- Three tasks involved
- Planned work for Lucid
- Handling hardware events
- DeviceKit-power quirks
- Power management packages
- Power (saving) states
- Architecture
- How to get disks to spin down and idle correctly (without excessive load cycling)
- 10.04
- 8.10 to 9.10
- 8.04 (Hardy)
- Comments
- How To Install gnome-power-manager on Ubuntu 20.04
- What is gnome-power-manager
- Install gnome-power-manager Using apt-get
- Install gnome-power-manager Using apt
- Install gnome-power-manager Using aptitude
- How To Uninstall gnome-power-manager on Ubuntu 20.04
- Uninstall gnome-power-manager And Its Dependencies
- Remove gnome-power-manager Configurations and Data
- Remove gnome-power-manager configuration, data, and all of its dependencies
- References
- Summary
Three tasks involved
Though power management will deal with these, the objectives of the tasks do not solely lie in power management. It may be adviseable to rely on tools specialized for their tasks, instead of implementing an incomplete power management utility.
Planned work for Lucid
Handling hardware events
The acpi-support package should be deprecated; however, new homes need to be found for its current contents.
- /etc/acpi/start.d: these are currently launched by the init script, which has no equivalent in other packages currently
- 10-save-dmidecode: superseded by /sys interfaces
- 60-asus-wireless-led: should be moved to the kernel (cf. https://bugs.edge.launchpad.net/bugs/22795)
- 90-hdparm.sh: init script in pm-utils? udev rule on each HD would be preferred (/lib/udev/hdparm already exists)
DeviceKit-power quirks
Previously, hal had a suspend/resume quirks database that was used to construct a correct commandline for pm-suspend. devicekit-power doesn’t have this; it needs to be implemented.
Power management packages
Foremost there is the apm and acpi support in the linux kernel.
They make those kind of «hard» events like the end of battery power or the pressing of the suspend or other (laptop) buttons available to our software world.
Then there are event manager daemons apmd and acpid
They provide means to execute commands on these external events. They run the scripts they find in their config directory tree under /etc/acpi, or /etc/apm respectively.
The package acpi-support provides a set of such scripts under /etc/acpi that deal with handling special acpi buttons on laptops.
The package pm-utils provides the pm-action, pm-hibernate, pm-suspend and pm-suspend-hybrid commands. They allow to trigger hard power management events by software. The pm-tools also provide script directories to hook-in other software when switching power (saving) states.
The gnome-power-manager is a program with a graphical user interface that subscribes itself to power events and acts on them. It shows you the battery status on laptops and dims down the screen if on battery for example. It will also shutdown or hibernate the computer after some idle time or before the battery runs out, if a user is logged in.
Disk idling
A separate task is allowing harddisks to idle, so they can be parked and spun-down for long enough periods of time. This is done by a package that is a little bit misleadingly called laptop-mode-tools but not «disk-idle». Disk idling has to deal with things like reading ahead and postponing disk activity. The program got its name from a kernel feature that is called laptop_mode and allows Linux to chunk up writes to filesystems and not write in between. But to really let a disk idle one has to manage other parts of the system that are relevant to letting disks idle also, like drive parameters, mount options, filesystem settings, cache sizes, sync logging programs etc. «laptop_mode» will do all that.
Disk idling is commonly needed, thus laptop-mode enabled, when laptops operate on batteries to extend the battery times. But for example in vehicles with external power supply disk idling may be needed even on AC. Not necessarily to leave the disk spun down, but to leave the heads parked for shock protection.
Disk spin-down and head parking should not be activated without controlled disk idling. The regular uncoordinated logging or journaling activity may spin up the disks back up almost immediately after spinning down and lead to excessive load cycling.
Power (saving) states
The Common power (saving) states are awake, standby, suspend and hibernate.
During the awake state all components of the computer are running.
During standby the CPU keeps running your programs but some components like the monitor and harddisks may be turned off. When you touch the mouse or keyboard or a harddisk is accessed by software they quickly wake up again.
In both the awake and the standby state the speed of modern CPUs may be throttled down,though. For example if not in use.
During suspend however the CPU is always stopped. In modern PCs even all other components except the RAM memory can be turned off. The RAM will hold the state.
During hibernation the state is written to harddisk and the whole computer is turned off.
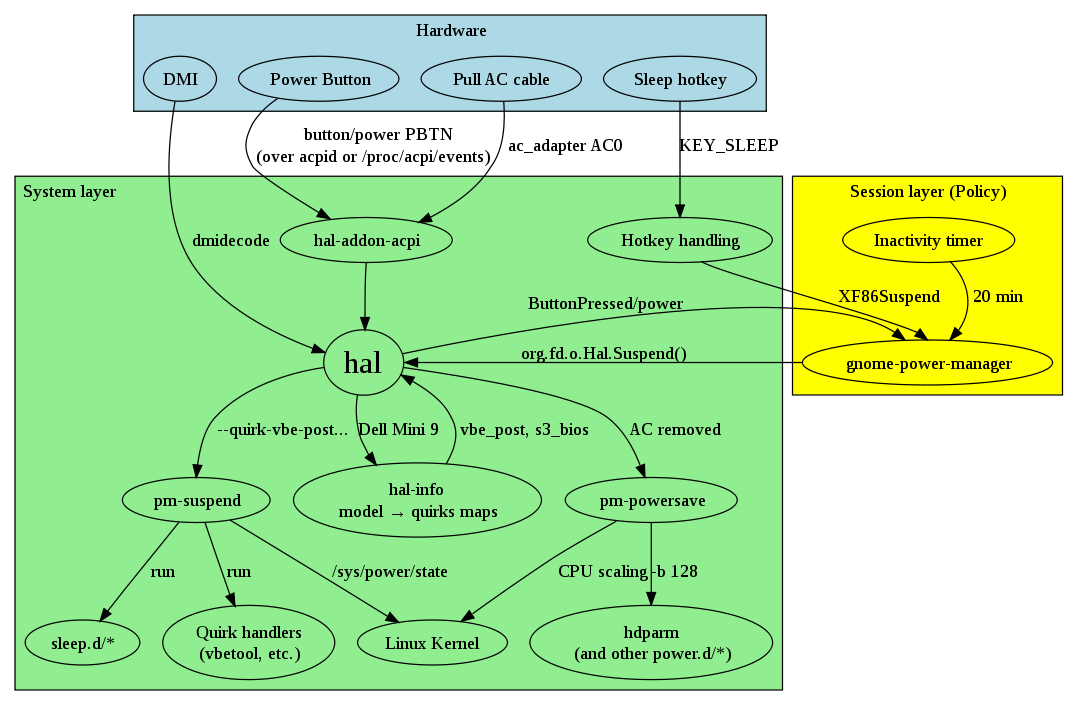
Architecture
This diagram shows how the kernel, hal, hal-info, pm-utils, and gnome-power-manager are plumbed together:
Please see Hotkeys/Architecture about the details of «Hotkey handling».
How to get disks to spin down and idle correctly (without excessive load cycling)
10.04
The laptop-mode-tools (disk idleing) package does not get installed by default any more, but just installing it should make disk idleing work (on battery) right away now.
8.10 to 9.10
8.04 (Hardy)
Unfortunately, ubuntu has mangled disk idling into event handling and power state switching in the past. And this did not deliver idle disks but break disk idling (laptop-mode) features by leaving undefined (factory default) apm settings in place.
- Enable CONTROL_HD_POWERMGMT=1 in /etc/laptop-mode/laptop-mode.conf
- (Bug 244832 missing hdparm -B setting during boot (fixed in intrepid 250935))
- (244838 laptop-mode needs to be activated in two places)
- (244836 /etc/acpi/power.sh overrides user settings (fixed in intrepid 250938))
(244831 /etc/acpi/power.sh overrides user scripts (fixed in intrepid 250938))
(244844 Adapt laptop-mode-tools invocation to ubuntu’s acpi-support / pm-utils packages (fixed in intrepid 250935))
- (239419 pm-utils has laptop-tools script which conflicts with laptop-mode-tools (not so in intrepid))
With the above changes hardy (ubuntu 8.04) will set the hdparm -B value to 254 when booting and thus override inadequately aggressive hardware defaults that cause load cycling. Not all harddisks will stop head parking with value 255 and some may even overheat. (hdparm -B255 turns off the disk’s apm feature, but this only turns off the spin down timer in many disks and doesn’t increase the head parking timer at all, which is the issue here.)
- 244833 missing hdparm -B setting during resume
244839 /etc/acpi/start.d and resume.d scripts are not run.
244844 Adapt laptop-mode-tools invocation to ubuntu’s acpi-support / pm-tools packages also:
238555 pm-utils doesn’t reload hdparm.conf after a suspend
Comments
Can someone maybe elaborate in the wiki why it’s not enabled by default? Without an explanation i’m wondering why, and if there maybe are good arguments against doing so.
- Ali, just copy /usr/lib/pm-utils/power.d/laptop-tools to /etc/pm/power.d/laptop-tools and insert the code near line 26 following guidelines in 239419
- Actually, to disabe this yet another «laptop-tools» script from pm-utils you just need to create an empty file (touch /etc/pm/power.d/laptop-tools). (Info also added above)
The issues described here are pointed out in the interesting bug 59695: «High frequency of load/unload cycles on some hard disks may shorten lifetime»
This opensuse wiki page might be useful for creating a proper solution for pm-utils — — AzraelNightwalker 2008-07-14 15:32:11
This page shows a simple script that successfully activates laptop-mode after resuming from suspend in Hardy. —AbtZ
PowerManagement (последним исправлял пользователь 62-2-76-204 2010-04-15 11:28:39)
The material on this wiki is available under a free license, see Copyright / License for details.
How To Install gnome-power-manager on Ubuntu 20.04
In this tutorial we learn how to install gnome-power-manager on Ubuntu 20.04.
What is gnome-power-manager
GNOME Power Manager is a session daemon for the GNOME desktop that takes care of system or desktop events related to power, and triggers actions accordingly. Its philosophy is to completely hide these complex tasks and only show some settings important to the user.
GNOME power manager displays and manages battery status, power plug events, display brightness, CPU, graphics card and hard disk drive power saving, and can trigger suspend-to-RAM, hibernate or shutdown events, all integrated to other components of the GNOME desktop. Description-md5: 1ece6a08127f01c856017ac9675775b5 Task: ubuntu-desktop-minimal, ubuntu-desktop, ubuntu-budgie-desktop
There are three ways to install gnome-power-manager on Ubuntu 20.04. We can use apt-get , apt and aptitude . In the following sections we will describe each method. You can choose one of them.
Install gnome-power-manager Using apt-get
Update apt database with apt-get using the following command.
After updating apt database, We can install gnome-power-manager using apt-get by running the following command:
sudo apt-get -y install gnome-power-managerInstall gnome-power-manager Using apt
Update apt database with apt using the following command.
After updating apt database, We can install gnome-power-manager using apt by running the following command:
sudo apt -y install gnome-power-managerInstall gnome-power-manager Using aptitude
If you want to follow this method, you might need to install aptitude first since aptitude is usually not installed by default on Ubuntu. Update apt database with aptitude using the following command.
After updating apt database, We can install gnome-power-manager using aptitude by running the following command:
sudo aptitude -y install gnome-power-managerHow To Uninstall gnome-power-manager on Ubuntu 20.04
To uninstall only the gnome-power-manager package we can use the following command:
sudo apt-get remove gnome-power-managerUninstall gnome-power-manager And Its Dependencies
To uninstall gnome-power-manager and its dependencies that are no longer needed by Ubuntu 20.04, we can use the command below:
sudo apt-get -y autoremove gnome-power-managerRemove gnome-power-manager Configurations and Data
To remove gnome-power-manager configuration and data from Ubuntu 20.04 we can use the following command:
sudo apt-get -y purge gnome-power-managerRemove gnome-power-manager configuration, data, and all of its dependencies
We can use the following command to remove gnome-power-manager configurations, data and all of its dependencies, we can use the following command:
sudo apt-get -y autoremove --purge gnome-power-managerReferences
Summary
In this tutorial we learn how to install gnome-power-manager package on Ubuntu 20.04 using different package management tools: apt, apt-get and aptitude.