- Как переименовать файл Linux
- Утилита MV для переименования файла Linux
- Команда rename для переименования файла Linux
- Утилита PYRENAMER для переименования файла
- Заключение
- How Do I Rename a File in the Ubuntu Terminal?
- Renaming Files in Ubuntu 20.04 LTS System Using Terminal
- Rename File in Ubuntu Using the mv Command
- Example
- How to Use the mv Command to Rename Multiple Files?
- How to Use the Rename Command to Rename Files in Ubuntu?
- Syntax of Rename Command
- Example
- Example
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Samreena Aslam
Как переименовать файл Linux
Процедуру переименования файла Линукс можно отнести к разряду элементарных задач, однако не все новички соглашаются с данным предположением. Они часто сталкиваются с трудностями в этом деле. Что касается опытных пользователей, то им тоже есть чему поучиться, когда речь заходит о возможностях Linux. Они не имеют особых проблем в работе с графическим интерфейсом, но тем самым отказываются от заманчивой гибкости системы, которую может обеспечить терминал. В данной статье мы поговорим о переименовании файла Линукс через терминал, а также затронем другие возможности системы.
Утилита MV для переименования файла Linux
В системе Линукс есть стандартная команда «mv». Обычно она доступна по молчанию, используется для перемещения файлов, что при некоторых условностях одновременно является и их переименованием. Как выглядит синтаксическая структура команды:
- -f – замена существующего файла.
- -i – запрос на необходимость замены файлов.
- -n – отказ от замены файлов.
- -u – замена тех файлов, которые были видоизменены.
- -v – демонстрация перечня обработанных файлов.
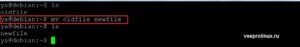
Итак, как переименовать файл Линукс при помощи стандартной программы? Для этого необходимо ввести в терминале название вспомогательной программы + текущее имя файла + новое название для файла.
Как видно из скриншота выше, команда mv переименовала файл «oldfile» в «newfile».
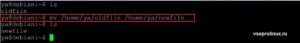
При необходимости переместить его из одного каталога в другой, это можно сделать с указанием полного пути например так:
$ mv /home/ya/oldfile /home/ya/newfile
Результат выполнения будет такой же.
Чтобы беспрепятственно переместить документ, нужно иметь права на запись в конкретный каталог. Что делать, если прав нет, и папка принадлежит иному юзеру системы?
Ответ: придется запускать утилиту через sudo или su.
ВАЖНО! при работе с чужими папками рекомендуется запускать утилиту mv с опцией -i. Таким образом, вы не сможете удалить информацию из папки – все данные останутся на месте, но уже с некоторыми коррективами.
Команда rename для переименования файла Linux
Для воплощения данной задумки в жизнь юзер системы может воспользоваться командой под названием «rename». Как и её аналоги, она тоже разработана для этих целей, но имеет за собой более обширный функционал. С её помощью легко выполнить массовое переименование документов Линукс. В отдельно взятых случаях это действительно необходимо.
Как выглядит синтаксическая структура команды:
rename опции старое_имя новое_имя файлы
Какие функции программы могут потребоваться пользователю Linux:
- —v – демонстрация перечня файлов, которые были обработаны.
- —n – запуск пробного режима (теста) для более подробного изучения специфики команды. Это означает, что заданные манипуляции не будут реализованы на практике.
- -f – опция для принудительной перезаписи файлов, которые уже наличествуют в системе.
И сразу же рассмотрим на примере. Допустим, нужно поменять название для всех txt файлов из каталога в .doc:
Примечание: наличие символа «*» в заданной команде подразумевает переименование всех файлов, которые содержатся в каталоге.
Утилита PYRENAMER для переименования файла
Некоторые пользователи Линукс не любят иметь дело с терминалом, и стараются находить альтернативные способы решения проблем, непосредственно связанных с системой. Если вы относитесь к числу таких людей, предлагаем вашему вниманию другой метод массового переименования файлов. Для реализации этой идеи вы можете воспользоваться графической утилитой pyrenamer. Это означает, что все действия можно выполнить при помощи мышки, но перед этим нужно установить программу:
Утилита представлена в виде окна, состоящего из нескольких блоков:
- Перечень файлов, которые необходимо видоизменить;
- Раздел настроек (здесь пользователь задает параметры переименования файлов);
- Дерево файловой системы.
В утилите pyrenamer часто встречаются подсказки, что значительно упрощает и ускоряет работу пользователю Линукс. С помощью данной программы можно выполнить не только массовое переименование файлов, но и выборочное – вплоть до одного файла. Pyrenamer является полноценным аналогом команды rename и утилиты mv, не уступая им в своей функциональности. Это прекрасный инструмент для тех, кто хочет вносить нужные правки в графическом интерфейсе, не прибегая к использованию терминала и сложных команд.
Заключение
В данной статье представлены самые простые и доступные способы переименования файлов в Линукс (через терминал и графический интерфейс), которые помогут новичку освоить свой дистрибутив.
How Do I Rename a File in the Ubuntu Terminal?
Renaming an existing file is a basic operation that usually does not require a specialized tool in any operating system. Renaming a single file in Linux is quite a simple task but renaming more than one or multiple files via terminal is a more challenging job for new Linux users. In all Linux distributions, the terminal is an essential command-line application for administering the Linux systems.
However, to use effectively this CLI application, you should have strong knowledge about basic Linux commands and fundamentals such as create, delete and renaming an existing file. Different commands are available in the Ubuntu Linux system to rename a file that we will explore in this article.
We will provide comprehensive details in this tutorial on how you can rename a file in Ubuntu using the command-line application Terminal. All commands have implemented for the demonstration on the Ubuntu 20.04 Linux system.
Renaming Files in Ubuntu 20.04 LTS System Using Terminal
The two different commands ‘mv’ and ‘rename’ are available in the Ubuntu Linux system to rename a file via terminal or command-line approach. Let us discuss each command in detail.
Rename File in Ubuntu Using the mv Command
Before using the ‘mv’ command, you should know how it works on your system. The basic syntax of the ‘mv’ command is given below:
The most popular ‘mv’ command options are provided below:
-f – Displays no message or alerts before overwriting a file name.
-i – Displays prompt confirmation or warning messages before renaming a file.
-u – It moves a file if the file does not exist on the specified destination or in case of a new file.
The file source can be the destination of one or more files. The destination only represents a single file.
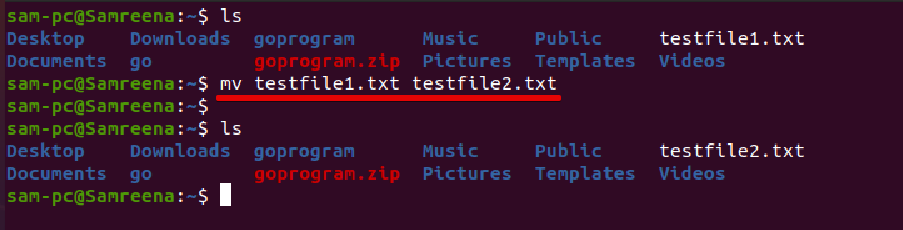
Example
For example, to rename the file ‘testfile1.txt’ to ‘testfile2.txt, you need to run the following command:
How to Use the mv Command to Rename Multiple Files?
Usually, you can only rename a single file using the move command. To rename multiple files using the mv command, you can use the mv command to combine with different commands. Let us say, mv command can be used along with for loop, while loop, and find command.
Let us explain with the help of an example. Here, we want to rename all .txt extension files of the current directory replaced with another .html extension. In this case, the following code will help us:
The above code will iterate using for loop through the files list having the .txt extension. After that, in the second line, it will replace each file extension .txt with .html. In the end, ‘done’ indicated the end of the for loop segment.
How to Use the Rename Command to Rename Files in Ubuntu?
Using the rename command, you can rename multiple files of a current directly at once. This command contains more advance features as compared to the ‘mv’ command. For renaming files using the rename command, you should have basic knowledge about regular expressions usage.
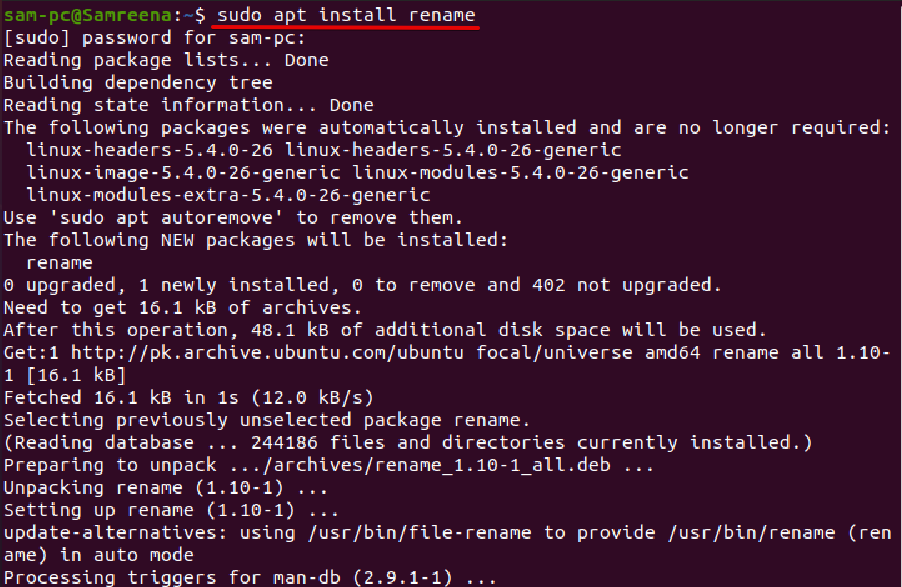
In most Linux distributions, the ‘rename’ command is installed by default. However, if you have not installed the rename command on your Ubuntu system then, it can be easily installed on Ubuntu and its derivatives by running the following command:
Syntax of Rename Command
Using the following syntax, you can use the rename command:
The rename command will rename files according to the specific regular Perl expressions.
Example
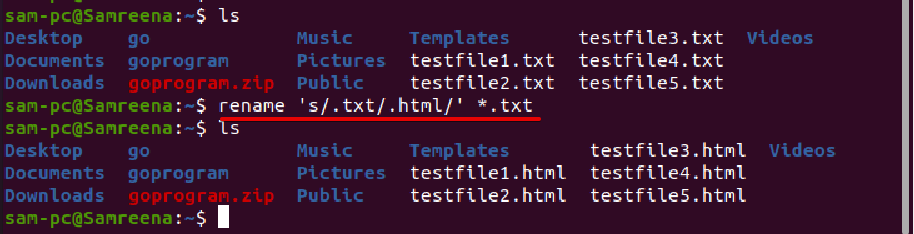
In the following example, we want to change the extension of all text files. So, we will change or replace all files with extension .txt to .html by executing the following command:
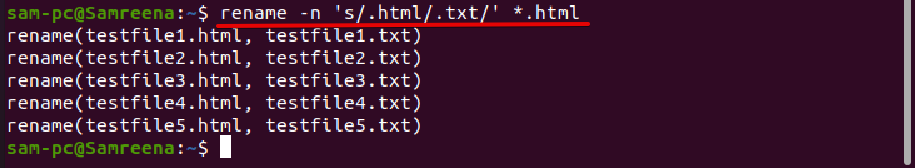
When you use the rename command followed by option ‘-n’, it also displays the file names to be renamed and renaming them as follows:
The above command displays the following result on the terminal window:
By default, the rename command does not overwrite an existing file. However, if you pass option -f along with the rename command then, it will help you to overwrite the existing files. Execute the following command to use the rename command followed by the -f option:
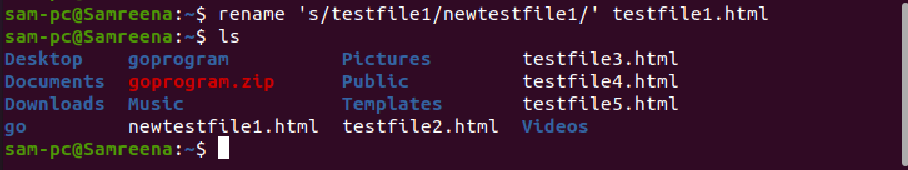
To change or rename the file name using rename command use the following command:
Example
For example, we want to rename a single file with the name ‘testfile.txt’ to newtestfile.txt. In this case, the above command will be modified into the following form:
To see more usage of rename command, let us try the following examples:
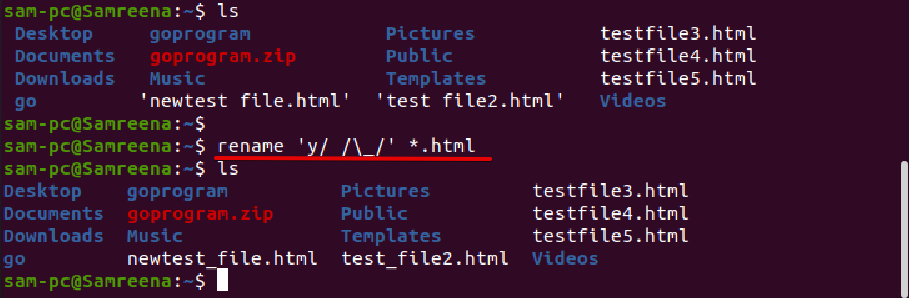
For example, to rename all those files, which contain spaces in file name and you want to replace it with underscores. In this case, the rename command will help you in the following way:
Using rename command, you can convert the file name in all lowercase letters as follows:
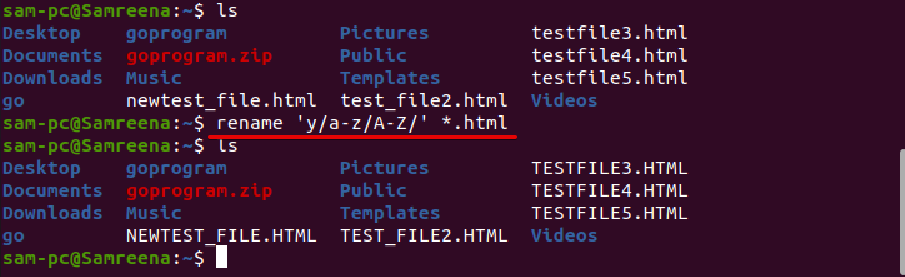
Similarly, to convert the file name to all uppercase letters, use the following command:
To explore more options and uses of rename command, type the following terminal command:
Conclusion
We discussed in this article how to rename files in Ubuntu 20.04 LTS distribution using the terminal application. Moreover, we explored the working and uses of the ‘mv’ and ‘rename’ commands for renaming a file. From the above discussion, we concluded mv command is useful for renaming a file but, rename command offers more advanced options for file renaming in the Ubuntu system.
About the author
Samreena Aslam
Samreena Aslam holds a master’s degree in Software Engineering. Currently, she’s working as a Freelancer & Technical writer. She’s a Linux enthusiast and has written various articles on Computer programming, different Linux flavors including Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, and Mint.