- Test Jumbo Frames and MTUs with Ping
- Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) Check
- How to check optimal MTU size for Routers
- The ICMP Package and MTU size
- ICMP packet at Network layer
- ICMP packet at Data Link layer
- ICMP Message Packet decoding in Wireshark
- Using Linux Ping set don’t fragment bit (DF-Bit-Set) in the Linux Shell and macOS Terminal
Test Jumbo Frames and MTUs with Ping
Jumbo Frames refer to Ethernet frames that carry a payload of up to 9000 bytes, instead of the standard 1500 bytes. These frames can increase network throughput and reduce CPU utilization.
Here’s how you can test Jumbo Frames on different operating systems:
In Windows, you can use the `ping` command with the `-f` (don’t fragment) and `-l` (size) options. Note that the MTU value is inclusive of headers which take 28 bytes , so use a size of 8972 bytes to test a Jumbo Frame of 9000 bytes. This is assuming your network adapters and switch are configured to handle Jumbo Frames.
ping destination_IP -f -l 8972
MacOS / Linux
On MacOS and Linux, the `ping` command works a little differently. The `-s` option is used to specify the size. The `-M do` option ensures that packets are not fragmented.
ping -s 8972 -M do destination_IP
Make sure to replace `destination_IP` with the IP address of the machine you are testing connectivity with. Also, the other machine must also be configured to handle Jumbo Frames.
Do remember that for Jumbo Frames to work, all devices in the network path must support them. This includes the network interface cards of the source and destination machines, switches, routers, and any other network devices between them.
If you’re unable to ping using the above commands, you might need to adjust the MTU setting on your network adapter to handle Jumbo Frames (usually setting it to 9000 should work). Be aware that incorrectly setting the MTU can cause network issues, so proceed with caution and only if you’re confident in what you’re doing.
To test the Jumbo Frames on a Cisco device, you can use the `ping` command with the `df-bit` (do not fragment) and `size` options. You would have to be in the privileged exec mode (enable mode) to do this.
Router# ping ip destination_IP size 8972 df-bit
Router# ping Protocol [ip]: Target IP address: destination_IP Repeat count [5]: Datagram size [100]: 8972 Timeout in seconds [2]: Extended commands [n]: y Source address or interface: Type of service [0]: Set DF bit in IP header? [no]: yes Validate reply data? [no]: Data pattern [0xABCD]: Loose, Strict, Record, Timestamp, Verbose[none]: Sweep range of sizes [n]: Type escape sequence to abort.
Just as in the previous examples, replace `destination_IP` with the IP address of the machine you are testing connectivity with.
Again, remember that all the devices in the network path must support and be configured for Jumbo Frames for them to work properly. Also, this assumes that your router is configured to support Jumbo Frames (i.e., the MTU on the router interfaces has been set to a size greater than the default, usually 9000 for Jumbo Frames).
As always, ensure you know the impact of changing these settings before doing so, as incorrectly setting the MTU or enabling Jumbo Frames without full network support can cause network issues.
Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) Check
The Maximum Transmission Unit describes the maximum packet size of a protocol in the network layer of the OSI model, which can be transmitted in networks without fragmenting the frames in the data link layer. This packet size fits into the payload of the data link layer protocol.
How to check optimal MTU size for Routers
To check the MTU of a path, you have to pass the parameter -f to ping to set the “don’t fragment bit (DF-Bit-Set)” for the ICMP test packets in the IPv4 header, only then you will receive a message if the MTU is exceeded.
The ICMP Package and MTU size
Run Ping in the Windows command prompt to determine the MTU size of a desired path.
The parameter -f specifies that the packages are not fragmented.
The size of the send buffer is specified with -l.
C:\> ping -4 -f 1.1.1.1 -l 1473 Pinging 1.1.1.1 with 1473 bytes of data: Packet needs to be fragmented but DF set. Packet needs to be fragmented but DF set. Packet needs to be fragmented but DF set. Packet needs to be fragmented but DF set. Ping statistics for 1.1.1.1: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 0, Lost = 4 (100% loss),As the above results show, the packets should be fragmented. If the -f parameter were omitted, the ping would respond with fragmentation, which we don’t want.
If you don’t get an reply but see “Packet needs to be fragmented but DF set.” you’ve not found the maximum ping size.
Hint. It is best to gradually reduce the ping with the MTU value, in steps of 10+/-10 (e.g. 1472, 1462, 1440, 1400) until a packet size has been reached that is no longer fragmented and a response is received.
C:\> ping -4 -f 1.1.1.1 -l 1472 Pinging 1.1.1.1 with 1472 bytes of data: Reply from 1.1.1.1: bytes=1472 time=7ms TTL=56 Reply from 1.1.1.1: bytes=1472 time=7ms TTL=56 Reply from 1.1.1.1: bytes=1472 time=7ms TTL=56 Reply from 1.1.1.1: bytes=1472 time=7ms TTL=56 Ping statistics for 1.1.1.1: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 7ms, Maximum = 7ms, Average = 7msThe above results indicate that the packets will not be fragmented.
To get the right MTU size, take 1472 and add 28 to it. In the example above, 1472 is the correct value, and the size is 1500 for the network in which you work.
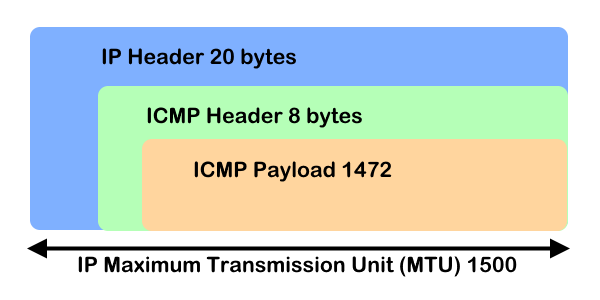
Calculation: 8 bytes for the ICMP-header + 20 bytes for the IP-header + 1472 bytes for the ICMP-payload: 8 + 20 + 1472 = 1500
The Control Message Protocol Protocol (ICMP) in layer 3 of the network layer, which is used by ping to send a message via the ICMP payload, which is encapsulated with the IP header. The MTU cannot exceed the size of the ICMP packet of 1500 bytes.
ICMP packet at Network layer
ICMP packet at Data Link layer
| Ethernet header | IP header | ICMP header | ICMP payload size | MTU (1514) |
| 14 | 20 bytes | 8 bytes | 1472 bytes (maximum) | 14 + 20 + 8 + 1472 = 1514 |
Note. default size of ICMP payload is 32 bytes and the maximum is 1472, if the size of the payload packet is greater than 1472 then packet gets fragmented into small packets.
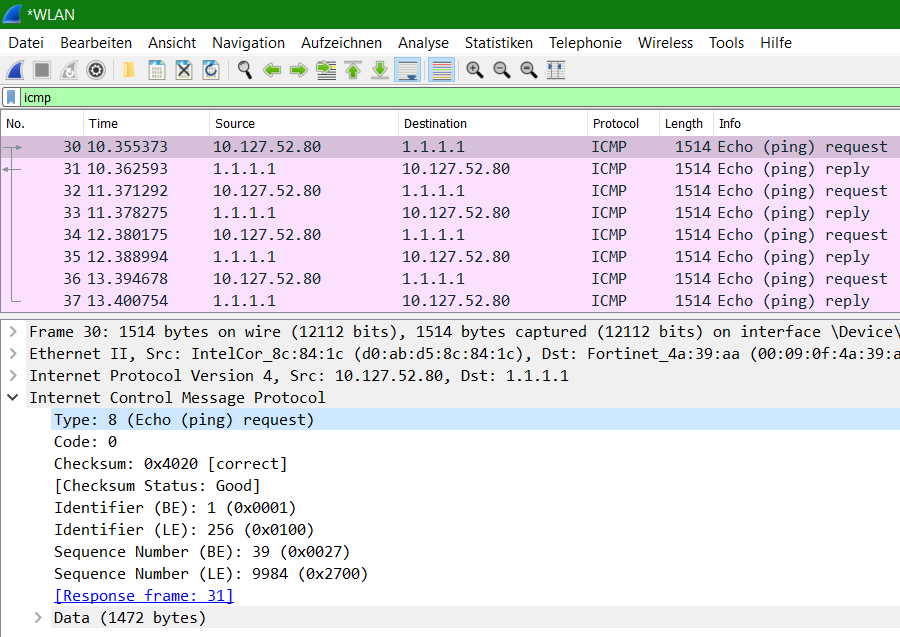
ICMP Message Packet decoding in Wireshark
The ICMP packet sent by the source machine is an echo request. The figure shows that ICMP query code 8 responds to the ping request.
Using Linux Ping set don’t fragment bit (DF-Bit-Set) in the Linux Shell and macOS Terminal
Use Linux ping in a terminal will using DF-bit-set do not fragment message.
$ ping -M do -s 1473 1.1.1.1 PING 1.1.1.1 (1.1.1.1) 1473(1501) bytes of data. ping: local error: Message too long, mtu=1500 ping: local error: Message too long, mtu=1500 ping: local error: Message too long, mtu=1500 ^C --- 1.1.1.1 ping statistics --- 3 packets transmitted, 0 received, +3 errors, 100% packet loss, time 31ms