- 6 Commands to Shutdown/Reboot the Linux system from Terminal
- Method-1: How to Shutdown and Reboot the Linux system using Shutdown Command
- Method-2: How to Shutdown and Reboot the Linux system using reboot Command
- Method-3: How to Shutdown and Reboot the Linux system using init Command
- Method-4: How to Shutdown the Linux system using halt Command
- Method-5:How to Shutdown the Linux system using poweroff Command
- Method-6: How to Shutdown and Reboot the Linux system using systemctl Command
- How to Restart or Reboot Linux Server from the Command Line
- Steps to Restart Linux using Command Prompt
- Restarting Local Linux Operating System
- Step 1: Open Terminal Window
- Step 2: Use the shutdown Command
- Alternative Option: Restart Linux with reboot Command
- Reboot Remote Linux Server
- Step 1: Open Command Prompt
- Step 2: Use SSH Connection Issue reboot Command
6 Commands to Shutdown/Reboot the Linux system from Terminal
Linux administrator performing many tasks in their routine work. The system Shutdown and Reboot task also included in that.It’s one of the risky task for them because some times it wont come back due to some reasons and they need to spend more time on it to troubleshoot.
These task can be performed through CLI in Linux. Most of the time Linux administrator prefer to perform these kind of tasks via CLI because they are familiar on this.
There are few commands are available in Linux to perform these tasks and user needs to choose appropriate command to perform the task based on the requirement.
All these commands has their own feature and allow Linux admin to use it.
When the system is initiated for Shutdown or Reboot. It will be notified to all logged-in users and processes. Also, it wont allow any new logins if the time argument is used.
I would suggest you to double check before you perform this action because you need to follow few prerequisites to make sure everything is fine.
Those steps are listed below.
- Make sure you should have a console access to troubleshoot further in case any issues arise. VMWare access for VMs and IPMI/iLO/iDRAC access for physical servers.
- You have to create a ticket as per your company procedure either Incident or Change ticket and get approval
- Take the important configuration files backup and move to other servers for safety
- Verify the log files (Perform the pre-check)
- Communicate about your activity with other dependencies teams like DBA, Application, etc
- Ask them to bring down their Database service or Application service and get a confirmation from them.
- Validate the same from your end using the appropriate command to double confirm this.
- Finally reboot the system
- Verify the log files (Perform the post-check), If everything is good then move to next step. If you found something is wrong then troubleshoot accordingly.
- If it’s back to up and running, ask the dependencies team to bring up their applications.
- Monitor for some time, and communicate back to them saying everything is working fine as expected.
This task can be performed using following commands.
- shutdown Command: shutdown command used to halt, power-off or reboot the machine.
- halt Command: halt command used to halt, power-off or reboot the machine.
- poweroff Command: poweroff command used to halt, power-off or reboot the machine.
- reboot Command: reboot command used to halt, power-off or reboot the machine.
- init Command: init (short for initialization) is the first process started during booting of the computer system.
- systemctl Command: systemd is a system and service manager for Linux operating systems.
Method-1: How to Shutdown and Reboot the Linux system using Shutdown Command
shutdown command used to power-off or reboot a Linux remote machine or local host. It’s offering
multiple options to perform this task effectively. If the time argument is used, 5 minutes before the system goes down the /run/nologin file is created to ensure that further logins shall not be allowed.
# shutdown [OPTION] [TIME] [MESSAGE]
Run the below command to shutdown a Linux machine immediately. It will kill all the processes immediately and will shutdown the system.
Alternatively we can use the shutdown command with halt option to bring down the machine immediately.
# shutdown --halt now or # shutdown -H now
Alternatively we can use the shutdown command with poweroff option to bring down the machine immediately.
# shutdown --poweroff now or # shutdown -P now
Run the below command to shutdown a Linux machine immediately. It will kill all the processes immediately and will shutdown the system.
If you run the below commands without time parameter, it will wait for a minute then execute the given command.
# shutdown -h Shutdown scheduled for Mon 2018-10-08 06:42:31 EDT, use 'shutdown -c' to cancel. [email protected]# Broadcast message from [email protected] (Mon 2018-10-08 06:41:31 EDT): The system is going down for power-off at Mon 2018-10-08 06:42:31 EDT!
All other logged in users can see a broadcast message in their terminal like below.
[[email protected] ~]$ Broadcast message from [email protected] (Mon 2018-10-08 06:41:31 EDT): The system is going down for power-off at Mon 2018-10-08 06:42:31 EDT!
# shutdown -H Shutdown scheduled for Mon 2018-10-08 06:37:53 EDT, use 'shutdown -c' to cancel. [email protected]# Broadcast message from [email protected] (Mon 2018-10-08 06:36:53 EDT): The system is going down for system halt at Mon 2018-10-08 06:37:53 EDT!
# shutdown -P Shutdown scheduled for Mon 2018-10-08 06:40:07 EDT, use 'shutdown -c' to cancel. [email protected]# Broadcast message from [email protected] (Mon 2018-10-08 06:39:07 EDT): The system is going down for power-off at Mon 2018-10-08 06:40:07 EDT!
This can be cancelled by hitting shutdown -c option on your terminal.
# shutdown -c Broadcast message from [email protected] (Mon 2018-10-08 06:39:09 EDT): The system shutdown has been cancelled at Mon 2018-10-08 06:40:09 EDT!
All other logged in users can see a broadcast message in their terminal like below.
[[email protected] ~]$ Broadcast message from [email protected] (Mon 2018-10-08 06:41:35 EDT): The system shutdown has been cancelled at Mon 2018-10-08 06:42:35 EDT!
Add a time parameter, if you want to perform shutdown or reboot in N seconds. Here you can add broadcast a custom message to logged-in users. In this example, we are rebooting the machine in another 5 minutes.
# shutdown -r +5 "To activate the latest Kernel" Shutdown scheduled for Mon 2018-10-08 07:13:16 EDT, use 'shutdown -c' to cancel. [[email protected] ~]# Broadcast message from [email protected] (Mon 2018-10-08 07:08:16 EDT): To activate the latest Kernel The system is going down for reboot at Mon 2018-10-08 07:13:16 EDT!
Run the below command to reboot a Linux machine immediately. It will kill all the processes immediately and will reboot the system.
Method-2: How to Shutdown and Reboot the Linux system using reboot Command
reboot command used to power-off or reboot a Linux remote machine or local host. Reboot command comes with two useful options.
It will perform a graceful shutdown and restart of the machine (This is similar to your restart option which is available in your system menu).
Run “reboot’ command without any option to reboot Linux machine.
Run the “reboot” command with -p option to power-off or shutdown the Linux machine.
Run the “reboot” command with -f option to forcefully reboot the Linux machine (This is similar to pressing the power button on the CPU).
Method-3: How to Shutdown and Reboot the Linux system using init Command
init (short for initialization) is the first process started during booting of the computer system.
It will check the /etc/inittab file to decide the Linux run level. Also, allow users to perform shutdown and reboot the Linux machine. There are seven runlevels exist, from zero to six.
Run the below init command to shutdown the system .
Run the below init command to reboot the system .
Method-4: How to Shutdown the Linux system using halt Command
halt command used to power-off or shutdown a Linux remote machine or local host.
halt terminates all processes and shuts down the cpu.
Method-5:How to Shutdown the Linux system using poweroff Command
poweroff command used to power-off or shutdown a Linux remote machine or local host. Poweroff is exactly like halt, but it also turns off the unit itself (lights and everything on a PC). It sends an ACPI command to the board, then to the PSU, to cut the power.
Method-6: How to Shutdown and Reboot the Linux system using systemctl Command
Systemd is a new init system and system manager which was implemented/adapted into all the major Linux distributions over the traditional SysV init systems.
systemd is compatible with SysV and LSB init scripts. It can work as a drop-in replacement for sysvinit system. systemd is the first process get started by kernel and holding PID 1.
It’s a parent process for everything and Fedora 15 is the first distribution which was adapted systemd instead of upstart.
systemctl is command line utility and primary tool to manage the systemd daemons/services such as (start, restart, stop, enable, disable, reload & status).
systemd uses .service files Instead of bash scripts (SysVinit uses). systemd sorts all daemons into their own Linux cgroups and you can see the system hierarchy by exploring /cgroup/systemd file.
# systemctl halt # systemctl poweroff # systemctl reboot # systemctl suspend # systemctl hibernate
How to Restart or Reboot Linux Server from the Command Line
It’s a cliché, but true – restarting a Linux server solves a wide variety of issues.
When a system is rebooted, any malfunctioning software is purged from active memory. When the system restarts, it loads a fresh, clean copy of the software into active memory. Also, some operating systems require a restart to process updates or configuration changes.
This guide will show you how to restart a Linux server using only the command-line or prompt.
- A system running a Linux operating system
- Access to a command-line interface (also known as a terminal)
- Root or sudo privileges
- (optional) SSH software package for communicating with a remote server
Steps to Restart Linux using Command Prompt
Restarting Local Linux Operating System
Step 1: Open Terminal Window
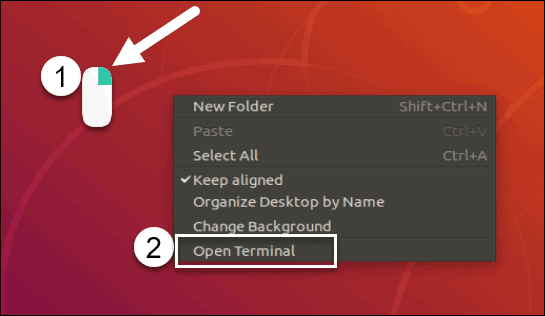
If your version of Linux uses a graphical interface, you can open a terminal window by right-clicking the Desktop > left-clicking Open in terminal.
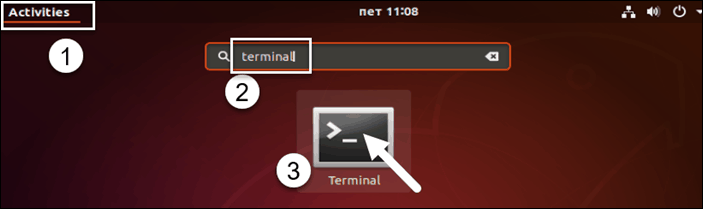
You can also click the main menu (usually found in the lower-left or upper-left corner) and type in terminal in the search bar. Click on the Terminal icon, as in the image below.
Step 2: Use the shutdown Command
Since powering off is one of the most basic functions of an operating system, this command should work for most distributions of Linux.
In a terminal window, type the following:
The sudo command tells Linux to run the command as an administrator, so you may need to type your password. The -r switch at the end indicates that you want the machine to restart.
Note: See our article for additional Linux shutdown command options.
Alternative Option: Restart Linux with reboot Command
Many Linux versions do not require administrator privileges to reboot. If you get a message that you do not have sufficient privileges, type:
Your system should close out of all open applications and restart.
Reboot Remote Linux Server
Step 1: Open Command Prompt
If you have a graphical interface, open the terminal by right-clicking the Desktop > left-clicking Open in terminal.
You can also click the main menu (usually found in the lower-left or upper-left corner), and then click Applications > System Tools > Terminal.
If you prefer using a keyboard shortcut, press Ctrl+Alt+T.
Step 2: Use SSH Connection Issue reboot Command
In a terminal window, type:
ssh -t user@server.com 'sudo reboot'Note: You may need to enter the password for the username you’ve used. Also, make sure you type the single-quote marks.
The ssh command tells your system to connect to another machine. The -t option forces the remote system to enter the command in a terminal. Replace user@server.com with the username @ server name that you want to restart.
The sudo reboot command can be switched out for sudo shutdown and the above options above can be used.
That is: -r tells it to restart, hh:mm sets a specific time, +mm sets a countdown.)
In this tutorial, you have learned how to restart a Linux server from the command prompt.
Rebooting a Linux system or server is designed to be simple, so you shouldn’t have any trouble. Just make sure you have saved all your work before restarting.