- Fix: cannot open output file permission denied
- Reason: Unauthorized Access
- Solution: Access/Grant the Directory Permissions
- Alternative Solution: Change the Output File Ownership
- Conclusion
- How to fix permission denied error in Linux? [Solutions]
- What is Linux Permission Denied Error?
- How To Fix Permission Denied Error in Linux?
- Representation of permissions
- Symbolic representation
- How to Solve Bash Permission Denied?
- Conclusion
- Ошибка «Permission denied» в Linux
- Изменение прав в терминале
- Изменение прав в файловом менеджере
- В заключение
Fix: cannot open output file permission denied
In Linux, every file and directory holds some permissions either it can be “read”, “write,” or “execute”.
In some cases, the file only has the “read” permission, which means that the user can only read that file and can not execute it. If the user executes that file, an error occurs in such a situation, such as “cannot open output file permission denied”.
In this guide, the causes and the possible solutions are described for the issue “cannot open output file permission denied”. The table of content of this guide is as follow:
Let’s get started with the first reason of the error.
Reason: Unauthorized Access
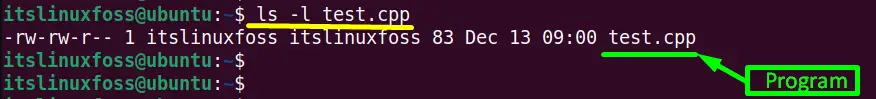
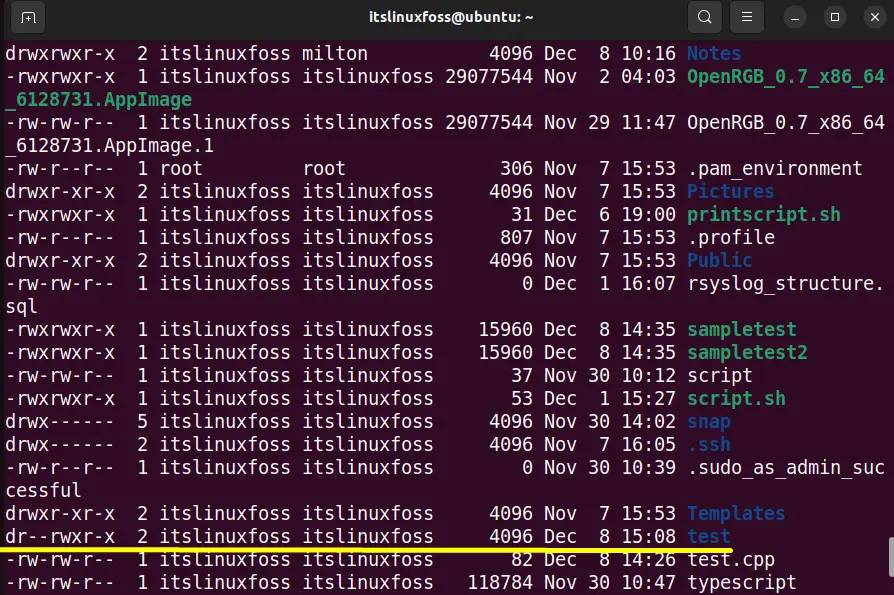
The error “cannot open output file permission denied” occurs because the currently logged-in user does not have the directory permissions. Suppose the “test” directory contains the “test.cpp” program having extension “.cpp” as shown in the screenshot:
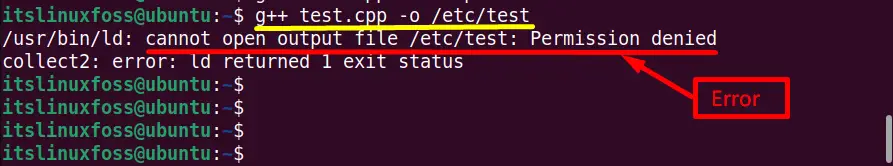
Convert the “test.cpp” into the executable file “test” to run in the “etc” directory by using the below-mentioned “g++” command. Use the “-o” flag with the command, as it will compile the “test.cpp” file and create the desired executable file “test”:
The above command generates an error because the user does not have the “/etc/” directory permissions. The user only has permission to write the files available in the directory.
To resolve this error, the user must have to change the permissions of the “/etc/” directory
Solution: Access/Grant the Directory Permissions
The user can execute the “test.cpp” program in the “test” directory by changing its permissions. As the owner “itslinuxfoss” does not have the “write” permissions of the “test” directory as shown in the screenshot:
To change the “test” directory permissions, follow the below-mentioned steps.
Step 1: Change the Directory Permissions
Change the “test” directory permissions to make the “test.cpp” writable and executable. For this purpose, use the “chmod(Change Directory)” command with the combination of “u+wx” and the target directory name in the terminal (Ctrl+Alt+T):
The “test” directory now has “write” and “execute” permissions.
Step 2: Execute the Program
Execute the “test.cpp” program, and it will definitely execute now. The compiler “g++” compile that program and displays the output:
The output verifies that the error “cannot open output file permission denied” has been fixed.
Alternative Solution: Change the Output File Ownership
Here is another solution to open the output file. To perform this task, change the ownership of the specified output file using the “chown” Linux command. Run the below command in the terminal to make the current user an “owner” of the directory:
$ sudo chown -R "$USER:" /path/to/the/directory
The above command contains the following components:
- chown: Linux command that is useful to change the ownership of file/directory.
- -R: This flag represents “recursive” as it changes the ownership of files and subdirectories located in a directory.
- $USER: The current user replaces the global variable.
- path/to/directory: Shows the specified directory path.
The current user is the directory owner and can open the desired output file.
That’s all about the reasons and fixes of the output file permissions error.
Conclusion
The “cannot open output file permission denied” can be resolved by “accessing the Directory Permissions”.The permissions can be changed using the “chmod(Change Directory)” command. This error occurs while executing the “C” program file to the targeted directory that does not have the “write” and “execute” permissions. This guide explains all the possible solutions to resolve the error “cannot open output file permission denied” in Linux.
How to fix permission denied error in Linux? [Solutions]
When you are working with the Linux Operating system then a common error occurs i.e. permission denied, In this article, you will get to know about how to ‘permission denied’ error in Linux?[linux permissions denied]
List of content you will read in this article:
In the Linux operating system, you cannot execute any command without proper permission. Every file and directory has some permission or privilege (read, write, or execute) associated with them. If you are not authorized to access the file or directory, executing any command on that will result as a “permission denied” error in Linux. This prevalent common can only be resolved by getting the proper access to that file and directory. In this article, we will help you with how to fix the permission denied errors in Linux and what type of error this is with the help of various Linux commands.
What is Linux Permission Denied Error?
This type of error will occur whenever you run a command for which you do not have the execute permission. Similarly, you cannot perform read or write actions if you do not have read or write permission for any file or directory. These Linux permissions are the primary reason behind the security of Linux, as they will help in protecting the data from unauthorized access.
Linux system has three types of permissions
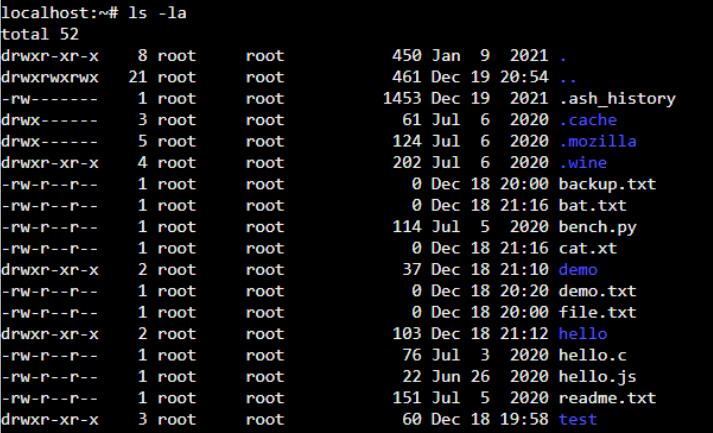
So, if you want to solve a Linux permission denied error, you can check your privileges for the specific file or folder using the following command.
This command will display the long listing of all files and folders along with the permission, as shown below.
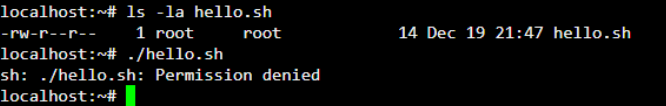
As shown below, we have created a shell script “hello.sh” without the execute permission. On executing “hello.sh”, you will get a “permission denied” error.
How To Fix Permission Denied Error in Linux?
For solving this error, you need to add the correct permissions to the file to execute. However, you need to be a “root” user or have sudo access for changing the permission. For changing the permission, Linux offers a chmod command. The chmod stands for change mod. This command has a simple syntax, as shown below.
chmod flags permissions filename
- Flags are the additional options that users can set.
- Permissions can either be read, write or execute in the file. You can represent them in symbolic form (r, w, and x) or octal numbers.
- The Filename specifies the file’s name for changing the permissions.
Representation of permissions
Below is the symbolic and octal representation of the user’s permissions while executing the “chmod” command. First, we will understand the representation before using it.
Symbolic representation
- r specifies the read permissions
- w specifies the write permissions
- x specifies the execute permissions
- Octal representation-
- 4 specifies the read permissions
- 2 specifies the write permissions
- 1 specifies the execute permissions
- 0 means no permissions issued.
How to Solve Bash Permission Denied?
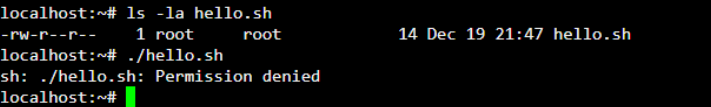
Now, we are aware of the error, as shown below.
Giving the appropriate permission to the user will solve the problem. Thus, we are giving the execute permission to the user to run the “hello.sh” shell script. Execute the below command to provide execute permission.
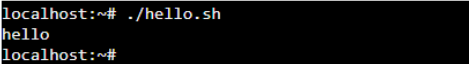
Now, we can see the change in the permission of the “hello.sh” script file. The above command provides the execute permission to the file. As you can see, the root user can make the required changes. If we execute the shell script, we should not get the error. Let’s try by running the below command.
After executing the “hello.sh”, we get the output that displays the “hello.” Changing permission has solved the problem of bash permission denied.
Conclusion
If you are a regular Linux user, you might have faced the “permission denied” error while executing various commands. This might be due to the incorrect privileges to run that command. Only a root user or user with sudo access can change the permissions for the file or directory you want to access or execute. If you are the correct user to make the required permission changes, you can run the “chmod” command and add the desired permission.
This is all about how you can solve/fix permission denied errors in Linux with the help of the above-listed commands/methods. If you think there are other alternatives to achieve the goal, you can put them down via the comment box. Also, you can buy a Linux VPS server to run and test the above-listed commands.
Ошибка «Permission denied» в Linux
Все операционные системы семейства Linux имеют четко разграниченные права доступа. В своей домашней директории пользователь может делать все, что ему угодно, до тех пор, пока укладывается в отведенные рамки. Попытка выйти за них приводит к появлению ошибки «Permission Denied».
Изменение прав в терминале
Рассмотрим вариант, в котором необходимо прочесть текстовый документ, созданный другим пользователем. Файлы TXT в Linux можно просматривать непосредственно в терминале с помощью команды «cat».
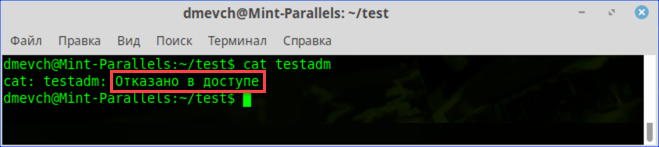
- Заходим в каталог с интересующим нас документом. Набираем команду «cat filename», подставляя вместо «filename» имя нужного файла. На скриншоте показана ошибка «Permission Denied», выглядящая в русской локализации как «Отказано в доступе».
Получаем ошибку «Permission Denied» при попытке просмотреть содержимое файла
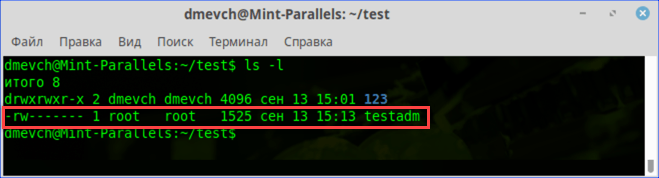
Проверяем права доступа к документу используя команду «ls -l»
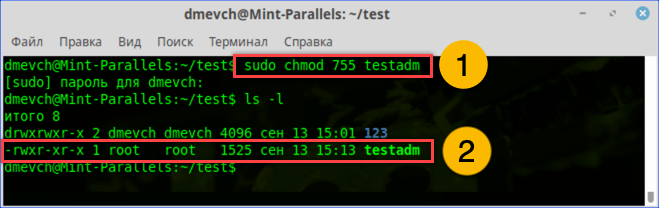
Используем команду «chmod» и административные права для получения доступа
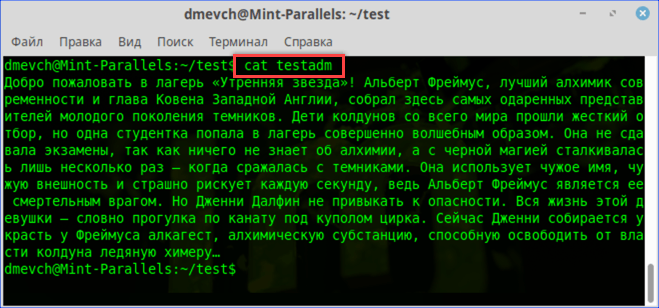
Просматриваем содержимое текстового документа командой «cat»
Изменение прав в файловом менеджере
Разберемся, как выполнить рассмотренную выше операцию в графическом интерфейсе, используя файловый менеджер из дистрибутива.
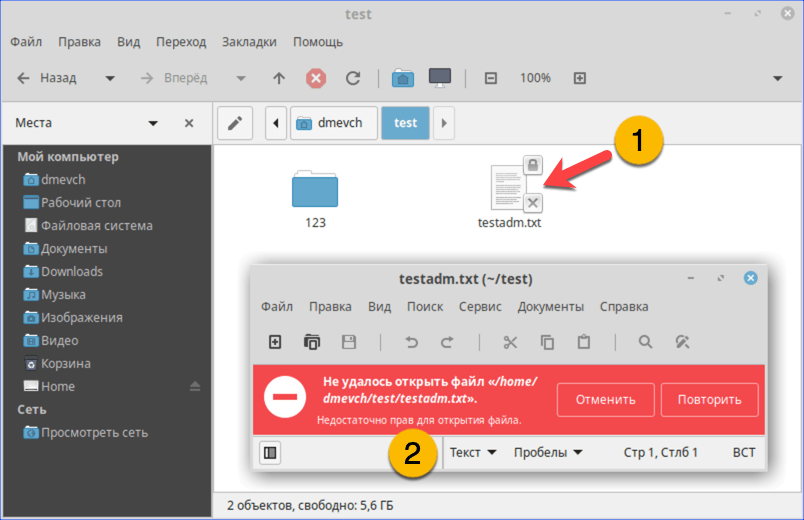
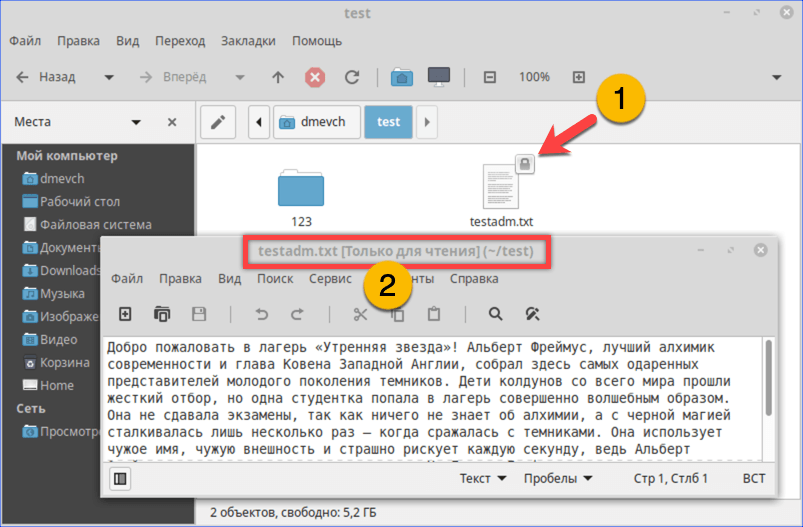
- Как видно на скриншоте, значок файла изначально имеет дополнительные символы, указывающие на то, что доступ у нему ограничен. При попытке посмотреть содержимое получаем графический вариант ошибки «Permission Denied».
При попытке открыть текстовый документ получаем ошибку «Permission Denied»
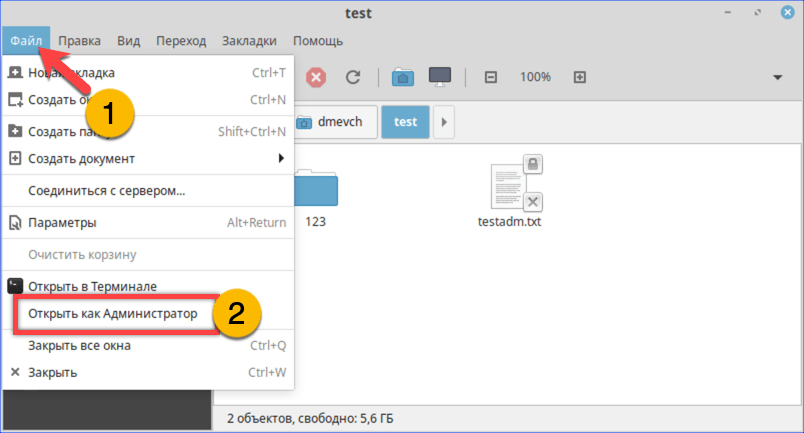
Открываем меню «Файл» и перезапускаем файловый менеджер от имени root
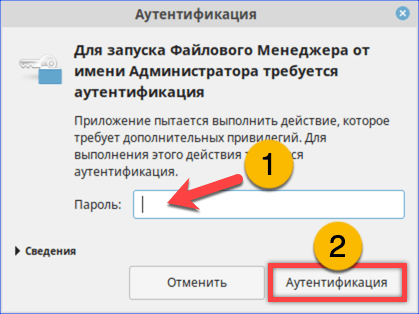
Набираем пароль root в окне аутентификации
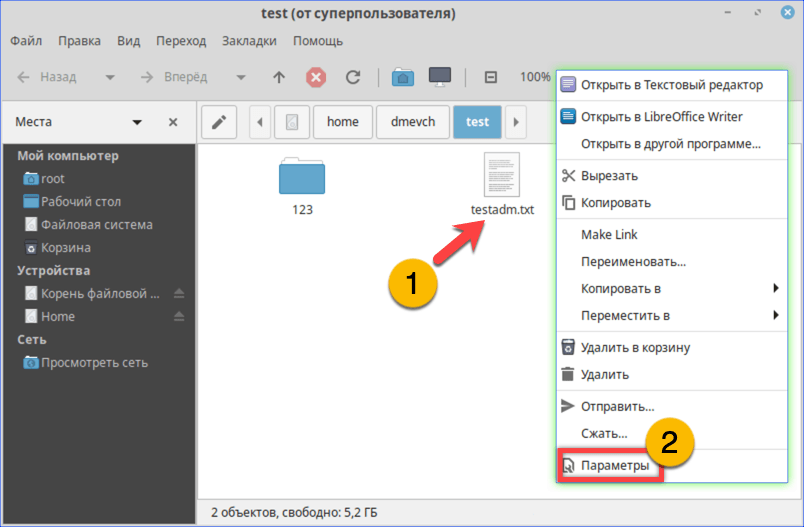
Открываем параметры файла с помощью контекстного меню
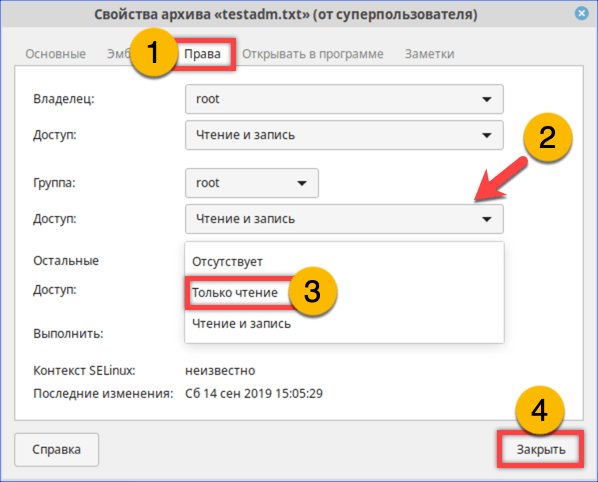
На вкладке «Права» разрешаем доступ для группы root и остальных пользователей
Открываем ранее недоступный файл в режиме чтения и изучаем содержимое
В заключение
Как видим, избавиться от ошибки Permission Denied достаточно просто. Решив изменить правда доступа к системным файлам, лишний раз убедитесь, что полностью уверены в своих действиях и понимаете последствия вносимых изменений.


![How to fix permission denied error in Linux? [Solutions]](https://monovm.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/permission-denied-linux327-main.webp)