- How to Remove Files and Directories in Linux Command Line [Beginner’s Tutorial]
- How to delete files in Linux
- 1. Delete a single file
- 2. Force delete a file
- 3. Remove multiple files
- 4. Remove files interactively
- How to remove directories in Linux
- 1. Remove an empty directory
- 2. Remove directory with content
- 3. Force remove a directory and its content
- 4. Remove multiple directories
- Summary
- Delete All Files of a Directory in Linux
- Properly removing all files in a directory
- Step 1: Go to the desired directory
- Step 2: List the directory contents
- Step 3: Delete all files and folders in the directory
- Conclusion
- How to remove all files of a directory in Linux
- How to remove all files in a directory of Linux
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Hammad Zahid
- Unix Command to Delete all files in a directory but preserve the directory
- 8 Answers 8
How to Remove Files and Directories in Linux Command Line [Beginner’s Tutorial]
Learn how to delete files and remove directories with rm command in Linux.
How to delete a file in Linux? How to delete a directory in Linux? Let’s see how to do both of these tasks with one magical command called rm.
How to delete files in Linux
Let me show you various cases of removing files.
1. Delete a single file
If you want to remove a single file, simply use the rm command with the file name. You may need to add the path if the file is not in your current directory.
If the file is write protected i.e. you don’t have write permission to the file, you’ll be asked to confirm the deletion of the write-protected file.
rm: remove write-protected regular file 'file.txt'?You can type yes or y and press enter key to confirm the deletion. Read this article to know more about Linux file permissions.
2. Force delete a file
If you want to remove files without any prompts (like the one you saw above), you can use the force removal option -f.
3. Remove multiple files
To remove multiple files at once, you can provide all the filenames.
rm file1.txt file2.txt file3.txtYou can also use wildcard (*) and regex instead of providing all the files individually to the rm command. For example, if you want to remove all the files ending in .hpp in the current directory, you can use rm command in the following way:
4. Remove files interactively
Of course, removing all the matching files at once could be a risky business. This is why rm command has the interactive mode. You can use the interactive mode with the option -i.
It will ask for confirmation for each of the file. You can enter y to delete the file and n for skipping the deletion.
rm: remove regular file 'file1.txt'? y rm: remove regular file 'file2.txt'? nYou just learned to delete files in the terminal. Let’s see how to remove directories in Linux.
How to remove directories in Linux
There is a command called rmdir which is short for remove directory. However, this rmdir command can only be used for deleting empty directories.
If you try to delete a non-empty directory with rmdir, you’ll see an error message:
rmdir: failed to remove 'dir': Directory not emptyThere is no rmdir force. You cannot force rmdir to delete non-empty directory.
This is why I am going to use the same rm command to delete folders as well. Remembering the rm command is a lot more useful than rmdir which in my opinion is not worth the trouble.
1. Remove an empty directory
To remove an empty directory, you can use the -d option. This is equivalent to the rmdir command and helps you ensure that the directory is empty before deleting it.
2. Remove directory with content
To remove directory with contents, you can use the recursive option with rm command.
This will delete all the contents of the directory including its sub-directories. If there are write-protected files and directories, you’ll be asked to confirm the deletion.
3. Force remove a directory and its content
If you want to avoid the confirmation prompt, you can force delete.
4. Remove multiple directories
You can also delete multiple directories at once with rm command.
Awesome! So now you know how to remove directory in Linux terminal.
Summary
Here’s a summary of the rm command and its usage for a quick reference.
| Purpose | Command |
|---|---|
| Delete a single file | rm filename |
| Delete multiple files | rm file1 file2 file3 |
| Force remove files | rm -f file1 file2 file3 |
| Remove files interactively | rm -i *.txt |
| Remove an empty directory | rm -d dir |
| Remove a directory with its contents | rm -r dir |
| Remove multiple directories | rm -r dir1 dir 2 dir3 |
I hope you like this tutorial and learned to delete files and remove directories in Linux command line. If you have any questions or suggestions, please leave a comment below.
Delete All Files of a Directory in Linux
Here is a quick Linux command tips on deleting the contents of a directory, not the directory itself.
At times you’ll need to delete all the files of a directory. Not the directory itself but the contents of the directory. You could do it to clean up a project, free up space or for any other purpose.
To empty a directory, you use the following command:
The wild card means everything here. So, you are instructing the rm command to remove everything in the given directory.
Please note that this is different than using rm on the directory name directly without /* . If you use rm -r dir , it will delete the directory along with its contents. That’s not always desirable. Is it?
Let’s see about deleting all the contents of a directory in detail.
Properly removing all files in a directory
Linux command line does not have a recycle bin. You have to be careful while deleting files. And if you have to remove multiple files using wildcard, you must be extra cautious.
This is why I advise switching to the directory you want to empty and then using the rm command. This reduces the risk of accidentally deleting the contents of a wrong directory.
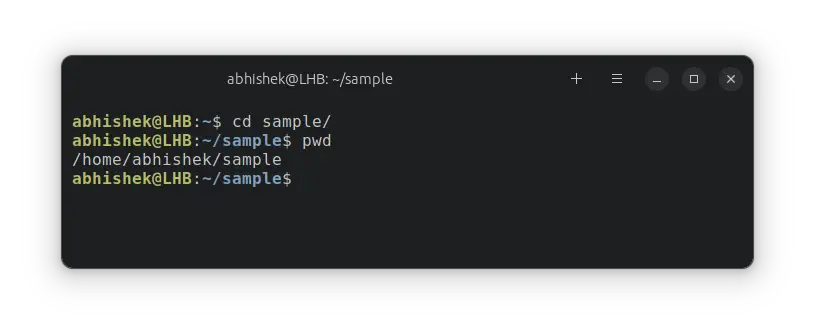
Step 1: Go to the desired directory
Use the cd command to switch to the directory you want to empty.
For example, I am going to delete all the contents of the /home/abhishek/sample directory. So, I switch to it first.
It’s good to ensure that you are in the current directory:
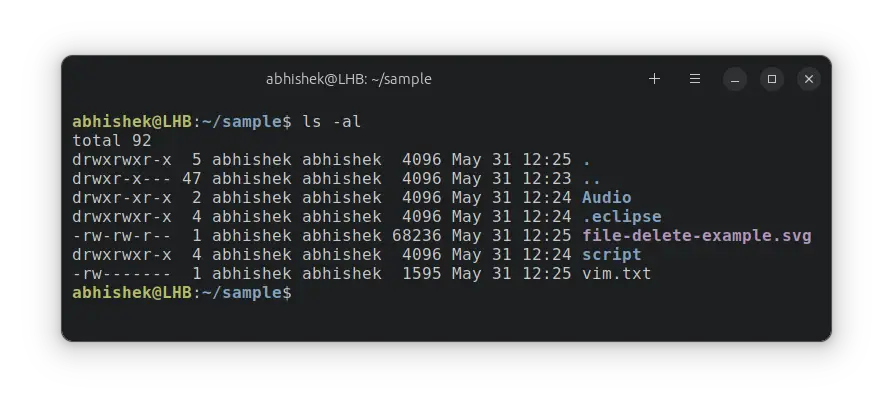
Step 2: List the directory contents
You should check the directory contents to ensure that you are not deleting any important files. I advise showing hidden files as well.
If there are sub-directories, please ensure nothing important is in there.
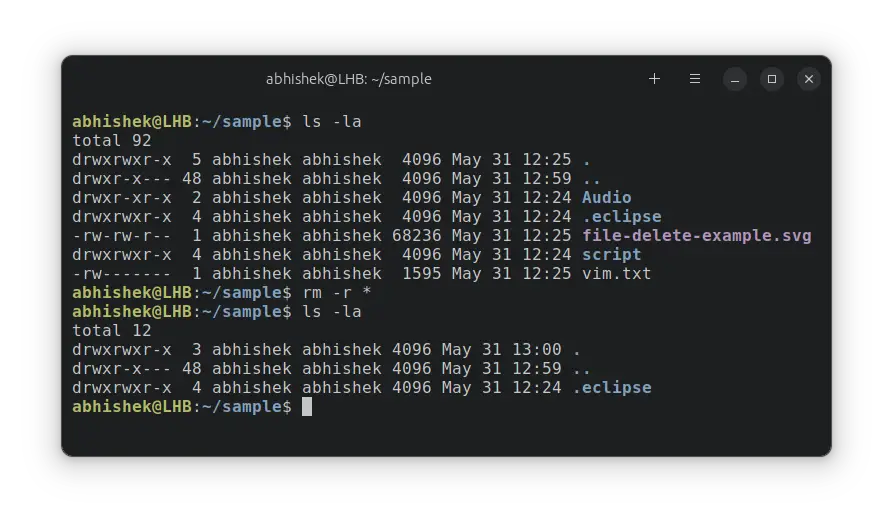
Step 3: Delete all files and folders in the directory
Once you are sure that nothing important is in the directory, it is time to delete the contents.
You can use the rm command like this:
Which is a way of instructing the rm command to delete everything it sees in the current directory recursively. The recursive option -r is essential for removing sub-directories.
Sometimes, there are write protected files and then you’ll be asked to confirm the removal. To avoid that, you can include the forced delete option -f .
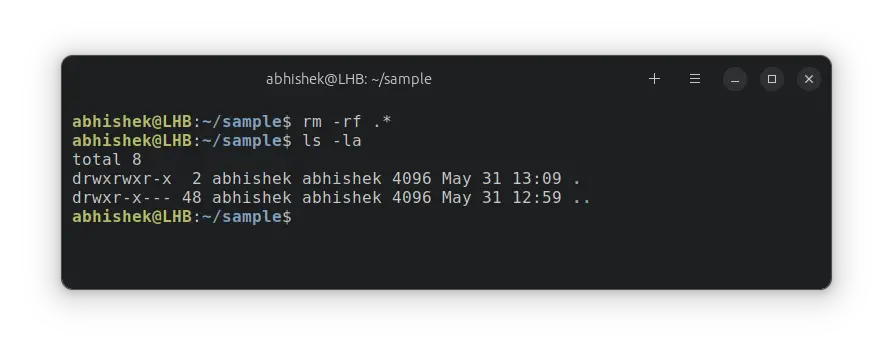
To delete only the hidden files, you can additionally run this command:
Conclusion
While deleting all the contents of a directory without deleting the directory itself seems like an easy job, things get a bit complicated if there are hidden files and folders.
In those cases, you have to run rm -rf .* after rm -rf * .
I hope you liked this quick little Linux command line tip. Let me know if you have questions or suggestions.
How to remove all files of a directory in Linux
Files are created and saved in the directories of Linux, they can be text files, image files, music files, or any other format. These files occupy some space and many files present in our system are purposeless, they should be deleted in order to make space for new files.
In Linux, we can either delete/remove a single file or delete all the files from a directory using a single command in a terminal. In this write-up, we will discuss the ways to remove all the files in a directory of Linux.
How to remove all files in a directory of Linux
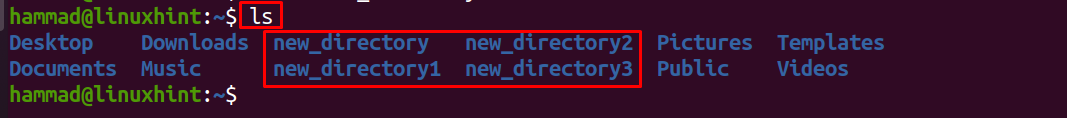
We have directories in a path /home/hammad/ with a name, new_directory, new_directory1, new_directory2, and new_directory3 that contain files, to view it, and list down the components of the path:
To view the files of “new_directory”, use the command:
To remove these files from the directory “new_directory”, we can simply use the command of “rm”, the general syntax of using the rm command is:
The explanation to the syntax is simple:
- Use the command of rm to remove the files from the directory
- Use any options like to display the progress, to remove it forcibly
- Type the pathname where the directory is located
- Mention the filenames which you want to remove or simply use “*” to remove all the files from the directory
Suppose we want to remove all the files from the “/home/hammad/new_directory/*” path, we will use the command:
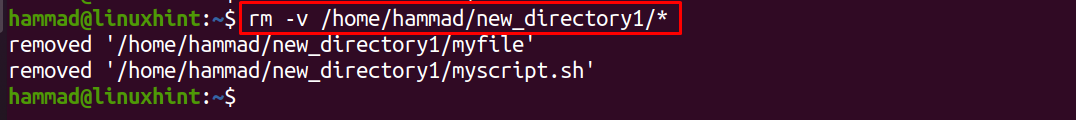
We can also display the progress of the removed files by using the flag “-v”, we will execute the command:
In the above command, the “-v” flag is used to display the progress of the command where “*” is used to delete all the files of the directory and for verification that all the files are deleted, we will again list down the content of the directory using the command:
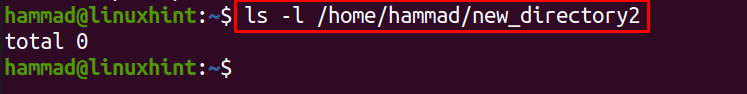
The above command verified that the directory contains no files and there are some other useful options as well; the “-f” which is used to delete the files forcibly and “-r” deletes the directory and its files, we will use all these flags altogether to delete the files of “new_directory2”
In the above output, we can see that the “-r” flag removes the sub directory, “officedirectory”, from the new_directory2, to list the files of new_directory2, we use the ls command:
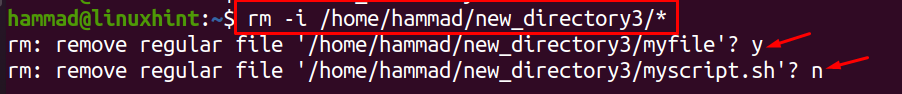
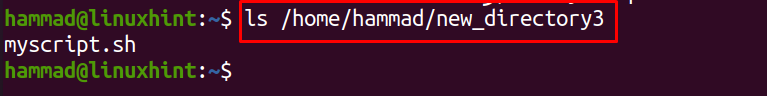
We have another option that is “-i”, if we use this option, it will ask for permission before deleting each file should we continue to delete it or not, if we still want to delete it, type “y” or “n” to cancel it. We will use “-i”, to delete files of new_directory3:
In the above command, it can be seen that we have confirmed to delete “myfile” and canceled to delete “myscript.sh”, to view the files in the folder:
We can see the “myscript.sh” file has not been removed from the directory.
To delete all the empty directories we use the “rmdir” command:
All the empty directories are removed, use ls command to verify:
Conclusion
Removing the files from the directory will create free space for the new files and applications. Therefore, files of no use should be removed from the system. To remove all the files from the directory the convenient way is to use the rm command which is discussed in this write-up. Different options can also be used along with the rm command which is also discussed with the help of examples.
About the author
Hammad Zahid
I’m an Engineering graduate and my passion for IT has brought me to Linux. Now here I’m learning and sharing my knowledge with the world.
Unix Command to Delete all files in a directory but preserve the directory
I am looking for a unix command to delete all files within a directory without deleting the directory itself. (note the directory does not contain subdirectories).
8 Answers 8
EDIT: added -i just in case (safety first). directory should be a full or relative path (e.g. /tmp/foo or ../trash/stuffs )
of course, you can always cd to your directory and then perform a «rm -i *» please note that the -i flag will force confirmation of each deletion, is there just for safety (nasty things will occurr if you misplace a / in your commandline and you provide a -r flag. )
I’m using rm -r * but it’s asking for a confirmation on each file deletion. To stop this it’s rm -rf * yes? Trying to delete all from current directory.
-r perform recursive deletion, -f forces deletion, assuming the rm command has not been aliased, I’d go with a rm -f *
it deletes all file inside the «yourdirectory» directory
I wouldn’t suggest to a unix newbie to use the -r switch, what if OP misplaces a / on the command line ?
Understandable but the issue is that i am clearing out spam from the remote qmail folder. There is thousands of messages to clear so I need a practical way of doing it without confirmation on each deletion.
You can use find /path/to/your/folder/ -delete to delete everything within that folder.
While a wildcard rm would braek with too many files («Argument list too long»), this works no matter how many files there are.
You can also make it delete only files but preserve any subdirectories:
find /path/to/your/folder/ -type f -delete You could also specify any other criteria find supports to restrict the «results».