- RS485 communication guide
- RS485 Data Analyzer
- What is RS-485?
- How far can you run RS485?
- What is RS485 communication protocol?
- RS-485 communication: main features
- Bi-directional half-duplex data transmission
- Symmetrical communication channel
- Multi-pointing
- What is RS485 Modbus protocol?
- RS485 vs RS232: Comparing serial communication protocols
RS485 communication guide
RS485 is a common communications standard that is widely used in data acquisition and control applications. One of its main advantages is that it allows putting several RS485 devices on the same bus which makes it possible for multiple nodes to connect with each other.
This article covers some of the most commonly asked aspects of RS-485 communications and tells what RS485 communication is and why RS-485 communication remains that popular.
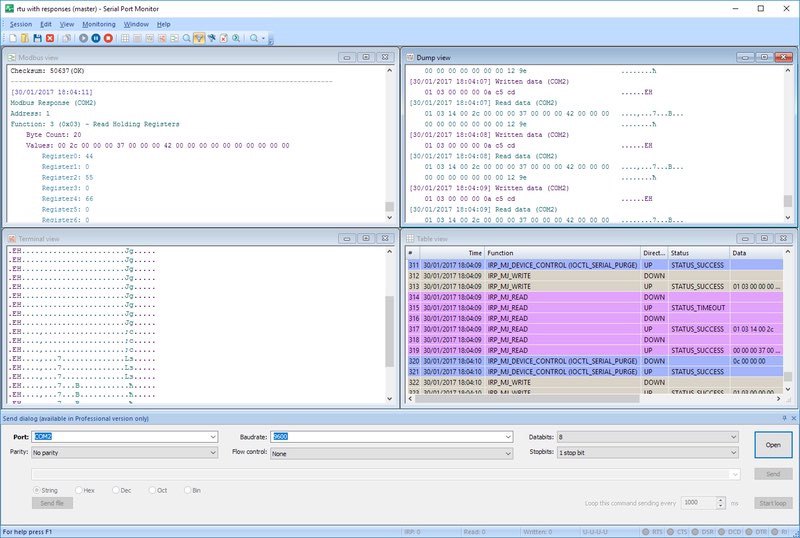
RS485 Data Analyzer
Working with serial apps and devices, specialists often rely on dedicated software, like RS485 Data Logger by Electronic Team, to sniff and analyze serial port activity, detect errors, compare received data, etc.
What is RS-485?
RS-485 (currently known as EIA/TIA-485) is a standard interface of the physical layer of communication, a signal transmission method, the 1st level of the OSI (Open System Interconnection) model. RS-485 has been created in order to expand the physical capabilities of RS-232 interface.
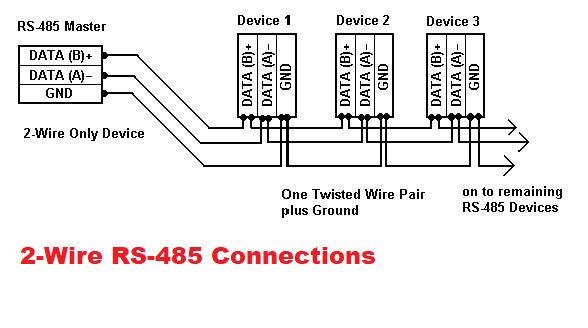
The serial EIA-485 connection is done using a cable of two or three wires: a data wire, a wire with inverted data, and, often, a zero wire (ground, 0 V). This way, transmitters and receivers exchange data via a twisted-pair cable of 22 or 24 AWG solid wires.
The main idea here is to transport one signal over two wires. While one wire transmits the original signal, the other one transports its inverse copy. Such transmission method provides high resistance to common-mode interference. The twisted-pair cable that serves as a transmission line can be shielded or unshielded.
How far can you run RS485?
Communication network built on the RS-485 interface consists of transceivers connected by a twisted pair (two twisted wires). The basic principle of RS-485 interface is differential (balanced) data transmission. That means one signal is transported over two wires. With that, one wire of the pair transmits the original signal and the other one transports its inverse copy.
As a result of differential signal transmission there is always a potential difference between the wires. This ensures high resistance to common mode interference. In addition, the twisted pair may be shielded, which ensures the protection of transmitted data. All this allows sending data over long distances at relatively high speeds, which can reach 100 kbits/s at 4000 feet .
4000 feet or about 1200 meters is the maximum cable length in RS-485 communications. A general guideline, however, is that the product of line length (in meters) and the data rate (in bits per second) should not be more than 108. For instance, a 20-meter cable allows a maximum data rate of 5 Mbits/s.
What is RS485 communication protocol?
When RS485 communication line is ready for operation at the physical level, it’s time to think about the data transfer protocol — an agreement between the system’s devices on the format of the data packets transmission.
By the nature of RS-485 interface, RS-485 devices cannot transmit and receive data at the same time, as it leads to a conflict of transmitters. Therefore, the deterministic behavior is mandatory to avoid collisions of data packets.
In RS485 communication protocol, the commands are sent by the node which is defined as a master. All other nodes connected to the master receive the data over RS485 ports. Depending on the information sent, zero or more nodes on the line respond to the master.
With that said, this type of communication is not the only possible way to exchange data over RS485 protocol. There are some other implementations of RS485 networks where every node can start the data transfer on its own. However, the risk of possible data loss is higher in such networks.
RS-485 communication: main features
- Two-way data exchange via one twisted pair of wires;
- support for several transceivers connected to the same line, i.e., the ability to create a network;
- long length of the communication line;
- high transmission speed.
Now, let’s take a closer look at the main characteristics of RS-485 communication:
Bi-directional half-duplex data transmission
Serial data stream can be transported in one direction, data transfer to the other side requires using a transceiver. A transceiver (commonly referred to as ‘driver’) is a device or an electrical circuit that forms a physical signal on the transmitter side.
Symmetrical communication channel
Receiving or transmitting data requires two equivalent signal wires. The wires are used to exchange data in both directions (alternatively). With the help of a twisted pair cable, the symmetrical channel significantly increases the stability of a signal and suppresses electromagnetic radiation generated by the useful signal.
Multi-pointing
RS-485 communication line can work with multiple receivers and transceivers connected. At the same time, one transmitter and several receivers can be attached to one communication line at a time. All the other transmitters that need to be connected should wait until the communication line is free for data transmission.
What is RS485 Modbus protocol?

One of the main features that differs RS485 communication from any other serial communication is the format of data exchanged. While RS232 devices connect over text (ASCII) protocols, most RS485 devices use Modbus.
Modbus is a serial communications protocol that is widely used by industrial electronic devices. In Modbus, the connection is established between a master (host) and slaves (COM-based devices)*. Modbus helps access the configuration of the devices and read the measures.
* On July 9, 2020 Modbus Organization replaces Master-Slave with Client-Server to describe Modbus communications, characterized by communication between client device (s), which initiates communication and makes requests of server device(s), which process requests and return an appropriate response (or error message).
The data exchange is initiated by a host. The host can switch its RS-485 driver to the transmission mode on its own, while the other RS485 drivers (slaves) work in the receiving mode. In order for a slave to answer the host over the communication line, the ‘master’ sends it a special command, which gives the intended device the right to switch its driver into a transmission mode for a certain time.
Modbus is one of the simplest protocols for the interaction of devices with each other. It is at the same time easy to implement for equipment manufacturers, which is the primary reason for its prevalence, and at the same time, it is difficult for an engineer, programmer, because it shifts onto his shoulders all the difficulties of implementation in the final solution, requiring him to work with multi-page tables of registers and variables, their addresses, various functions of writing and reading and data conversion.
RS485 vs RS232: Comparing serial communication protocols
The RS485 and RS232 serial communication protocols have been in use for over 50 years and are still widely used throughout business and industry. Expanding the capabilities of the RS232 standard was the impetus for developing the RS485 protocol. The following table provides an overview of the two standards.
| Protocol | RS232 | RS485 |
| Protocol type | Duplex | Half-duplex |
| Signal type | Unbalanced | Balanced |
| Number of devices | 1 transmitter and 1 receiver | Up to 32 transmitters and 43 receivers |
| Maximum data transfer | 19.2Kbps for 15 meters | 10Mbps for 15 meters |
| Maximum cable length | Approximately 15.25 meters at 19.2Kbps | Approximately 1220 meters at 100 Kbps |
| Output current | 500mA | 250mA |
| Minimum input voltage | +/- 3V | 0.2V differential |
Now, let’s take a look at the main differences between the two protocols.
Number of Transmitters and Receivers
The RS232 Serial Interface is designed to connect two devices. The protocol enables communication between a single transmitter and receiver. Using an RS485 interface, up to 32 serial devices can be connected to one transmitter.
Making effective use of serial devices often involves converting between RS232, RS485, and USB signals. This is partly due to hardware manufacturers’ concentration on providing USB connectivity rather than serial ports on laptop and desktop machines. Conversion enables older devices to coexist with new hardware that lacks serial interfaces.
Devices using the RS232 protocol are limited to a distance of 15 meters between transmitter and receiver while still achieving the maximum data transmission rate. This length can be extended if slower data rates can be tolerated.
The operation distance is substantially extended in the RS485 protocol. It supports maximum data rates at a length of 1200 meters, making the RS485 protocol an excellent choice for communication between physically distant pieces of equipment.
The transmission speed possible with an RS232 interface is 1Mb/s for a distance of up to 15 meters. RS485 offers greater speeds of up to 10Mb/s over a distance of 15 meters. When taken to its maximum length of 1200 meters, the RS485 protocol transmits data at 100Kb/s.
Electrical Noise Concerns and Ground Potential
An RS232 interface is a system based on voltage levels and performs optimally in situations where there are minimal differences in ground potential. Environments that exhibit high levels of electrical noise and variable ground potential impact RS232’s ability to transfer data efficiently and can lead to data loss or corruption.
The RS485 protocol employs a differential voltage system that allows it to operate effectively in environments with higher levels of electrical noise. A byproduct of the differential voltage system is the extended data transfer distance, increased transmission speed, and lower voltage use seen with RS485.