- 5 Linux Commands to Shutdown and Reboot the System
- 1. «shutdown» command
- 2. «reboot» command
- 3. «halt» command
- 4. «poweroff» command
- 5. REISUB — R E I S U B key strokes
- 10 Comments
- How to Restart or Reboot Linux Server from the Command Line
- Steps to Restart Linux using Command Prompt
- Restarting Local Linux Operating System
- Step 1: Open Terminal Window
- Step 2: Use the shutdown Command
- Alternative Option: Restart Linux with reboot Command
- Reboot Remote Linux Server
- Step 1: Open Command Prompt
- Step 2: Use SSH Connection Issue reboot Command
- How To Restart/Reboot Linux?
- Why Reboot Linux?
- Reboot/Restart Linux with reboot Command
- Reboot/Restart Linux with shutdown Command
- Reboot/Restart Remote Linux with reboot or shutdown Commands
- Reboot/Restart Remote Linux with init Command
- Reboot/Restart Linux with systemctl Command
- Reboot/Restart Linux in GNOME Desktop
- Reboot/Restart Linux in KDE Desktop
5 Linux Commands to Shutdown and Reboot the System
On Linux, like all tasks, the shutdown and restart operations can also be done from the command line.
The commands are shutdown, halt, poweroff, reboot and REISUB keystrokes.
In this post I am going to show you how to shutdown or restart a linux system using these commands.
The commands are useful specially when you have to reboot a remote linux server, where only shell access is available and no gui.
Servers often need a restart when upgrades are installed or need to shutdown for other maintainance tasks.
The commands are available on any linux system like centos, ubuntu, debian, fedora or suse and do not require the installation of any extra packages.
1. «shutdown» command
The first command is the shutdown command and it can be used to shutdown a system or restart it. It is commonly used to shutdown or reboot both local and remote machines.
shutdown arranges for the system to be brought down in a safe way. All logged-in users are notified that the system is going down and, within the last five minutes of TIME, new logins are prevented.
shutdown [OPTION] [TIME] [MESSAGE]
To shutdown a machine call the shutdown command like this
The h option is for halt which means to stop. The second parameter is the time parameter. «now» means that shutdown the system right away.
The time parameter can be specified in minutes or hours also. For example
# shutdown -h +5 "Server is going down for upgrade. Please save your work."
The above command shall flash the message to all other logged in users and give them 5 minutes before the system goes for shutdown.
The shutdown command can be used to restart a system with the r option instead of the h option. Usage is same as before. Just replace the h option with r option.
# shutdown -r +5 "Server will restart in 5 minutes. Please save your work."
All other logged in users will see a broadcast message in their terminal like this
[[email protected] ~]# Broadcast message from [email protected] (/dev/tty1) at 21:35 . The system is going down for reboot in 5 minutes! Server will restart in 5 minutes. Please save your work.
At this point a shutdown can be cancelled by calling shutdown with «c» option.
2. «reboot» command
Next command is the reboot command. It can be used to shutdown or reboot linux.
The following command will shutdown linux.
The «p» options stands for poweroff.
To reboot linux just call the reboot command directly without any options.
This will perform a graceful shutdown and restart of the machine. This is what happens when you click restart from your menu.
Reboot linux forcibly
The following command will forcefully reboot the machine. This is similar to pressing the power button of the CPU. No shutdown takes place. The system will reset instantly.
The man page explains it as follows
When called with --force or when in runlevel 0 or 6, this tool invokes the reboot(2) system call itself (with REBOOTCOMMAND argument passed) and directly reboots the system. Otherwise this simply invokes the shutdown(8) tool with the appropriate arguments without passing REBOOTCOMMAND argument.
3. «halt» command
The next command is the halt command. This can shutdown a system
The halt command also has a force option, but you do not want to use it. It is supposed to shutdown the system instantly. But its behaviour may not be consistent. Desktops might hang on running this command.
4. «poweroff» command
There is another command exactly same as the halt command. It does the same things and takes the same options.
5. REISUB — R E I S U B key strokes
The above shown commands can be used when you are in control of your system. What if the system has hanged and is not responding at all. And you do not want to press the power button on the CPU which might lead to data corruption. To save from such a situation, comes the magic sysRQ keys.
A special combination of key presses that will allow you to reboot your linux system, no matter how much it is hanged. Check the wikipedia article. for more information.
A common use of the magic SysRq key is to perform a safe reboot of a Linux computer which has otherwise locked up. This can prevent a fsck being required on reboot and gives some programs a chance to save emergency backups of unsaved work.
Warning : Pressing the following keys would instantly reboot your system. Its similar to pressing the power button of your CPU or executing the reboot -f command.
Now in place of the B key we have to use R E I S U letters first. Each key does a task as mentioned below
unRaw (take control of keyboard back from X), tErminate (send SIGTERM to all processes, allowing them to terminate gracefully), kIll (send SIGKILL to all processes, forcing them to terminate immediately), Sync (flush data to disk), Unmount (remount all filesystems read-only), reBoot.
1. Hold down the Alt and SysRq (Print Screen) keys.
2. While holding those down, type the following keys in order, several seconds apart: R E I S U B
3. Computer should reboot.
Make sure to have some time gap between each of keys R E I S U B.
The sysrq feature can be controlled by changing the value of /proc/sys/kernel/sysrq. To check if sysrq is enabled on the system or not, echo the value. It should be non zero.
$ cat /proc/sys/kernel/sysrq 176
A Tech Enthusiast, Blogger, Linux Fan and a Software Developer. Writes about Computer hardware, Linux and Open Source software and coding in Python, Php and Javascript. He can be reached at [email protected] .
10 Comments
How to Restart or Reboot Linux Server from the Command Line
It’s a cliché, but true – restarting a Linux server solves a wide variety of issues.
When a system is rebooted, any malfunctioning software is purged from active memory. When the system restarts, it loads a fresh, clean copy of the software into active memory. Also, some operating systems require a restart to process updates or configuration changes.
This guide will show you how to restart a Linux server using only the command-line or prompt.
- A system running a Linux operating system
- Access to a command-line interface (also known as a terminal)
- Root or sudo privileges
- (optional) SSH software package for communicating with a remote server
Steps to Restart Linux using Command Prompt
Restarting Local Linux Operating System
Step 1: Open Terminal Window
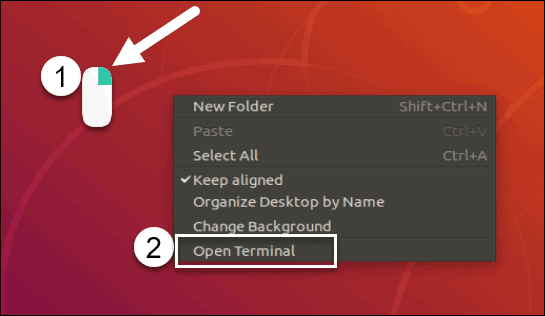
If your version of Linux uses a graphical interface, you can open a terminal window by right-clicking the Desktop > left-clicking Open in terminal.
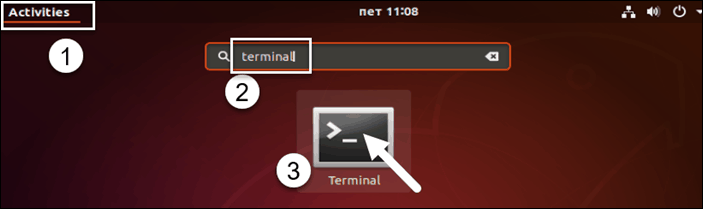
You can also click the main menu (usually found in the lower-left or upper-left corner) and type in terminal in the search bar. Click on the Terminal icon, as in the image below.
Step 2: Use the shutdown Command
Since powering off is one of the most basic functions of an operating system, this command should work for most distributions of Linux.
In a terminal window, type the following:
The sudo command tells Linux to run the command as an administrator, so you may need to type your password. The -r switch at the end indicates that you want the machine to restart.
Note: See our article for additional Linux shutdown command options.
Alternative Option: Restart Linux with reboot Command
Many Linux versions do not require administrator privileges to reboot. If you get a message that you do not have sufficient privileges, type:
Your system should close out of all open applications and restart.
Reboot Remote Linux Server
Step 1: Open Command Prompt
If you have a graphical interface, open the terminal by right-clicking the Desktop > left-clicking Open in terminal.
You can also click the main menu (usually found in the lower-left or upper-left corner), and then click Applications > System Tools > Terminal.
If you prefer using a keyboard shortcut, press Ctrl+Alt+T.
Step 2: Use SSH Connection Issue reboot Command
In a terminal window, type:
ssh -t user@server.com 'sudo reboot'Note: You may need to enter the password for the username you’ve used. Also, make sure you type the single-quote marks.
The ssh command tells your system to connect to another machine. The -t option forces the remote system to enter the command in a terminal. Replace user@server.com with the username @ server name that you want to restart.
The sudo reboot command can be switched out for sudo shutdown and the above options above can be used.
That is: -r tells it to restart, hh:mm sets a specific time, +mm sets a countdown.)
In this tutorial, you have learned how to restart a Linux server from the command prompt.
Rebooting a Linux system or server is designed to be simple, so you shouldn’t have any trouble. Just make sure you have saved all your work before restarting.
How To Restart/Reboot Linux?
As a flexible operating system, Linux provides a lot of different commands and ways to reboot or restart the system. The restarting Linux and rebooting Linux are the same terms simply used to describe shutting down the Linux and starting it automatically. In this tutorial, we will learn how to reboot/restart Linux with different command-line tools and GUI menus.
Why Reboot Linux?
Linux is known as stable and long running operating system which do not or rerarely requires reboot. But there are some cases we may need to reboot the Linux. Here are some of them.
- Run Linux system with the new kernel version.
- Free system resources and start from the scratch.
Reboot/Restart Linux with reboot Command
The original and the most popular command to reboot/restart the Linux is the reboot command. Actually the reboot command is an alias to the shutdown command with the -r option. The reboot command calls “shutdown -r” which is used to reboot system.
If you get an error or warning related with the privileges you can use the sudo with the reboot command like below.
Reboot/Restart Linux with shutdown Command
The shutdown command is mainly used to shutdown the system but it can be also used to reboot/restart the Linux. By default the shutdown commands shutdown the system but by using the -r option the system restarted/rebooted.
After the shutdown command is executed the shutdown/reboot process starts after 1 minute delay. This is also expressed with the following message after the shutdown command.
Reboot scheduled for Sun 2021-01-24 14:07:24 +03, use 'shutdown -c' to cancel.
We can cancel this reboot/restart process by calling following shutdown command with the -c option.
We can also specify some delay for the reboot/restart proces explicitly. The -t option is used to specify delay. In the following example we will set 5 minutes delay for the reboot/restart.
Reboot/Restart Remote Linux with reboot or shutdown Commands
Even the restart and shutdown commands are used to reboot/restart the local Linux system they can be also used to restart/reboot remote Linux box. They can be used with the ssh command and connection in different ways but the most practical way is calling them from the local computer whiout getting an interactive remote SSH shell. In the following example we reboot/restart the remote Linux system which has IP address 192.168.1.10.
ssh ismail@192.168.1.10 "/sbin/reboot"Alternatively the shutdown command can be used too.
ssh ismail@192.168.1.10 "/sbin/shutdown -r"Reboot/Restart Remote Linux with init Command
The init.d is old school system used to manage the Linux system state and services. Very similar to the systemctl it is used to manage service but also can be used to restart the system. The init.d has run levels where run level 6 is defined as reboot. So changing the run level to the 6 restarts the system. The telinit command is used to change the run level.
Reboot/Restart Linux with systemctl Command
The systemctl command if a command provided by the systemd which is used to manage services and system state. Even the systemctl mainly used to manage system services like SSH, NFS, Network etc. it can be also used to manage the system state. The systemctl command cna be used to reboot/restart the Linux system.
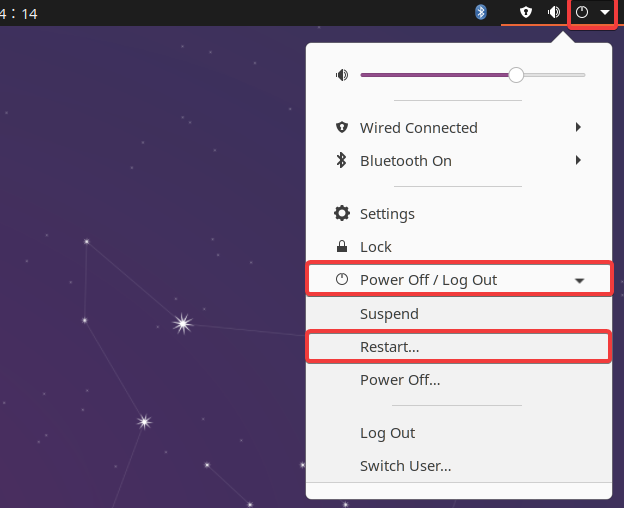
Reboot/Restart Linux in GNOME Desktop
The Linux can be rebooted or restart by using GUI tools which are provided via desktop environments. GNOME desktop can be rebooted/restart from the left right corner menu Power Off/Log Out -> Restart is selected.
Reboot/Restart Linux in KDE Desktop
KDE Desktop environment is another popular Desktop environment which also provides the Restart function via the Start Menu. First click to the Start Menu icon and then hover to the Leave like below. The last stes is Restart.