- 15+ ping command examples in Linux [Cheat Sheet]
- Syntax to use ping command
- Different examples to use ping command in Linux
- 1. ping command to check the network connectivity of target host
- 2. Specify the number of pings to be performed with ping command
- 3. Check localhost network with ping command
- 4. Set interval seconds between sending each packet with ping command
- 5. Perform flood ping towards target host
- 6. Specify the number of data bytes to be sent with ping command
- 7. Display only the summary lines for ping command output
- 8. Set special IP timestamp options
- 9. Specify the timeout in seconds for ping command
- 10. Set time to wait for a response for ping command
- 11. Send multiple packets while waiting for replies with ping command
- 12. Set the IP time to live with ping command
- 13. Print timestamps with ping command
- 14. Use IPv4 or IPv6 address with ping command
- 15. Perform audible ping
- 16. Report ICMP ECHO reply for ping command
- 17. Print full user-to-user latency with ping command
- Conclusion
- Ping Command in Linux [How to Ping in Linux]
- What Is Ping Command? [How to Use Linux Ping]
- More Linux Ping Command Options
- Conclusion
15+ ping command examples in Linux [Cheat Sheet]
ping (Packet Internet Groper) is a command-line utility in Linux to check the network connectivity between host and host/server. It also helps to test, diagnose, and troubleshoot network connectivity issues. With the ping command, you can know if a server is up and running. The ping sends ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) ECHO_REQUEST messages to the specified host and waits for the reply. If the host is available, it sends an ICMP echo reply message (ECHO_RESPONSE). If ping does not receive any reply packets, it will exit with code 1.
Syntax to use ping command
The syntax for the ping command is:
Some options available in the ping command are given below.
Different examples to use ping command in Linux
1. ping command to check the network connectivity of target host
You can run the ping command without any option to check if the server of the target host is up and running. For example, to test our website, you can use the website name or IP address.
Sample Output:
You need to press Ctrl+C to stop the ping otherwise it will keep sending the packets infinitely. DUP! are the duplicate packets caused by inappropriate link-level retransmissions.
2. Specify the number of pings to be performed with ping command
When you specify the count N, the ping command stops sending the packets after N replies. You do not have to stop the ping with Ctrl+C.
Sample Output:
3. Check localhost network with ping command
You can ping localhost to check if you have a network connection.
Sample Output:
4. Set interval seconds between sending each packet with ping command
The -i option set interval time in seconds to wait before sending each packet. The default is to wait for one second between each packet, or not to wait in flood mode.
Sample Output:
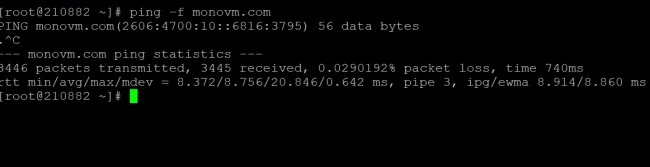
5. Perform flood ping towards target host
The -f option is used to run the flood ping. In flood ping, for every ECHO_REQUEST sent a period ».» is printed, and for every ECHO_REPLY received a backspace is printed. The interval time is zero and the packets are sent one hundred times per second. Only the super-user can use this option with zero intervals.
Sample Output:
6. Specify the number of data bytes to be sent with ping command
The -s option specifies the number of data bytes to be sent. The default size is 56 ICMP data bytes which become 64 bytes when combined with the 8 bytes of ICMP header data.
Sample Output:
7. Display only the summary lines for ping command output
The -q option can be used to display only the summary lines at startup time and when finished.
Sample Output:
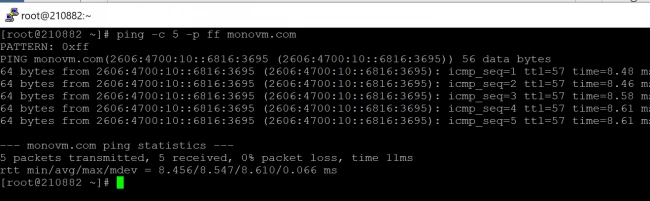
8. Set special IP timestamp options
The -T option sets special IP timestamp options. timestamp option can be:
- tsonly: only timestamps
- tsandaddr: timestamps and addresses
- tsprespec host1 [host2 [host3 [host4]]]: timestamp prespecified hops
Sample Output:
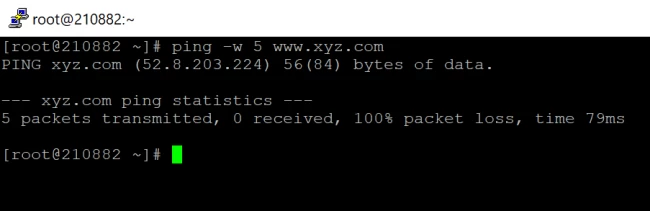
9. Specify the timeout in seconds for ping command
The -w option specifies a ( timeout in seconds) before ping exits regardless of how many packets have been sent or received. ping waits for the reply in seconds.
Sample Output:
10. Set time to wait for a response for ping command
The -W option is used to set the time to wait for a response, in seconds. The option affects only timeout in absence of any responses otherwise, ping waits for two RTTs (round-trip time).
Sample Output:
11. Send multiple packets while waiting for replies with ping command
The -l option specifies the number of packets that are to be sent while waiting for replies. Only the super-user can select preload more than 3.
Sample Output:
12. Set the IP time to live with ping command
You can use -t option to set the IP time to live (TTL). It limits the number of network hops. The value ranges between 1 and 255.
Sample Output:
13. Print timestamps with ping command
The -D option prints the timestamps before every line.
Sample Output:
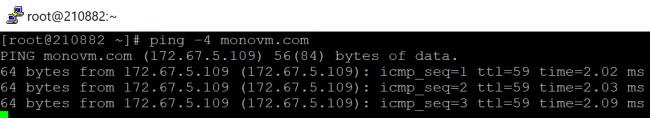
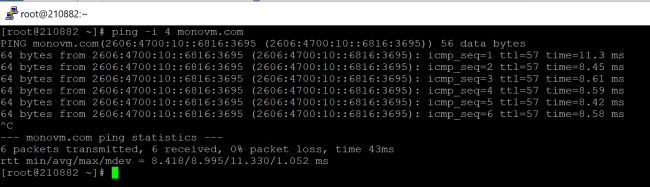
14. Use IPv4 or IPv6 address with ping command
The -4 and -6 options are used to specify the IPv4 and IPv6 addresses respectively.
Sample Output:
When you use the IPv6 address with -4 option, it shows an error message.
ubuntu@golinux:~$ ping -4 2606:4700::6813:9a5c ping: 2606:4700::6813:9a5c: Address family for hostname not supported 15. Perform audible ping
When the -a option is used, the system will produce a sound if there is a reply from the host.
Sample Output:
16. Report ICMP ECHO reply for ping command
The -O option reports outstanding ICMP ECHO reply before sending the next packet. It is useful together with the -D option to log
output to a diagnostic file and search for missing answers.
Sample Output:
17. Print full user-to-user latency with ping command
Normally, ping prints network round trip time which can be different, for example, due to DNS failures. The -U option can be used to print full user-to-user latency.
Sample Output:
Conclusion
This tutorial teaches you to use ping command with different options in a Linux system. ping is a useful tool that allows you to test the connectivity of a specified host on the network. If you still have any confusion, please let us know in the comment section.
Ping Command in Linux [How to Ping in Linux]
Ping command in Linux is the best solution to find that how your network connection is performing or also helpful while troubleshooting, testing, and diagnosing network connectivity issues. To help you to understand Linux ping command this article will guide you.
List of content you will read in this article:
Checking for the concept of Ping command in Linux? If yes, then this is the right place where you will get complete information and commands of Linux ping. Packet InterNet Groper is the full form for Ping. Software/Service determines whether or not a given IP address, host, or server is available from your network. The ping tool is often used to look for and diagnose network errors. Its mechanism is basic, but it saves time. It operates by sending a packet to the given IP address/client/server address and measuring the time it takes for that host to respond.
This is often referred to as latency. PING is the most popular method of troubleshooting any link. For example, it will respond or echo. Ping sends a packet containing the message «PING» to a server/host and receives a copy of the message from that host/server. Ping determines the «Round Trip Time» (or RTT) needed for a packet to hit a specific server or host.
One of the most commonly used methods for troubleshooting, monitoring, and diagnosing network access problems is the ping command. Linux Ping sends one or more ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) Echo Request packets to a designated network destination IP and waits for a response. When the shipment arrives at its destination, it receives an ICMP echo reply.
You can use the ping command to verify; if a remote destination IP is working or not. You should also search for packet loss and determine the round-trip delay when communication is established. Ping is included in the iputils (or iputils-ping) kit, pre-installed on almost all Linux distributions. In this guide, we will explain brief information on what is ping command is, how to use Linux ping and how does it works.
What Is Ping Command? [How to Use Linux Ping]
The ping command has the following syntax:
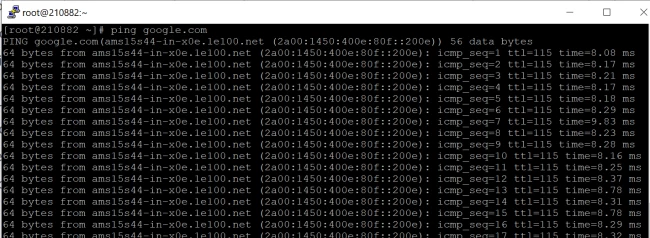
Let’s ping google.com to understand how the ping command works:
The output of the ping will be something like this:
PING google.com (172.217.22.206) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from muc11s01-in-f14.1e100.net (172.217.22.102): icmp_seq=1 ttl=53 time=40.2 ms
64 bytes from muc11s01-in-f14.1e100.net (172.217.22.102): icmp_seq=2 ttl=53 time=41.8 ms
64 bytes from muc11s01-in-f14.1e100.net (172.217.22.102): icmp_seq=3 ttl=53 time=47.4 ms
64 bytes from muc11s01-in-f14.1e100.net (172.217.22.102): icmp_seq=4 ttl=53 time=41.4 ms
^C
— google.com ping statistics —
We’ll go into the most popular ping command options in the below-given section.
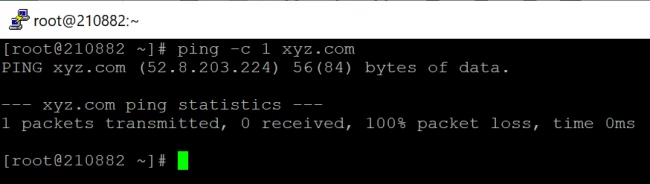
Option 1: How to Select the number of packets you want to transfer.
Ping will continuously transfer the ICMP packets until an interrupt signal is received. Using the -c alternative followed by the number of packages to send before ping exits to specify the number of Echo Request packages to send before ping exits:
To ping xyz.com just once, for example, you will type:
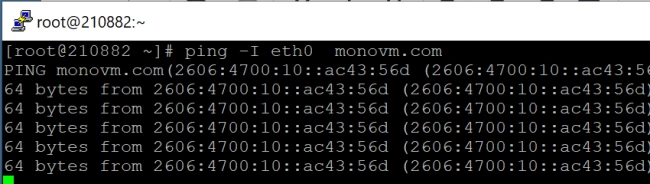
Option 2: How to choose a source interface.
The ping command’s default action is to deliver ICMP packages over the default path. If your computer has several interfaces, you can use the -I option to define the source interface:
ping -I INTERFACE_NAME DESTINATION
Using em2 as a source interface, run the following command to ping xyz.com:
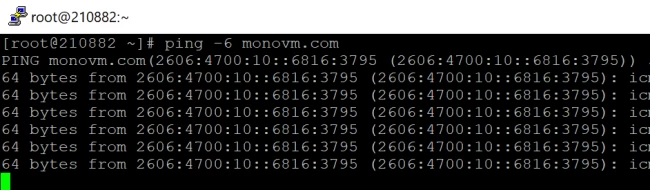
Option 3: How to Specify the Internet Protocol
Depending on your machine’s DNS settings, the ping command can use either IPv4 or IPv6. If you’re using IPv6, use the -6 option or ping6:
Pass the -4 alternative to use IPv4, or use its alias ping4:
Option 4: How to Timeout Ping?
Use the -w alternative to interrupt pinging after a certain amount of time.
After 5 seconds, the pinging will cease.
Option 5: How to PING Flooding
It is used to send packets as quickly as possible. This is used to evaluate the efficiency of a network.
Option 5: How to Filling Data Packet
Using the -p alternative, we can fill the packet with data. -p ff, for example, -p ff would fill the packet with ones.
Option 6: How to Adjust the Time Frame in Ping
By default, ping waits 1 second before sending the next packet; however, the -i alternative can adjust this time.
More Linux Ping Command Options
| Ping Option | The output of the Command |
| a | It will give a sound when a peer can be reached. |
| b | It will allow you to ping broadcast IP addresses. |
| B | Prevents the ping to change the source address of the probe. |
| c (count) | It will limit you to send the number of ping requests. |
| d | It will set the SO-DEBUG option on the used socket. |
| f | This will Flood by sending hundreds of packets per second over a network. |
| i (interval) | This will inform you that how many successful packets have been transmitted into the specified time interval. By default value = 1 Second |
| I (interface address) | I will help you st set your source IP address to a specified interface IP address. It is required while pinging IPv6 link-local address. For this, use an IP address or name of the device. |
| l (preload) | I will define the number of packets you can send without waiting for a response. You can specify the value higher than 3 and by giving yourself superuser permissions. |
| n | This will display IP addresses as output rather than hostnames. |
| q | This will show you quiet output that will ping line displayed and summary of the ping command at the end. |
| T (TTL) | It will Set Time To Live. |
| v | It will give verbose output. |
| V | It will show the ping version and exit to a new command prompt line. |
| w (deadline) | Before you exist a ping command, it will specify the time limit, regardless of how many packets have been sent or received. |
| W (timeout) | It determines the time in seconds for which you need to wait for a response. |
Conclusion
Ping uses ICMP to send an ICMP echo message to the designated host, and then an ICMP returns a message if that host is open. Ping is usually calculated in milliseconds, and it comes pre-installed on any modern operating system. Ping is a network command-line interface for checking a host’s IP-level reliability on a server.
This article helped you to understand the concept of ping command in Linux, how to. ping in Linux and how to use the Linux ping command. If you have any more commands associated with Ping commands, please suggest them via the comment box listed below.
People Are Also Reading:

















![Ping Command in Linux [How to Ping in Linux]](https://monovm.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/cover651-main.webp)