- Подсчитываем md5 (хеш-сумму) в Linux
- После записи дистрибутива Linux на оптический диск нужно проверить целостность, узнать его MD5 сумму
- Проверка контрольной суммы md5 linux
- NAME
- SYNOPSIS
- DESCRIPTION
- BUGS
- AUTHOR
- REPORTING BUGS
- COPYRIGHT
- SEE ALSO
- Проверка целостности скачанного файла
- How to Use the md5sum Command in Linux
- The md5sum Command with Examples
- Read in Binary Mode
- Read in Text Mode
- Create a BSD-Style Checksum
- Validate md5 Checksum with a File
- Validate Multiple Files
- Display Only Modified Files
- Generate Status Only
- Check Improperly Formatted Checksum Lines
- Skip Reporting Status for Missing Files
- Show Help and Version Information
Подсчитываем md5 (хеш-сумму) в Linux
Проверить MD5 (хеш-сумму) в Linux проще всего именно в терминале. Через какой-либо графический интерфейс необходимо будет сделать больше манипуляций, чем просто скомандовать в терминале Linux следующее:
md5sum /home/pavel/Дистрибутивы/lubuntu-12.04-desktop-i386.iso
Само собой разумеющееся путь до необходимого вам файла, (/home/pavel/Дистрибутивы/lubuntu-12.04-desktop-i386.iso) необходимо прописывать свой, тот который соответствует нужному объекту для подсчета MD5 суммы в Linux.
Чтобы не вводить путь к файлу вручную, его можно скопировать следующим образом. Через файловый менеджер заходим в каталог, где собственно находится тот нужный нам файл. Адресную строку в файловом менеджере необходимо перевести из вида «иконок» в текстовый вид, клавишами , дальше можно скопировать путь либо с помощью мышки через правый клик, либо клавишами . Переходим в терминал и к написанной команде «md5sum» через пробел добавляем наш путь с полным названием файла.
$ md5sum /home/pavel/Дистрибутивы/lubuntu-12.04-desktop-i386.iso 0fc9564b8fde8ff56100c3d7814fa884 /home/pavel/Дистрибутивы/lubuntu-12.04-desktop-i386.iso
Команды в Linux являются стандартном для всех и значит, что команда md5sum подойдет для любого дистрибутива Linux, в котором бы вы не находились. Это и есть одно из достоинств командной строки.
Проверка MD5 (хеш-сумм) требуется после загрузки больших файлов, которые не смогут нормально работать, если какие-либо файлы повредились или каким-то образом изменились. Проверка MD5 сумм в основном применятся к .iso файлам, чаще всего к дистрибутивам. Если .ISO файл поврежден, то его не стоит записывать на USB брелок (флешку), а тем более на оптический диск, дистрибутив Linux при установке будет сообщать об ошибке каких-либо файлов.
После записи дистрибутива Linux на оптический диск нужно проверить целостность, узнать его MD5 сумму
В этой статье мы продолжим углубляться в мир командной строки и сверим MD5 записанного оптического с MD5 суммой исходного файла .ISO с помощью консольной утилиты isoinfo. Для начала мы выудим немного первичной информации о записанном диске командой:
Где /dev/sr0 это DVD-ROM, для уточнения имени вашего примонтированного оптического диска, в том случае если он у вас не один, можно найти по выводу этой команды:
Из имеющейся информации после ввода:
Будет иметься примерно следующее:
CD-ROM is in ISO 9660 format System id: Volume id: Lubuntu 12.04 i386 Volume set id: Publisher id: Data preparer id: XORRISO-1.0.8 2011.04.14.073001, LIBISOBURN-1.0.8, LIBISOFS-1.0.8, LIBBURN-1.0.6 Application id: Copyright File id: Abstract File id: Bibliographic File id: Volume set size is: 1 Volume set sequence number is: 1 Logical block size is: 2048 Volume size is: 352406 El Torito VD version 1 found, boot catalog is in sector 320 Joliet with UCS level 3 found Rock Ridge signatures version 1 found Eltorito validation header: Hid 1 Arch 0 (x86) ID '' Key 55 AA Eltorito defaultboot header: Bootid 88 (bootable) Boot media 0 (No Emulation Boot) Load segment 0 Sys type 0 Nsect 4 Bootoff 52A18 338456
Для нас важны эти строчки:
Logical block size is: 2048 Volume size is: 352406
Далее будем подставлять эти строки в следующую команду, которая нам сообщит MD5 сумму
dd if=/dev/sr0 bs=2048 count=352406 conv=notrunc,noerror | md5sum -b
Обратите внимание на три пункта, которые вы должны подставить свои:
- /dev/sr0 — путь до оптического диска (если он у вас один, значит этот пункт без изменений)
- bs= 2048 — у вас своё значение «Logical block size is:»
- count=352406 — из значения «Volume size is:».
После подсчета вы получите примерно следующее:
352406+0 записей считано 352406+0 записей написано скопировано 721727488 байт (722 MB) 322e76e15cbe9ae4b964f3e6cbe49e37 *- , 55,3223 c, 13,0 MB/c
322e76e15cbe9ae4b964f3e6cbe49e37 — это и есть MD5 сумма диска. Если, она совпадает со значение указанном на сайте, где вы скачивали файл или с исходным файлом на компьютере, то значит, диск записался без ошибок. На практике бывает, что сумма MD5 часто не совпадает с суммой MD5 указанной на сайте из-за ошибок при чтении диска.
Проверка контрольной суммы md5 linux
NAME
md5sum - compute and check MD5 message digest
SYNOPSIS
DESCRIPTION
Print or check MD5 (128-bit) checksums. With no FILE, or when FILE is -, read standard input. -b, --binary read in binary mode -c, --check read MD5 sums from the FILEs and check them --tag create a BSD-style checksum -t, --text read in text mode (default) The following five options are useful only when verifying checksums: --ignore-missing don't fail or report status for missing files --quiet don't print OK for each successfully verified file --status don't output anything, status code shows success --strict exit non-zero for improperly formatted checksum lines -w, --warn warn about improperly formatted checksum lines --help display this help and exit --version output version information and exit The sums are computed as described in RFC 1321. When checking, the input should be a former output of this program. The default mode is to print a line with checksum, a space, a character indicating input mode ('*' for binary, ' ' for text or where binary is insignificant), and name for each FILE. BUGS
The MD5 algorithm should not be used any more for security related purposes. Instead, better use an SHA-2 algorithm, implemented in the programs sha224sum(1), sha256sum(1), sha384sum(1), sha512sum(1)
AUTHOR
Written by Ulrich Drepper, Scott Miller, and David Madore.
REPORTING BUGS
GNU coreutils online help: http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/> Report md5sum translation bugs to http://translationproject.org/team/>
COPYRIGHT
Copyright © 2016 Free Software Foundation, Inc. License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later http://gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html>. This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it. There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.
SEE ALSO
Full documentation at: http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/md5sum> or available locally via: info '(coreutils) md5sum invocation'
© 2019 Canonical Ltd. Ubuntu and Canonical are registered trademarks of Canonical Ltd.
Проверка целостности скачанного файла
В Ubuntu и других дистрибутивах Linux также можно воспользоваться графической программой Gtkhash, установить ее можно командой:
sudo apt-get install gtkhash
В Windows используйте программу HashCalc. Ее можно скачать с официального сайта: slavasoft.com
В результате программа должна показать контрольную сумму (набор букв и цифр), примерно в таком виде:
463e4e1561df2d0a4e944e91fcef63fd
Ее нужно сверить с контрольной суммой, указанной на официальном сайте.
Если контрольная сумма совпала, значит можно использовать файл, а если не совпала — скачать файл заново.
Когда скачиваете образ системы, то проверять контрольную сумму нужно обязательно. В остальных случаях, например при скачивании видео и музыки — на ваше усмотрение.
- Сайт
- Об Ubuntu
- Скачать Ubuntu
- Семейство Ubuntu
- Новости
- Форум
- Помощь
- Правила
- Документация
- Пользовательская документация
- Официальная документация
- Семейство Ubuntu
- Материалы для загрузки
- Совместимость с оборудованием
- RSS лента
- Сообщество
- Наши проекты
- Местные сообщества
- Перевод Ubuntu
- Тестирование
- RSS лента
© 2018 Ubuntu-ru — Русскоязычное сообщество Ubuntu Linux.
© 2012 Canonical Ltd. Ubuntu и Canonical являются зарегистрированными торговыми знаками Canonical Ltd.
How to Use the md5sum Command in Linux
When you download a file from the internet, it is a good safety practice to check whether you received the original version. Comparing checksums you received from the file creator with the ones you obtain by checking the file yourself is a reliable way to confirm your download’s integrity.
The md5sum command in Linux helps create, read, and check file checksums.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to use the md5sum command to validate the files you receive.
The md5sum Command with Examples
When used on a file without any options, the md5sum command displays the file’s hash value alongside the filename. The syntax is:
After obtaining the hash value, compare it with the MD5 value provided by the file creator.
Note: While md5sum is a reliable method for testing whether the file you received has been compromised, it is useful only if you know that the website you downloaded it from is secure. If hackers gain access to the website, they can change both the file and its checksum, making it appear as if the file you are downloading is safe.
Read in Binary Mode
To read the file in binary mode, use the -b option ( —binary ):
The * character before the file name means that md5sum read it in binary mode.
Read in Text Mode
Use the -t option ( —text ) to read the file in text mode:
Text mode is the default mode for reading files with md5sum .
Create a BSD-Style Checksum
Using the —tag option outputs the hash value in the BSD-style format:
Validate md5 Checksum with a File
To check a file by comparing its hash value with the value provided in a hash file, use the -c option.
1. As an example, create a hash file containing the md5sum output:
md5sum [filename] > [file-containing-hashes]2. Use the following syntax to compare the hash value from the file you created against the current hash value of the .txt file:
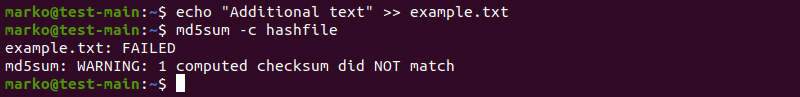
md5sum -c [file-containing-hashes]3. If you change the contents of the file and repeat the check, a warning message is displayed:
Validate Multiple Files
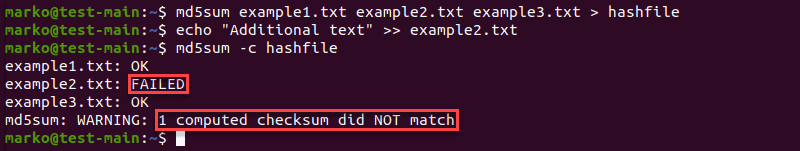
Use the same md5sum -c procedure to check the integrity of multiple files:
md5sum [filename1] [filename2] [filename3] > [file-containing-hashes]In the following example, the contents of example2.txt have changed, resulting in a warning message from md5sum :
Display Only Modified Files
The —quiet option displays only the files whose hash value has changed. It skips the output of validated files.
md5sum --quiet -c [file-containing-hashes]Generate Status Only
The md5sum command with the —status option does not produce any output but returns 0 if there are no changes and 1 if it detects changes. This argument is useful for scripting, where there is no need for standard output.
The example script below illustrates the use of the —status option:
#!/bin/bash md5sum --status -c hashfile Status=$? echo "File check status is: $Status" exit $StatusWhen the script executes, it shows status 1 , meaning that md5sum detected the change made earlier in example2.txt .
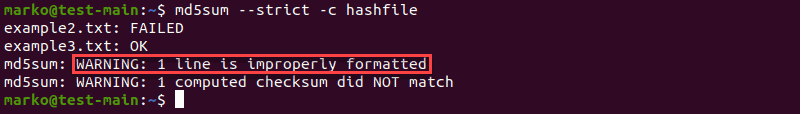
Check Improperly Formatted Checksum Lines
Add the —strict option to exit non-zero for improperly formatted hash values:
md5sum --strict -c [file-containing-hashes]The example shows the output of md5sum —strict when you put invalid characters in the first line of the file containing hashes:
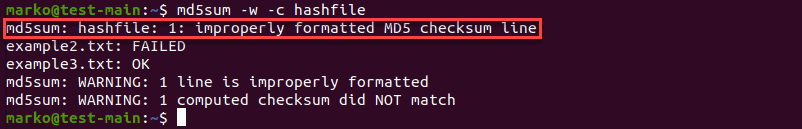
To display which line has an invalid hash, use -w ( —warn ):
md5sum -w -c [file-containing-hashes]The example above shows the -w option displaying that the improperly formatted MD5 checksum line is line 1 of the file.
Skip Reporting Status for Missing Files
By default, md5sum shows warnings about the files it cannot find on the system. To override this behavior, use the —ignore-missing option:
md5sum --ignore-missing -c [file-containing-hashes]In the example below, example1.txt was deleted before running the md5sum command. The output ignores the deleted file:
Show Help and Version Information
To get the official help for the md5sum command, type:
To check md5sum version, type:
Note: You should also check out our overview of the diff command to learn how to compare two files line by line.
After completing this tutorial, you should know how to properly use the md5sum command to create, print, or check MD5 checksums.
Marko Aleksić is a Technical Writer at phoenixNAP. His innate curiosity regarding all things IT, combined with over a decade long background in writing, teaching and working in IT-related fields, led him to technical writing, where he has an opportunity to employ his skills and make technology less daunting to everyone.
The echo command prints out a text string you provide as the output message. This tutorial covers the echo.
The ls command (short for list) lists information about directories and any type of files in the working.
A list of all the important Linux commands in one place. Find the command you need, whenever you need it or.
Creating a file in Linux might seem straightforward, but there are some surprising and clever techniques. In.