- Поддержка аутентификации Kerberos для компьютеров под управлением UNIX и Linux
- Поддержка Kerberos для компьютеров UNIX и Linux в Operations Manager
- Предварительные требования
- Включение или отключение проверки подлинности Kerberos на сервере управления или сервере шлюза
- Проверка аутентификации Kerberos с помощью консоли
- Проверка аутентификации Kerberos с помощью командной строки
- Troubleshoot Kerberos Authentication on Linux
- Troubleshooting Linux Kerberos System Setup and Monitoring Problems
- Troubleshooting Linux Kerberos Client Utility Issues
- Method 1: Using the Klist Command
- Method 2: Using Kinit Command to Check for Issues on KDC Client
- Method 3: Using kinit Command to Check SMP Problems
- Method 4: Using the ktpass Command
- Troubleshooting KDC Support Issues
- Troubleshooting Keytab Issues
- About the author
- Kennedy Brian
Поддержка аутентификации Kerberos для компьютеров под управлением UNIX и Linux
Поддержка этой версии Operations Manager завершена. Рекомендуется выполнить обновление до Operations Manager 2022.
System Center Operations Manager версии 1801 и более поздних версий взаимодействует с компьютерами с UNIX и Linux с использованием протокола SSH и веб-служб для управления (WS-Management). Все действия с агентами, например установка, обновление и удаление агентов, выполняются через SSH и для них нужна привилегированная учетная запись. Обнаружение и мониторинг агентов выполняются через WS-Management и для них достаточно учетной записи низкого уровня.
Теперь Operations Manager поддерживает аутентификацию Kerberos во всех сценариях, где сервер управления взаимодействует с компьютерами UNIX и Linux по протоколу WS-Management. Поддержка аутентификации Kerberos для компьютеров UNIX и Linux повышает безопасность, поскольку серверу управления теперь не нужно использовать обычную аутентификацию для службы удаленного управления Windows (WinRM).
Не отключать обычную проверку подлинности для WinRM, если вы не используете проверку подлинности Windows Kerberos.
Поддержка Kerberos для компьютеров UNIX и Linux в Operations Manager
| Действие | Протокол | Поддержка аутентификации Kerberos |
|---|---|---|
| Установка агента | SSH | Нет |
| Удаление агента | SSH | Нет |
| Обновление агента | SSH | Нет |
| Восстановление агента | SSH | Нет |
| Мониторинг с использованием агента | WS-Man | Да |
| Обнаружение агента | WS-Man | Да |
Предварительные требования
Мониторинг UNIX и Linux с помощью Operations Manager поддерживается во многих операционных системах.
Следующее подмножество этих операционных систем теперь поддерживает обмен WS-Management через Kerberos: (Будет поддерживаться только последняя выпущенная версия каждого дистрибутива.)
| Операционная система | Версия |
|---|---|
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server | 6 |
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server | 7 |
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server | 8 |
| CentOS | 6 |
| CentOS | 7 |
| UBUNTU Server | 14 |
| UBUNTU Server | 15 |
| Операционная система | Версия |
|---|---|
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server | 6 |
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server | 7 |
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server | 8 |
| CentOS | 7 |
| Rocky Linux | 8 |
| AlmaLinux | 8 |
| SLES | 12 |
| SLES | 15 |
| Debian | 9 |
| Debian | 10 |
| Debian | 11 |
| Oracle Linux | 7 |
| Oracle Linux | 8 |
| Сервер Ubuntu | 16 |
| Сервер Ubuntu | 18 |
| Сервер Ubuntu | 20 |
| Операционная система | Версия |
|---|---|
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server | 7 |
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server | 8 |
| CentOS | 7 |
| Rocky Linux | 8 |
| AlmaLinux | 8 |
| SLES | 12 |
| SLES | 15 |
| Debian | 9 |
| Debian | 10 |
| Debian | 11 |
| Oracle Linux | 7 |
| Oracle Linux | 8 |
| Сервер Ubuntu | 16 |
| Сервер Ubuntu | 18 |
| Сервер Ubuntu | 20 |
- Агенты UNIX или Linux должны быть присоединены к домену.
- Учетные записи запуска от имени должны быть настроены для использования доменных учетных записей, связанных с соответствующим профилем запуска от имени Unix/Linux.
- Включение аутентификации Kerberos возможно лишь в том случае, если все взаимодействующие с сервером управления агенты компьютеров UNIX и Linux поддерживают протокол Kerberos. Смешанный режим проверки подлинности, при котором некоторые агенты используют обычную проверку подлинности, а другие используют Kerberos, не поддерживается. Вместо этого используйте отдельные пулы ресурсов и серверы управления.
Включение или отключение проверки подлинности Kerberos на сервере управления или сервере шлюза
Используйте следующую процедуру, чтобы включить или отключить проверку подлинности Kerberos на сервере управления или сервере шлюза.
- Откройте консоль управления от имени учетной записи, которая включена в роль «Администраторы» для Operations Manager.
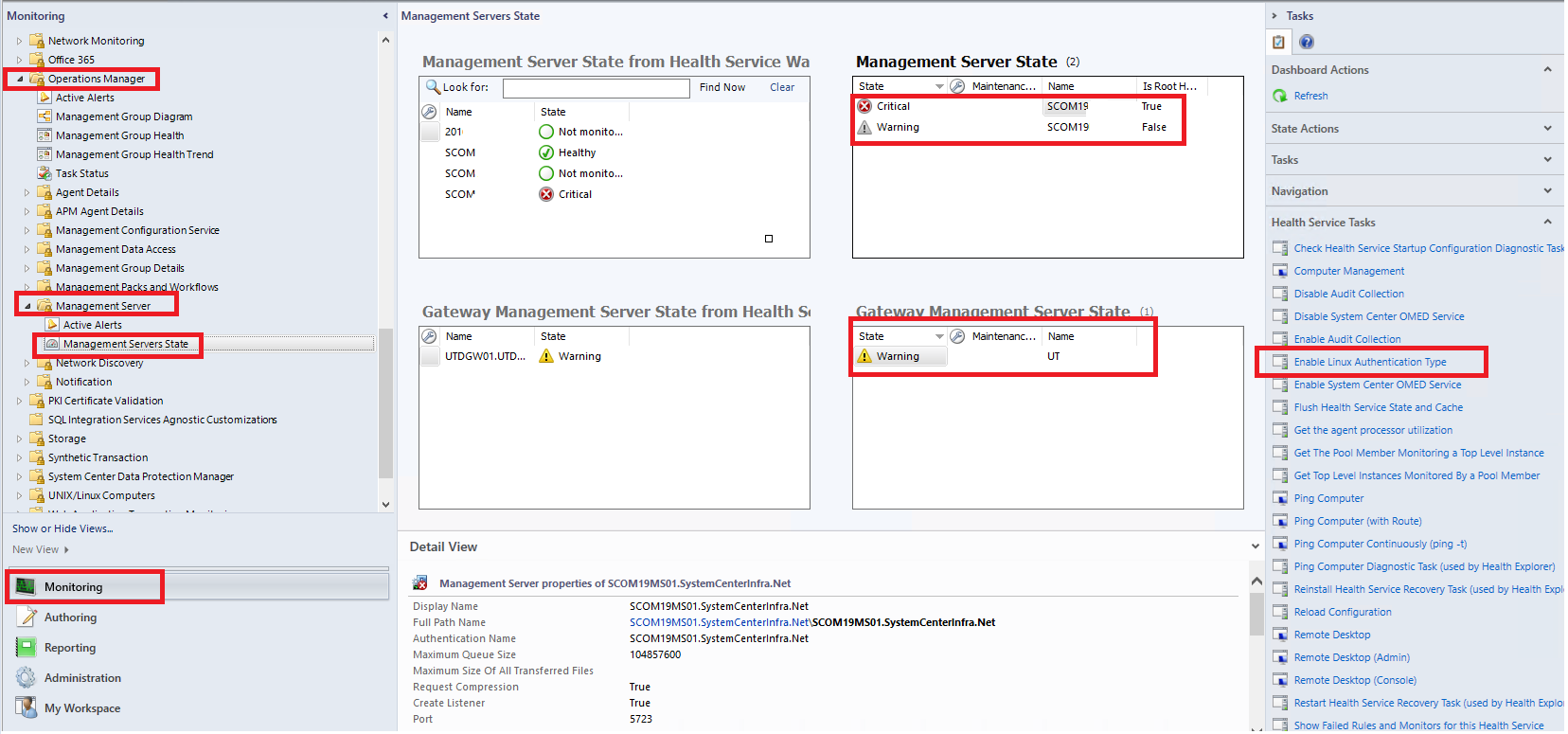
- Выберите значение для параметра Management Server State (Состояние сервера управления) или Gateway Server State (Состояние сервера шлюза), как показано ниже:
- Для серверов управления выберите элементы МониторингOperations ManagerСервер управленияManagement Servers StateManagement Server State (Состояние серверов управления > Состояние сервера управления).
- Для серверов управления шлюзами выберите МониторингOperations ManagerСервер управленияManagement Servers StateGateway Management Server State (Состояние серверов управления > Состояние сервера управления шлюзом).
Эта задача устанавливает параметр реестра Authentication, расположенный по следующему адресу:
HKLM:\Software\Microsoft\Microsoft Operations Manager\3.0\Setup\Linux Auth в Kerberos.
Повторите описанные выше действия на всех серверах управления в пуле ресурсов UNIX и Linux, для которых необходимо выполнить проверку подлинности Kerberos в агентах SCX.
Проверка аутентификации Kerberos с помощью консоли
Чтобы убедиться, что аутентификация Kerberos работает правильно, выполните следующие действия в консоли Operations Manager.
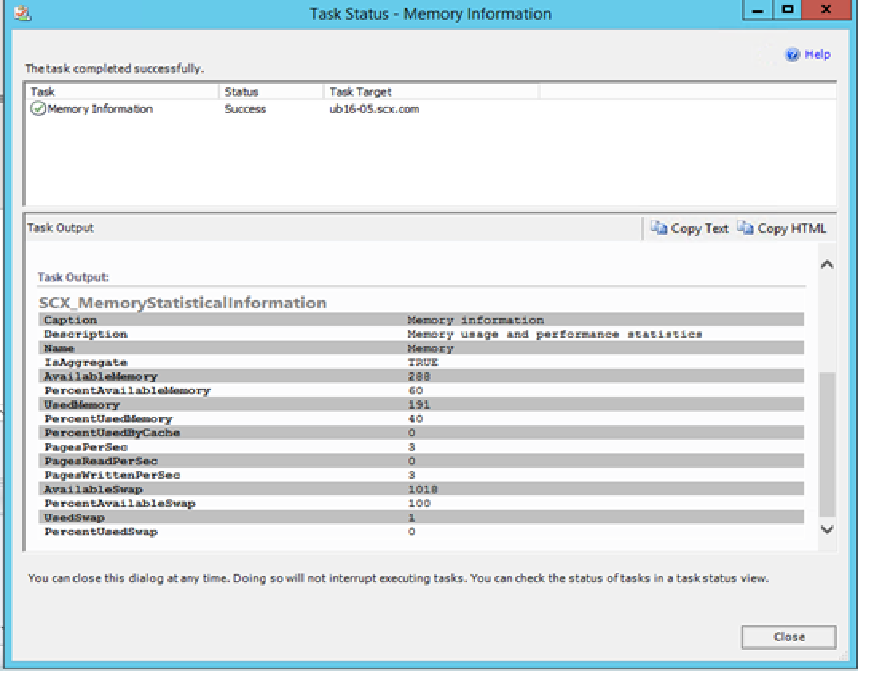
- Выберите Мониторинг>компьютеров> UNIX/Linux Выберите компьютер UNIX или Linux.
- В области задач справа выберите Сведения о памяти.
- Убедитесь, что задача выполняется успешно.
Проверка аутентификации Kerberos с помощью командной строки
Чтобы средствами командной строки проверить работу аутентификации Kerberos для взаимодействий между сервером управления и агентами UNIX или Linux, выполните следующие действия.
- Запустите командную строку от имени администратора на сервере управления и выполните приведенный ниже скрипт, заменив соответствующие сведения на имя сервера, имя пользователя и пароль.
winrm e http://schemas.microsoft.com/wbem/wscim/1/cim-schema/2/SCX_Agent?__cimnamespace=root/scx -r:https://:1270 -u: -p: -auth:Kerberos -skipcacheck -skipcncheck -encoding:utf-8 Troubleshoot Kerberos Authentication on Linux
Like many other authentication protocols, you may often face problems configuring Linux to authenticate with Kerberos. Of course, issues always vary depending on your stage of authentication.
This article addresses some of the issues you may find. Some of the issues that we include here are:
- Issues arising from system setup
- Issues arising from client utilities and failure to use or manage the Kerberos environment
- KDC encryption issues
- Keytab problems
Troubleshooting Linux Kerberos System Setup and Monitoring Problems
Notably, the problems you may face with Linux Kerberos often begin from the setup stage. And the only way you can minimize setup and monitoring issues is by following these steps:
Step 1: Ensure you have a functional Kerberos protocol correctly installed in both machines.
Step 2: Synchronize the time on both machines to ensure that they run on a similar time frame. Notably, use the network time synchronization (NTS) to ensure that the machines are within 5 minutes of each other.
Step 3: Check if all hosts in the domain network service (DNS) have the correct entries. While at that, ensure that each entry in the host file has relevant IP addresses, host names, and fully-qualified domain names (FQDN). A good entry should look like this:
Troubleshooting Linux Kerberos Client Utility Issues
If you are finding it difficult to manage client utilities, you can always use the following three methods to solve the issues:
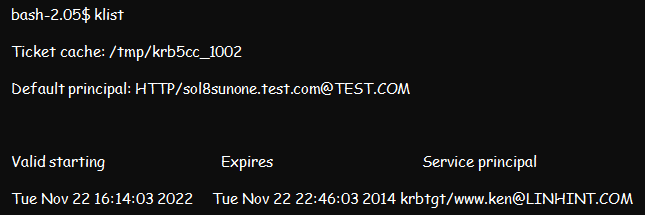
Method 1: Using the Klist Command
The Klist command will help you visualize all tickets in any credentials cache or the keys in the key tab file. Once you have the tickets, you can forward the details to complete the authentication process. A Klist output for troubleshooting client utilities will look like this:
Method 2: Using Kinit Command to Check for Issues on KDC Client
You can also use the Kinit command to confirm if you have any issues with your KDC host and KDC client. The Kinit utility will help you obtain and cache a ticket-granting ticket for the service principal and the user. Client utility problems could always result from a wrong principal name or a wrong user name.
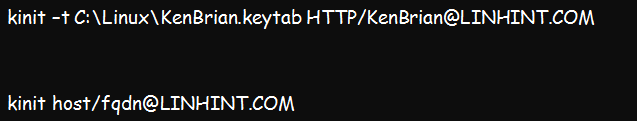
Below is the Kinit syntax for the user principal:
The above command will prompt for a password as it creates a user principal. When running the command, ensure that you replace the username with a valid entry from your directory.
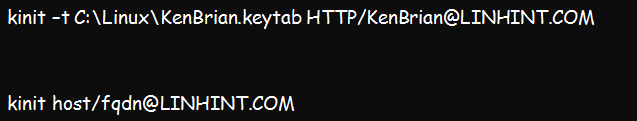
On the other hand, the Kinit syntax for service principal is similar to the details in the below screenshot. Note that this can vary from one host to another:
Interestingly, the Kinit command for the service principal will not prompt any passwords since it uses the bracketed key tab file to authenticate the service principal.
Method 3: Using kinit Command to Check SMP Problems
You can also run the below command irrespective of whether the above kit command worked or not. It helps to determine if there are any issues with the SMP host. Notably, this is more useable when testing your sever on mail.company.com.
Your kinit command will take the below structure:
Method 4: Using the ktpass Command
Sometimes the problem could be a problem with your passwords. To ascertain that this is not the cause of your Linux Kerberos issues, you can verify your ktpass utility version.
Troubleshooting KDC Support Issues
Kerberos can often fail due to an array of issues. But sometimes, the issues could result from KDC encryption support. Notably, such a problem will bring the message below:
Do the following in case you receive the above message:
- Verify if your KDC settings block or restrict any encryption types
- Confirm if your server account has all the encryption types checked.
Troubleshooting Keytab Issues
You can take the following steps if you encounter any key tab issues:
Step 1: Verify that both the location and name of the key tab file for the host are similar to the details in krb5.conf file.
Step 2: Verify if the host and client servers have principal names.
Step 3: Confirm the encryption type before creating a key tab file.
Step 4: Verify the validity of the key tab file by running the below kinit command;
The above command should return no error if you have a valid key tab file. But in case of an error, you can verify the validity of the SPN using this command:
The above utility will prompt you to key in your password. Failure to ask for a password implies that your SPN is invalid or unidentifiable. Once you key in a valid password, the command will not return any error.
The above are some common problems you might encounter when configuring or authenticating with Linux Kerberos. This write-up also contains the possible solutions for each of the issues you might face.
About the author
Kennedy Brian
Brian is a computer scientist with a bias for software development, programming, and technical content development. He has been in the profession since 2015. He reads novels, jogs, or plays table tennis whenever not on gadgets. He is an expert in Python, SQL, Java, and data and network security.