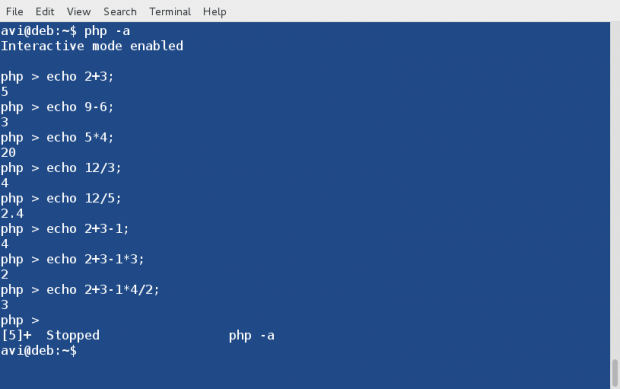
3. Run PHP in Interactive mode and do some mathematics. Here option ‘-a‘ is for running PHP in Interactive Mode.
# php -a Interactive shell php > echo 2+3; 5 php > echo 9-6; 3 php > echo 5*4; 20 php > echo 12/3; 4 php > echo 12/5; 2.4 php > echo 2+3-1; 4 php > echo 2+3-1*3; 2 php > exit
Press ‘exit‘ or ‘ctrl+c‘ to close PHP interactive mode.
4. You can run a PHP script simply as, if it is a shell script. First Create a PHP sample script in your current working directory.
# echo -e '#!/usr/bin/php\n' > phpscript.php
Notice we used #!/usr/bin/php in the first line of this PHP script as we use to do in shell script (/bin/bash). The first line #!/usr/bin/php tells the Linux Command-Line to parse this script file to PHP Interpreter.
Second make it executable as:
5. You will be surprised to know you can create simple functions all by yourself using the interactive shell. Here is the step-by step instruction.
Start PHP interactive mode.
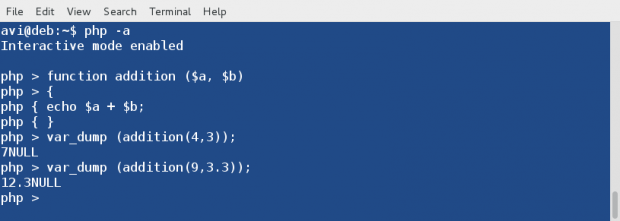
Create a function and name it addition. Also declare two variables $a and $b.
php > function addition ($a, $b)
Use curly braces to define rules in between them for this function.
Define Rule(s). Here the rule say to add the two variables.
All rules defined. Enclose rules by closing curly braces.
Test function and add digits 4 and 3 simply as :
php > var_dump (addition(4,3));
Sample Output
You may run the below code to execute the function, as many times as you want with different values. Replace a and b with values of yours.
php > var_dump (addition(a,b));
php > var_dump (addition(9,3.3));
Sample Output
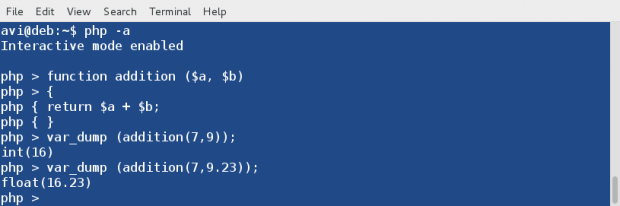
You may run this function till you quit interactive mode (Ctrl+z). Also you would have noticed that in the above output the data type returned is NULL. This can be fixed by asking php interactive shell to return in place of echo.
Simply replace the ‘echo‘ statement in the above function with ‘return‘
and rest of the things and principles remain same.
Here is an Example, which returns appropriate data-type in the output.
Always Remember, user defined functions are not saved in history from shell session to shell session, hence once you exit the interactive shell, it is lost.
Hope you liked this session. Keep Connected for more such posts. Stay Tuned and Healthy. Provide us with your valuable feedback in the comments. Like ans share us and help us get spread.