- How to Restart Networking in Debian Linux
- Restarting Networking on Debian 8 Wheezy and Older:
- Installing Network Manager on Debian 9 Stretch:
- Using Network Manager to Configure Networking:
- Restarting a Single Connection Using Network Manager:
- Restarting Network Manager:
- About the author
- Shahriar Shovon
- Tutorial Restart Networking on Debian 10
- How to Restart Networking on Debian 10
- Restart Networking on Debian 10 | Debian 9
- How to restart network from the command-line
- Conclusion
- How to restart network services in Linux
- Get network Service Status
- For latest (Ubuntu/Debian/Mint)
- For CentOS 8 / Fedora
- Stop Network Services
- For Ubuntu/Debian/Mint
- For CentOS 8/Fedora
- Start Network Service
- For Ubuntu/Debian/Mint
- For CentOS 8/Fedora
- Restart Network Service
- For Ubuntu/Debian/Mint
- For CentOS 8/Fedora
- Conclusion
How to Restart Networking in Debian Linux
On Linux, one of the basic things you do is configure the network. Once you make changes, you have to restart the networking service in order for the changes to take effect.
In this article, I will show you how to configure the network easily and restart them properly on Debian Linux. Let’s get started.
Restarting Networking on Debian 8 Wheezy and Older:
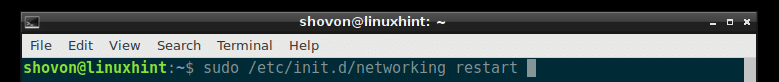
On Debian Linux, the network configuration is stored in /etc/network/interfaces file. On older version of Debian, when you make changes to /etc/network/interfaces file, you can restart networking with the following command:
The network service should be restarted. But on Debian 9 Stretch, that no longer works due to a bug.
Installing Network Manager on Debian 9 Stretch:
You can directly configure a network interface using /etc/network/interfaces file manually if you like. But the good news is, you don’t have to do that. On recent Linux distributions such as Debian 9 Stretch, networking can be managed by the Network Manager. It makes configuring a network really easy. Network Manager has command line utilities for network configuration.
If you have minimal server version of Debian 9 Stretch installed, you may not have Network Manager installed. In that case, you have to install Network Manager.
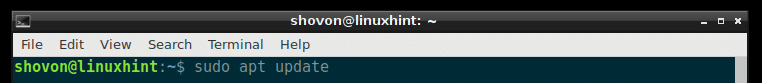
First update the package repository cache with the following command
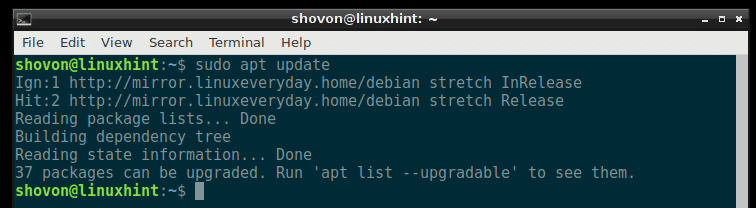
The package repository cache should be updated.
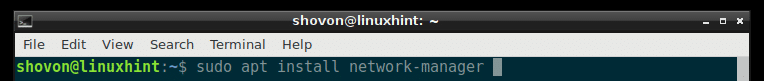
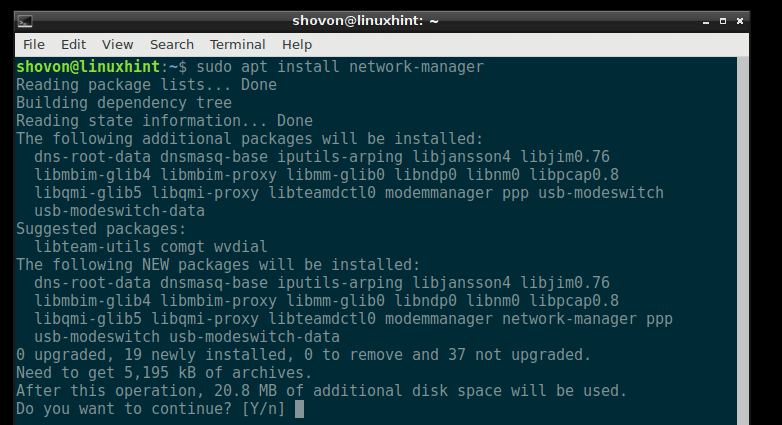
Now install Network Manager with the following command:
Press y and then press to continue.
Network Manager should be installed.
Using Network Manager to Configure Networking:
Network Manager has nmtui terminal based interactive tool that you can use to configure networking on Debian 9 Stretch.
To start nmtui, run the following command:
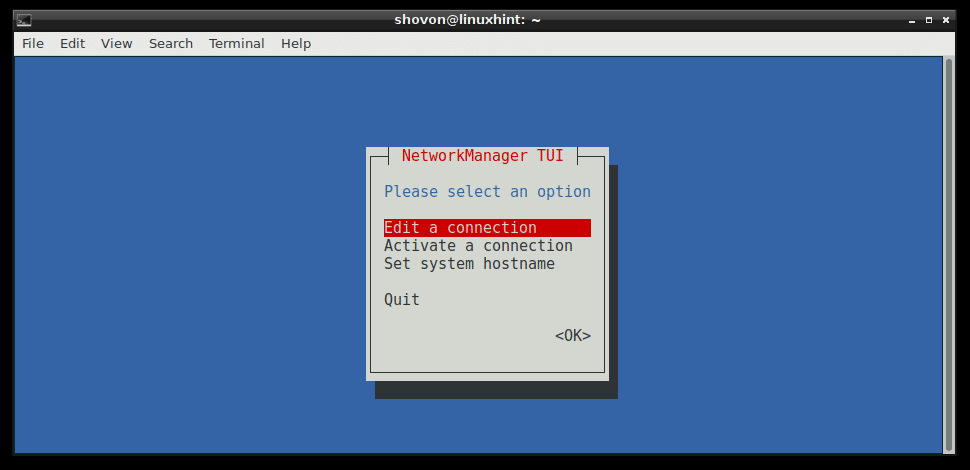
You should see the following window. From here you can set hostname, edit/add network connection, and active/deactivate network connections that you created.
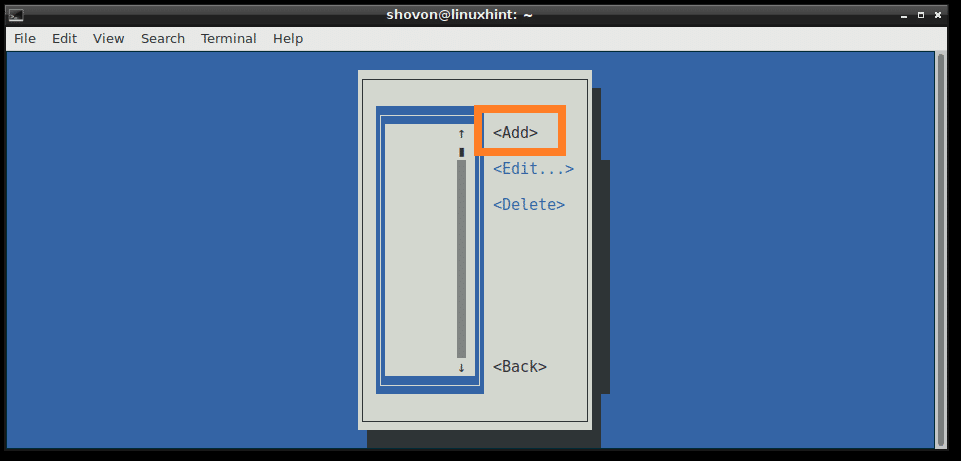
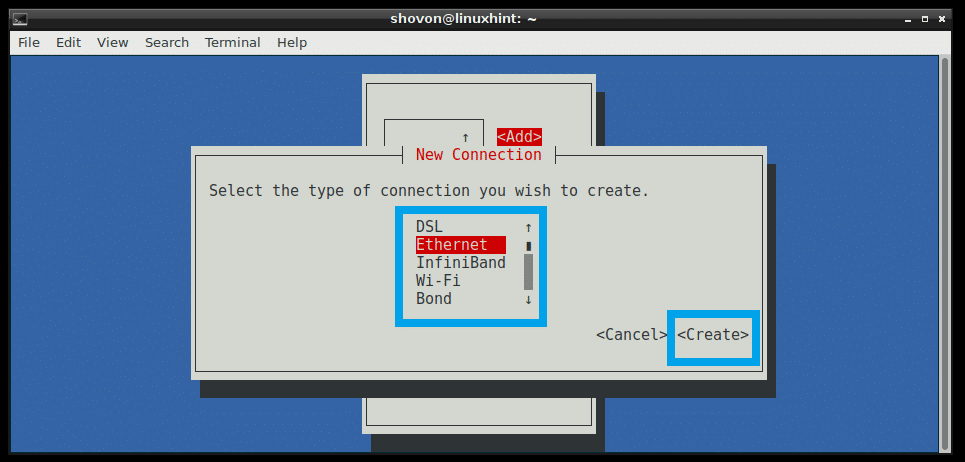
To create a connection, go to Edit a connection. Then press to select and then press .
Now select your connection method. I am going for Ethernet as I have a wired connection. Now press and select and then press .
Now type in a Profile name. It can be anything you want. I recommend you make it short and easy. Now type in a Device identified. I have only one physical Ethernet cable connected to my computer and is recognized as ens33, so I typed that. You can run ip link show command to find out your Device identifier.
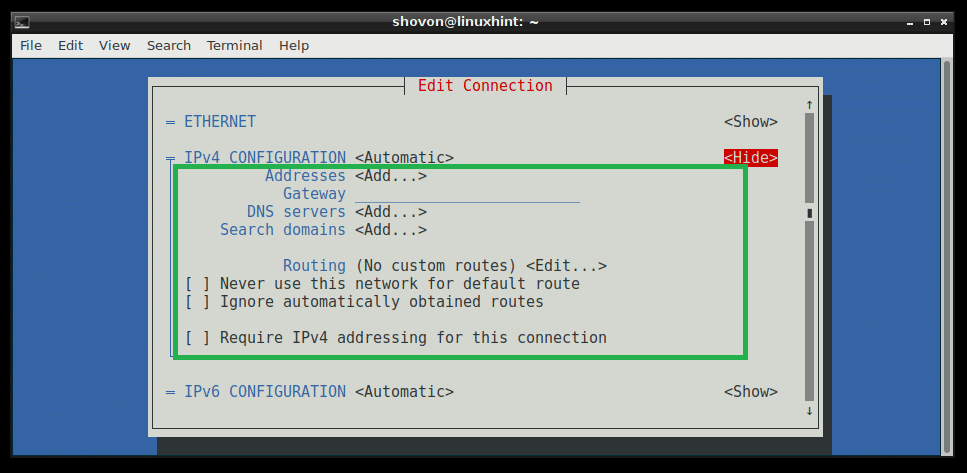
If you want to use DHCP to get the IP address for this network interface, then that’s pretty much everything you need to do. But if you want to assign a static IPv4 or IPv6 address, then you have to press to go to for IPv4 CONFIGURATION or IPv6 CONFIGURATION or both depending on your need. Then press . Then you should see something like this. Type in your IP Address, Gateway, DNS servers information, Routing and other information.
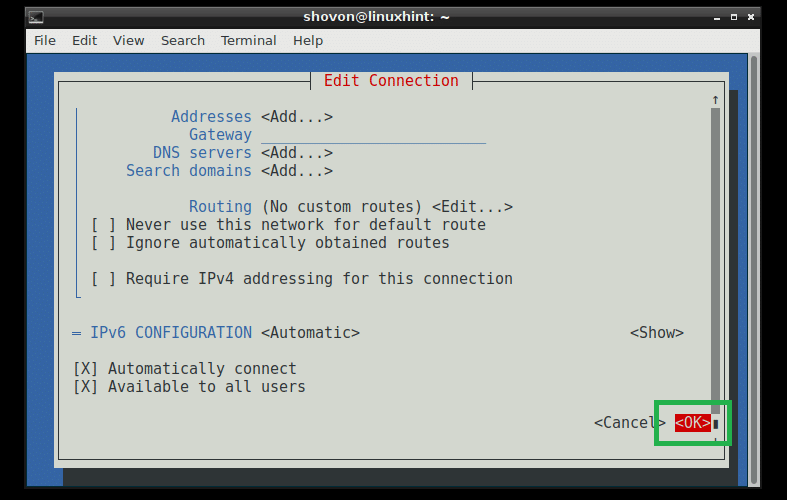
Once you’re done, scroll down using the and go to and then press .
Your connection should be created and activated.
NOTE: Network Manager do not manage interfaces defined in /etc/network/interfaces file. So if the interface you’re configuring with Network Manager is also configured using the /etc/network/interfaces file, then be sure to comment it out or remove it from the /etc/network/interfaces file for Network Manager to work with that interface.
Restarting a Single Connection Using Network Manager:
In the earlier section, I showed you how to create a connection using Network Manager. In this section I will show you how to restart the connection.
When you edit a connection, you must restart the connection for the changes to take effect.
You can use the nmtui utility to restart a connection using the Terminal based user interface.
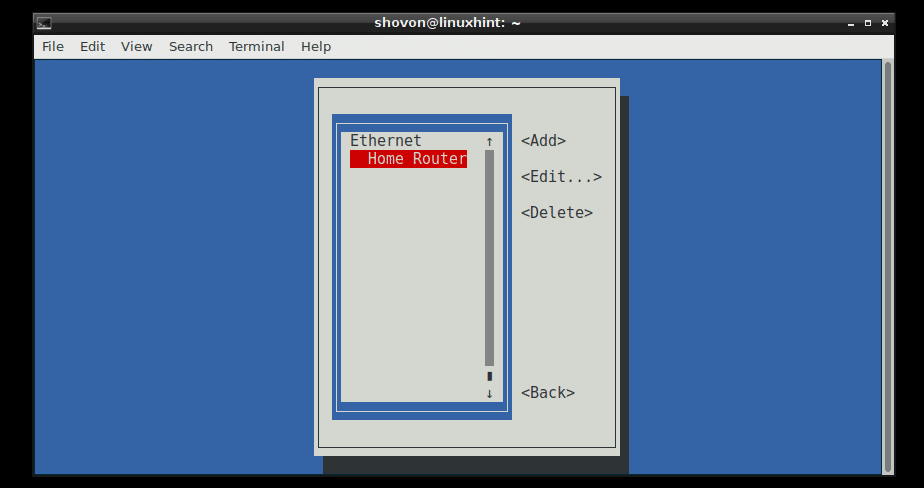
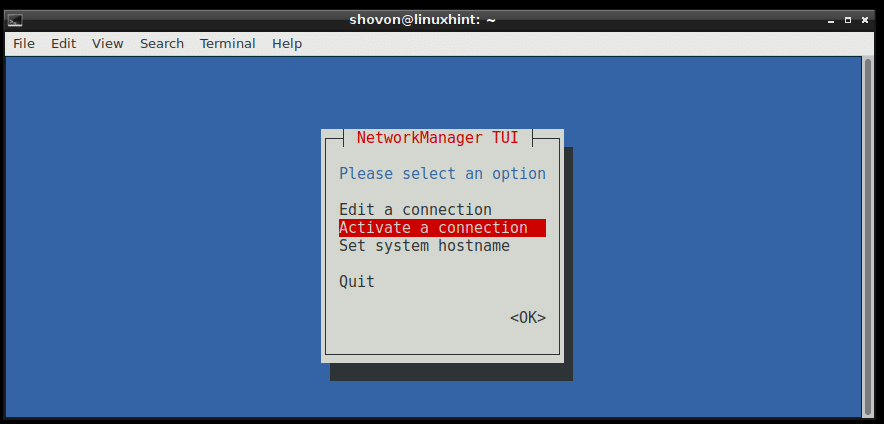
Run nmtui and go to Activate a connection.
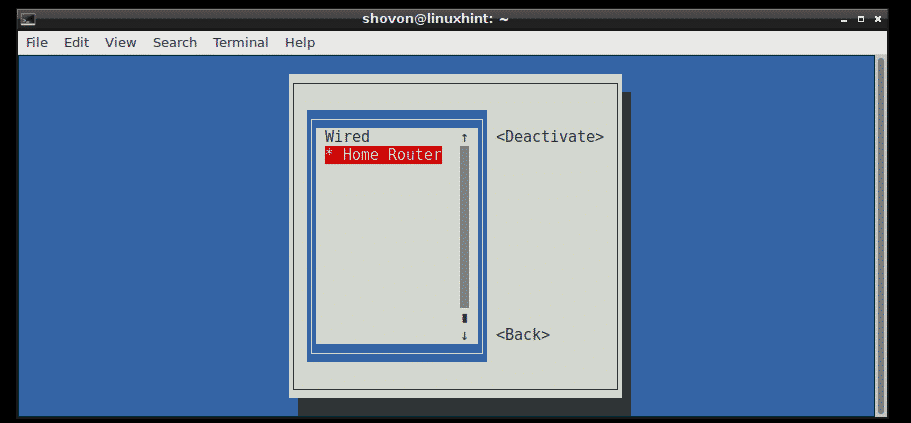
Now select your Connection from the list, in my case the Home Router, then press .
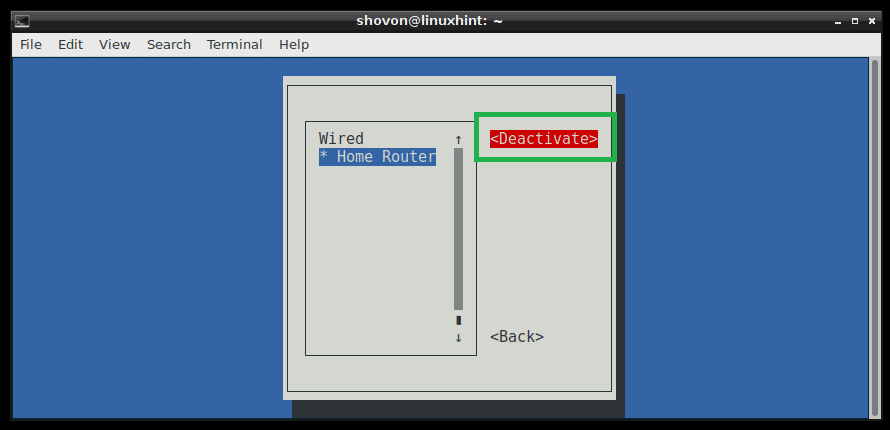
Now while is selected, press to deactivate the connection first.
Now while is selected, press to activate the connection again. Your changes should be applied.
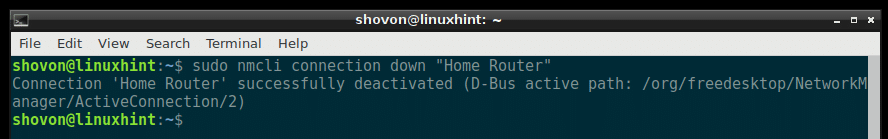
You can do the same thing from the terminal using the nmcli command.
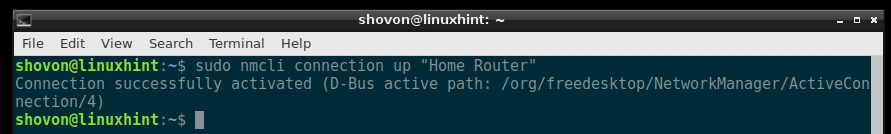
Deactivate the Home Router connection with the following command:
To Activate the Home Router connection again, run the following command:
You can also Restart the connection with a single command:
Restarting Network Manager:
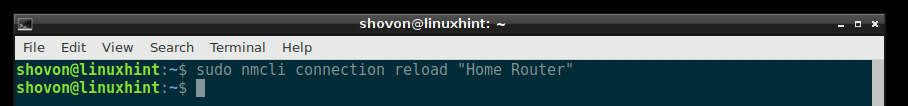
If you have a lot of connection, which may take a lot of time to restart one by one, then you can just restart the Network Manager service with the following command:
The Network Manager service should restart.
That’s how you Restart Networking Properly on Debian Linux. Thanks for reading this article.
About the author
Shahriar Shovon
Freelancer & Linux System Administrator. Also loves Web API development with Node.js and JavaScript. I was born in Bangladesh. I am currently studying Electronics and Communication Engineering at Khulna University of Engineering & Technology (KUET), one of the demanding public engineering universities of Bangladesh.
Tutorial Restart Networking on Debian 10
Network configuration is one of the most basic and required tasks in Linux distributions. After you make the necessary changes to the configuration file, you will need to restart the network service. In this article, we want to introduce you to Tutorial Restart Networking on Debian 10. You can visit the packages available in Eldernode to purchase a Linux VPS server.
How to Restart Networking on Debian 10
You can restart the network service on Linux using different commands. To restart the network service, you can use the commands mentioned in the following sections on your Debian distribution. After making a change to the server network configuration file, you must restart the server network service to reflect the changes. This tutorial describes the steps to restart the network on the Debian server. Please be with us.
Restart Networking on Debian 10 | Debian 9
In this step, we intend to restart the network. To do this you can easily enter the following command:
sudo /etc/init.d/networking restartIt should be noted that in the Debian 10 Linux distribution, the network configuration is stored in the /etc/network/interface file. After running the above command, you can use the following command to check the status of the server network:
sudo /etc/init.d/networking statussudo systemctl status networkingAfter running the above command, you can use the following commands to stop and start using. The important point is that you should not run them in a remote ssh session because you will be disconnected.
sudo /etc/init.d/networking stopsudo /etc/init.d/networking startYou can also run Debian Linux with systemd:
sudo systemctl restart networkingHow to restart network from the command-line
In this section, to restart the network from the command line, you have the following 4 options that you can use. The first option to restart the network from the command line is to use the netplan command:
The second way to restart the network administrator is to use the systemctl command:
sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager.serviceThe next method is similar to the above command, which is done by executing the system command:
sudo service network-manager restartIn this section, it should note that the network administrator control with the nmcli command launches the network administrator directly:
sudo nmcli networking offConclusion
There are several situations in which you may have to restart your network via Debian. This may be due to a change in network settings. It may also be because the network connection is not working properly. In general, whenever there is a problem with the system, the most appropriate way is to restart. In this article, we tried to introduce you to Tutorial Restart Networking on Debian 10.
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 3.9 / 5. Vote count: 7
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
How to restart network services in Linux
Sometimes, when you changed the network configuration or due to some network problems, you may need to restart the network services again on your Linux system to solve your problem. In this article, we will talk about how to restart the networking services on in different Linux distributions (Ubuntu, Debian, LinuxMint and CentOS) by using the command line. We have implemented different commands on Ubuntu 20.04 and CentOS 8 system. All commands which we have executed on Ubuntu 20.04 can be also used for Debian and LinuxMint distributions.
Get network Service Status
You can get the network services running status by using the following command:
For latest (Ubuntu/Debian/Mint)
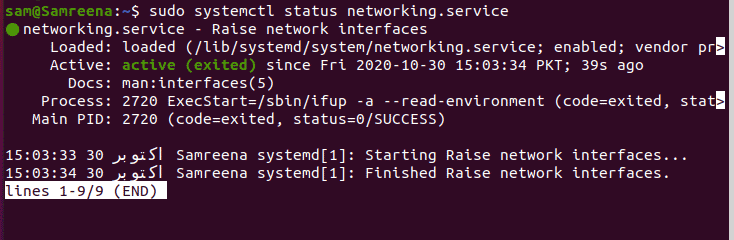
To check the networking services are running on your system or not, by using the following ‘systemctl’ command you can view the networking service status on your Ubuntu/Debian/Mint system:
$ sudo systemctl status networking
$ sudo systemctl status networking.service
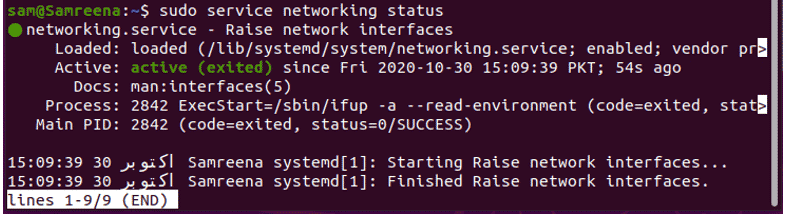
You can also display the networking service status by using the service command which is given as follows:
$ sudo service networking status
$ /etc/init.d/networking status
For CentOS 8 / Fedora
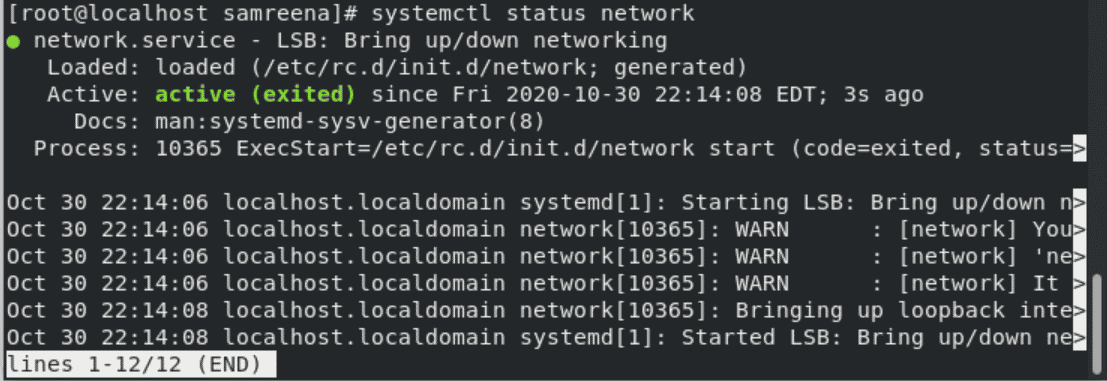
If you are using CentOS 8 then you can check the network service status by using the following command:
If you received an error like ‘network.service unit not found’ then, you will run the following command to start the network manager:
# systemctl start NetworkManager
Now, start the network services and you can get network status by using the above-mentioned command.
Stop Network Services
You can stop your network services through the method which is mentioned below. But, if you have a remote connection with SSH, we are not recommended you to stop the service because it may create problems.
For Ubuntu/Debian/Mint
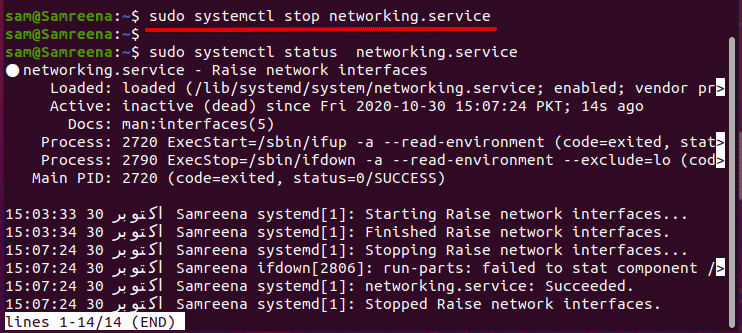
You can use the ‘stop’ option with the above ‘networking’ command on Ubuntu, Debian, Kali, Mint distributions in order to stop network services.
$ sudo /etc/init.d/networking stop
$ sudo systemctl stop networking.service
For CentOS 8/Fedora
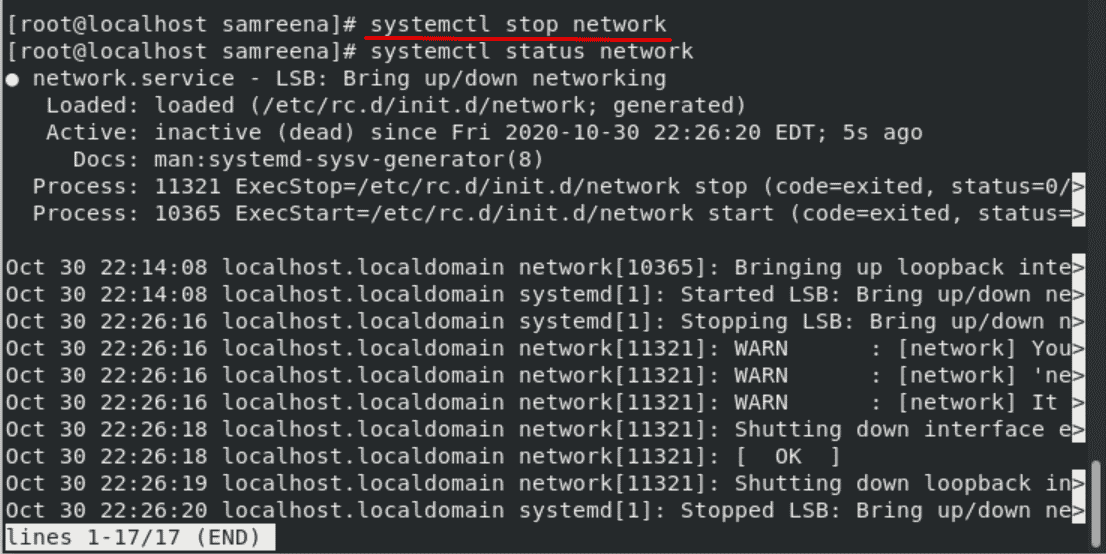
In CentOS 8, using the following command you can stop network services:
Now, if you will check the network status you will see that network services are stopped on your system.
Start Network Service
If networking services are stopped on your system then, you start these services on the Linux system.
For Ubuntu/Debian/Mint
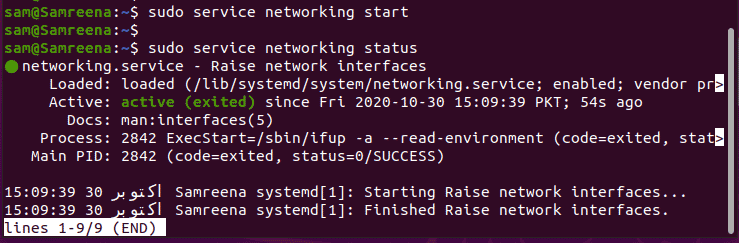
You can also start the network services by using the service command. Use ‘start’ option to start the network service on your Ubuntu. Debian and LinuxMint distributions.
$ sudo service networking start
$ sudo systemctl start networking.service
$ $ sudo /etc/init.d/networking start
For CentOS 8/Fedora
In CentOS 8, by using the following command you can start the network service on your system:
Restart Network Service
You can also restart the network service by using the following command on Linux distributions:
For Ubuntu/Debian/Mint
Type the following command to restart the network service on Ubuntu, Debian, and Linux Mint:
$ /etc/init.d/networking restart
$ sudo systemctl restart networking.service
$ sudo systemctl restart networking
For CentOS 8/Fedora
Use the following command to restart the network service on CentOS 8:
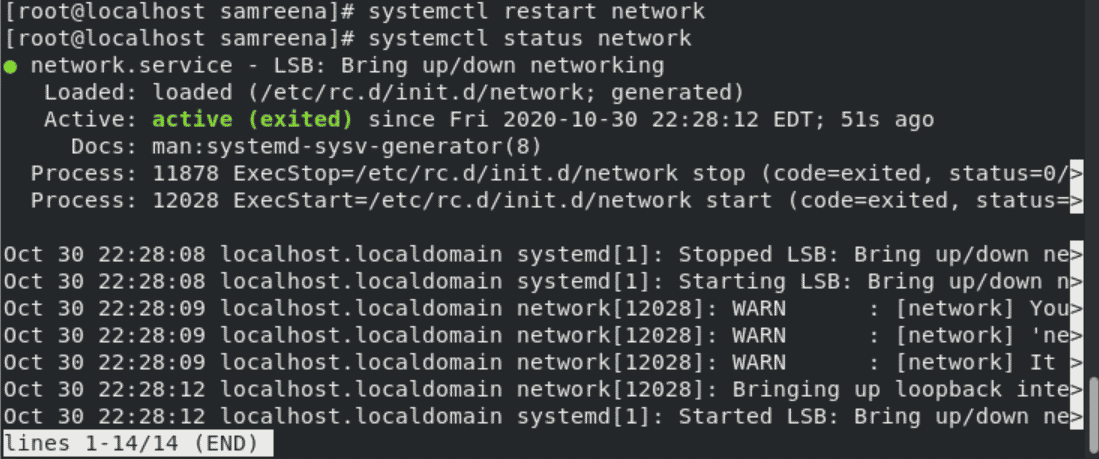
# systemctl restart network
If you get the following error on the terminal then, you need to start the NetworkManager services on your system by using the following command:
# systemctl start NetworkManager
Now, again restart the network service. You will see the following output on the CentOS system:
Conclusion
From the above information, we have explored how to start, stop, and restart the network service on different Linux distribution like Ubuntu, Debian, Linux Mint, and CentOS 8. Moreover, you can troubleshoot the network error through the NetworkManager tool on CentOS 8. If you need more details then, you can implement all command on your system and then let us know about your problems. Please don’t stop services if you have a remote ssh connection that may create a problem.
Samreena Aslam holds a master’s degree in Software Engineering. She’s a technical writer and has written various articles on different Linux flavours including Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS and Mint as well as programming guides in various programming languages