- Как узнать сетевую карту в Linux
- Информация о сетевой карте с помощью Ethtool
- Информация о сетевой карте в lshw
- Список сетевых карт в lspci
- Информация о сетевой карте с помощью ip
- Выводы
- Find Out Network Adapters Available in Ubuntu Linux
- Alternate method to know the network adapter
- How can I check the information of currently installed WiFi drivers?
- 6 Answers 6
Как узнать сетевую карту в Linux
Иногда нужно посмотреть сетевые карты в Linux, подключенные к компьютеру, узнать имя продукта или технические характеристики карты, а также скорость передачи данных. Например, когда вы хотите проверить совместимость сетевого драйвера или модуля ядра с Ethernet адаптером необходимо знать его аппаратные спецификации, такие как: номер модели и производитель, (например: Broadcom NetXtreme, Intel I350), скорость (например: (1 Гбит/сек, 10 Гбит/сек), режим соединения (full/half duplex) и т д.
Также эта информация вам понадобится, если вы хотите подобрать драйвер для своего wifi адаптера. В этой инструкции я расскажу как узнать сетевую карту Linux и посмотреть все доступные ее характеристики.
Информация о сетевой карте с помощью Ethtool
Если вас интересует информация о проводной сетевой карте Ehternet, то вы можете воспользоваться утилитой Ethtool. Это инструмент командной строки для проверки и изменения настроек PCI Ethernet карт. Для установки Ethtool в Ubuntu или Debian используйте команду:
В других дистрибутивах установка производится аналогичным образом, только нужно использовать подходящий пакетный менеджер.
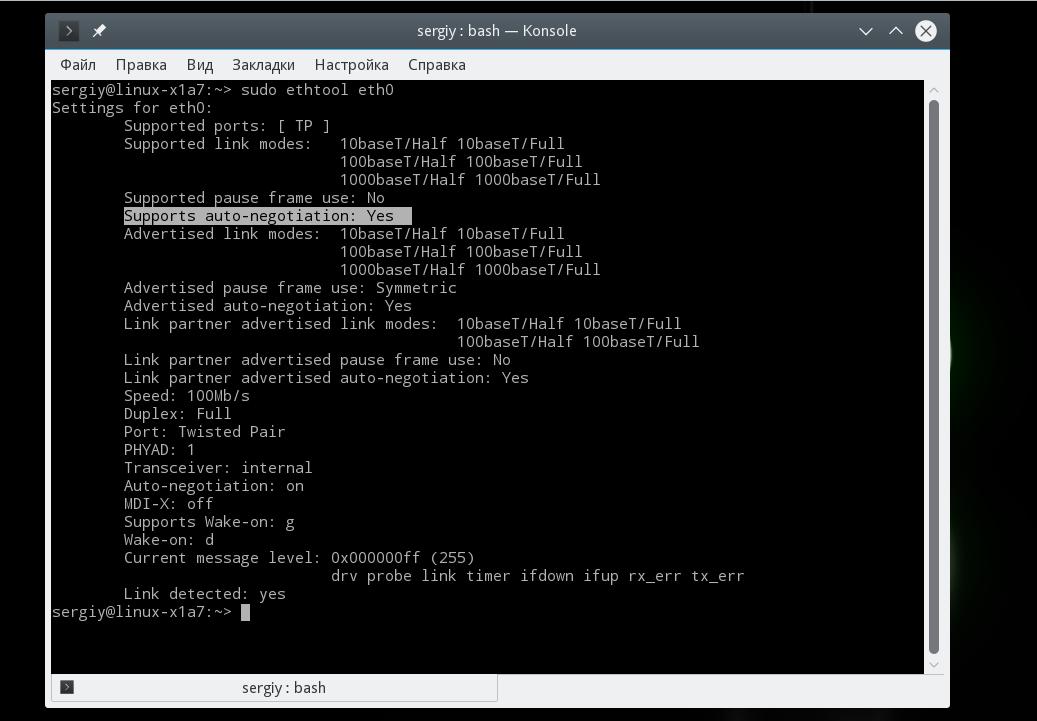
Для отображения настроек сетевой карты в ethtool запустите утилиту передав в параметрах имя сетевого адаптера. Права суперпользователя здесь нужны для того, чтобы утилита могла получить информацию о настройках локальной сети и статусе соединения.
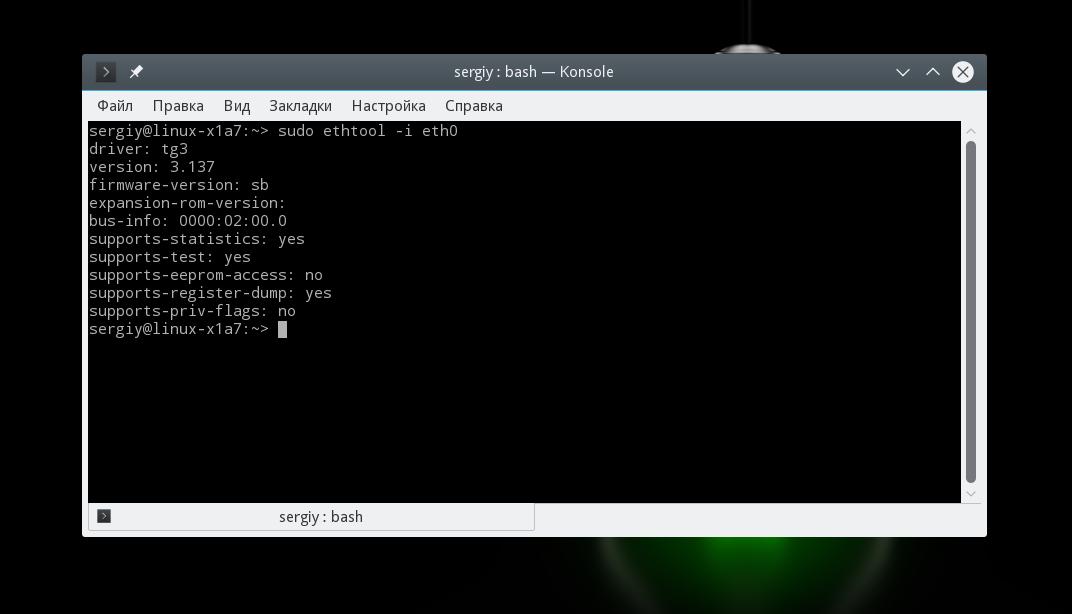
Здесь вы можете посмотреть поддерживаемые режимы работы Supported link modes, скорость Speed и тип коннектора Port, а также состояние подключения. Для просмотра информации о сетевом драйвере и прошивке используйте опцию i:
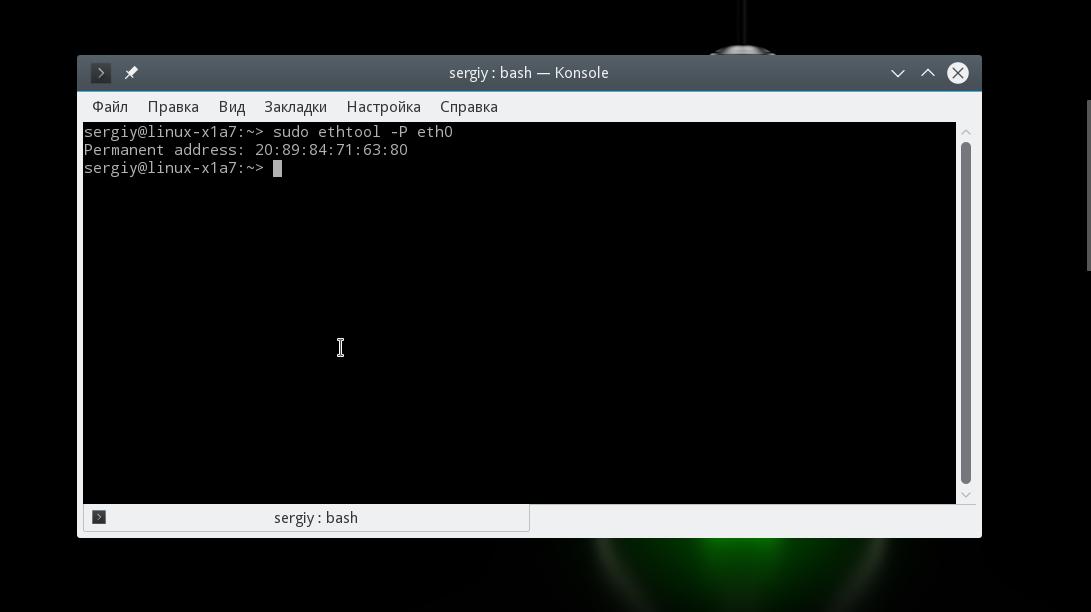
Здесь вы можете видеть какие режимы поддерживает прошивка, а также ее версию. Если вас интересует MAC адрес выполните:
Информация о сетевой карте в lshw
Во втором способе мы воспользуемся утилитой для отображения подробной информации об аппаратуре Linux — lshw. С помощью нее вы можете посмотреть информацию не только о карте Ethernet, но и о Wifi адаптере, а также посмотреть список сетевых карт.
Для установки lshw на Ubuntu или Debian наберите:
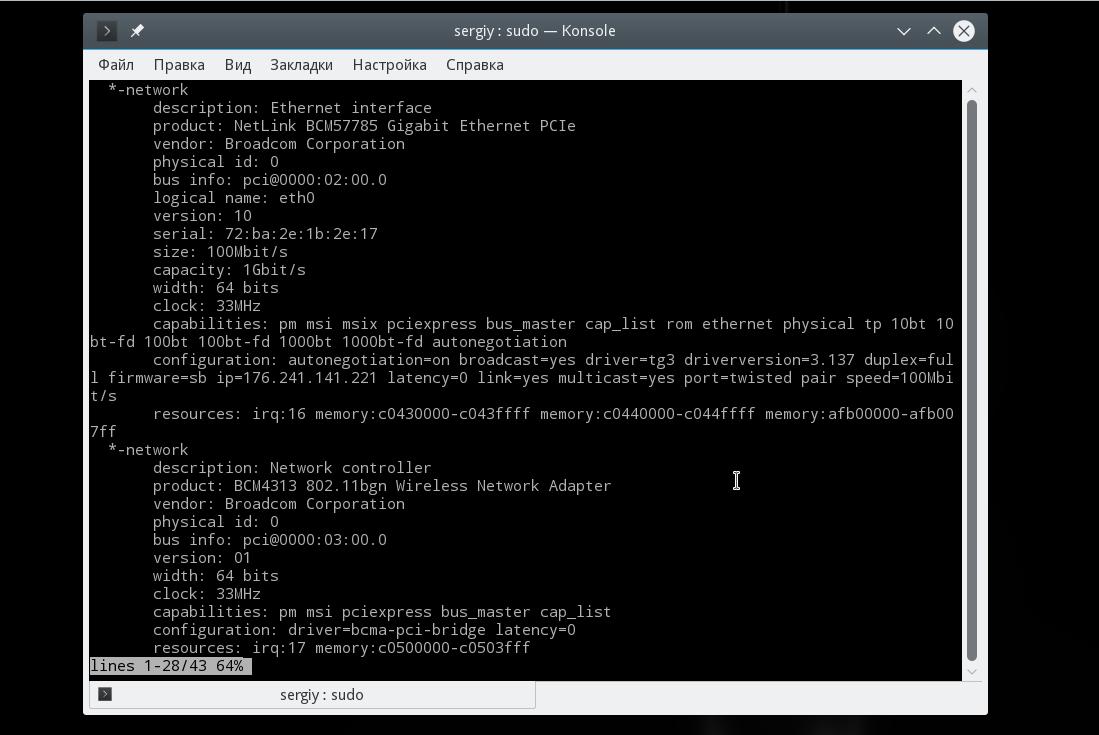
Чтобы посмотреть узнать сетевую карту linux и просмотреть подробные сведения о ней, запустите утилиту со следующими параметрами:
В выводе команды вы увидите все подключенные к системе сетевые интерфейсы, кроме того, тут показывается более подробная информация, чем в выводе предыдущей утилиты. В самом начале вы видите производителя — vendor и имя продукта — product, скорость передачи данных size, а также в разделе configuration можно найти поле driver, где указан используемый драйвер.
Список сетевых карт в lspci
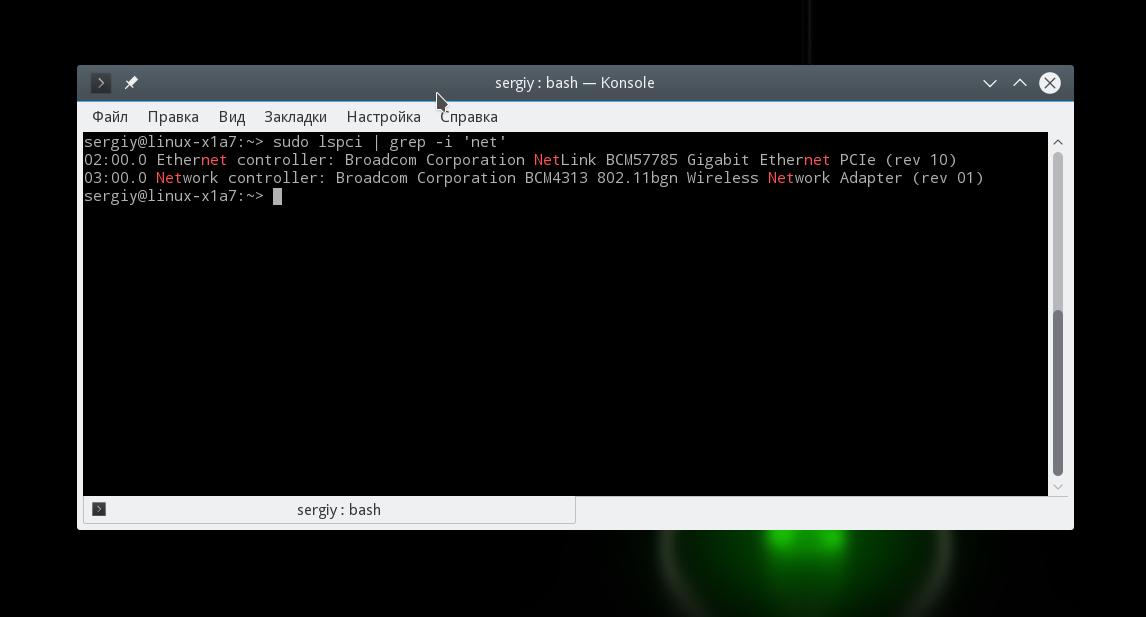
Если вам нужно узнать только продукт и имя производителя вашей сетевой карты можно использовать lspci. Обычно lscpi уже предустановлена в системе, но если нет ее можно установить командой:
sudo apt install pciutils
Теперь для просмотра доступных сетевых карт используйте:
Тут вы можете видеть, что к системе подключены две сетевые карты linux, для проводного интернета и беспроводная, обе от Broadcom.
Информация о сетевой карте с помощью ip
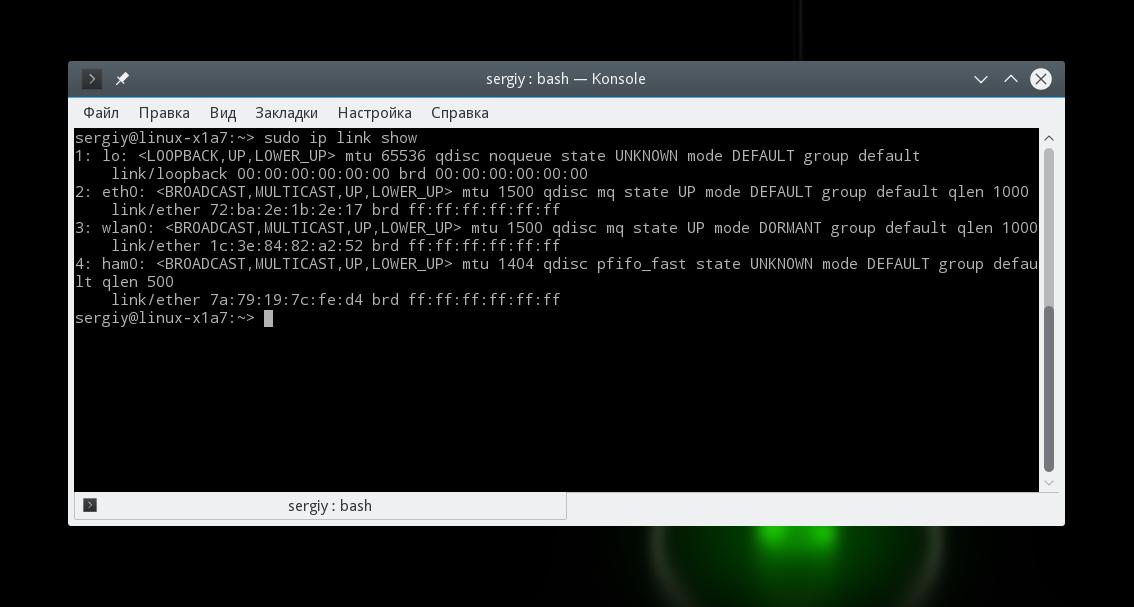
Утилита ip позволяет посмотреть более подробную информацию о сетевом протоколе для вашей карты. Для просмотра информации выполните:
На снимке экрана вы видите две физические сетевые карты linux — wlan0 и eth0, а также два виртуальных устройства. Для каждой из карт можно узнать состояние и MAC адрес.
Выводы
В этой статье мы рассмотрели несколько способов узнать сетевую карту Linux. Вы можете посмотреть не только производителя и название устройства, но и его характеристики, такие как скорость сетевой карты linux, используемый драйвер и MAC адрес. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
Find Out Network Adapters Available in Ubuntu Linux
Wondering which network adapters you are using in Ubuntu or any other Linux OS? It is very easy to to find out the manufacturer of the network adapters in your computer in Linux. Open a terminal and use the following command:
If the above command doesn’t work with sudo, remove the super user privileges. Weird but helps. The output of the command reads like this:
*-network
description: Wireless interface
product: BCM4360 802.11ac Wireless Network Adapter
vendor: Broadcom Corporation
physical id: 0
bus info: [email protected]:03:00.0
logical name: wlan0
version: 03
serial: 9c:f3:87:c1:5d:6a
width: 64 bits
clock: 33MHz
capabilities: bus_master cap_list ethernet physical wireless
configuration: broadcast=yes driver=wl0 driverversion=6.30.223.248 (r487574) ip=192.168.1.23 latency=0 multicast=yes wireless=IEEE 802.11abg
resources: irq:18 memory:b0600000-b0607fff memory:b0400000-b05fffff
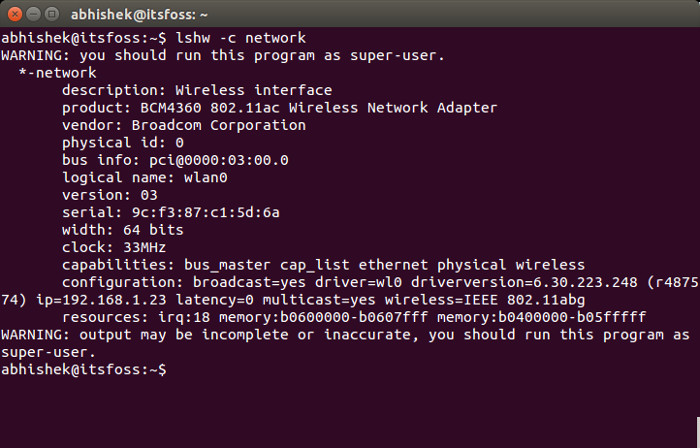
As you can see, the wireless network adapter in my Macbook Air is BCM4360, a troublesome wireless adapter because of which often Ubuntu does not detect wireless networks.
lshw command actually used to list hardware in Linux and hence the command is named lshw. With the option network, it filters the result for networking hardware only.
Alternate method to know the network adapter
Alternatively, you can use lspci command that displays the information about PCI buses in the system. You should not need super user privileges to use this command. Just type the command in terminal:
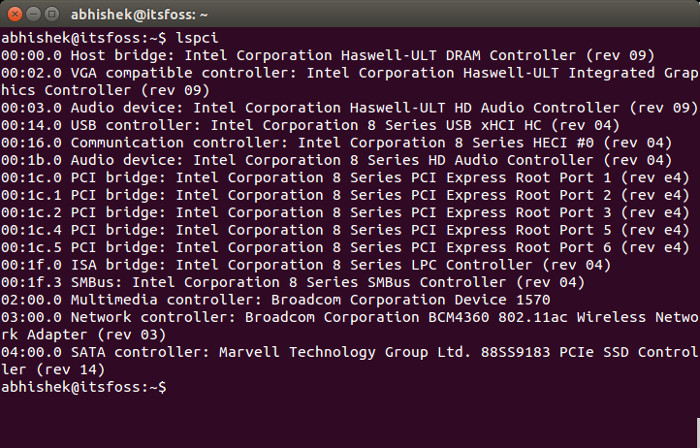
The output of the command reads as:
00:00.0 Host bridge: Intel Corporation Haswell-ULT DRAM Controller (rev 09)
00:02.0 VGA compatible controller: Intel Corporation Haswell-ULT Integrated Graphics Controller (rev 09)
00:03.0 Audio device: Intel Corporation Haswell-ULT HD Audio Controller (rev 09)
00:14.0 USB controller: Intel Corporation 8 Series USB xHCI HC (rev 04)
00:16.0 Communication controller: Intel Corporation 8 Series HECI #0 (rev 04)
00:1b.0 Audio device: Intel Corporation 8 Series HD Audio Controller (rev 04)
00:1c.0 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation 8 Series PCI Express Root Port 1 (rev e4)
00:1c.1 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation 8 Series PCI Express Root Port 2 (rev e4)
00:1c.2 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation 8 Series PCI Express Root Port 3 (rev e4)
00:1c.4 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation 8 Series PCI Express Root Port 5 (rev e4)
00:1c.5 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation 8 Series PCI Express Root Port 6 (rev e4)
00:1f.0 ISA bridge: Intel Corporation 8 Series LPC Controller (rev 04)
00:1f.3 SMBus: Intel Corporation 8 Series SMBus Controller (rev 04)
02:00.0 Multimedia controller: Broadcom Corporation Device 1570
03:00.0 Network controller: Broadcom Corporation BCM4360 802.11ac Wireless Network Adapter (rev 03)
04:00.0 SATA controller: Marvell Technology Group Ltd. 88SS9183 PCIe SSD Controller (rev 14)
These command gives you information about both wired and wireless network adapters. You might have noticed that there is no wired network adapter for my system in the output above. The reason is that I am using a Macbook Air and it does not have an Ethernet port.
I hope this quick post helped you to find the network adapters in your Linux system. Any questions or suggestions are always welcomed.
How can I check the information of currently installed WiFi drivers?
When I clicked on additional drivers on Ubuntu 12.04, I could not see any drivers.. How can I check what drivers are installed for WiFi on Ubuntu environment.
It’s not really possible (or useful) to enumerate all available device drivers in Linux (even when restricted to a particular device class). However, you can enumerate all available drivers that are capable of handling a particular device and, more importantly, the one currently claiming the device, i. e. the driver used to “drive” it.
6 Answers 6
The following commands are run in a terminal. Open one by Ctrl + Alt + T .
To check what drivers your wireless adapter is currently using, you may run the following command:
- lshw lists information on your hardware
- -C network filters the output to only show the network class.
In the output, look for the entry with description: Wireless interface .
Here’s the output from my Ubuntu:
alaa@aa-lu:~$ sudo lshw -C network [sudo] password for alaa: *-network description: Wireless interface product: RTL8723AE PCIe Wireless Network Adapter vendor: Realtek Semiconductor Co., Ltd. physical id: 0 bus info: pci@0000:08:00.0 logical name: wlan0 version: 00 serial: 24:ec:99:21:c9:29 width: 64 bits clock: 33MHz capabilities: pm msi pciexpress bus_master cap_list ethernet physical wireless configuration: broadcast=yes driver=rtl8723ae driverversion=3.8.0-27-generic firmware=N/A ip=192.168.1.74 latency=0 link=yes multicast=yes wireless=IEEE 802.11bgn resources: irq:17 ioport:3000(size=256) memory:c3000000-c3003fff
In the configuration line (line before last), you’ll see the driver currently being used by my card. I’ve highlighted it in the output.
Alternatively, you can use the command:
- lspci lists information on your PCI connected cards
- -nnk instructs lspci to output more information about these cards (including the driver being used)
- | pipes the output to the next command
- grep 0280 filters the output to show lines containing 0280 , which is the PCI class code for wireless PCI controllers in Ubuntu.
- -A2 shows two more lines of information.
Here’s the output from my Ubuntu:
08:00.0 Network controller [0280]: Realtek Semiconductor Co., Ltd. RTL8723AE PCIe Wireless Network Adapter [10ec:8723] Subsystem: Realtek Semiconductor Co., Ltd. Device [10ec:0724] Kernel driver in use: rtl8723ae
Once you determine the driver you’re using, you can use the following command to show more information about it:
To check what wireless drivers you currently have installed, but not necessarily being used by anything, you can do the following command:
find /lib/modules/$(uname -r)/kernel/drivers/net/wireless -name '*.ko' The above command will list all drivers you have installed. This will probably be an exhaustive list, because these are preinstalled drivers on your Ubuntu to make it possible for people to use their wireless drivers as soon as they install Ubuntu.