- 5.2. The Virtual Machine Manager Interface
- 5.2.1. The Virtual Machine Manager Main Window
- 5.2.1.1. The main window menu bar
- 5.2.1.2. The main window toolbar
- 5.2.1.3. The Virtual Machine list
- 5.2.2. The Virtual Machine Window
- 5.2.2.1. The Virtual Machine window menu bar
- 5.2.2.2. The Virtual Machine window toolbar
- 5.2.2.3. The Virtual Machine pane
- The virtual machine console
- The virtual machine details window
- The snapshots window
- Chapter 5. Managing virtual machines in the web console
- 5.1. Overview of virtual machine management using the web console
- 5.2. Setting up the web console to manage virtual machines
- 5.3. Renaming virtual machines using the web console
- 5.4. Virtual machine management features available in the web console
- 5.5. Differences between virtualization features in Virtual Machine Manager and the web console
5.2. The Virtual Machine Manager Interface
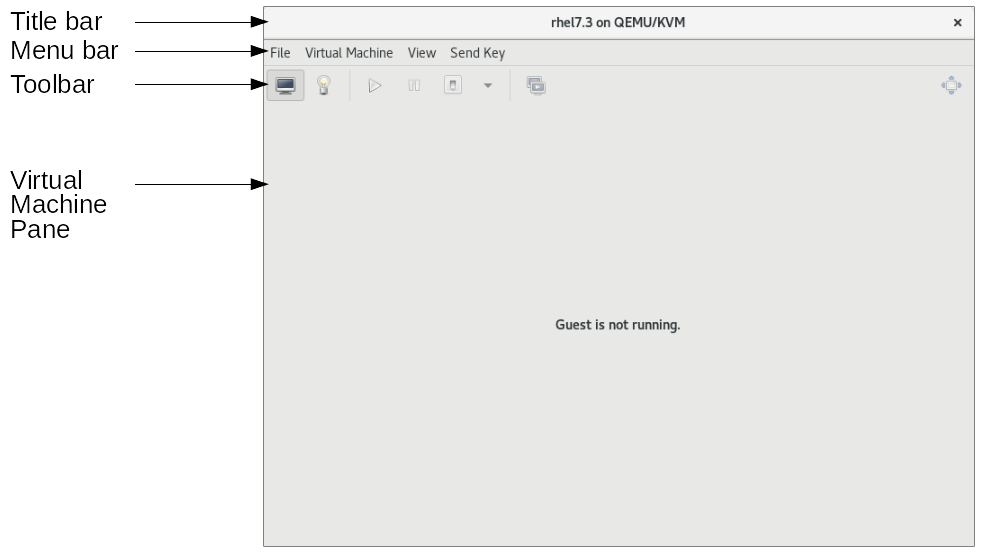
The following sections provide information about the Virtual Machine Manager user interface. The user interface includes The Virtual Machine Manager main window and The Virtual Machine window.
5.2.1. The Virtual Machine Manager Main Window
Figure 5.2. The Virtual Machine Manager window
5.2.1.1. The main window menu bar
Table 5.1. Virtual Machine Manager main window menus
| Menu name | Menu item | Description |
|---|---|---|
| File | Add Connection | Opens the Add Connection dialog to connect to a local or remote hypervisor. For more information, see Adding a Remote Connection in the Red Hat Enterprise Linux Virtualization Deployment and Administration Guide. |
| New Virtual Machine | Opens the New VM wizard to create a new guest virtual machine. For more information, see Creating Guests with virt-manager in the Red Hat Enterprise Linux Virtualization Deployment and Administration Guide. | |
| Close | Closes the Virtual Machine Manager window without closing any Virtual Machine windows. Running virtual machines are not stopped. | |
| Exit | Closes the Virtual Machine Manager and all Virtual Machine windows. Running virtual machines are not stopped. | |
| Edit | Connection Details | Opens the Connection Details window for the selected connection. |
| Virtual Machine Details | Opens the Virtual Machine window for the selected virtual machine. For more information, see The Virtual Machine pane. | |
| Delete | Deletes the selected connection or virtual machine. | |
| Preferences | Opens the Preferences dialog box for configuring Virtual Machine Manager options. | |
| View | Graph |
5.2.1.2. The main window toolbar
Table 5.2. Virtual Machine Manager main window toolbar
Save — Saves the state of the selected virtual machine to a file. For more information, see Saving a Guest Virtual Machine’s Configuration in the Red Hat Enterprise Linux Virtualization Deployment and Administration Guide.
5.2.1.3. The Virtual Machine list
The virtual machine list displays a list of virtual machines to which the Virtual Machine Manager is connected. The virtual machines in the list are grouped by connection. You can sort the list by clicking on the header of a table column.
Figure 5.3. The Virtual Machine list
The virtual machine list displays graphs with information about the resources being used by each virtual machine. You make resources available for display from the Polling tab of the Preferences dialog in the Edit menu. The following is a list of the resources that can be displayed in the virtual machine list:
You can select the resources to display using the Graph menu item in the View menu.
5.2.2. The Virtual Machine Window
Figure 5.4. The Virtual Machine window
5.2.2.1. The Virtual Machine window menu bar
Table 5.3. Virtual Machine window menus
| Menu name | Menu item | Description |
|---|---|---|
| File | View Manager | Opens the main Virtual Machine Manager window. |
| Close | Closes only the Virtual Machine window without stopping the virtual machine. | |
| Exit | Closes the all Virtual Machine Manager windows. Running virtual machines are not stopped. | |
| Virtual Machine | Run | Runs the virtual machine. This option is only available if the virtual machine is not running. |
| Pause | Pauses the virtual machine. This option is only available if the virtual machine is already running. | |
| Shut Down | Opens a menu to select one of the following actions to perform on the virtual machine: |
Always — The display of the virtual machine is always scaled to the Virtual Machine window.
Only when Fullscreen — The display of the virtual machine is only scaled to the Virtual Machine window when the Virtual Machine window is in Full screen mode..
Never — The display of the virtual machine is never scaled to the Virtual Machine window.
Auto resize VM with window — The display of the virtual machine resizes automatically when the Virtual Machine window is resized.
5.2.2.2. The Virtual Machine window toolbar
Table 5.4. Virtual Machine window toolbar
5.2.2.3. The Virtual Machine pane
The virtual machine console
Figure 5.5. The Virtual Machine console
You can interact with the virtual machine console using the mouse and keyboard in the same manner you interact with a real machine. The display in the virtual machine console reflects the activities being performed on the virtual machine.
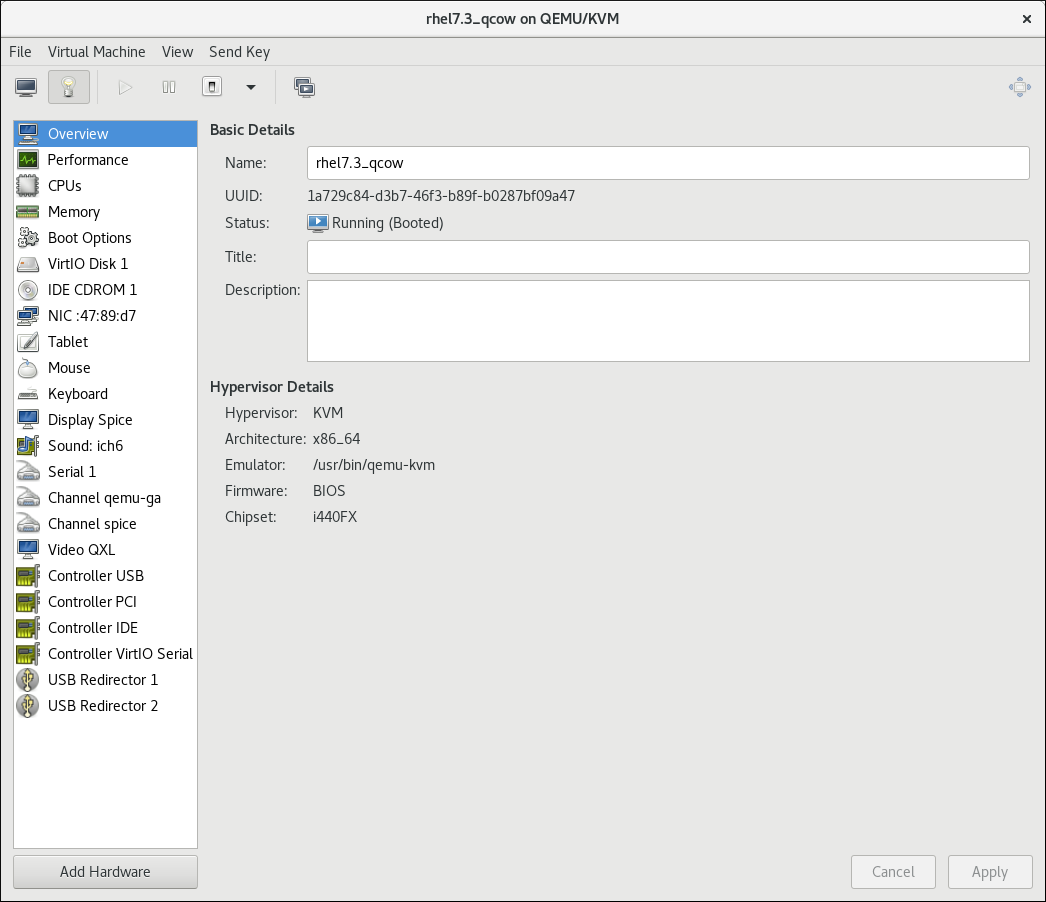
The virtual machine details window
The virtual machine details window provides detailed information about the virtual machine, its hardware and configuration.
Figure 5.6. The Virtual Machine details window
The virtual machine details window includes a list of virtual machine parameters. When a parameter in the list is selected, information about the selected parameter appear on the right side of the virtual machine details window. You can also add and configure hardware using the virtual machine details window.
For more information on the virtual machine details window, see The Virtual Hardware Details Window in the Red Hat Enterprise Linux Virtualization Deployment and Administration Guide.
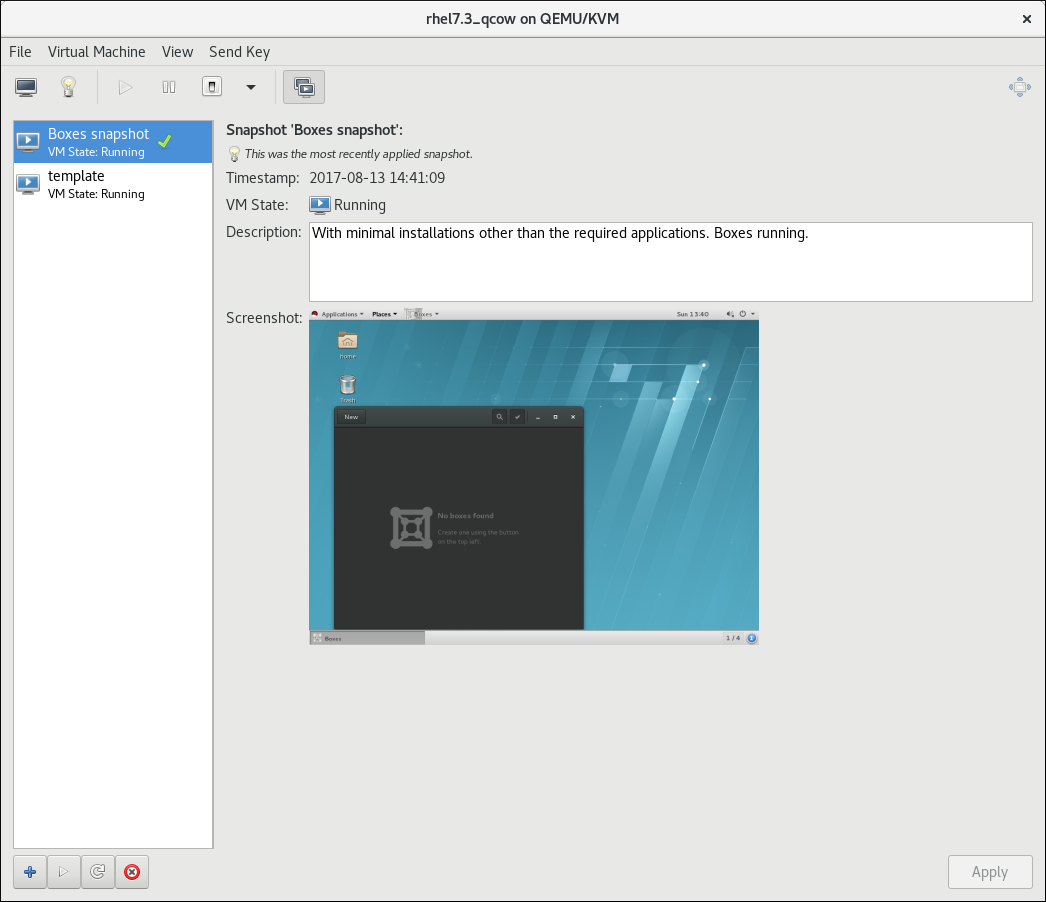
The snapshots window
Figure 5.7. The Virtual Machine snapshots window
The virtual machine snapshots window includes a list of snapshots saved for the virtual machine. When a snapshot in the list is selected, details about the selected snapshot, including its state, description, and a screenshot, appear on the right side of the virtual machine snapshots window. You can add, delete, and run snapshots using the virtual machine snapshots window.
For more information about managing snapshots, see Managing Snapshots in the Red Hat Enterprise Linux Virtualization Deployment and Administration Guide.
Chapter 5. Managing virtual machines in the web console
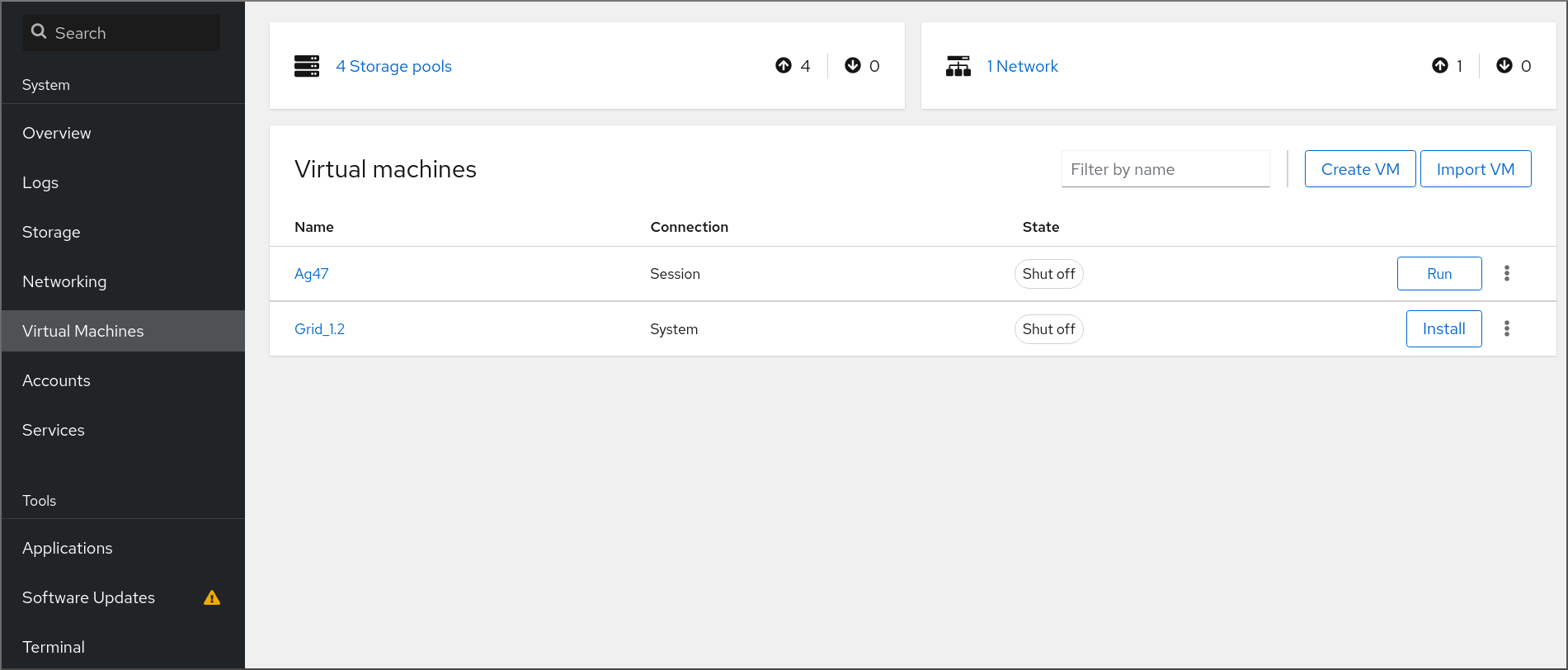
To manage virtual machines in a graphical interface on a RHEL 8 host, you can use the Virtual Machines pane in the RHEL 8 web console.
5.1. Overview of virtual machine management using the web console
The RHEL 8 web console is a web-based interface for system administration. As one of its features, the web console provides a graphical view of virtual machines (VMs) on the host system, and makes it possible to create, access, and configure these VMs.
Note that to use the web console to manage your VMs on RHEL 8, you must first install a web console plug-in for virtualization.
- For instructions on enabling VMs management in your web console, see Setting up the web console to manage virtual machines.
- For a comprehensive list of VM management actions that the web console provides, see Virtual machine management features available in the web console.
- For a list of features that are currently not available in the web console but can be used in the virt-manager application, see Differences between virtualization features in Virtual Machine Manager and the web console.
5.2. Setting up the web console to manage virtual machines
Before using the RHEL 8 web console to manage virtual machines (VMs), you must install the web console virtual machine plug-in on the host.
Prerequisites
- Ensure that the web console is installed and enabled on your machine.
# systemctl status cockpit.socket cockpit.socket - Cockpit Web Service Socket Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/cockpit.socket [. ] - Install the cockpit-machines plug-in.
# yum install cockpit-machines Verification
- Access the web console, for example by entering the https://localhost:9090 address in your browser.
- Log in.
- If the installation was successful, Virtual Machines appears in the web console side menu.
Additional resources
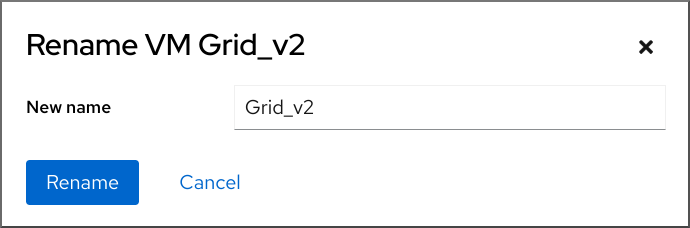
5.3. Renaming virtual machines using the web console
After create a virtual machine (VM), you might wish to rename the VM to avoid conflicts or assign a new unique name based on your use case. You can use the RHEL web console to rename the VM.
Prerequisites
- In the Virtual Machines interface, click the Menu button ⋮ of the VM that you want to rename. A drop down menu appears with controls for various VM operations.
- Click Rename . The Rename a VM dialog appears.
Verification
5.4. Virtual machine management features available in the web console
Using the RHEL 8 web console, you can perform the following actions to manage the virtual machines (VMs) on your system.
Table 5.1. VM management tasks that you can perform in the RHEL 8 web console
Create a VM and install it with a guest operating system
Start, shut down, and restart the VM
Connect to and interact with a VM using a variety of consoles
View a variety of information about the VM
Adjust the host memory allocated to a VM
Manage network connections for the VM
Manage the VM storage available on the host and attach virtual disks to the VM
Configure the virtual CPU settings of the VM
Manage virtual optical drives
5.5. Differences between virtualization features in Virtual Machine Manager and the web console
The Virtual Machine Manager ( virt-manager ) application is supported in RHEL 8, but has been deprecated. The web console is intended to become its replacement in a subsequent major release. It is, therefore, recommended that you get familiar with the web console for managing virtualization in a GUI.
However, in RHEL 8, some VM management tasks can only be performed in virt-manager or the command line. The following table highlights the features that are available in virt-manager but not available in the RHEL 8.0 web console.
If a feature is available in a later minor version of RHEL 8, the minimum RHEL 8 version appears in the Support in web console introduced column.
Table 5.2. VM managemennt tasks that cannot be performed using the web console in RHEL 8.0
Setting a virtual machine to start when the host boots
Suspending a virtual machine