- 6 способов просмотреть список сетевых интерфейсов в Debian
- Вывод списка сетевых интерфейсов в Debian
- Использование команды ip
- Использование команды netstat
- Список сетевых интерфейсов с помощью файловой системы /sys
- Использование команды ifconfig
- Использование команды nmcli для списка сетевых интерфейсов
- Использование /proc/net/dev
- Заключение
- Похожие записи:
- List Network Interfaces in Debian 10
- Method #1: IP Command
- Method #2: ifconfig Command
- Method #3: netstat Command
- Method #4: nmcli Command
- Method #5: /sys/class/net Directory
- Method #6: /proc/net/dev File
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Karim Buzdar
- List network interfaces on Linux
- Show network interfaces
- Linux
- The old way: ifconfig
- Modern version: using the ip command
- Show the default gateway
- AIX and Solaris
- Frequently Asked Questions
- How can I see the MTU of an interface?
- What command can I use to display the default gateway on Linux?
- How can I test if my network configuration is correct?
6 способов просмотреть список сетевых интерфейсов в Debian
Сетевой менеджер часто оказывается в ситуациях, когда ему приходится изменять различные сетевые конфигурации. Для этого ему необходимо знать обо всех доступных сетевых интерфейсах в его системе. Поэтому в этой статье мы расскажем о методах, которые вы можете использовать для составления списка сетевых интерфейсов в Debian.
Вывод списка сетевых интерфейсов в Debian
Для вывода списка сетевых интерфейсов в Debian вы можете воспользоваться любым из шести методов, описанных ниже:
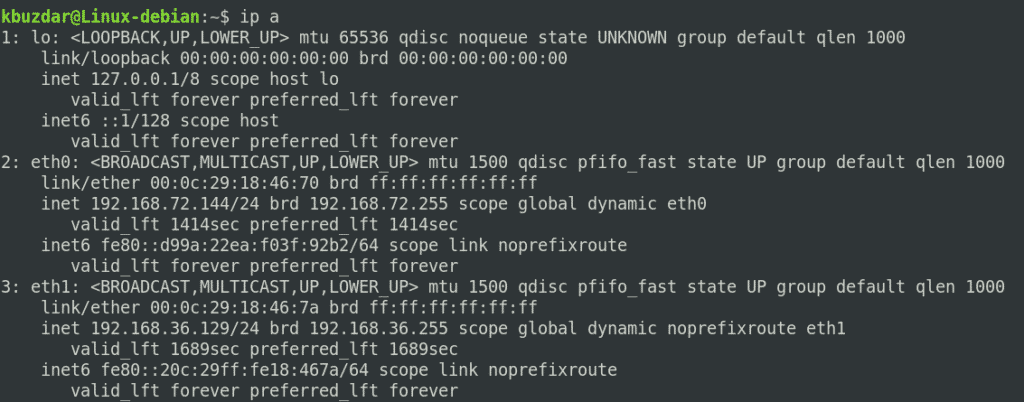
Использование команды ip
Чтобы составить список сетевых интерфейсов в Debian с помощью команды IP, вам нужно выполнить следующие шаги:
Запустите терминал в Debian 11 и введите в нём следующую команду, после чего нажмите клавишу Enter:
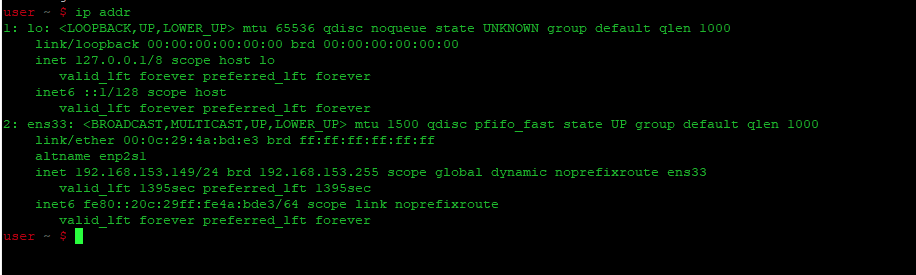
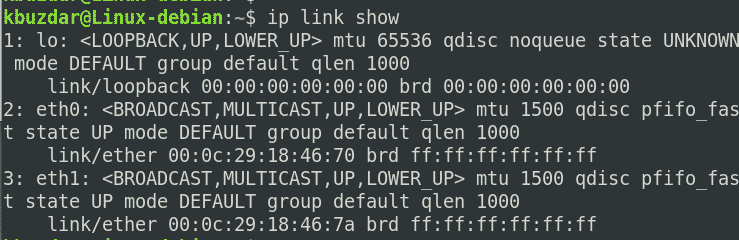
Как только эта команда будет успешно выполнена, вы сразу же сможете увидеть все ваши сетевые интерфейсы на терминале, как показано на следующем изображении:
Также вы можете ввести следующую команду в терминале и нажать клавишу Enter:
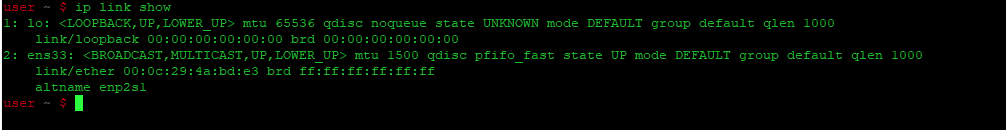
Вывод вышеупомянутой команды показан на рисунке ниже:
Использование команды netstat
Для получения списка сетевых интерфейсов с помощью команды netstat в Debian 11, вам нужно выполнить следующие шаги:
Прежде всего, вам нужно запустить терминал в Debian 11. После этого введите в терминале следующую команду и нажмите клавишу Enter:
Если при выполнении этой команды вы получите сообщение об ошибке, то, вероятно, вам нужно установить пакет net-tools перед выполнением этой команды. Это можно сделать, набрав в терминале следующую команду и нажав клавишу Enter:
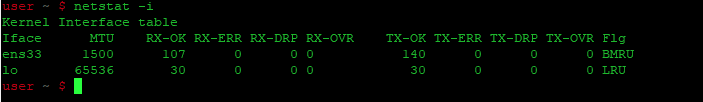
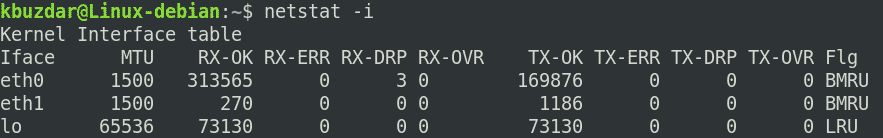
sudo apt install net-toolsКак только команда netstat будет успешно выполнена, вы сможете увидеть все ваши сетевые интерфейсы на терминале, как показано на рисунке ниже:
Список сетевых интерфейсов с помощью файловой системы /sys
Чтобы составить список сетевых интерфейсов в Debian с помощью команды ls, вам нужно выполнить следующие шаги:
Запустите терминал в Debian и введите в нём следующую команду, после чего нажмите клавишу Enter:
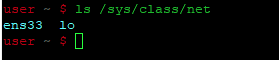
В результате успешного выполнения этой команды на вашем терминале появится следующее сообщение:
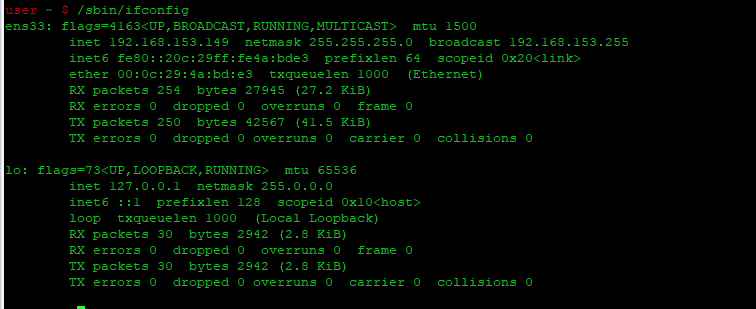
Использование команды ifconfig
Для получения списка сетевых интерфейсов с помощью команды ifconfig в Debian, вам нужно выполнить следующие шаги:
Прежде всего, вам нужно запустить терминал в Debian. Затем введите в терминале следующую команду и нажмите клавишу Enter для её выполнения:
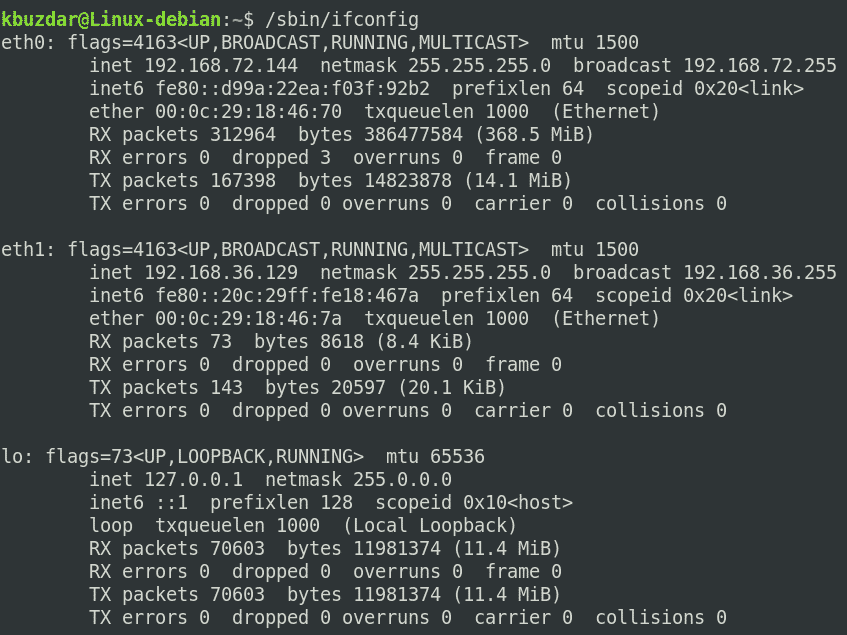
Как только эта команда будет успешно выполнена, вы сможете увидеть список всех ваших сетевых интерфейсов в терминале, как показано на рисунке ниже:
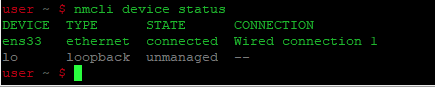
Использование команды nmcli для списка сетевых интерфейсов
Чтобы вывести список сетевых интерфейсов в Debian с помощью команды nmcli, вам нужно выполнить следующие шаги:
Запустите терминал в Debian и установите в нём Network Manager, набрав следующую команду и нажав клавишу Enter:
sudo apt install network-managerНаконец, выполните следующую команду в терминале и нажмите клавишу Enter:
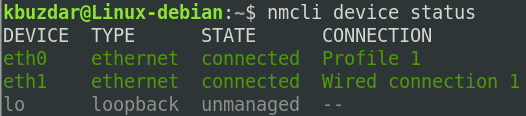
Как только эта команда будет успешно выполнена, вы сможете увидеть все ваши сетевые интерфейсы на терминале, как показано на рисунке ниже:
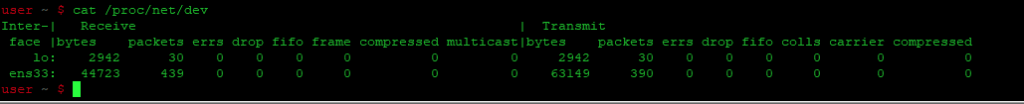
Использование /proc/net/dev
Чтобы получить список сетевых интерфейсов с помощью команды cat в Debian, вам нужно выполнить следующие шаги:
Прежде всего, вам нужно запустить терминал в Debian 11. Затем введите в терминале следующую команду и нажмите клавишу Enter:
Результат выполнения этой команды показан на рисунке ниже:
Заключение
Следуя любому из методов, рассмотренных в этой статье, вы можете легко узнать все ваши сетевые интерфейсы. Все эти методы довольно просты и удобны для выполнения. Более того, они будут отлично работать в системах Debian.
Похожие записи:
List Network Interfaces in Debian 10
As a system administrator or a normal user, you often need to perform network configurations. Before doing so, you should know how many network interfaces are available in your system. This article will discuss various ways to list network interfaces in Debian systems.
The commands listed in this article were run using the command-line Terminal application. To launch the Terminal application in Debian, click the Activities tab in the top left corner of the desktop and type terminal in the search bar. When the search result appears, click on the Terminal icon to open the Terminal.
Note: All the commands discussed in this article have been executed with the Debian 10 Buster system.
Method #1: IP Command
The most common and easiest way to list network interfaces is by using the IP command. This command provides a wide array of information about your system’s network interfaces.
To list the network interfaces in your system, issue the following command in Terminal:
The above command lists all the network interfaces available in your system. The above output shows that there are three interfaces in the system: one loopback interface (lo) and two Ethernet interfaces (eth0 and eth1) are listed, along with other statistics. This command will also show some other useful information about the network interfaces, including IP address, status (UP or DOWN), MAC address, etc.
Note: You may have different network interface names based on your system’s hardware.
You can also use the following IP command to list the network interfaces:
Method #2: ifconfig Command
The ifconfig command has now become obsolete but is still supported in many Linux distributions. You can use the ifconfig command to list the network interfaces available in your system.
Instead of typing ifconfig, type the command /sbin/ifconfig to list the network interfaces in your system.
In addition to listing the network interfaces, the above command will show other useful information about the network interfaces, including IP address, MTU size, number of sent/received packets, etc.
Method #3: netstat Command
The netstat command can also be used to list the network interfaces available in your system. To do so, type netstat, followed by the -i flag, as follows:
The above command lists the available network interfaces in your system, along with other useful information, such as the number of sent received packets, MTU size, etc.
Method #4: nmcli Command
The nmcli command also provides information about network interfaces. The nmcli command is available with Debian distributions that are running on GUI interfaces. However, if you are working on a non-GUI system, you will need to install the network manager using the following command in Terminal:
Once installation is complete, run the below commands in Terminal to enable and start the network manager:
To list the available network interfaces in your system, run the below command in Terminal:
The above command lists brief information about the available network interfaces.
Method #5: /sys/class/net Directory
You can also view network interfaces in your system by viewing the contents of the /sys/class/net directory. To do so, run the following command in Terminal:
The above command returns a concise output displaying only the names of the interfaces available in your system.
Method #6: /proc/net/dev File
The /proc/net/dev file also contains information about network interfaces. You can view the available network interfaces in your system by viewing the contents of this file. Run the following command in the Terminal to do so:
The above command lists the network interfaces available in the system, along with some other information about the interfaces.
Conclusion
The great thing about Linux is that it allows you to perform the same job in different ways. This article discussed various methods through which you can list the network interfaces in your Debian system.
About the author
Karim Buzdar
Karim Buzdar holds a degree in telecommunication engineering and holds several sysadmin certifications. As an IT engineer and technical author, he writes for various web sites. He blogs at LinuxWays.
List network interfaces on Linux
The network configuration is a common place to start during system configuration, security audits, and troubleshooting. It can reveal useful information like MAC and IP addresses. This guide helps you to gather this information on Linux, including listing all available network interfaces and its details.
Show network interfaces
Linux
Every Linux distribution is using its own way of configuring the network configuration details. Therefore, it is good to know which tools can be used to query these details in a generic way. So these commands should be working on the popular distributions like Arch Linux, CentOS, Debian, Gentoo, RHEL, and Ubuntu.
The old way: ifconfig
Previously the most obvious command to obtain the available network interfaces was using the ifconfig command. As some systems no longer have that command installed by default, we will also look at using alternative ip. If you still have ifconfig available, run it with the -a parameter.
Depending on what particular information you need, you can use grep to get you the right lines. The ifconfig command on Linux actually has the most option available, so have a look at the man page for all details.
Modern version: using the ip command
Newer Linux distributions now ship only the ip command. It is advised to start using this command instead of ifconfig, as its output works better with newer machines. Especially when using containerized applications, dynamic routing, and network aliases.
The easiest way to see what network interfaces are available is by showing the available links.
Linux network interfaces with ip link show command
Another option to show available network interfaces is by using netstat.
Note: the column command is optional, but provides a friendlier output for the eye.
Show the default gateway
The default gateway is the system that receives traffic for networks outside your own. On Linux systems, this gateway is typically received via DHCP or manually configured in a text configuration file.
Using the ip command
The output may look like this:
default via 123.12.0.1 dev eth0 onlink 10.17.0.0/16 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 10.17.0.3 123.12.0.0/18 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 123.123.0.3
With netstat
The default gateway can be listed with the netstat command.
The output will be something like this:
Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags MSS Window irtt Iface default 123.12.0.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0 10.17.0.0 * 255.255.0.0 U 0 0 0 eth0 123.12.0.0 * 255.255.192.0 U 0 0 0 eth0
The second column shows the gateway. When it lists an asterisk (*), it means it uses the default gateway.
AIX and Solaris
These two old style platforms have of course ifconfig still available. By using the -a parameter, all interfaces will be displayed.
ifconfig -a | grep «flags ez-toc-section» > DragonBSD, FreeBSD, NetBSD
On the systems running BSD, it is also the ifconfig tool that can be used.
ifconfig -l
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I see the MTU of an interface?
Use the ip show link command.
What command can I use to display the default gateway on Linux?
Use the ip route command to show routing information, including the default gateway and the network interface it uses.
How can I test if my network configuration is correct?
Test if you can reach or access both devices on your network as outside of it. This way you know that your IP address and gateway is correctly set up. If you can only access remote systems by IP address, then check your name server configuration, typically stored in /etc/resolv.conf. Another useful tool to test your system, including your network configuration, is by using auditing tool Lynis. It will test for connectivity of the name servers and retrieves the most important parts of the network settings.
Did this article help you? Become part of the community and share it on your favorite website or social media. Do you have additional tips regarding the network configuration on Linux? Share it in the comments!
One more thing.
Keep learning
So you are interested in Linux security? Join the Linux Security Expert training program, a practical and lab-based training ground. For those who want to become (or stay) a Linux security expert.
Security scanning with Lynis and Lynis Enterprise
Run automated security scans and increase your defenses. Lynis is an open source security tool to perform in-depth audits. It helps with system hardening, vulnerability discovery, and compliance.