- How can I display all users and groups with a command?
- 2 Answers 2
- You must log in to answer this question.
- Related
- Hot Network Questions
- Subscribe to RSS
- Посмотреть группы пользователя в Linux
- Список групп пользователя Linux
- Просмотреть список всех групп в Linux
- Добавление пользователя в Linux
- Управление группами юзера в Linux
- Модифицирование первичной группы пользователя в Linux
- How do I List All Groups in Linux
- Types of Groups in Linux
- Listing Users on Linux
- Listing Users Using the /etc/passwd File
- Listing Usernames Using awk
- Listing Usernames Using getent
- Listing the Connected Users on Your Linux Host
- Listing Groups Using /etc/group File
- Listing Groups Using getent
- Listing Groups for the Current User
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Simran Kaur
How can I display all users and groups with a command?
users and groups commands display users currently logged in, and groups a user belongs to respectively.
How to display a list of all users and all groups by command-line?
2 Answers 2
You can display with the help of compgen builtin command as follows:
- To display all users run following command:
However you can also display all users by cut -d «:» -f 1 /etc/passwd .
Nice! it might be preferable to use getent passwd / getent group instead of cat’ing the local files ( getent should work for non-local accounts as well)
Well, on my ubuntu, I have some files created by docker mount with 999:999 as user:group , but unfortunately none of the above commands prints them.
Here we are going to use getent for the detailed the info
We can list the user with the following command:
We can list the group as follows:
To fetch detail a specific user
Replace the lalit with your user name. Lalit will not be in every system 🙂
You can read the more into about getent here
You must log in to answer this question.
Related
Hot Network Questions
Subscribe to RSS
To subscribe to this RSS feed, copy and paste this URL into your RSS reader.
Site design / logo © 2023 Stack Exchange Inc; user contributions licensed under CC BY-SA . rev 2023.7.17.43535
Ubuntu and the circle of friends logo are trade marks of Canonical Limited and are used under licence.
By clicking “Accept all cookies”, you agree Stack Exchange can store cookies on your device and disclose information in accordance with our Cookie Policy.
Посмотреть группы пользователя в Linux
Я использую Ubuntu Linux, но данная команда работает в различных дистрибутивах Linux. Поскольку в Linux все имеется файлом, то такая система позволяет регулировать доступ к любому действию в этой операторной системе с помощью установки прав доступа на файлы. Но еще при создании Linux, разработчики постигнули, что этого явно недостаточно. В операционных системах семейства Linux у пользователя имеется основная группа, а также определённое количество дополнительных групп. Это удачное, стратегически обмысленное решение. Понимание групп, к каким принадлежит пользователь в Ubuntu очень важно — т.к. дает понимание того, к каким файлам user имеет доступ. Пользователи и группы пользователей используются на GNU/Linux для управления доступом — то имеется, для управления доступом к системным файлам, каталогам и переферии. Linux предлагает относительно несложные и грубые механизмы контроля доступа по умолчанию.
Список групп пользователя Linux
Вы сможете посмотреть список групп пользователя Linux двумя основными способами. Это команда id, какую мы уже разбирали в статье о том, как узнать id пользователя Linux, и команда groups. Чтобы вывести всю данные о пользователе, используйте id:
Все группы, созданные в системе, находятся в файле /etc/group. Посмотрев содержание этого файла, вы можете узнать список групп linux, которые уже есть в вашей системе. И вы станете удивлены.
Если вы не введете имя пользователя, по умолчанию будет применено ваше имя. К примеру:
frame@ubuntuServ:$ groups
frame adm dialout cdrom floppy audio dip video plugdev lpadmin scanner admin fuse
Вы вдобавок можете проверить какие группы принадлежат другому пользователю, включая root:
frame@ubuntuServ:$ groups root
root : root fuse
Помимо стандартных root и users, здесь есть еще пару десятков групп. Это группы, сделанные программами, для управления доступом этих программ к общим ресурсам. Каждая группа позволяет чтение или запись определенного файла или каталога системы, тем самым регулируя полномочия юзера, а следовательно, и процесса, запущенного от этого пользователя. Здесь можно считать, что пользователь — это одно и то же что процесс, поэтому что у процесса все полномочия пользователя, от которого он запущен.
Просмотреть список всех групп в Linux
Когда вы хотите просмотреть список всех групп в вашей системе, вы можете использовать бригаду getent:
Этот вывод также покажет вам, какие учетные записи юзеров являются членами групп.
Добавление пользователя в Linux
Добавление пользователя осуществляется при поддержки команды useradd. Пример использоания:
Управление группами юзера в Linux
Управлять группами можно и с помощью графического интерфейса. В KDE есть программа Kuser умышленно предназначенная для этого, в Gnome это выполняется с помощью настроек системы. Кроме того, в известных дистрибутивах есть отдельные инструменты, такие как YaST в OpenSUSE или Настройки Ubuntu. Но с графичным интерфейсом я думаю вы разберетесь. А мы рассмотрим управление группами linux через терминал. Для начала разберемся с файлами, а уже потом с пользователями.
При создании файла ему назначается основная группа юзера который его создал. Это просто например:
Здесь вы можете видеть, что владелец всех папок sergiy и группа также sergiy. Правильно, так как эти пользователи были созданы мной. Но давайте пойдем дальше:
Модифицирование первичной группы пользователя в Linux
Хотя учетная запись пользователя может быть долею нескольких групп, одна из групп всегда является «основной группой», а остальные представляются «вторичными группами». Файлы и папки, созданные пользователем, будут соответствовать первичной команде.
Чтобы изменить основную группу, которой назначен пользователь, запустите бригаду usermod, заменив groupname на имя группы, которую вы хотите сделать основной и username на имя переписной записи пользователя.
usermod -g groupname username
Обратите внимание на -g здесь. При использовании маленькой буквы g вы назначаете основную группу. Когда вы используете верхний регистр -G, как указано реке, вы назначаете новую вторичную группу.
Как видите, всё очень просто. Вы можете дословно с помощью одной команды посмотреть группы пользователей Linux, причём не только для нынешного пользователя, а для всех, кто вас интересует. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!
How do I List All Groups in Linux
Linux systems may have several users that are divided into many groups. These groups are the collection of users with the same set of privileges like reading, writing, or executing permission for a particular file or resources shared among the users of that group. Linux allows you to add a new user or the existing user to the existing group for utilizing the privileges of that particular group that it will grant. We will learn about the various Linux groups and how to list all the members of the group.
Types of Groups in Linux
Linux has two types of groups that contain several users:
- Primary or Login Group: it is the group associated with the files created by a specific user. The name for that primary group has the same name as the user’s name that will create that specific file. Each user must belong to exactly a single group.
- Secondary or Supplementary Group: you can use this type of group to grant privileges to a set of users that belong to that group. A user can be assigned to no or more secondary groups.
Listing Users on Linux
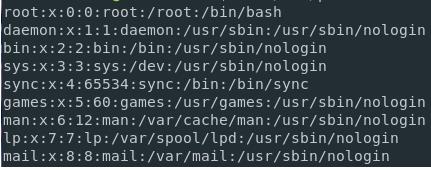
For listing all the users present on the Linux system, you can run the cat command on the ‘/etc/passwd” file. This command will help in returning the number of users that are present on the Linux system.
Also, use the “less” or “more” command for navigating within the user’s list.
Listing Users Using the /etc/passwd File
For listing the usernames on the Linux system, you can use the “cat” command and then pipe the output to the “cut” command to isolate the usernames available in the first column in the list. Run the below-mentioned command as shown below.
Listing Usernames Using awk
For listing the usernames on the Linux system, use the “cat” command and then pipe the output to the “awk” command that works similar to the “cat” command.
Here we are using the “awk” interpreter, as shown below.
Listing Usernames Using getent
Use the getent command along with the “passwd” argument for listing the usernames available on Linux. Also, you can mention the optional user that you want to be displayed on the screen.
The getent command retrieves the entries from the Name Service Switch databases. It is a Unix utility for retrieving entries from various data sources. Check the list of the data sources available from the nsswitch.conf, which is stored at /etc.
If you want to list all the users with the help of the getent function, you can run the following command.
Listing the Connected Users on Your Linux Host
To get the list of the users connected to the Linux system, you can use the following command.
Using this command, you will provide the connected users’ list and the shell they are using.
Also, you can use the “users” command to get the same result as the “who” command, as shown below.
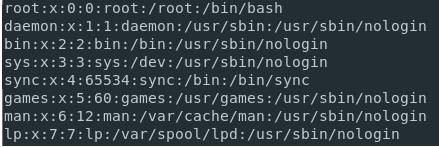
Listing Groups Using /etc/group File
Use the most commonly used “cat” command to get the list of the groups available in the “/etc/group” file. When you run the command, you will get the list of the groups.
But if you are looking for the group names that are present in the “/etc/group” file, use the cat command and then pipe the output to the “cut” command as shown below.
Also, if you want to isolate one group to check what users belong to that group, use the below command.
Listing Groups Using getent
You can use the “getent” command for listing the users on the Linux system.
If you do not provide the key, you will get the entire group file.
Listing Groups for the Current User
Using the “group” command will display a list of groups a specific user is in.
If you do not provide any argument, you will get the list of the groups for the user that runs the command.
Conclusion
The Linux system contains users and groups in different files. Sometimes it becomes important to get the user details and to which group they belong. Thus Linux offers some commands that will help you to achieve that. You can run some commands to get the user details and the group to which they belong. You can also get the complete list of users on the Linux system, active users, and groups names.
You can go through this article to get various commands for getting the list of all the groups in Linux and understand how they work.
About the author
Simran Kaur
Simran works as a technical writer. The graduate in MS Computer Science from the well known CS hub, aka Silicon Valley, is also an editor of the website. She enjoys writing about any tech topic, including programming, algorithms, cloud, data science, and AI. Travelling, sketching, and gardening are the hobbies that interest her.