- How to Remove Software Repositories from Ubuntu
- Method 1. Remove the repository using apt 🤖
- Method 2. Remove the software repository in Ubuntu using GUI 🖥️
- Method 3. Remove the repository by removing its directory (for experts 🧑💻)
- Additional Step: Remove GPG keys after removing the repository (for advanced users)
- Careful with what you add and what you remove
- How to remove/delete a PPA repository in Ubuntu 22.04
- How to Remove/Delete a PPA repository in Ubuntu 22.04?
- Method 1: Remove/delete a PPA Repository in Ubuntu Using Terminal
- Method 2: Remove/Delete a PPA Repository in Ubuntu Using GUI
- Conclusion
- How to apt-delete-repository? [duplicate]
- 1 Answer 1
- Linked
- Related
- Hot Network Questions
How to Remove Software Repositories from Ubuntu
From apt-add-repository to Software & Updates tool, here are several ways to remove software repositories from Ubuntu.
- Using apt-add-repository command to remove the repository
- Using GUI to remove the repository (for desktop users)
- By modifying the file contents of the /etc/apt/sources.list file (for experts)
But before that, I highly advise getting familiar with the concept of package managers and repositories if you are new to this concept.
Method 1. Remove the repository using apt 🤖
Did you know you can also use the apt command to remove repositories? Well, technically, it’s not part of the core apt command but it works in similar fashion.
You can use the add-apt-repository or apt-add-repository commands (both represent the same command) while dealing with external repositories.
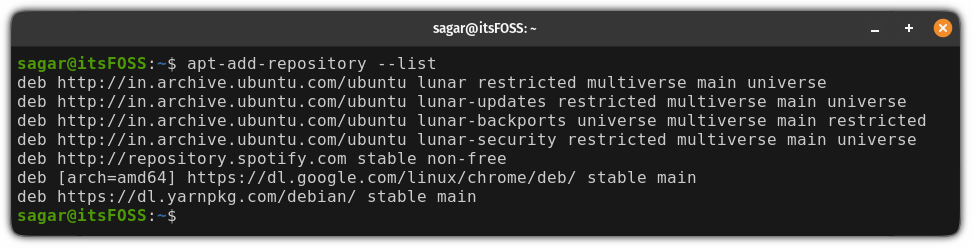
First, list the added repositories using the following command:
Once done, you can use the apt-add-repository command with the -r flag in shown manner to remove the directory:
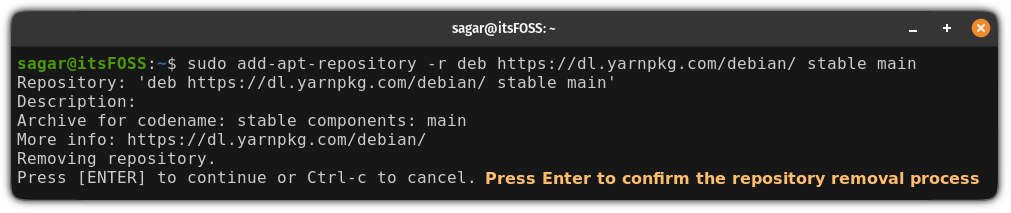
sudo apt-add-repository -r repo_nameFor example, if I want to remove the yarn repository, I would have to use the following command:
sudo add-apt-repository -r deb https://dl.yarnpkg.com/debian/ stable mainPress the Enter key for confirmation.
Next, update the repositories using the following:
And now, if you list enabled repositories, you won’t find the removed repository here:
Method 2. Remove the software repository in Ubuntu using GUI 🖥️
Removing a repository you know nothing about is not recommended as it may restrict you from installing your favorite package in the future, so make sure you know what you are up to.
Being one of the best distros for beginners, You can use GUI to remove the repository without needing the terminal.
To do so, first, open the software and updates the app from the system menu:
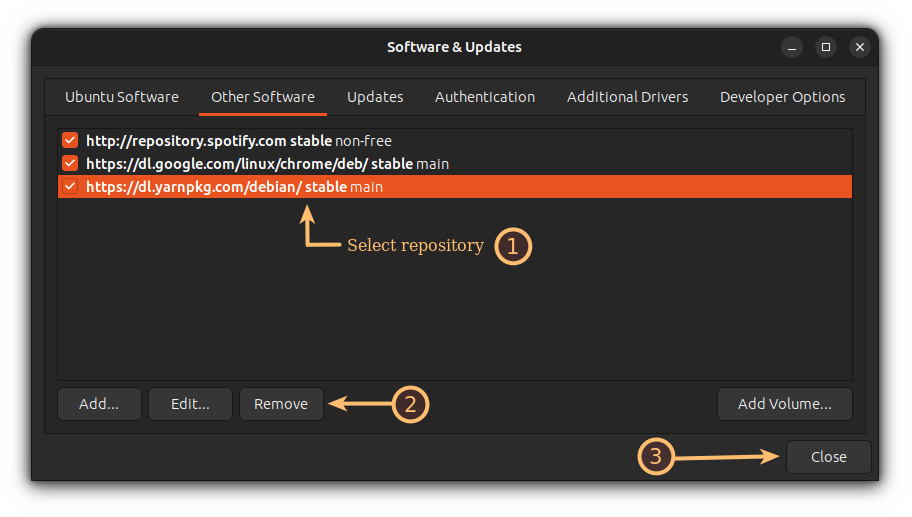
Now, click on Other Software section, and it will list PPAs and external repositories in your system.
The ones listed as checked ✅ are enabled ones.
To remove a repository, you’d have to follow three simple steps:
- Select a repository that needs to be removed
- Click on the remove button
- And finally, hit the close button
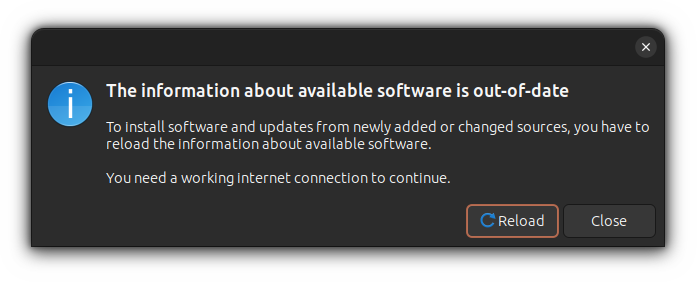
Once you click on the close button, it will open a prompt asking you to update the information as you make changes.
Simply click on the Reload button:
Alternatively, you can update the repository from the command line to take effect from the changes:
Method 3. Remove the repository by removing its directory (for experts 🧑💻)
Previously, I explained how you could use tools (GUI and CLI) to remove a repository; here, you will modify the system directory (/etc/apt/sources.list.d) responsible for managing repositories.
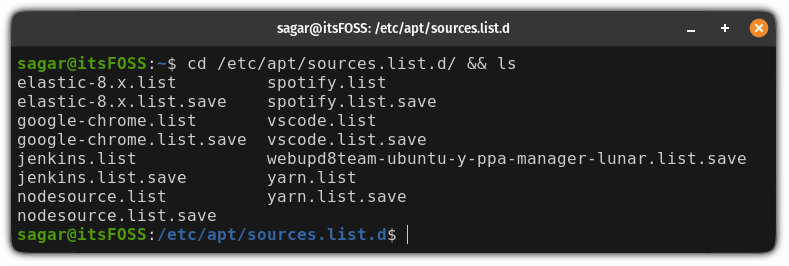
So first, change your working directory to sources.list.d and list its contents:
cd /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ && lsHere, you will find the list of all the repositories.
If you notice carefully, there will be two files for one repo. Once with the .list extension and one with the .save extension.
You will have to remove the one having the .list extension:
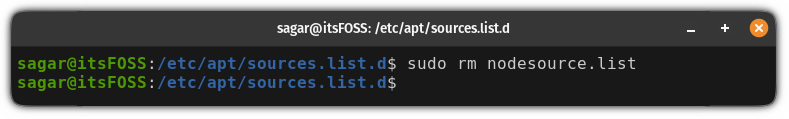
For example, here, I removed the node repo using the command below:
To take effect from the changes, update the repository index with:
Want to know more about the sources.list? Read this article.
Additional Step: Remove GPG keys after removing the repository (for advanced users)
If you wish to remove the GPG keys after removing the repository, here’s how you do it.
First, list the existing GPG keys using the following command:
Now, the output may seem confusing to some users.
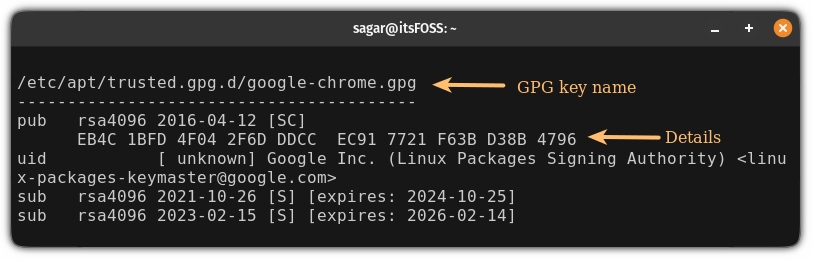
- The GPG key name will be placed above the dashed line (—-)
- The public key is in the second line
For example, here’s the relevant data of the Chrome GPG key:
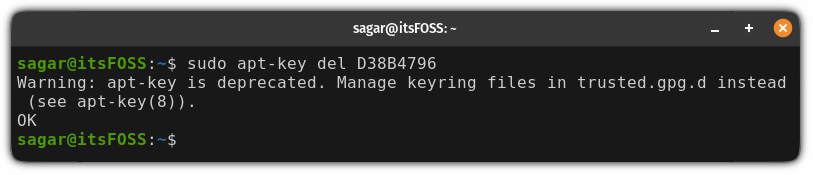
To remove the GPG key, you can use the last two strings of the public key (without any space).
For example, here’s how I will remove the GPG key of the Chrome browser using the last two strings of its public key (D38B 4796):
Similarly, you can also use the entire public key. But this time, you have to include spaces between two strings, as shown:
sudo apt-key del "72EC F46A 56B4 AD39 C907 BBB7 1646 B01B 86E5 0310"Careful with what you add and what you remove
Especially when you are a new Linux user, you will encounter many exciting things and repositories you will add and remove.
While it is good to experiment, you should always be careful about anything you add/remove to your system. You should keep some things in mind, like: Does it include updated packages? Is it a trusted or maintained repository?
Being cautious will keep your system free from unnecessary repositories and packages.
I hope this guide helps you remove the repository you do not want!
Feel free to let me know if you face any issues in the comments below, and consider joining our It’s FOSS Community forum to get faster help!
How to remove/delete a PPA repository in Ubuntu 22.04
PPA (Personal Package Archive) contains a set of packages hosted by the Launchpad server, also known as unofficial repositories. There are a lot of packages that do not come in the default repository of Ubuntu, and to install them, we have to add their PPA repositories to the Ubuntu sources.list. However, having unnecessary and unwanted PPA can slow down the system update process and consume storage, and in such a scenario, it is better to remove or delete such repositories.
This blog will explore the method of removing and deleting the PPA repository in Ubuntu 22.04.
How to Remove/Delete a PPA repository in Ubuntu 22.04?
There are two important methods to remove a PPA repository:
Below-given section will discuss both methods in detail.
Method 1: Remove/delete a PPA Repository in Ubuntu Using Terminal
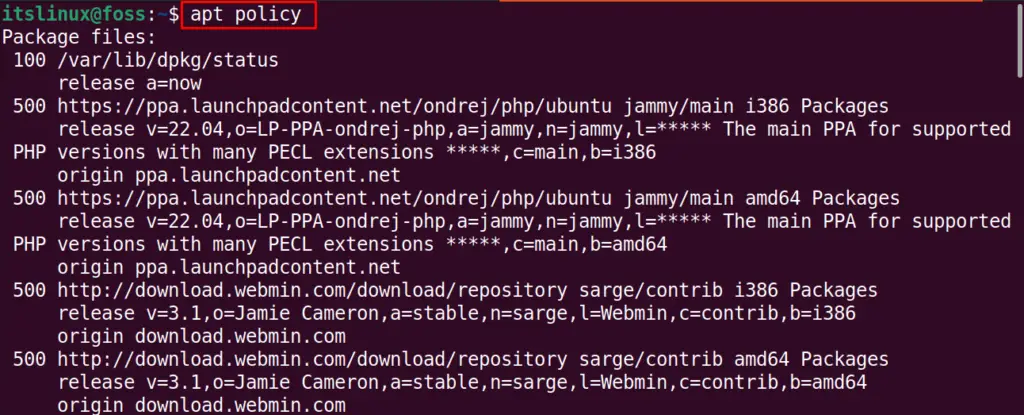
Firstly, we will list down all the added PPA repositories in Ubuntu:
As you can see in the given output, some PPA repositories have been added. Now, to delete these repositories through the terminal, we have three possible methods:
- Use the add-apt-repository command
- Remove it from sources.list
- Use the ppa-purge command
Check out each of them one by one!
Example 1: Use add-apt-repository Command to Remove a PPA repository
In Ubuntu, the utility of the add-apt-repository has been pre-installed to manage the PPA repositories, if you want to use this utility to remove the PPA repository, then the general syntax will be:
$ sudo add-apt-repository --remove [ppa:ppa-file]Here, the add-apt-utility runs with its “–remove” option and type the PPA repository name instead of [ppa:ppa-file].
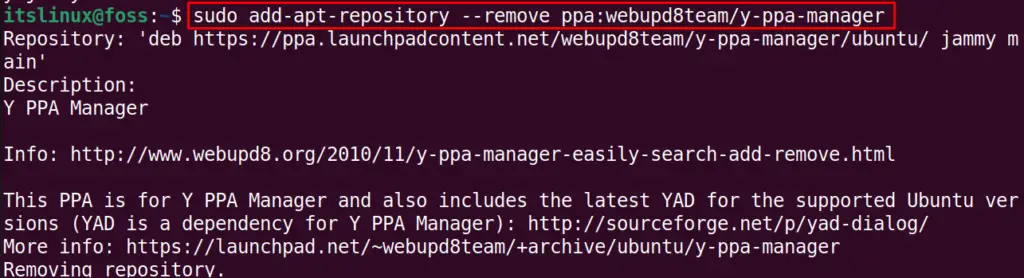
For example, we will remove the “webupd8team” repository by following the above general syntax:
$ sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:webupd8team/y-ppa-managerNote: You can also use the “-r” option instead of “–remove” in the above command.
Example 2: Removing a PPA repository from sources.list
You may know that all the packages and added repositories are stored in the /etc/apt/sources.list.d/. So, we can also remove the PPA repository directly from the sources list with the rm command.
For example, we will remove the PHP repository from the sources.list:
$ sudo rm /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ondrej-ubuntu-php-jammy.listThe execution of the above command indicates that the repository has been removed successfully.
Example 3: Use ppa-purge Command to Remove a PPA repository
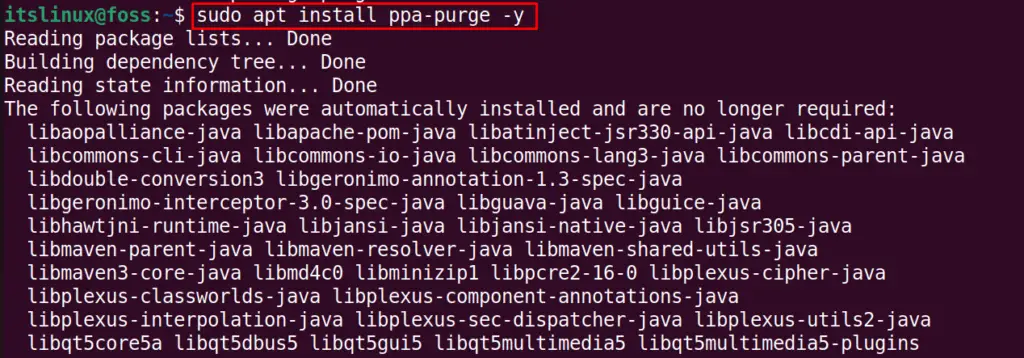
To use the ppa-purge command firstly, install it with the help of apt:
$ sudo apt install ppa-purge -yAfter doing so, execute the ppa-purge command and specify the repository name you want to remove. For example, to remove the light table PPA repository, we will execute the command:
$ sudo ppa-purge ppa:dr-akulavich/lighttableNow, let’s check out the GUI method to perform the same operation.
Method 2: Remove/Delete a PPA Repository in Ubuntu Using GUI
To remove the PPA repository using GUI, we will search and open the “Software & Updates” app in the Application’s search bar:
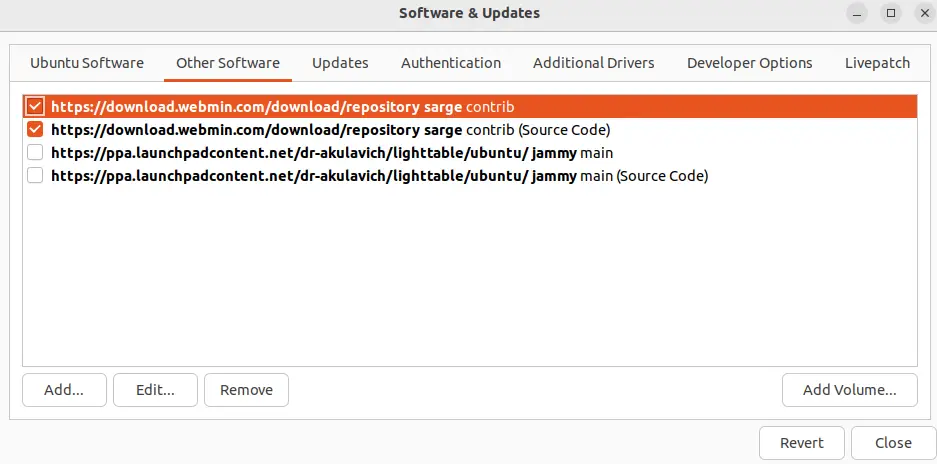
Then, navigate to the “Other Software” tab:
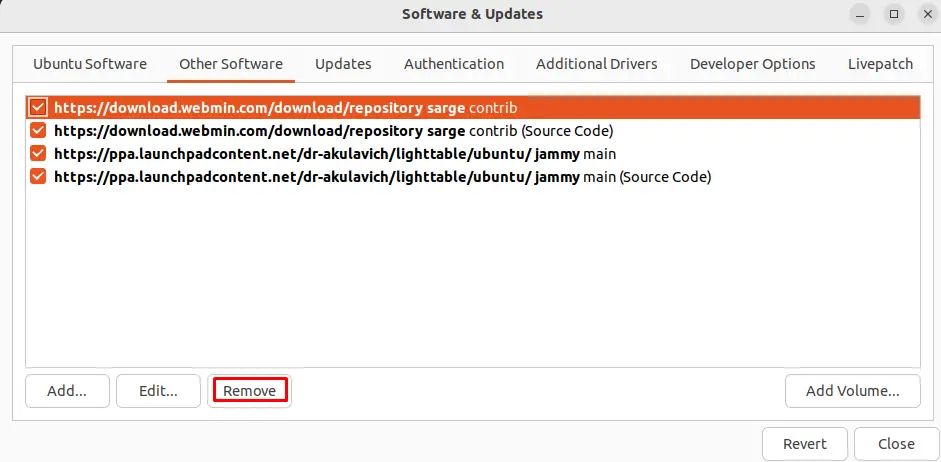
Mark the PPA repositories checkboxes, which you want to remove and click on the “Remove” button:
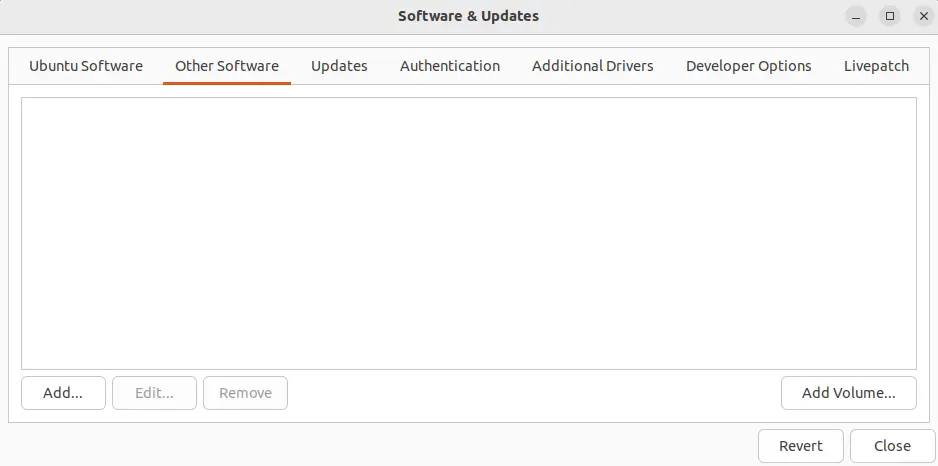
As a result, the selected PPA repositories will be removed from your Ubuntu 22.04 system:
We have provided different methods related to removing PPA repositories in Ubuntu 22.04.
Conclusion
To remove or delete a PPA repository in Ubuntu 22.04, you can use the “add-apt-repository” command with the “–remove” option, “ppa-purge” command, or directly remove it from the sources.list. Moreover, the selected PPA repository can also be removed through GUI using the “Software & Updates” app. This guide demonstrated the procedure of removing a PPA repository in Ubuntu 22.04.
TUTORIALS ON LINUX, PROGRAMMING & TECHNOLOGY
How to apt-delete-repository? [duplicate]
where the command add-apt-repository is in the package software-properties-common . I could not find the systemback entry in /etc/apt/sources.list . How can you run the reverse of the command?
1 Answer 1
To remove a repository, you have to do two things:
- Remove it from sources.list . If it was added by add-apt-repository then you will find it in its own file in /etc/apt/sources.list.d , not in the main sources.list .
sudo rm /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nemh-systemback-precise.list As mentioned in the comments by @SeF, you can use the following command:
Note: the short key id is no longer shown when you use the apt-key list command, but it is actually the last 8 characters of the long key that is shown.
I think @SeF you should make your comment an actual answer as that should be the accepted answer to this question. As a comment, albeit with high vote count, it is not given the attention it deserves.
Linked
Related
Hot Network Questions
Site design / logo © 2023 Stack Exchange Inc; user contributions licensed under CC BY-SA . rev 2023.7.14.43533
Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds. UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
This site is not affiliated with Linus Torvalds or The Open Group in any way.
By clicking “Accept all cookies”, you agree Stack Exchange can store cookies on your device and disclose information in accordance with our Cookie Policy.