- Rename a File in Linux – Bash Terminal Command
- How to Use the Linux mv Command
- How to Name Files in Bulk Using mv
- Conclusion
- How Do I Rename a File in the Ubuntu Terminal?
- Renaming Files in Ubuntu 20.04 LTS System Using Terminal
- Rename File in Ubuntu Using the mv Command
- Example
- How to Use the mv Command to Rename Multiple Files?
- How to Use the Rename Command to Rename Files in Ubuntu?
- Syntax of Rename Command
- Example
- Example
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Samreena Aslam
- Переименование файлов в Linux
- Переименование командой mv
- Переименование файла
- Переименование директории
- Переименование и перемещение
- Переименование командой rename
- Изменение расширения файлов
- Замена пробелов на подчеркивание
- Конвертация имен файлов в строчные буквы
- Конвертация имен файлов в прописные буквы
- Показать, что именно будет переименовано, но не переименовывать
- Массовое переименование с использованием программ
Rename a File in Linux – Bash Terminal Command
Zaira Hira
Renaming files is a very common operation whether you are using the command line or the GUI.
Compared to the GUI (or Graphical User Interface), the CLI is especially powerful. This is in part because you can rename files in bulk or even schedule the scripts to rename files at a certain point in time.
In this tutorial, you will see how you can rename files in the Linux command line using the built-in mv command.
How to Use the Linux mv Command
You can use the built-in Linux command mv to rename files.
The mv command follows this syntax:
mv [options] source_file destination_fileHere are some of the options that can come in handy with the mv command:
- -v , —verbose : Explains what is being done.
- -i , —interactive : Prompts before renaming the file.
Let’s say you want to rename index.html to web_page.html . You use the mv command as follows:
zaira@Zaira:~/rename-files$ mv index.html web_page.html Let’s list the files and see if the file has been renamed:
zaira@Zaira:~/rename-files$ ls web_page.htmlHow to Name Files in Bulk Using mv
Let’s discuss a script where you can rename files in a bulk using a loop and the mv command.
Here we have a list of files with the extension .js .
zaira@Zaira:~/rename-files$ ls -lrt total 0 -rw-r--r-- 1 zaira zaira 0 Sep 30 00:24 index.js -rw-r--r-- 1 zaira zaira 0 Sep 30 00:24 config.js -rw-r--r-- 1 zaira zaira 0 Sep 30 00:24 blog.jsNext, you want to convert them to .html .
You can use the command below to rename all the files in the folder:
for f in *.js; do mv -- "$f" "$.html"; doneLet’s break down this long string to see what’s happening under the hood:
- The first part [ for f in *.js ] tells the for loop to process each “.js” file in the directory.
- The next part [ do mv — «$f» «$.html ] specifies what the processing will do. It is using mv to rename each file. The new file is going to be named with the original file’s name excluding the .js part. A new extension of .html will be appended instead.
- The last part [ done ] simply ends the loop once all the files have been processed.
zaira@Zaira:~/rename-files$ ls -lrt total 0 -rw-r--r-- 1 zaira zaira 0 Sep 30 00:24 index.html -rw-r--r-- 1 zaira zaira 0 Sep 30 00:24 config.html -rw-r--r-- 1 zaira zaira 0 Sep 30 00:24 blog.htmlConclusion
As you can see, renaming files is quite easy using the CLI. It can be really powerful when deployed in a script.
What’s your favorite thing you learned here? Let me know on Twitter!
You can read my other posts here.
How Do I Rename a File in the Ubuntu Terminal?
Renaming an existing file is a basic operation that usually does not require a specialized tool in any operating system. Renaming a single file in Linux is quite a simple task but renaming more than one or multiple files via terminal is a more challenging job for new Linux users. In all Linux distributions, the terminal is an essential command-line application for administering the Linux systems.
However, to use effectively this CLI application, you should have strong knowledge about basic Linux commands and fundamentals such as create, delete and renaming an existing file. Different commands are available in the Ubuntu Linux system to rename a file that we will explore in this article.
We will provide comprehensive details in this tutorial on how you can rename a file in Ubuntu using the command-line application Terminal. All commands have implemented for the demonstration on the Ubuntu 20.04 Linux system.
Renaming Files in Ubuntu 20.04 LTS System Using Terminal
The two different commands ‘mv’ and ‘rename’ are available in the Ubuntu Linux system to rename a file via terminal or command-line approach. Let us discuss each command in detail.
Rename File in Ubuntu Using the mv Command
Before using the ‘mv’ command, you should know how it works on your system. The basic syntax of the ‘mv’ command is given below:
The most popular ‘mv’ command options are provided below:
-f – Displays no message or alerts before overwriting a file name.
-i – Displays prompt confirmation or warning messages before renaming a file.
-u – It moves a file if the file does not exist on the specified destination or in case of a new file.
The file source can be the destination of one or more files. The destination only represents a single file.
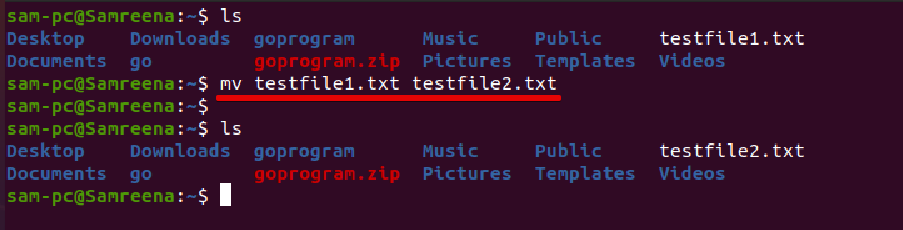
Example
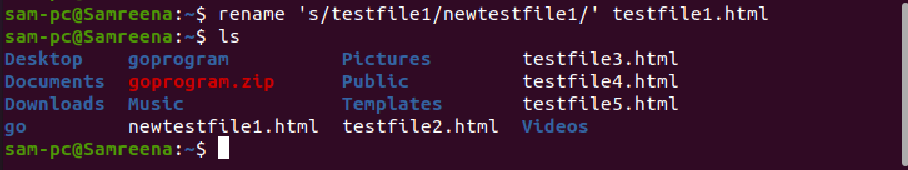
For example, to rename the file ‘testfile1.txt’ to ‘testfile2.txt, you need to run the following command:
How to Use the mv Command to Rename Multiple Files?
Usually, you can only rename a single file using the move command. To rename multiple files using the mv command, you can use the mv command to combine with different commands. Let us say, mv command can be used along with for loop, while loop, and find command.
Let us explain with the help of an example. Here, we want to rename all .txt extension files of the current directory replaced with another .html extension. In this case, the following code will help us:
The above code will iterate using for loop through the files list having the .txt extension. After that, in the second line, it will replace each file extension .txt with .html. In the end, ‘done’ indicated the end of the for loop segment.
How to Use the Rename Command to Rename Files in Ubuntu?
Using the rename command, you can rename multiple files of a current directly at once. This command contains more advance features as compared to the ‘mv’ command. For renaming files using the rename command, you should have basic knowledge about regular expressions usage.
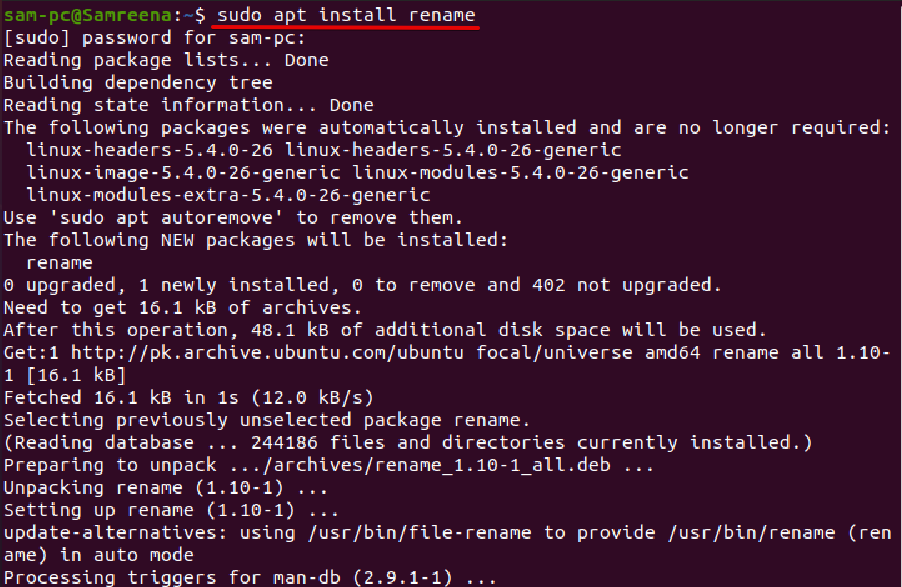
In most Linux distributions, the ‘rename’ command is installed by default. However, if you have not installed the rename command on your Ubuntu system then, it can be easily installed on Ubuntu and its derivatives by running the following command:
Syntax of Rename Command
Using the following syntax, you can use the rename command:
The rename command will rename files according to the specific regular Perl expressions.
Example
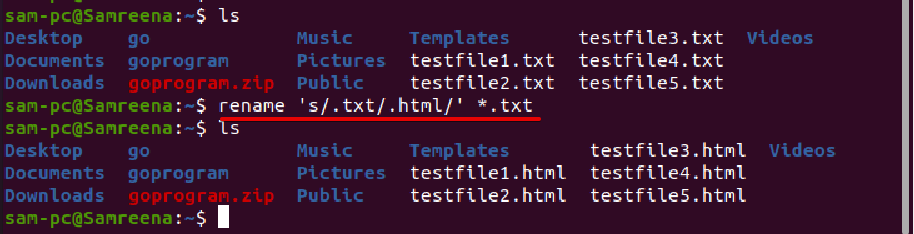
In the following example, we want to change the extension of all text files. So, we will change or replace all files with extension .txt to .html by executing the following command:
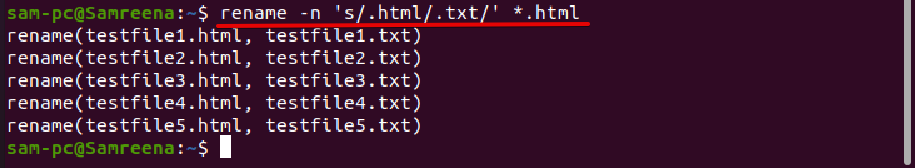
When you use the rename command followed by option ‘-n’, it also displays the file names to be renamed and renaming them as follows:
The above command displays the following result on the terminal window:
By default, the rename command does not overwrite an existing file. However, if you pass option -f along with the rename command then, it will help you to overwrite the existing files. Execute the following command to use the rename command followed by the -f option:
To change or rename the file name using rename command use the following command:
Example
For example, we want to rename a single file with the name ‘testfile.txt’ to newtestfile.txt. In this case, the above command will be modified into the following form:
To see more usage of rename command, let us try the following examples:
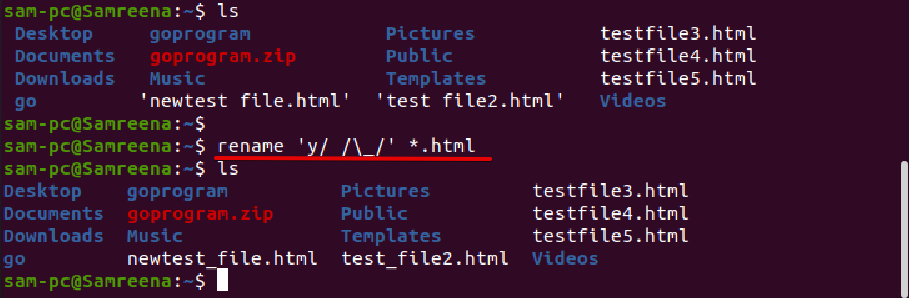
For example, to rename all those files, which contain spaces in file name and you want to replace it with underscores. In this case, the rename command will help you in the following way:
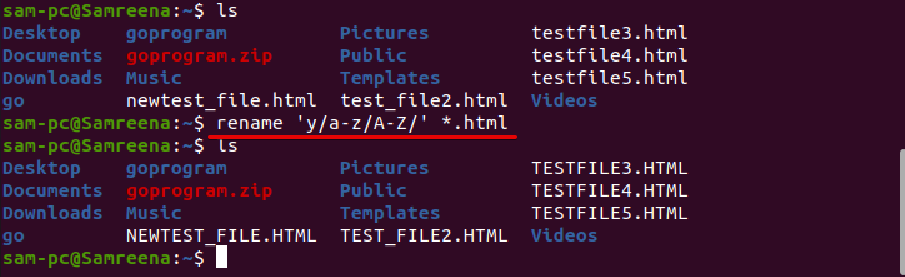
Using rename command, you can convert the file name in all lowercase letters as follows:
Similarly, to convert the file name to all uppercase letters, use the following command:
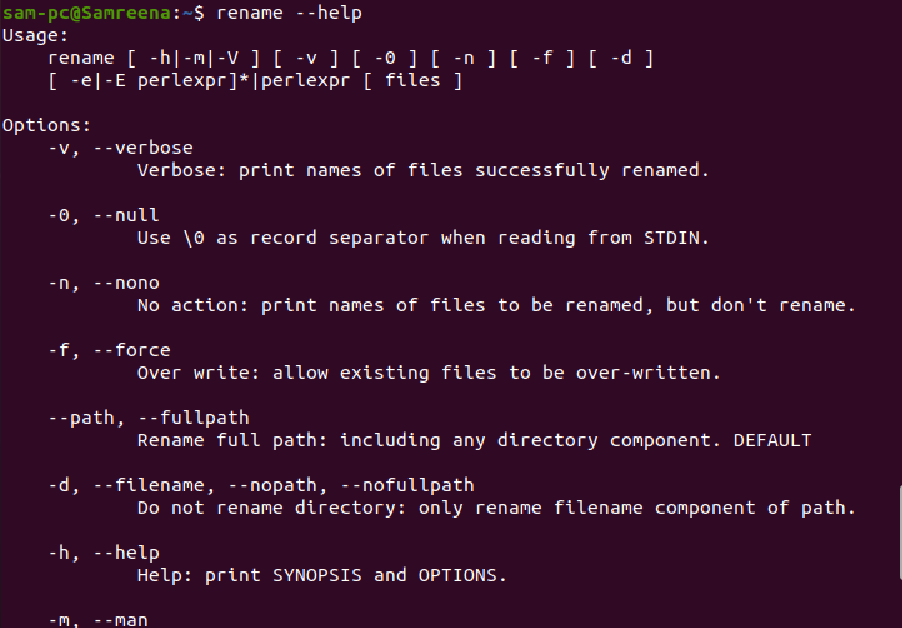
To explore more options and uses of rename command, type the following terminal command:
Conclusion
We discussed in this article how to rename files in Ubuntu 20.04 LTS distribution using the terminal application. Moreover, we explored the working and uses of the ‘mv’ and ‘rename’ commands for renaming a file. From the above discussion, we concluded mv command is useful for renaming a file but, rename command offers more advanced options for file renaming in the Ubuntu system.
About the author
Samreena Aslam
Samreena Aslam holds a master’s degree in Software Engineering. Currently, she’s working as a Freelancer & Technical writer. She’s a Linux enthusiast and has written various articles on Computer programming, different Linux flavors including Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, and Mint.
Переименование файлов в Linux
Переименование файлов в Linux можно выполнять средствами графических программ, а также через командную строку. Можно переименовать один файл, а можно сразу группу файлов — массовое переименование. Рассмотрим различные способы, с помощью которых можно переименовывать файлы в Linux.
Переименование командой mv
Команда mv (от слова move) используется для переименования или перемещения файлов и директорий из командной строки.
Синтаксис команды mv очень простой:
источник — файл(ы) или директория, которую необходимо переместить или переименовать.
назначение — файл или директория, в которую будет перемещен источник .
Основные опции:
-f — перезаписывать существующие файлы.
-n — не перезаписывать существующие файлы.
-i — выдавать запрос на перезапись существующих файлов.
-u — не перемещать файлы, которые уже существуют, если существующие файлы новее (время модификации новее).
-v — выводить имя каждого файла перед его переносом.
Как задавать имена файлов и директорий для переименования:
- Чтобы переименовать файл с помощью команды mv нужно в качестве источника задать данный файл, а в качестве назначения указать новое имя файла.
- Если указывается путь до файла, то директории должны совпадать, иначе файл будет перемещен в другую директорию.
- Если в качестве источника указать файл, а в качестве назначения путь до файла в другой директории и задать новое имя файла, то файл будет перемещен в другую директорию и переименован.
- Если в качестве источника указана директория, а в качестве назначения задано новое имя для данной директории, то директория будет просто переименована. Если же директория назначения уже существует, то директория источник будет перемещена в директорию назначения .
Переименование файла
Переименование файла myfile1.dat в файл myfile2.dat:
Переименование файла с указанием пути до файла:
mv /home/pingvinus/myfile1.dat /home/pingvinus/myfile2.datПереименование директории
Переименование директории /home/pingvinus/mydir1 в директорию /home/pingvinus/mydir2 . Справедливо, если /home/pingvinus/mydir2 не существует.
mv /home/pingvinus/mydir1 /home/pingvinus/mydir2Если /home/pingvinus/mydir2 существует, то, выполнив команду:
mv /home/pingvinus/mydir1 /home/pingvinus/mydir2директория mydir1 будет перемещена внутрь директории /home/pingvinus/mydir2 . То есть mydir1 будет в результате находиться по адресу /home/pingvinus/mydir2/mydir1 .
Переименование и перемещение
Если в качестве файла назначения указан новый путь и новое имя файла, то файл будет перемещен и переименован. Например, следующая команда перемещает файл myfile1.dat в директорию /home/pingvinus/dir и переименовывает его в myfile2.dat :
mv /home/pingvinus/myfile1.dat /home/pingvinus/dir/myfile2.datПереименование командой rename
Команда rename служит для массового (пакетного) переименования файлов. Она позволяет выполнять замену определенных символов или частей имени файла и использованием Perl-регулярных выражений.
Если вдруг в вашем дистрибутиве нет команды rename , то ее можно установить, выполнив (выберите соответствующую команду для вашего дистрибутива):
sudo apt install rename sudo yum install prename yaourt -S perl-rename старое_имя — регулярное выражение или часть имени файла, которое нужно заменить на новое_имя .
новое_имя — задает результирующее имя файла (может быть регулярным выражением).
Основные опции:
-f — перезаписывать существующие файлы.
-n — вывести список файлов, которые будут переименованы и их новые имена, но не выполнять переименование.
-v — вывести список обработанных файлов.
Проще всего понять, как пользоваться данной командой, на примерах.
Изменение расширения файлов
Массово изменить расширение .html на .php у всех html-файлов.
По умолчанию rename не перезаписывает существующие файлы. Чтобы существующие файлы перезаписывались, используется опция -f :
Замена пробелов на подчеркивание
Заменить все символы пробелов в имени файлов на символ подчеркивания:
Конвертация имен файлов в строчные буквы
Конвертация имен файлов в прописные буквы
Показать, что именно будет переименовано, но не переименовывать
Чтобы избежать ошибок при переименовании файлов, особенно при использовании сложных регулярных выражений, можно сначала вывести список того, что будет переименовано, но не запускать само переименование. Для этого служит опция -n .
Например, мы хотим изменить расширение у файлов с .jpeg на .jpg . Используем опцию -n , чтобы просто вывести какие файлы будут переименованы:
Полное описание команд mv и rename можно получить, выполнив в терминале команды:
Массовое переименование с использованием программ
Для массового переименования файлов можно воспользоваться программами: