- Как исправить read only file system в Linux
- Ошибка read only file system в Linux
- How to Fix Read Only File System Error on Ubuntu
- How to Fix Read Only File System Error on Ubuntu
- read-only file system for Ubuntu
- The read-only file system cannot be removed using rm.
- Fixing the Read-Only File System Error on Linux
- File System Errors and the Remount-ro Option
- Read-only File System on Virtual Machines
- “Read-only File System” Error and Solutions
- Read-only File System Error Cases
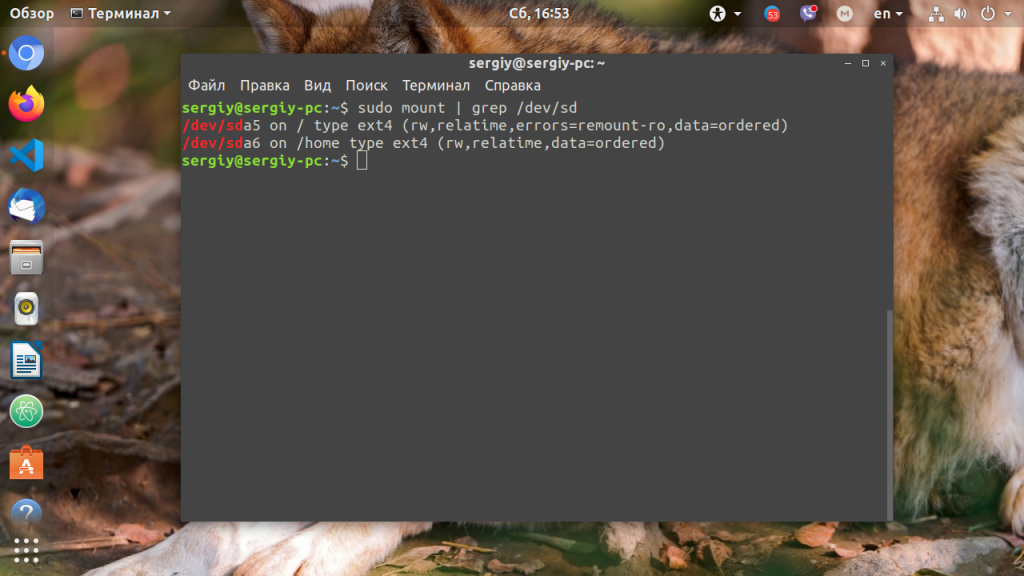
- List Mounted File Systems
- Re-Mount File System
- Reboot System
- Check File System For Errors
- Re-Mount File System In Read-Write
Как исправить read only file system в Linux
Ошибка read only file system может возникнуть при загрузке с LiveCD диска или в режиме восстановления вашего дистрибутива. Она означает, что файловая система в которую вы пытаетесь вести запись примонтирована только для чтения. Этому может быть несколько причин. Есть файловые системы, которые доступны только для чтения это файловая система оптических дисков — ISO, а также файловая система образов SquashFS.
С такими файловыми системами вы сделать ничего не сможете. Для изменения данных в них, надо распаковать образ, изменить данные и запаковать его обратно. Но что касается обычных файловых систем, таких как EXT4, BTRFS, XFS, то их можно монтировать и для чтения и для записи.
Ошибка read only file system в Linux
В этой небольшой статье мы рассмотрим как исправить read only file system Linux перемонтировав файловую систему для записи. Первым делом надо определиться с точкой монтирования, для которой надо разрешить запись. Попытаемся создать файл в корневом каталоге:
Ошибка, файловая система корневого каталога доступна только для чтения. Чтобы посмотреть все точки монтирования доступные в системе выполните в терминале:
В данном случае, корневая файловая система и есть точкой монтирования. Но у вас, например, возникнут проблемы с созданием файла в домашней папке, то надо будет уже перемонтировать /home. Смотрите внимательно. Когда точка монтирования выбрана, осталось её примонтировать с правами на запись:
sudo mount -o remount,rw /home
После этого вы сможете создать файл без каких-либо проблем. После завершения работы, во избежание повреждения данных при перезагрузке, желательно перемонтировать файловую систему обратно в режим только для чтения:
Теперь вы знаете что означает эта ошибка и как с ею справится. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
How to Fix Read Only File System Error on Ubuntu
The “Read-only file system…” error is a file system-related error. This could happen in many circumstances for various causes. In this article, we will discuss how to fix read only file system error on Ubuntu.
A filesystem is a grouping of data (files and directories) kept on a storage device in Linux. The filesystem is used by your operating system to report the physical location and positioning of the files. The files would appear as invisible or random bits without the filesystem.
Each file system also has its own permissions, which control which users or groups can read and write files. The “Read-only file system” problem on Ubuntu will be fixed with this guide.
How to Fix Read Only File System Error on Ubuntu
read-only file system for Ubuntu
By default, Ubuntu has a read-only file system. It implies that the user cannot change or remove files from the system. It helps to safeguard system data and folders and stop unintentional removals. Linux distribution Ubuntu uses the read-only ShrinkFS file system.
This file system saves disk space. It can be used to keep executables, configuration files, and other information that shouldn’t be changed by the user. Linux distribution Ubuntu comes included with a read-only file system. The “Btrfs” file system aims to increase performance and dependability.
The read-only file system cannot be removed using rm.
An error warning will appear if you attempt to delete a read-only file system while the machine is running. It is thus because you cannot delete the file system, which is a component of the computer’s main operating system.
Fixing the Read-Only File System Error on Linux
In some cases, the file system in Linux can switch to a read-only mode. This means that you can only read data from the hard disk, and when you try to write any changes or create a new file, you get an error saying that the file system is read-only.
File System Errors and the Remount-ro Option
Check the disk mounting options used when booting Linux
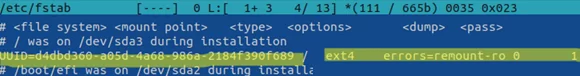
First, check the disk mount settings for the Linux startup. You will find the file system mount options in the /etc/fstab.
Note that the fstab file contains a line to mount the root directory, like this one here:
UUID=00000000-0000-0000-0000-00000000 / ext4 errors=remount-ro 0 1
The errors=remount-ro parameter means that the specific device will be mounted in the read-only mode in case there are problems detected on the device’s file system. In this case, you must use FSCK to perform the disk check.
Common file systems such as EXT4/BTRFS/XFS can be mounted as read-only or read-write, unlike ISO or SquashFS file systems which are read-only.
If errors are found on the disk, you can use one of the three options errors=[continue|remount-ro|panic] :
- continue – ignore the errors,
- remount-ro – remount the disk in read-only mode;
- panic – halt the system.
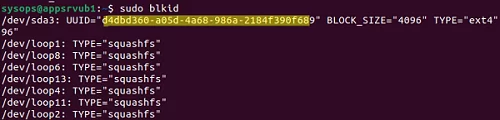
You can map the UUID of the drive to the name of the device with the command:
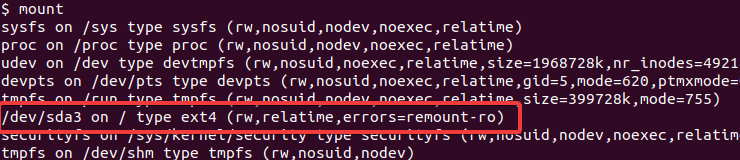
In this example, you will see that your UUID corresponds to the device /dev/sda3.
Another way to get device names and mount points is to use the command
In this example, the errors are detected in the root directory, which is the mount point. That’s why the only way to check it is to boot your computer from the LiveCD. Use the following command to fix file system errors:
$ sudo fsck –y UUID=00000000-0000-0000-0000-00000000
If you cannot check the disk right now and want to switch the file system out of read-only mode immediately, then run the command:
Read-only File System on Virtual Machines
If your external shared storage (storage array) is unavailable, the file system of the Linux partition in the virtual machine becomes read-only.
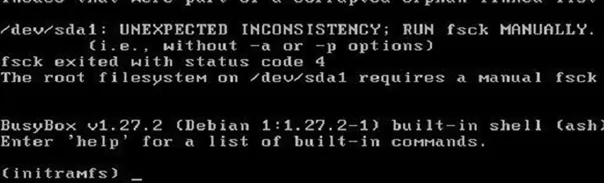
You may find that your Linux VM fails to boot at all, and all you have is the initramfs command line with a warning:
UNEXPECTED INCONSISTENCY: RUN fsck MANUALLY. Fsck exitrd with code 4. The root file system of /dev/sdx requires a manual fsck.
Initramfs is the tmpfs-based initial file system in RAM, which contains the tools and scripts for managing disks, file systems, etc. After entering the initramfs, you will get an error message.
If there are no errors, just type exit. Otherwise, run a disk check:
Specify the volume you want to check manually (in our case, it’s /dev/sda3).
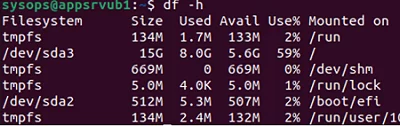
Use the command below to check all connected file systems:
“Read-only File System” Error and Solutions
The “Read-only file system …” is an error that is related to the file system. This error may occur in different situations for different reasons. This error simply expresses that the target file system is mounted as read-only mode and it can not be written or changed.
Read-only File System Error Cases
There may be different “read-only file system” error cases. Generally, they are not directly causing this error. The main reason is the file system is mounted as read-only for different reasons. Below we list some cases of this error.
While trying to restart apache2 web server you may get this error like below.
$ sudo service apache2 start[sudo] password for username:sudo: unable to open /var/lib/sudo/user: Read-only file system* Starting web server apache2
List Mounted File Systems
First, we will list already mounted file systems. The mount command can be used to listed mounted file systems. The output may a bit long but just find the lines related to the root path and home path.
Re-Mount File System
The first step to solving a read-only file system error is remounted file system. Because the file system may be mounted as read-only for different reasons which occur once in a time. So remounting file system will mount it in a normal state. Specified file systems located in the /etc/fstab configuration file can be remounted with the following command. This operation requires root privileges as expected.
Reboot System
Another way to solve read-only file system error is rebooting the system. Rebooting the system make a fresh start where prevous error are cleared which may be related libraries, configuration, temporary changes etc.
Check File System For Errors
Rebooting the system generally checks the file system for errors and if it is errors they are fixed. But in some cases, this may not work. We can explicitly check errors and fix them automatically by using the fsck command.
Re-Mount File System In Read-Write
The file system is configured to be mounted as read-only by default. But these file systems can be also mounted as read and write. The rw option can be used to mount read and write.