- Introducing the Red Hat Universal Base Image
- Reasons to Use UBI
- More Than a Base Image
- Three Base Images
- Pre-Built Language Runtime Container Images
- Associated Packages
- RHEL is the Foundation
- Now and into The Future
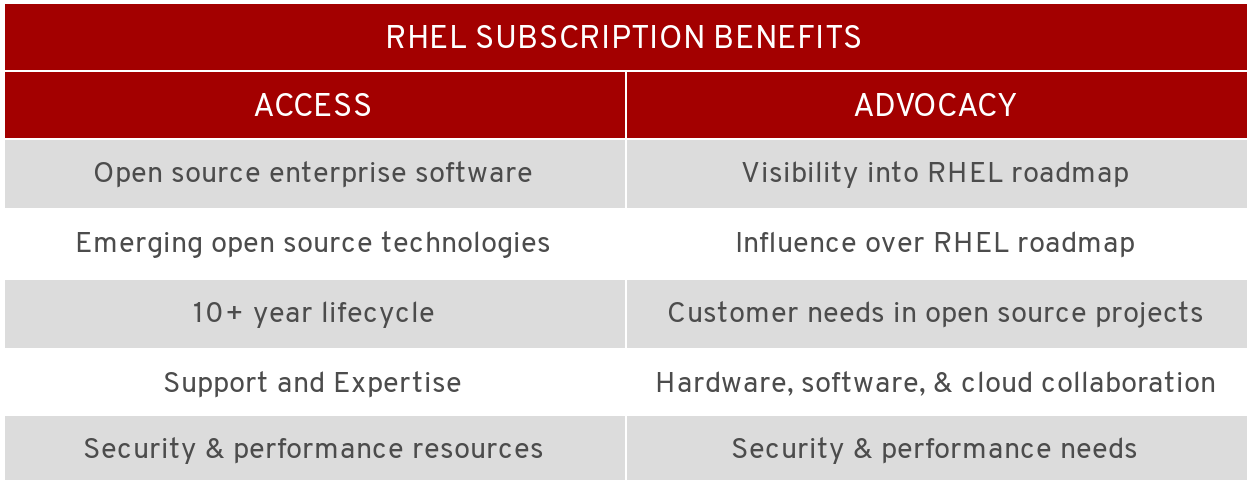
- Getting Access
- Chapter 3. Downloading a RHEL installation ISO image
- 3.1. Types of installation ISO images
- 3.2. Downloading an ISO image from the Customer Portal
- 3.3. Downloading an ISO image using curl
Introducing the Red Hat Universal Base Image
Containers offer a lighter-weight version of the Linux operating system’s userland stripped down to the bare essentials, but it’s still an operating system and the quality of a container matters just as much as the host operating system. This is why we have offered Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) images since Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 GA, to offer customers certified and up-to-date enterprise-grade containers. Running RHEL container images on RHEL container hosts offers compatibility and portability between environments, not to mention familiarity. There was one problem. You couldn’t easily share it with others, even if they were a Red Hat Enterprise Linux customer or partner.
With the release of the Red Hat Universal Base Image (UBI), you can now take advantage of the greater reliability, security, and performance of official Red Hat container images where OCI-compliant Linux containers run — whether you’re a customer or not. This means you can build a containerized application on UBI, push it to a container registry server of your choosing, and share it. The Red Hat Universal Base Image can allow you to build, share and collaborate on your containerized application where you want.
With UBI, you can have the freedom to share and run your applications anywhere. But when you run them on Red Hat platforms like Red Hat OpenShift and Red Hat Enterprise Linux, there is additional value. Subscribers have access to product features and advocacy in the direction of the product roadmap. Running UBI on RHEL/OpenShift you can get:
Reasons to Use UBI
Here’s a set of wants and needs that might help you figure out if UBI is right for your needs:
- My developers want a container image they can distribute more broadly
- My operations team wants a supportable base image with an enterprise lifecycle
- My architects want to deliver a Kubernetes Operator to my customers
- My customers want enterprise support in their Red Hat environment
- My community wants to share containerized applications more freely
If you said yes to one or more of these questions, or similarly formulated questions, then check out UBI.
More Than a Base Image
Less than a full operating system, UBI is three things:
- A set of three base images ( ubi, ubi-minimal, ubi-init )
- A set of language runtime images ( nodejs, ruby, python, php, perl , etc.)
- A set of associated packages in a YUM repository which satisfy common application dependencies
UBI is designed to be a foundation for cloud-native and web applications use cases, developed in containers. All UBI content is a subset of RHEL. All of the packages in UBI come from RHEL channels and are supported like RHEL when run on a Red Hat supported platforms like OpenShift & RHEL.
It takes a lot of engineering, security analysis and resources to provide quality support for container images. It requires testing not just of the base images, but also their behavior on a given container host.
To help ease upgrade challenges, Red Hat has focused heavily on engineering and support, allowing UBI 7 to be run on RHEL 8 hosts, and UBI 8 to be run on RHEL 7 hosts. This gives users greater flexibility and confidence during platform upgrades in the container image or the underlying hosts. These can now be broken up into two separate projects.
Three Base Images
Minimal — Designed for applications that contain their own dependencies (Python, Node.js, .NET, etc.)
- Minimized pre-installed content set
- No suid binaries
- Minimal package manager (install, update, and remove)
Platform — For any application that runs on RHEL
- Unified, OpenSSL crypto stack
- Full YUM stack
- Includes useful basic OS tools (tar, gzip, vi, etc.)
Multi-Service — Eases running multiple services in a single container
Pre-Built Language Runtime Container Images
In addition to the base images which allow you to install languages, UBI provides developers pre-built images to consume a number of language runtimes. In many instances, developers can just consume an image and start working on the application they are building.
With the launch of UBI, Red Hat is providing two sets of images, one based on RHEL 7 and another set based on RHEL 8. Derived from Red Hat Software Collections (RHEL 7) and Application Streams (RHEL 8), these runtimes are scheduled for updates via up to four release trains per year so that you can have access to the latest, current versions.
Here’s the set of container images provided for UBI 7:
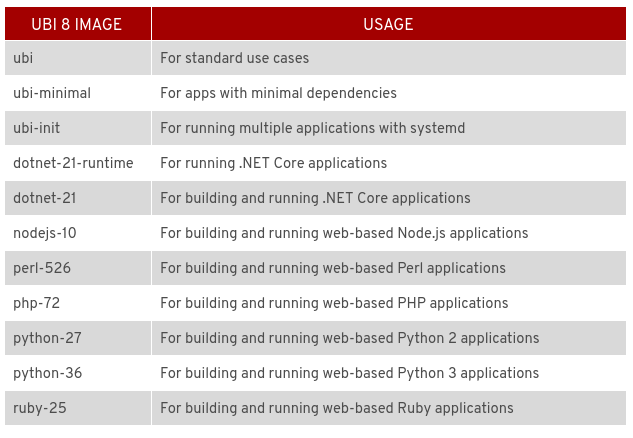
Here’s the set of container images provided for UBI 8:
Associated Packages
Consuming pre-built images is great. Red Hat keeps them up to date and releases them when a new version of RHEL is released and when critical CVEs are patched, mirroring the RHEL image policy. We have designed this one so you can just pull one of these images and start building your application.
But, sometimes when you are building an application, you need that one extra package. Or sometimes, you need a package updated to make your application work. That’s why UBI also comes with a set of RPMs available via yum, and distributed on a highly available content delivery network. When you run a yum update in your CI/CD at that critical moment when you have to do a production release, you are hitting the same infrastructure our customers use.
RHEL is the Foundation
Containerized applications represent a wave of innovation in enterprise IT. They are game-changers in how they improve the development and maintenance of traditionally-monolithic applications. But containers aren’t a panacea. In the enterprise world, operating systems need stability, reliability and security tools, guidance, and timely fixes. These are needs that Red Hat Enterprise Linux is designed to answer. Here are just a few of the Red Hat teams working on base images:
- A performance engineering team, charged with updating and maintaining fundamental libraries like glibc and OpenSSL, as well as language runtimes like Python and Ruby, designed to provide robust performance and work reliably with the workloads you choose to containerize.
- A Product Security team dedicated to making sure the same libraries and languages receive timely security fixes — measured by an associated Container Health Index grade.
- Product management and engineering teams dedicated to adding new features and driving a long lifecycle which is designed to give you confidence in an investment to build on top of it.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux is subscription-based, meaning your organization doesn’t have to shell out for licenses per release and support on top of those license fees. When you subscribe to RHEL, you’re entitled to run any of the current versions of RHEL. This includes access to Red Hat support and the goodness of a more secure, hardened and trusted Linux operating system. Red Hat Enterprise Linux serves as a great host and image for containers, but for many developers, they need to support a wider range of use cases, some of which may be outside of the supported scenarios for the world’s leading enterprise Linux operating system. That’s where UBI comes into play.
Now and into The Future
Perhaps today, you’re just looking for a base image to get you started with building a simple containerized application. Or, perhaps you are moving from standalone containers running on a container engine to a cloud-native world building and certifying Operators designed to run on OpenShift. Either way, we believe that UBI can provide a great foundation.
Containers encapsulate a lightweight operating system userspace in a new packaging format and Red Hat is the enterprise-grade Linux operating system leader. UBI is designed to set a new industry standard for container development by making enterprise-grade containers available to ISVs, customers and open source communities.
In particular, ISVs can standardize on a single, trusted foundation for their containerized applications, including Kubernetes Operators. ISVs using UBI can take advantage of Red Hat Container Certification and Red Hat OpenShift Operator Certification for continuous verification of software deployed on a Red Hat platform like OpenShift.
Getting Access
Getting started is designed to be easy. Podman is available not only in RHEL, but Fedora, CentOS, and for several other Linux distributions. You can just pull an image from one of these repositories and go.
podman pull registry.access.redhat.com/ubi8/ubi podman pull registry.access.redhat.com/ubi8/ubi-minimal podman pull registry.access.redhat.com/ubi8/ubi-init
podman pull registry.access.redhat.com/ubi7/ubi podman pull registry.access.redhat.com/ubi7/ubi-minimal podman pull registry.access.redhat.com/ubi7/ubi-init
Chapter 3. Downloading a RHEL installation ISO image
You can download Red Hat Enterprise Linux by visiting the Red Hat customer portal or you can choose to download it using the curl command.
3.1. Types of installation ISO images
Two types of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 installation ISO images are available from the Red Hat Customer Portal.
It is a full installation program that contains the BaseOS and AppStream repositories. With a DVD ISO file, you can complete the installation without access to additional repositories.
You can use a Binary DVD for 64-bit IBM Z to boot the installation program using a SCSI DVD drive, or as an installation source.
The Boot ISO image is a minimal installation that can be used to install RHEL in two different ways:
- When registering and installing RHEL from the Content Delivery Network (CDN).
- As a minimal image that requires access to the BaseOS and AppStream repositories to install software packages. The repositories are part of the DVD ISO image that is available for download from the Red Hat Customer Portal. Download and unpack the DVD ISO image to access the repositories.
The following table contains information about the images that are available for the supported architectures.
Table 3.1. Boot and installation images
x86_64 DVD ISO image file
x86_64 Boot ISO image file
AArch64 DVD ISO image file
AArch64 Boot ISO image file
ppc64le DVD ISO image file
ppc64le Boot ISO image file
s390x Boot ISO image file
Additional resources
3.2. Downloading an ISO image from the Customer Portal
The Boot ISO image is a minimal image file that supports registering your system, attaching subscriptions, and installing RHEL from the Content Delivery Network (CDN). The DVD ISO image file contains all repositories and software packages and does not require any additional configuration.
Prerequisites
- You have an active Red Hat subscription.
- You are logged in to the Product Downloads section of the Red Hat Customer Portal at Product Downloads.
- Open the browser and access https://access.redhat.com/downloads/content/rhel. This page lists popular downloads for Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
- Click Download Now beside the ISO image that you require.
- If the desired version of RHEL is not listed, click All Red Hat Enterprise Linux Downloads .
- From the Product Variant drop-down menu, select the variant and architecture that you require.
- Optional: Select the Packages tab to view the packages contained in the selected variant. For information about the packages available in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8, see the Package Manifest document.
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux Binary DVD image.
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux Boot ISO image.
Additional images may be available, for example, preconfigured virtual machine images.
3.3. Downloading an ISO image using curl
With the curl tool, you can fetch the required file from the web using the command line to save locally or pipe it into another program as required. This section explains how to download installation images using the curl command.
Prerequisites
- The curl and jq packages are installed. If your Linux distribution does not use yum or apt , or if you do not use Linux, download the most appropriate software package from the curl website.
- You have an offline token generated from Red Hat API Tokens.
- You have a checksum of the file you want to download from Product Downloads.
- Create a bash file with the following content:
#!/bin/bash # set the offline token and checksum parameters offline_token emphasis"> " checksum= # get an access token access_token=$(curl https://sso.redhat.com/auth/realms/redhat-external/protocol/openid-connect/token -d grant_type=refresh_token -d client_id=rhsm-api -d refresh_token=$offline_token | jq -r '.access_token') # get the filename and download url image=$(curl -H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" "https://api.access.redhat.com/management/v1/images/$checksum/download") filename=$(echo $image | jq -r .body.filename) url=$(echo $image | jq -r .body.href) # download the file curl $url -o $filename
$ chmod u+x FILEPATH/FILENAME.sh
Use password management that is consistent with networking best practices.
- Do not store passwords or credentials in a plain text.
- Keep the token safe against unauthorized use.
Additional resources