- How To Install Pip on Linux Mint 20
- Install Pip on Linux Mint 20
- How to Install Python PIP in Linux
- Installing Python in Linux Systems
- Installing Python PIP in Linux Systems
- Install Python Packages via PIP in Linux
- How to Install PIP in Linux Mint 20
- Installing PIP for Python 3
- Installing PIP for Python 2
- Using PIP
- Install a package
- Remove a package
- List packages
- View installed package information
- Uninstalling PIP
- About the author
- Karim Buzdar
How To Install Pip on Linux Mint 20
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Pip on Linux Mint 20. For those of you who didn’t know, Pip is a tool for installing Python packages. With pip, you can search, download, and install packages from Python Package Index (PyPI) and other package indexes. With the help of pip, you can also install the package of a particular version. Most importantly pip has a feature to manage full lists of packages and corresponding version numbers, possible through a “requirements” file. It performs the same basic job as an easy install, but with some extra features.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘ sudo ‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you through the step-by-step installation of Pip on a Linux Mint 20 (Ulyana).
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Linux Mint 20 (Ulyana).
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- A non-root sudo user or access to the root user . We recommend acting as a non-root sudo user , however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Pip on Linux Mint 20
Step 1. Before running the tutorial below, it’s important to make sure your system is up to date by running the following apt commands in the terminal:
Step 2. Installing Pip on Linux Mint 20.
Now to install PIP on Linux Mint using the following command:
sudo apt install python3-pip
Once the installation of PIP is finished, you can verify it by making use of the following command in terminal:
Now to install PIP on Linux Mint enter the following command:
First, add the required repository:
sudo add-apt-repository universe sudo apt update
After updating the package manager index to install PIP for Python 2 enter the following in the terminal:
To verify if PIP is successfully installed, run the following command:
Step 3. Basic Usage pip command.
After installing the python-pip package, the pip command will be available on the system. There are multiple options available with the pip command:
To install the new python package type:
pip install Package_Names
For example, to install Scrapy through Pip you would run the following command:
To uninstall python package installed by pip type:
pip uninstall Package_Names
To search python package type:
For more Pip options and usage examples you can use the –help flag:
[root@idroot.us ~]# pip --help Usage: pip [options] Commands: install Install packages. uninstall Uninstall packages. freeze Output installed packages in requirements format. list List installed packages. show Show information about installed packages. search Search PyPI for packages. wheel Build wheels from your requirements. zip DEPRECATED. Zip individual packages. unzip DEPRECATED. Unzip individual packages. bundle DEPRECATED. Create pybundles. help Show help for commands. General Options: -h, --help Show help. -v, --verbose Give more output. Option is additive, and can be used up to 3 times. -V, --version Show version and exit. -q, --quiet Give less output. --log-file Path to a verbose non-appending log, that only logs failures. This log is active by default at /home/sharad/.pip/pip.log. --log Path to a verbose appending log. This log is inactive by default. --proxy Specify a proxy in the form [user:passwd@]proxy.server:port. --timeout Set the socket timeout (default 15 seconds). --exists-action Default action when a path already exists: (s)witch, (i)gnore, (w)ipe, (b)ackup. --cert Path to alternate CA bundle. [root@idroot.us ~]#
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Pip. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the latest version of Pip Python on the Linux Mint system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Python website.
If you don’t have time to do all of this stuff, or if this is not your area of expertise, we offer a service to do “VPS Manage Service Offer”, starting from $10 (Paypal payment). Please contact us to get the best deal!
How to Install Python PIP in Linux
PIP is simply a Python Package Installer, which is used to retrieve and install Python-related packages from indexes such as the Python Package Index.
Python programming language continues to make a name for itself in the Linux operating system ecosystem due to the following obvious reasons:
- Python is easy to learn due to its simple structure.
- Python is a highly invested programming language in the field of data science.
- The versatile nature of Python programming language makes it adaptable to numerous platforms.
- The Python demand in the job market continues to grow.
- It has numerous libraries.
- Python programming language has countless learning resources applicable to both newbies and advanced Python learners.
With that said, this article is here to walk us through the installation of PIP on various Linux distributions.
Installing Python in Linux Systems
The first step is to make sure that we have Python3 installed on our Linux systems, which comes preinstalled on most of the Linux distributions.
You can simply verify the installation of the Python version on your system by running the following commands on your terminal.
If Python is not installed, you can install it on your Linux distribution as shown.
$ sudo apt install python3 [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] $ sudo yum install python3 [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky Linux/AlmaLinux] $ sudo emerge -a dev-lang/python [On Gentoo Linux] $ sudo apk add python3 [On Alpine Linux] $ sudo pacman -S python3 [On Arch Linux] $ sudo zypper install python3 [On OpenSUSE]
Installing Python PIP in Linux Systems
Now that we have Python installed on our Linux systems, it’s time to install its package installer which will enable us to fetch and install Python-related packages and libraries to use on our various projects.
The surest approach to installing PIP on any Linux distribution is via the package manager as shown.
$ sudo apt install python3-pip [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] $ sudo yum install python3-pip [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky Linux/AlmaLinux] $ sudo emerge -a dev-lang/pip [On Gentoo Linux] $ sudo apk add py3-pip [On Alpine Linux] $ sudo pacman -S python-pip [On Arch Linux] $ sudo zypper install python3-pip [On OpenSUSE]
Once installed, you can check the installed PIP version:
Install Python Packages via PIP in Linux
To install a Python package via PIP, we will adhere to the following command:
To uninstall a Python package via PIP, use.
$ pip3 uninstall packageName
To search a Python package via PIP, use.
For a complete PIP user guide, run the command:
We have successfully demonstrated how to install and use PIP on any Linux distribution. Feel free to leave a comment or feedback.
How to Install PIP in Linux Mint 20
PIP is a command-line utility that helps you to install various Python packages on your system. It allows you to search and install the packages from the python package index and other package index repositories. PIP does not come installed in Linux Mint; however, it can be installed easily.In this tutorial, we will describe to you how to install PIP in the Linux Mint system. We will cover the installation of PIP utility for both Python 2 and Python 3.We have explained the procedure and commands on Linux Mint 20 OS. More or less, the same procedure can be followed in older Mint versions.
Note: For installing or removing any package in any Linux distribution, including Linux Mint, you must be root user or normal user with sudo privileges. Moreover, we will be using the command line Terminal application for the installation process. To open the command line Terminal, use the Ctrl+Alt+T keyboard shortcut.
Installing PIP for Python 3
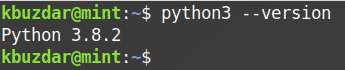
For Python 3, you will need to install the PIP3 package. Python 3 is already installed on Linux Mint 20 system. You can verify it using the following command in Terminal:
If it is installed, you will see the following similar output.
Now to install PIP for Python3 in you Linux Mint system, follow the below procedure:
1. Update the system repository index using the following command in Terminal.
When prompted for the password, provide a sudo password.
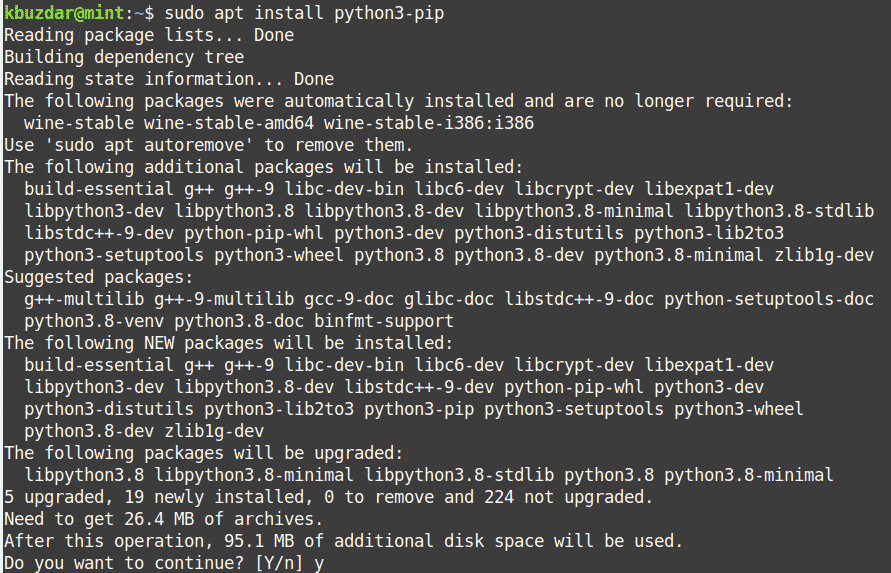
2. Then install PIP for Python 3 using the following command in Terminal:
After running the above command, the system might ask for confirmation that if you want to continue the installation or not. Press y to continue; after that, the installation of PIP will be started on your system.
3. Once the installation of PIP is completed, you can verify it using the following command in Terminal:
From the output, you will see a version number similar to this, which implies that the PIP has successfully installed on your system.
Installing PIP for Python 2
For Python 2, you will need to install PIP2. PIP2 package does not exist in the official Mint repositories. However, you can install it using the get-pip.py script. Follow the below steps to install PIP for python 2.
1. Add the required repository using the following command in Terminal:
2. Then update the system’s repository index with that of the newly added universe repository. Issue the following command in Terminal to do so:
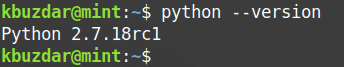
3. Python2 is not installed by default in the Linux Mint 20 system. You can install it with the following command in Terminal:
To verify if PIP is successfully installed, issue the following command in Terminal:
4. Download the get-pip.py script. Issue the following command in Terminal to do so:
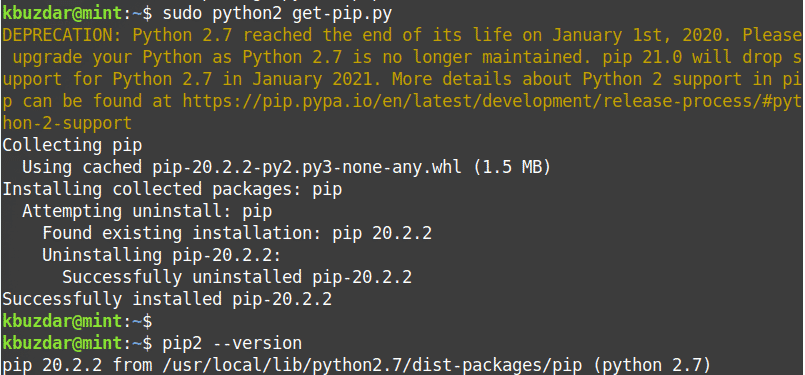
5. Now, run the get-pip.py script as the sudo user. Issue the following command in Terminal to do so:
6. You can verify the installation using the following command in Terminal:
The above output shows that the PIP for python2 has been successfully installed.
Using PIP
Now that you have learned to install PIP for python 3 and python 2, let’s have a look at some of the basic and useful PIP commands.
The following are the basic PIP commands that work with PIP3. If you have installed PIP2, just replace “pip3” with “pip”.
To view all the PIP commands along with their options and a brief description, you can use the following command in Terminal:
Search for a package
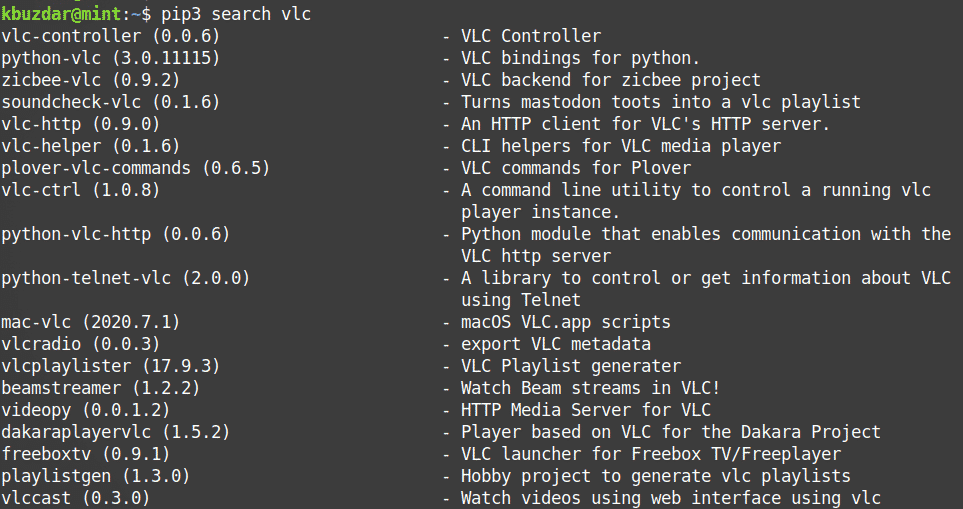
To search for a package whose name or description contains a matching , use the following command syntax:
For instance, if you search for a keyword “vlc”, it will return all the packages whose names or description contains the keyword “vlc”.
Install a package
To install a package using PIP, use the following command syntax:
For instance, to install vlccast package, the command would be:
Remove a package
To remove a package installed via PIP, use the following command syntax:
For instance, to remove vlccast package, the command would be:
List packages
To list all the installed PIP packages, use the following command in Terminal:
View installed package information
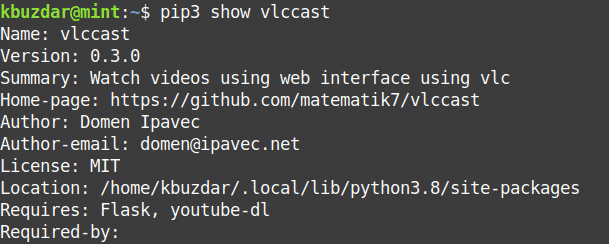
To view installed package information, you can use the following command syntax:
For instance, to search for information regarding the installed “vlccast” package, the command would be:
Uninstalling PIP
In case, you want to uninstall PIP3 from your system, use the following command in Terminal:
In case, you want to uninstall PIP2 from your system, use the following command in Terminal:
This is how you can install and use PIP in Linux Mint 20 system. You have also learned how to uninstall PIP if you no longer need it. I hope it will be helpful for you!
About the author
Karim Buzdar
Karim Buzdar holds a degree in telecommunication engineering and holds several sysadmin certifications. As an IT engineer and technical author, he writes for various web sites. He blogs at LinuxWays.