- Tools to Access The Linux File System from Windows
- Differences between Windows and Linux file systems
- Read-Only Access to Linux Filesystem from Windows
- Read & Write Access to Linux Filesystem from Windows
- Как читать разделы диска с Ext2/3/4 (Linux) при работе в Windows
- Как «прочитать» информацию на разделах с файловыми системами Ext2, Ext3, Ext4
- Способ 1 (через спец. драйвер)
- Способ 2 (через дополнения к TC)
- Способ 3 (с помощью LiveCD)
- Access Linux filesystems in Windows and WSL 2
- Getting started
- Accessing these files with File Explorer
- Limitations
- Give us your feedback!
- Read Linux File systems on Windows using DiskInternals Linux Reader
- DiskInternals Linux Reader
- Read Linux File systems on Windows
Tools to Access The Linux File System from Windows
One of the most popular problems with dual-booting Linux and Windows operating systems is the ability to access Windows files from within Linux but the inability of the reverse; this is due to the way Linux and Windows file systems are set up.
The point of today’s articles is to recommend the most reliable tools that you can install to easily access your Linux files from within your Windows installation. But first, you should know how the file system in Windows and Linux differ.
Differences between Windows and Linux file systems
- The Linux filesystem is case-sensitive so you can have file names like fossmint.html and Fossmint.html in the same directory. This can’t happen on Windows because the file system is not case-sensitive as sees both file names as the same.
- Windows file systems are in the FAT (FAT12, FAT16, and FAT32) and NTFS formats while Linux file systems are in Ext2, Ext3, Ext4, JFS, XFS, etc.
- Windows disks are partitioned and given letters e.g. C: for local disk and E: for a removable disk. In Linux, everything is under the root directory denoted by / and all devices are treated as files. E.g. /dev/cdrom for removable media.
- Linux doesn’t lock access to files as often as Windows and thus allows files to be deleted in situations wherein they wouldn’t be if the user was on Windows. For example, on Windows, you can’t delete a video file that was previously running a VLC without quitting the app. On Linux, you might even be able to delete the file while it’s still running in VLC.
So the most important home point is that while Linux has native support for Windows file systems i.e. NTFS and FAT, we need a 3rd party application to access Linux files from Windows.
These are the best tools available for free.
Read-Only Access to Linux Filesystem from Windows
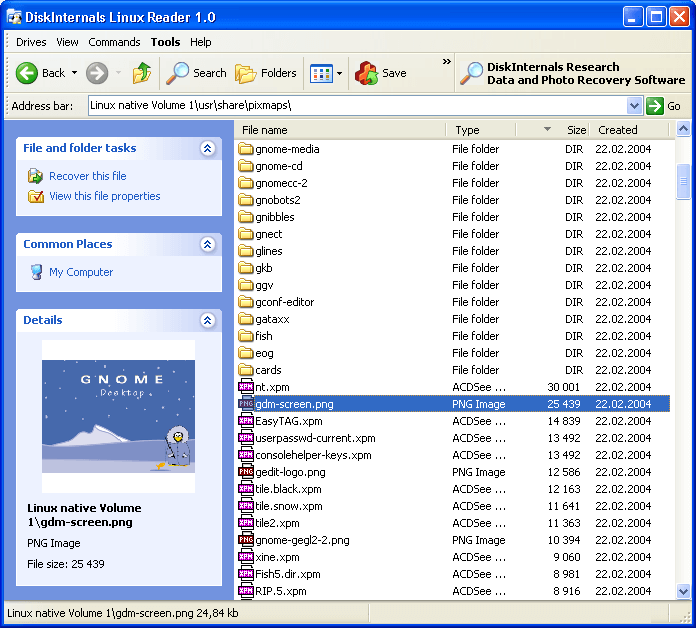
DiskInternals Linux Reader allows users safe and quick read-only access to Ext2, Ext3, and Ext4 Linux files using a UI similar to that of the default Windows Explorer to view and extract files. It is free software but offers a pro version with extra features.
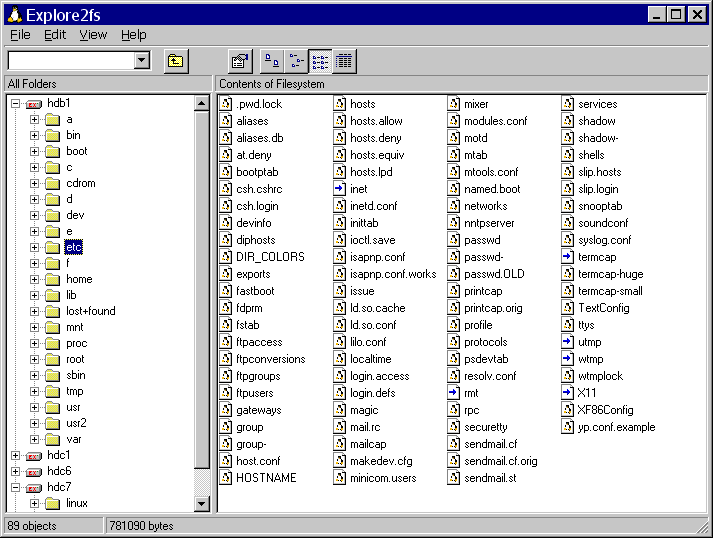
Explore2fs is a GUI drag& drop file explorer for Ex2 and Ex3 file systems. It runs on all Windows versions to allow users to read files but without the ability to make any changes.
Read & Write Access to Linux Filesystem from Windows
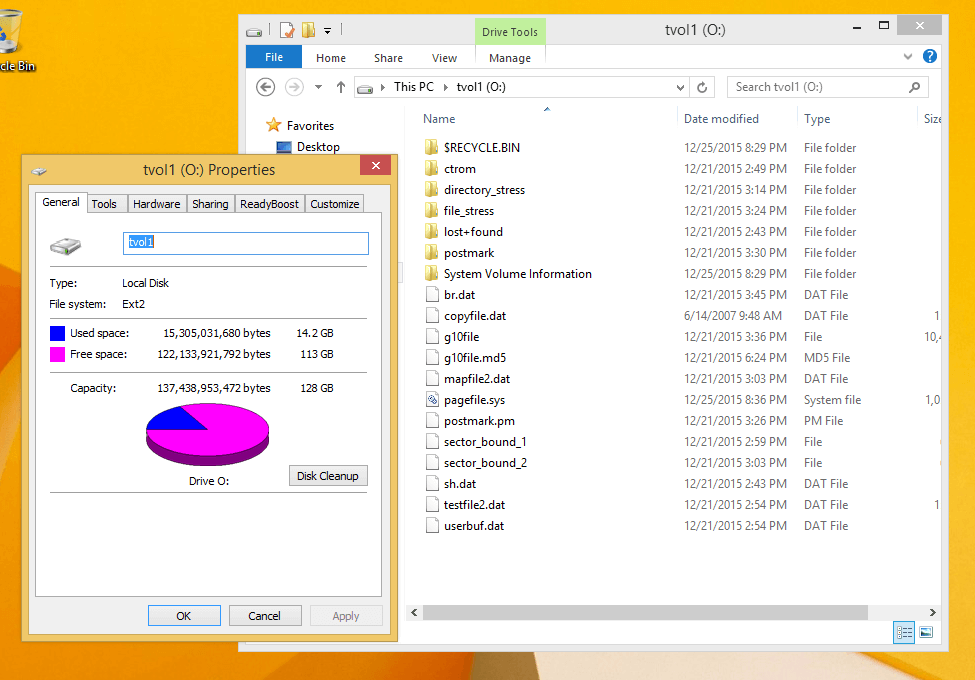
EX2 Installable File System for Windows is a freeware that provides Windows users will full read and write access to Linux Ext2 volumes by installing a pure kernel mode file system driver which extends the Windows file system to include the Ext2 file system.
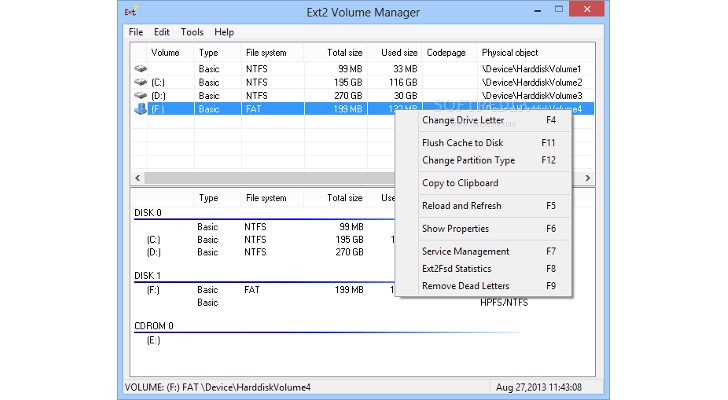
With EX2 IFS, you can view Linux partitions in the disk management application and assign drive letters to them. Mind you, Ext2 Volume manager and Ext2 IFS need to be run with Compatibility mode enabled on Windows 8 and later.
Ext2Fsd is an open-source Linux Ext2 and Ext3 file system driver for all Windows versions with the option to access files in both read-only and read & write modes. However, Ext4 file systems load in read-only mode by default due to Ext2Fsd limited support.
Experts advise that accessing files from other operating systems is best done in read-only mode in other to avoid unfixable mistakes or data corruption. While the odds of such happening are slim in my opinion, always be careful when working with files. I’m not worried because it’s not the same as playing around in sever directories.
I hope this article is useful to you in getting on with your daily tasks. Do you already use any of the software on the list? Or do you have notable mentions to suggest? Add yours in the section below.
Как читать разделы диска с Ext2/3/4 (Linux) при работе в Windows
Доброго дня!
К сожалению «обычная» версия Windows не позволяет работать с дисками, отформатированными в файловые системы (ФС) Ext2, Ext3, Ext4 (используются в Linux). Всё, что доступно — это узнать о их существовании в управлении дисками, а вот скопировать файл — уже проблема.
Наиболее сподручный и самый удобный вариант (на мой взгляд) — установить в Windows спец. драйвер, который позволит ОС работать с дисками Ext2/3/4 также, как если бы они были отформатированы в NTFS (скажем). Т.е. любая программа в Windows (тот же проводник) сможет в обычном режиме работать с диском. Удобно?
Как «прочитать» информацию на разделах с файловыми системами Ext2, Ext3, Ext4
Способ 1 (через спец. драйвер)
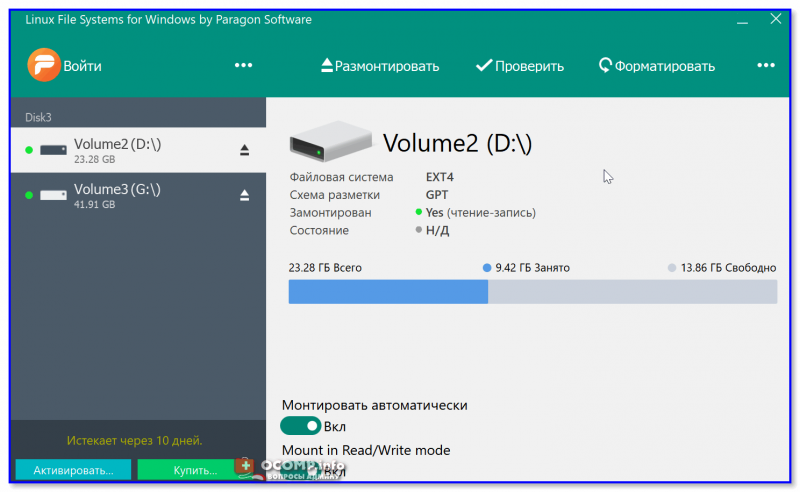
Подобные «драйверы» есть от нескольких производителей. Я бы выделил продукт от Paragon (ссылка на офиц. сайт с драйвером). Почему:
- поддержка ФС: Ext2, Ext3, Ext4 (чтение + запись); Btrfs, XFS (только чтение);
- после установки драйвера — ничего «делать» не нужно: просто Windows начинает видеть накопители с Ext4+;
- совместим с ОС Windows 7/8/10 (плюс есть пробный период, которого хватает для возникшей задачи (обычно)).
Обратите внимание, что «ненужные» разделы диска можно откл. и не монтировать. Настройка драйвера позволяет это сделать.
Главное окно (Linux File Systems for Windows by Paragon Software)
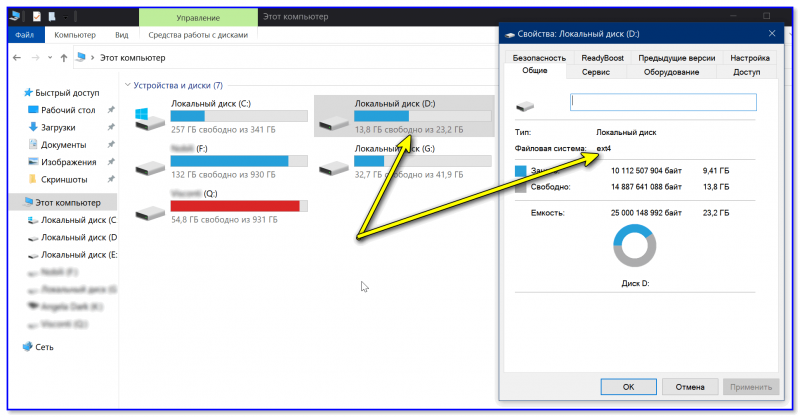
На скрине ниже привел окно проводника: как видите, раздел отображает как «обычный» — на него также можно что-нибудь скопировать / удалить.
Этот компьютер — диски с ФС EXT4 появились в проводнике
👉 Дополнение!
На Sourceforge можно также найти бесплатный драйвер файловой системы Ext2/3/4 для Windows 7/8/10* (ориг. название: Ext2Fsd).
Сразу отмечу, что на некоторых ОС Windows 10 — драйвер этот ведет себя нестабильно, и не позволяет прочитать информацию с нужного раздела.
Продукт от Paragon, конечно, выигрывает.
Способ 2 (через дополнения к TC)
TC — это сокращенное название файлового коммандера Total Commander (некая замена проводнику). К этой программе есть очень много плагинов, и, разумеется, для чтения Ext2/3/4 ФС тоже есть!
Покажу по шагам, как в нем открыть подобный раздел диска.
1) Сначала устанавливаем сам Total Commander. Ссылка на офиц. сайт.
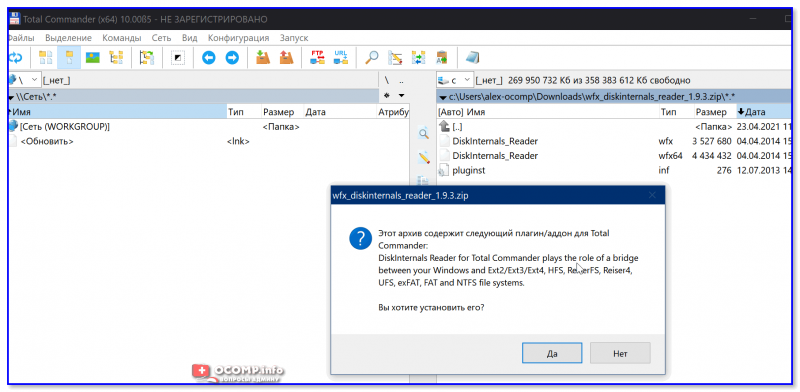
2) Далее необходимо загрузить плагин DiskInternals Reader с офиц. сайта (он идет в архиве ZIP — извлекать не нужно).
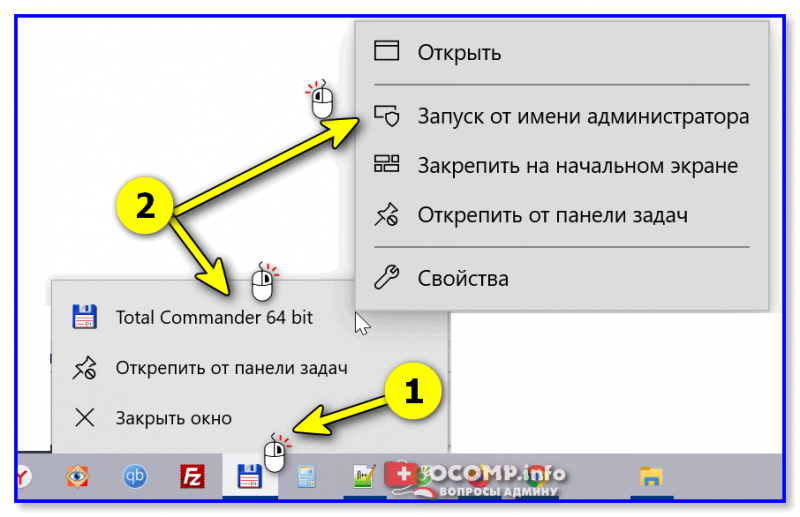
3) После необходимо запустить TC от имени администратора (просто кликните правой кнопкой мыши по значку. ). 👇
Запуск TC от имени админа
4) Затем необходимо открыть архив ZIP с плагином DiskInternals Reader в Total Commander — тогда он предложит вам установить плагин. Разумеется, соглашаетесь! 👌
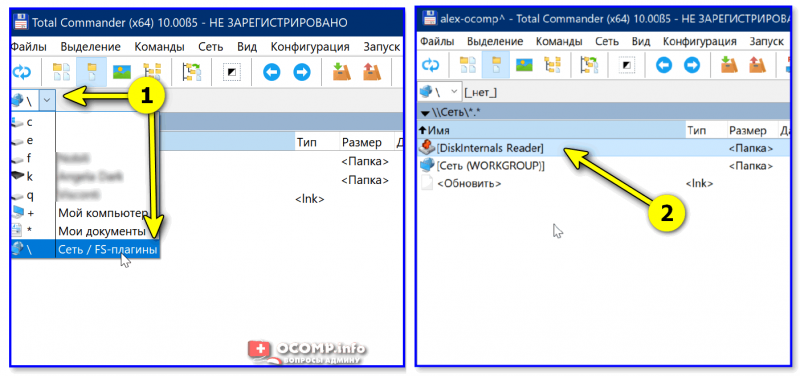
5) Далее необходимо закрыть TC и снова его запустить от имени админа. В меню выбора диска укажите вариант «Сеть / FS-плагины» — далее кликните по значку DiskInternals Reader (см. стрелки 1, 2 на скрине ниже 👇).
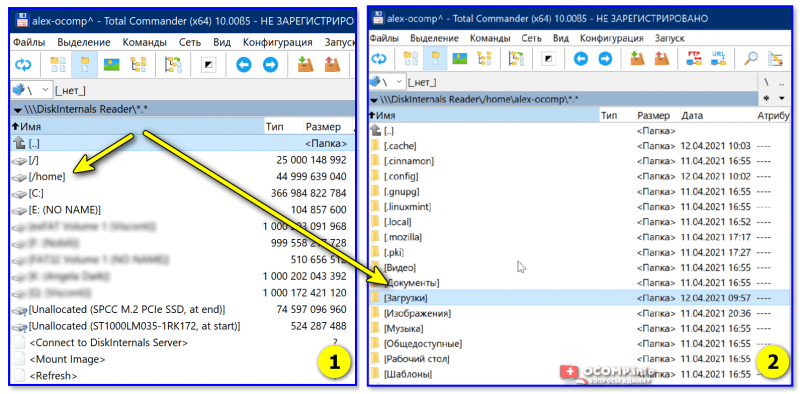
6) Собственно, далее появиться список всех дисков (в том числе и Ext2/3/4) — их можно открыть и скопировать с них нужную информацию. Задача решена?! 👌
Файлы читаются, можно копировать
Способ 3 (с помощью LiveCD)
Вообще, этот вариант, конечно, не относится к работе из-под Windows. Однако, он вполне себе годен для какой-то разовой работы (например, для копирования и переноса папки с файлами). К тому же аварийный LiveCD с Linux никогда не помешает — вдруг чего. 👌
1) Дистрибутивы Linux с поддержкой работы LiveCD — 👉 можете найти в моей подборке
2) Загруженный ISO-файл с нужной версией дистрибутива Linux необходимо правильно записать на флешку.
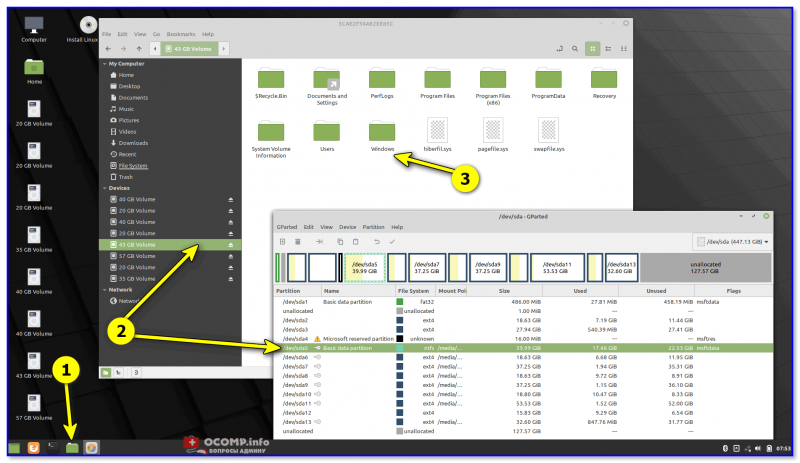
3) Далее останется только загрузиться с этой флешки с помощью Boot Menu (вызывается сразу после вкл. ПК). Если вы выберите дистрибутив Linux для новичка — то работать с ним весьма просто (ничуть не сложнее, чем с проводником Windows).
Linux Mint загружена с LiveCD
Access Linux filesystems in Windows and WSL 2
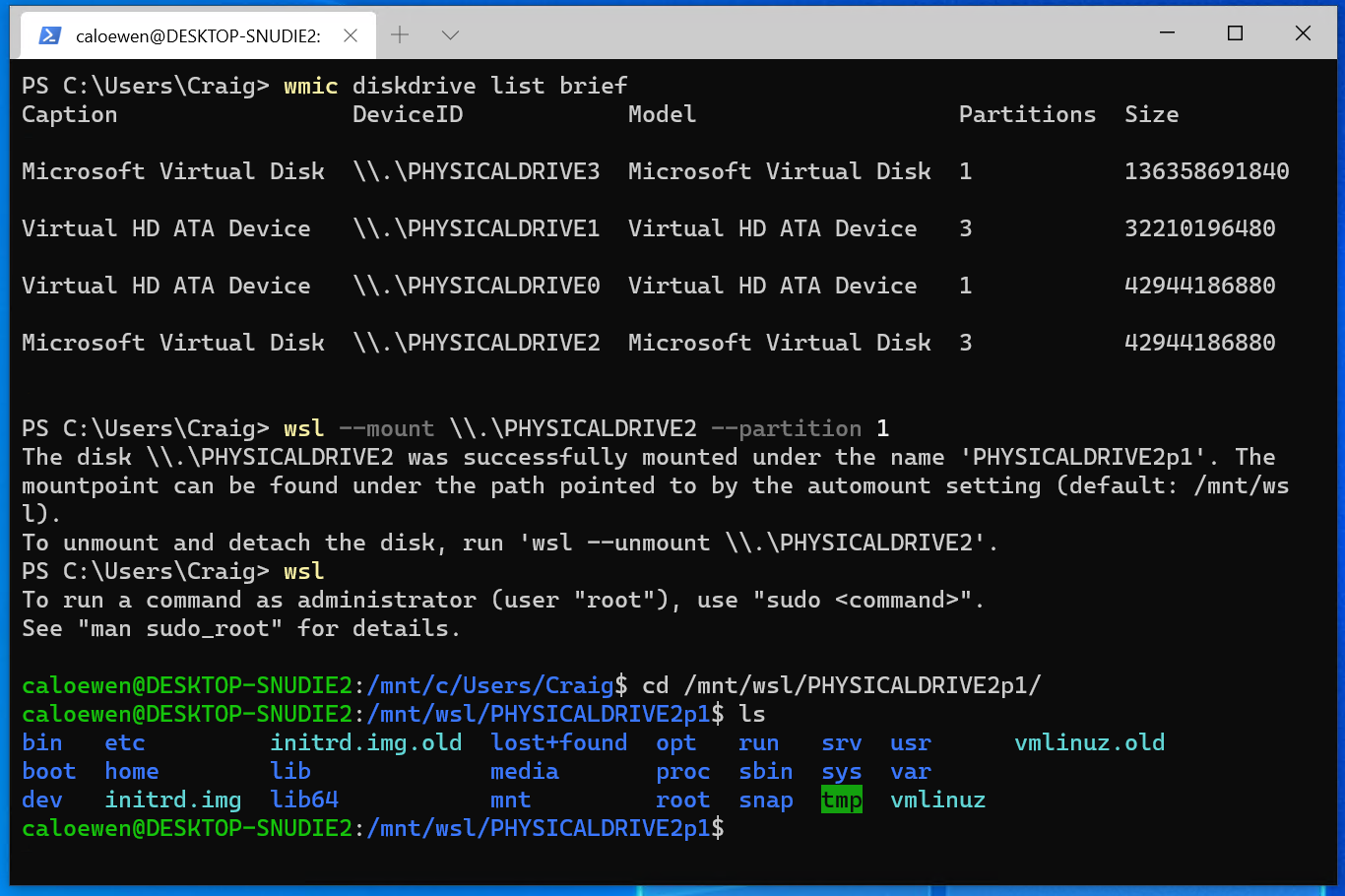
Starting with Windows Insiders preview build 20211, WSL 2 will be offering a new feature: wsl —mount . This new parameter allows a physical disk to be attached and mounted inside WSL 2, which enables you to access filesystems that aren’t natively supported by Windows (such as ext4). So, if you’re dual booting with Windows & Linux using different disks, you can now access your Linux files from Windows!
Getting started
wmic diskdrive list brief The disks paths are available under the ‘DeviceID’ columns. Usually under the \\.\\\.\PHYSICALDRIVE* format. Below is an example of mounting a specific partition of a given hard disk into WSL and browsing its files.
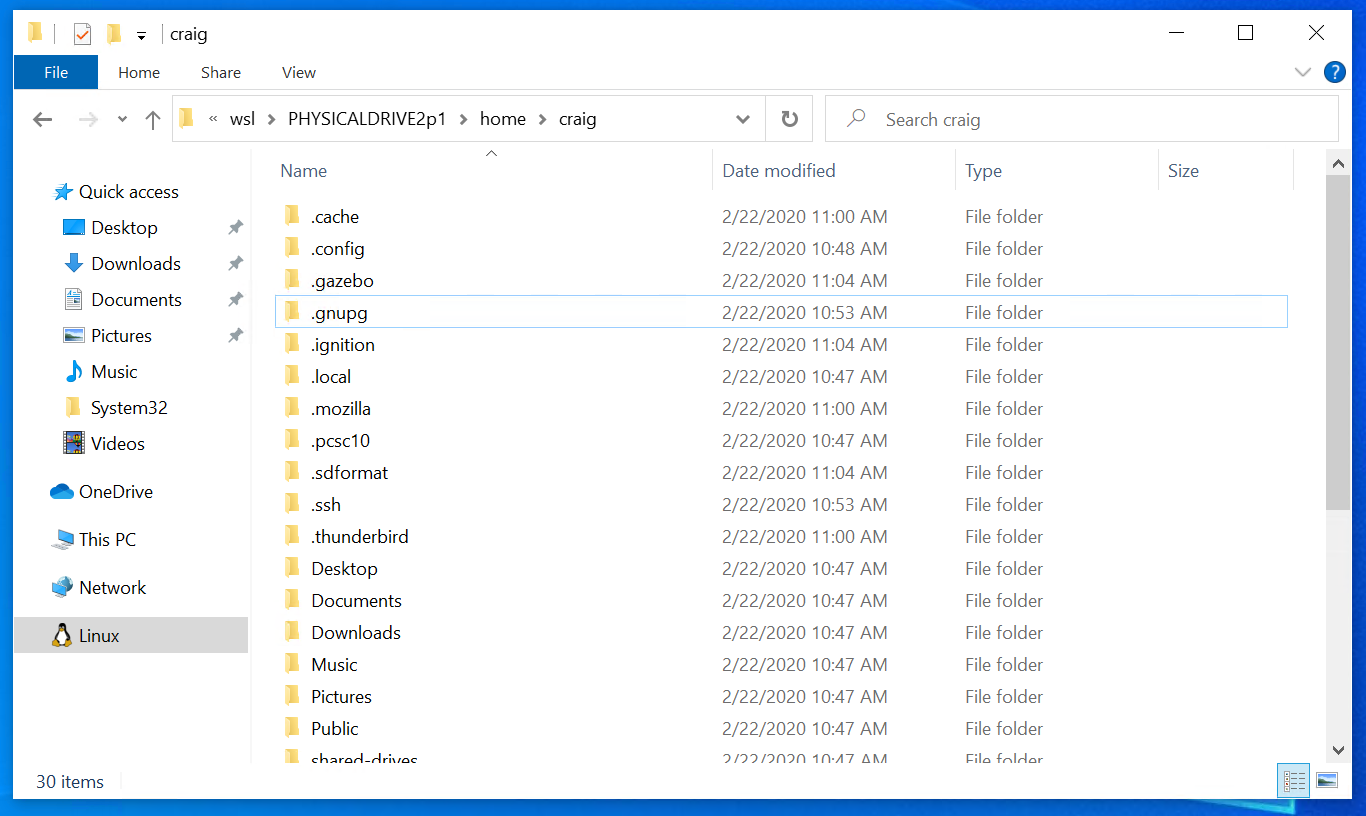
Accessing these files with File Explorer
Once mounted, it’s also possible to access these disks through the Windows explorer by navigating to \wsl$ and then to the mount folder.
Limitations
By default, wsl —mount attempts to mount the disk as ext4. To specify a filesystem, or for more advanced scenarios, check out Mount a disk in WSL 2. Also please note that this feature comes with the limitation that only physical disks can be attached to WSL 2. At this time, it’s not possible to attach a single partition. More details on the limitations here.
Give us your feedback!
If you run into any issues, or have feedback for our team please file an issue on our Github , and if you have general questions about WSL you can find all of our team members that are on Twitter on this twitter list.
Read Linux File systems on Windows using DiskInternals Linux Reader
Do you dual boot between Windows and Linux on your computer? This is a new way people use their computers to enjoy the benefits of both operating systems. The only problem that users face on Windows is that they are not able to access their files that were created in Linux. Even though both operating systems are on the same device, they follow a different file system. While Linux can easily read the NTFS file system in which Windows stores files, Windows cannot read Linux’s file system. In this post, we’ve covered a free tool called Linux Reader which solves this exact problem by letting you read files from a Linux filesystem on Windows.
DiskInternals Linux Reader
DiskInternals Linux Reader is completely free and lets you access files from Ex2/3/4, UFS2, HFS, and ReiserFS/4 file systems. Apart from that, the tool can also read normal Windows-supported file systems such as NTFS, Fat, exFat, etc.
However complex it may seem, Linux Reader makes it simple to access files from a Linux filesystem in Windows. The tool only provides read-only access, which means you cannot accidentally mess up with your Linux file system from Windows.
Read Linux File systems on Windows
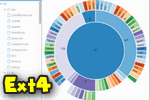
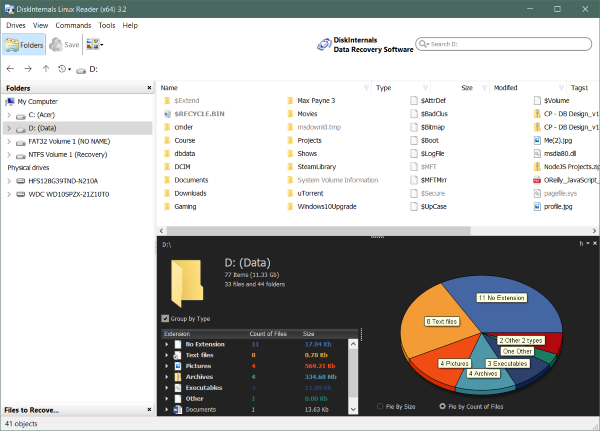
The program has a neat interface that resembles somewhat with Windows Explorer, which makes Linux Reader an easy-to-use and understand tool. You can open any drive which has been formatted to be used with Linux. And you can browse its content like any other drive. The program has almost all of the standard features, such as a search box, navigation buttons, recent files, and folders. Also, you can specify a view and sort files on all the available properties.
If you are on the root of a drive, Linux Reader will show you some stats like the count of different types of files. It also displays a pie chart which can be customized a little. All these nifty little features come in handy when you are browsing files from a foreign file system.
You can preview all sorts of files, or you can save them on your Windows area to edit it and work on it. Right-click a file or folder and click on Save to save it inside Windows. You will need to specify a directory in which the files should be saved.
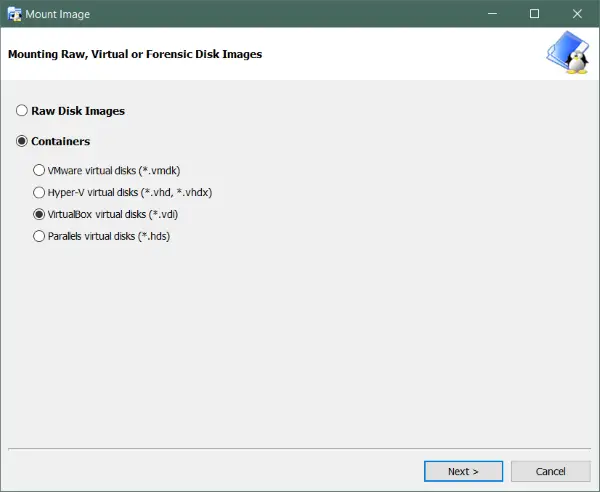
Linux Reader also lets you mount Raw Disk Images or Virtual Disks. So, any work done in a virtual machine can also be retrieved, and all the files can be easily accessed. This is a nice feature if you work a lot on virtual machines or if you have a raw disk image of your file system. To mount a drive, go to Drives menu and select Mount Image. In the next step, select the type of image you have and enter the path to that file, and you are done.
Linux Reader is a great tool and a quick, safe option to access files from a Linux file system. It is free, easy to use and gets the job done. The added features, such as support for disk images and the ability to connect to a DiskInternals Recovery Server, are a plus.
All in all, this is a must-have tool if you dual boot on your computer or happen to use Linux alongside Windows in any other way. Click here to download Linux Reader.