- Пошаговая установка PyCharm на Linux
- Установка PyCharm с помощью Snap
- Установка PyCharm с помощью tar
- 1: Загрузите архив
- 2: Извлеките архив
- 3: Сделайте файл PyCharm исполняемым
- Настройка Pycharm в Linux
- Заключение
- Command-line interface
- Launcher for a standalone instance
- Shell scripts generated by the Toolbox App
- Change shell scripts location
- Rename shell scripts
- Change shell scripts location
- Rename shell scripts
- Change shell scripts location
- Rename shell scripts
- Command-line arguments
- Commands
- Options
Пошаговая установка PyCharm на Linux
PyCharm — это интегрированная среда разработки для Python, созданная командой Jetbrains. Она предлагает умный редактор кода, а также инструменты для отладки, рефакторинга и профилирования кода.
Помимо этого, данный инструмент также имеет встроенный терминал и интегрирован с основными системами управления версиями (Git, SVN и т. д.) и виртуальными машинами, такими как Docker и Vagrant.
Именно благодаря своей многофункциональности PyCharm быстро стал одной из самых популярных IDE среди разработчиков. Поскольку многие разработчики используют Linux, в этом мануале мы рассмотрим, как установить PyCharm на сервер Linux.
Есть два основных способа установить PyCharm в Linux. Первый использует официальный пакет tar, выпущенный JetBrains, а другой — пакет Snap.
Установка PyCharm с помощью Snap
Snap-пакет — это пакет приложений, разработанный Canonical. Они распространяются как универсальные пакеты и поддерживаются всеми основными дистрибутивами, включая Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Debian, Arch, Fedora и Manjaro. Полный список поддерживаемых дистрибутивов см. здесь .
Чтобы установить пакеты через snap, нам сначала нужно установить snapd в вашу систему. Чтобы сделать это, обратитесь к этому руководству .
Теперь, чтобы установить PyCharm, выполните следующую команду:
sudo snap install pycharm-community —classic \\For free version
sudo snap install pycharm-professional —classic \\For paid version
Установка PyCharm с помощью tar
Этот метод просто требует загрузки и распаковки архива и может использоваться на абсолютно любом дистрибутиве Linux.
1: Загрузите архив
Перейдите на страницу загрузки Pycharm и загрузите любой пакет на ваше усмотрение. В этом уроке мы установим пакет Community (Free).
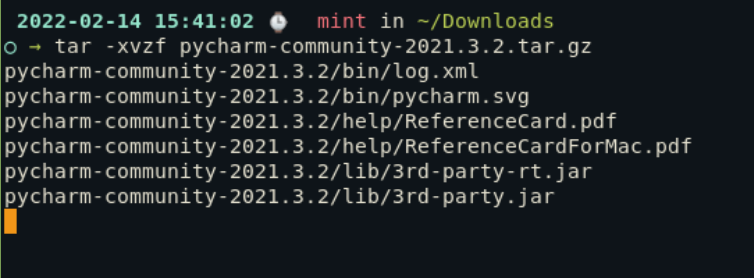
2: Извлеките архив
После того, как вы загрузили пакет tar, распакуйте его с помощью команды tar.
tar -xvzf /path/to/pycharm/tarball
- x : извлекает файл tar.
- v : предоставляет расширенный вывод
- z : использует gzip (для файлов tar.gz)
- f : указывает входной файла
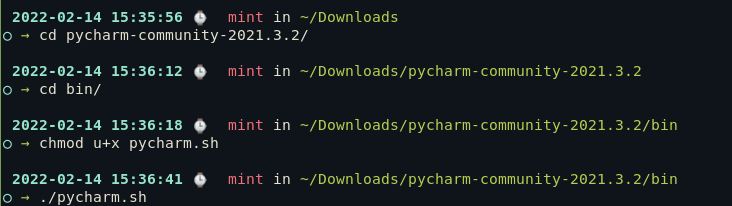
3: Сделайте файл PyCharm исполняемым
Используя Tarballs, нам не нужно ничего устанавливать. Достаточно просто распаковать архив и сделать сценарий оболочки исполняемым, предоставив ему определенные разрешения.
Для этого перейдите в извлеченную папку (она должна быть в той же папке, что и архив), войдите в bin и используйте команду chmod на файл оболочки PyCharm.
cd pycharm-community-2021.3.2/bin/
chmod u+x pycharm.sh
./pycharm.sh
Настройка Pycharm в Linux
Если вы установили Pycharm с помощью snap-пакета , вы можете запустить его из меню «Пуск» или введя Pycharm в терминале. Если вы установили его через tarball, просто перейдите в папку bin извлеченной папки pycharm и запустите файл pycharm.sh, набрав ./pycharm.sh в терминале.
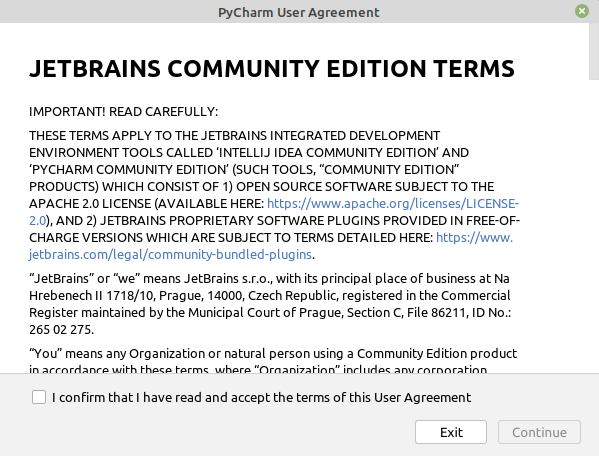
Когда вы запускаете PyCharm в первый раз, вам будет предложено принять условия использования. После принятия Условий PyCharm спросит вас, хотите ли вы анонимно отправлять статистику.
Приняв необходимые условия, вы можете начать разрабатывать свой первый проект в Pycharm или открыть уже существующий проект, если у вас такой есть. Помимо этого, вы также можете открыть проект из VCS (например Git).
Заключение
В этом руководстве вы узнали, как установить Pycharm — интегрированную среду разработки, широко используемую программистами по всему миру. Как вы теперь знаете, его можно установить либо с помощью файла tar, либо с помощью менеджера пакетов snap. Чтобы узнать больше о Pycharm, ознакомьтесь с документацией инструмента .
Command-line interface
Use PyCharm features from the command line: open files and projects, view diffs, merge files, apply code style, formatting, and inspect the source code.
For information about running command-line tools from inside PyCharm, see Terminal emulator.
Launcher for a standalone instance
The installation directory contains batch scripts and executables for launching PyCharm, formatting the source code, and running inspections. To use them from the Command Prompt cmd.exe , add the location of the PyCharm bin folder to the PATH environment variable. For example, if you installed PyCharm to C:\Program Files\JetBrains\PyCharm , you can use the following command:
This command changes the PATH environment variable for the current shell only (the current instance of cmd.exe ). If you want to update it permanently for the current user, run setx :
To update it system-wide for all users, run setx /M instead of setx .
The installer can do this for you if you select Add launchers dir to the PATH on the Installation Options step of the setup wizard.
After you configure the PATH variable, you can run the executable from any working directory in the Command Prompt: pycharm64.exe . Alternatively, you can use the batch script: pycharm.bat .
To run PyCharm from the shell, use the open command with the following options:
- -a : specify the application.
- —args : specify additional arguments when passing more than just the file or directory to open.
- -n : open a new instance of the application even if one is already running.
For example, you can run PyCharm.app with the following command:
If PyCharm is not in the default /Applications directory, specify the full path to it.
You can create a shell script with this command in a directory from your PATH environment variable. For example, create the file /usr/local/bin/pycharm with the following contents:
Make sure you have permissions to execute the script and since /usr/local/bin should be in the PATH environment variable by default, you should be able to run pycharm from anywhere in the shell.
On Linux, the installation directory contains the launcher shell script pycharm.sh under bin . For example, if you installed PyCharm to /opt/pycharm , you can run the script using the following command:
You can create a symbolic link to the launcher script in a directory from the PATH environment variable. For example, if you installed PyCharm to /opt/pycharm and want to create a link named pycharm in /usr/local/bin , run the following command:
Since /usr/local/bin should be in the PATH environment variable by default, you should be able to run the pycharm command from anywhere in the shell.
If you installed PyCharm as a snap package, you can use the corresponding launcher: pycharm-professional or pycharm-community .
Shell scripts generated by the Toolbox App
If you are using the Toolbox App to install and manage JetBrains products, you can use shell scripts for launching your IDEs from the command line.
Toolbox App generates shell scripts automatically and places them to the following folders:
By default, the Toolbox App puts shell scripts in a directory from the system PATH environment variable, so you can run the name of the script as a command to launch PyCharm from any working directory.
Change shell scripts location
- Open the Toolbox App, click the Toolbox App menu icon in the top right corner, and select Settings .
- On the Settings tab, expand the Tools section, and specify another folder in the Shell scripts location field.
Rename shell scripts
If you have several versions of the same IDE, the Toolbox App generates a shell script for each version with a unique name. You can change the name of the shell script for an IDE instance in the settings for this specific instance.
- Open the Toolbox App.
- Click next to an IDE instance and select Settings .
- At the bottom of the Configuration section, change the Shell script name field.
By default, the Toolbox App puts shell scripts in a directory from the system PATH environment variable, so you can run the name of the script as a command to launch PyCharm from any working directory.
Change shell scripts location
- Open the Toolbox App, click the Toolbox App menu icon in the top right corner, and select Settings .
- On the Settings tab, expand the Tools section, and specify another folder in the Shell scripts location field.
Rename shell scripts
If you have several versions of the same IDE, the Toolbox App generates a shell script for each version with a unique name. You can change the name of the shell script for an IDE instance in the settings for this specific instance.
- Open the Toolbox App.
- Click next to an IDE instance and select Settings .
- At the bottom of the Configuration section, change the Shell script name field.
By default, the Toolbox App puts shell scripts in a directory from the system PATH environment variable, so you can run the name of the script as a command to launch PyCharm from any working directory.
Change shell scripts location
- Open the Toolbox App, click the Toolbox App menu icon in the top right corner, and select Settings .
- On the Settings tab, expand the Tools section, and specify another folder in the Shell scripts location field.
Rename shell scripts
If you have several versions of the same IDE, the Toolbox App generates a shell script for each version with a unique name. You can change the name of the shell script for an IDE instance in the settings for this specific instance.
- Open the Toolbox App.
- Click next to an IDE instance and select Settings .
- At the bottom of the Configuration section, change the Shell script name field.
Command-line arguments
The launcher script accepts commands, options, and other arguments to modify its behavior:
Without any arguments, the script launches PyCharm.
Path to file or directory
Open the file or directory specified as the argument.
Commands
Open the diff viewer to see the differences between two specified files.
Open the Merge dialog to merge the specified files.
Apply code style formatting to the specified files.
Perform code inspection on the specified project.
Options
Do not show the splash screen when loading PyCharm.
Do not reopen projects and show the welcome screen. This can help if a project that was open crashes PyCharm.
Do not load manually installed plugins. This can help if a plugin that you installed crashes PyCharm. You will be able to start the IDE and either disable or uninstall the problematic plugin.
Wait for the files to be closed before returning to the command prompt.
For example, you can open file.txt with the following command:
pycharm64.exe —wait file.txt
The shell will be waiting until file.txt is closed.