- How to Rename a Directory in Linux: Ubuntu, Fedora, + More
- Using the «mv» Command
- Using the File Browser
- Using the «Rename» Command
- Renaming Multiple Directories
- Finding and Changing a Directory Name
- Expert Q&A
- You Might Also Like
- How to Rename a Directory in Linux
- Renaming Directories With the mv Command
- Renaming Directories With the rename Command
- Renaming a Single Directory With the rename Command
- Renaming Multiple Directories With the rename Command
- Renaming Directories With the find Command
- Renaming Directories With Bash Scripts
How to Rename a Directory in Linux: Ubuntu, Fedora, + More
This article was co-authored by wikiHow staff writer, Travis Boylls. Travis Boylls is a Technology Writer and Editor for wikiHow. Travis has experience writing technology-related articles, providing software customer service, and in graphic design. He specializes in Windows, macOS, Android, iOS, and Linux platforms. He studied graphic design at Pikes Peak Community College.
Do you want to change the name of a directory or folder in Linux? Most Linux distributions have a graphical user interface with a file browser application that you can use to rename files and folders. However, you can change the name of a directory or folder in all versions of Linux using a few basic Terminal commands. This wikiHow article teaches you how to rename a directory in all versions of Linux.
- The «mv» command can be used to rename directories and other files.
- The syntax to change a directory name is «mv .»
- You can also use the «rename» command or the file browser to change a directory name.
Using the «mv» Command
. On most Linux distributions, the Terminal has an icon that resembles a black screen with a white cursor. You can click the Terminal icon in your Apps menu or press the keyboard shortcut, «Ctrl + Alt + T» to open the Terminal.
- To change directories, type cd followed by the path, then press Enter.
- For example, if you want to rename a directory called «Important» in your Documents directory, you’d enter cd /home/yourusername/Documents and press Enter.
- Do not press Enter just yet. There is still more you need to type to complete the command.
- —backup : This will create a backup of all the files being moved.
- -f . This option will force an overwrite of any files or folders without a prompt.
- -i : This option will prompt you before overwriting any files or folders.
- -v : This option will explain everything that is being done by the command.
- To view all directories and folders in your current directory, type ls -la and press Enter. This will show all folders and hidden folders as well as which user has permission to access these folders.
- If you are not in the directory that contains the directory that you want to change, you will need to add the path to where you want to save the new directory name. For example, /home/user/new_directory . You can also do this to change the location of the directory.
- The entire command should look something like the following: mv -v /home/username/temp_dir /home/username/new_dir .
Using the File Browser
Open your File Browser app. This will be different with each Linux distribution. On Ubuntu and Fedora, it’s the app called «Files» and it has an icon that resembles a file cabinet drawer. Click the Files app to open Files.
Right-click the folder you want to rename. You can rename folders using the graphical user interface the same way you would using Windows or macOS. Simply right-click the folder you want to rename.
Enter a new name and click Rename . A box will appear with a field you can use to enter the new name for your folder. Enter the new name and click Rename. This will instantly rename the folder.
Using the «Rename» Command
. On most Linux distributions, the Terminal has an icon that resembles a black screen with a white cursor. You can click the Terminal icon in your Apps menu or press the keyboard shortcut «Ctrl + Alt + T» to open the Terminal.
- Debian/Ubuntu: sudo apt install rename
- Fedora: sudo yum install prename
- Arch Linux: sudo pacman -S install rename
- To change directories, type cd followed by the path, then press Enter.
- For example, if you want to rename a directory called «Important» in your Documents directory, you’d enter cd /home/yourusername/Documents and press Enter.
- -v : This command will add information about actions taking place.
- -n . This command will not take any action. You can use it to test your command to see if it works before changing the command for real.
- -f : This command will force overwrite any directories without prompting you.
Type the name of the directory you want to change. Enter the name of the old directory next in the command line.
- Alternatively, you can search for multiple folders by entering patterns instead of the name of a folder. To do so, you would type ‘s///’ instead of the old and new names for the directory. For example, if you have a bunch of folders named «Untitled», you could type ‘s/Untitled//’ to search for all folders with the name «Untitled». If you want to search for all folders that begin with a capital letter, you would type ‘s/A-Z//’ .
- The entire command should look something like rename -v Untitled New_folder_Name Untitled and press Enter.
Renaming Multiple Directories
. On most Linux distributions, the Terminal has an icon that resembles a black screen with a white cursor. You can click the Terminal icon in your Apps menu or press the keyboard shortcut «Ctrl + Alt + T» to open the Terminal.
- For example, you can type and press enter to create a new shell file called «change_directories.sh».
Type for d in *; do on the first line. This creates a loop in which the script will check all files within the directory the shell file is in.
- Alternatively, you can add a new name to the end of each directory instead of changing it completely. To do so, mv —«$d» «$_$(«) instead. For example, if you want to add the date to the end of each directory, you could type mv — «$d» «$_$(date +%Y%m%d)» on the third line.
Type done on the fifth line. This ends the script. The entire script should look something like the following:
for d in *; do if [ -d "$d" ]; then mv -- "$d" "$d>_$(date +%Y%m%d)" fi done
Save the shell file and exit VIM. To do so, press Esc. Then type :wq and press Enter. This will save the file and exit VIM. You will be returned to the standard Terminal interface.
- Make sure you are in the same directory as the shell file. To change directories, type cd followed by the path of the shell file (i.e., cd /home/user/ and press Enter.
Execute the script. To do so, simply type the name of the shell file (i.e, ./change_directories.sh and press Enter.
Finding and Changing a Directory Name
. If you’re not sure where the directory is that you want to rename, you can use the find command to find it. Start by opening a Terminal window.
- Don’t press Enter just yet. You still need to add the part of the command that will change the directory name.
- The entire command should look something like find . -depth -type d -name temp_directory -execdir mv <> new_directory_name \;
Expert Q&A
You Might Also Like
Can Linux Run .exe Files? How to Run Windows Software on Linux
How to Open Linux Firewall Ports: Ubuntu, Debian, & More
How to Run an INSTALL.sh Script on Linux in 4 Easy Steps
Use Ping in Linux: Tutorial, Examples, & Interpreting Results
How to Delete Read-Only Files in Linux
How to Install Linux on Your Computer
How to Install Software on Linux: Packages, Compiling, & More
How to Rename a Directory in Linux
Renaming a directory is one of the most basic tasks you will perform on any operating system. The Linux terminal offers several different ways to rename directories using commands and scripts.
In this tutorial, we will go over the different methods you can use to rename a directory in Linux through the terminal window.
- A system running a Linux distribution
- An account with sudo privileges
- Access to the terminal window/command line
- Access to a text editor, such as Vim or Nano
Renaming Directories With the mv Command
The primary function of the mv command in Linux is moving files and directories from one place to another. It uses the following command syntax:
mv [options] [source] [destination]Note: To learn more about using the mv command, check out our guide to moving directories in Linux.
If the destination directory does not exist, the mv command renames the source directory instead. In this case, the syntax changes to:
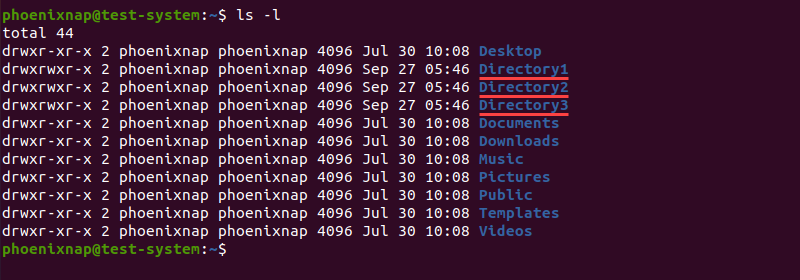
mv [options] [current directory name] [new directory name]As an example, let’s say we have Directory1, Directory2, and Directory3 in our Home directory:
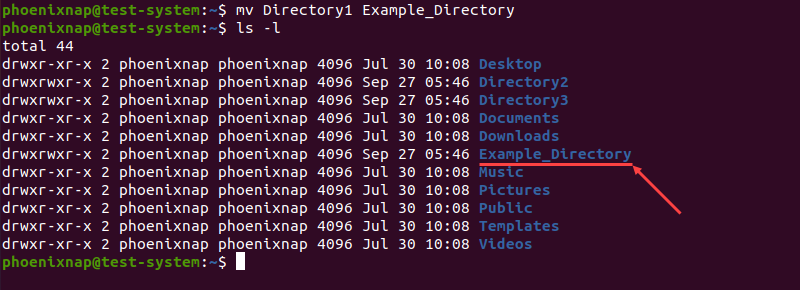
To rename Directory1 into Example_Directory with the mv command, use:
mv Directory1 Example_DirectoryThere is no output if the command is successful, so we need to use the ls command to verify the name change:
Renaming Directories With the rename Command
The rename command in Linux is a dedicated command used to change the names of files and directories. Using this command makes it easier to rename multiple directories at the same time.
Note: The rename command is not included in all Linux distributions by default. If your system is missing the rename command, install it with:
- For Ubuntu and Debian, use sudo apt install rename
- For CentOS and Fedora, use sudo yum install prename
- For Arch Linux, use sudo pacman -S rename
Renaming a Single Directory With the rename Command
The rename command uses the following syntax:
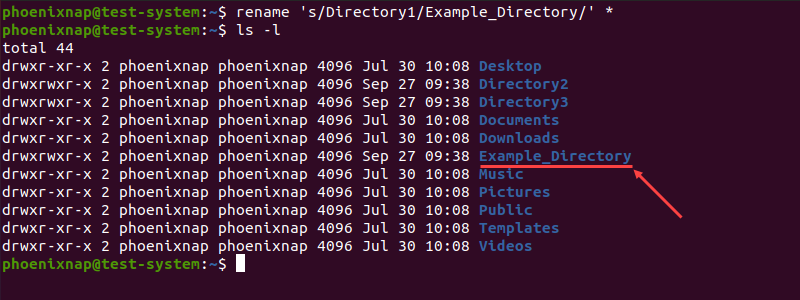
rename [options] 's/[expression]/[replacement]/' [file name]The command renames the file by replacing the first occurrence of the expression with the replacement. For example, if we want to rename Directory1 to Example_Directory:
rename 's/Directory1/Example_Directory/' *In this example, we can see that the rename command syntax consists of several sections:
- rename : Invokes the rename command.
- s : Short for substitute, indicates that we are replacing the expression with the replacement.
- / Directory1 : Specifies the expression or the part of the old directory name that you want to replace.
- /Example_Directory /: Defines the replacement or the new directory name.
- * : Searches the Home directory for names matching the provided expression.
Verifying the Home directory content with the ls command shows that the directory now has a new name:
Renaming Multiple Directories With the rename Command
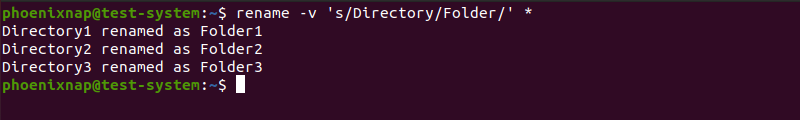
The rename command provides a way to rename multiple directories at the same time without using bash scripts. For instance, if we want to rename Directory1, Directory2, and Directory3 to Folder1, Folder2, and Folder3:
rename -v 's/Directory/Folder/' *- -v : Invokes the verbose output, listing each step of the process.
- ‘s/Directory/Folder/’ : Replaces Directory in the names of the search results with Folder.
- * : Searches the Home directory for names matching the provided expression.
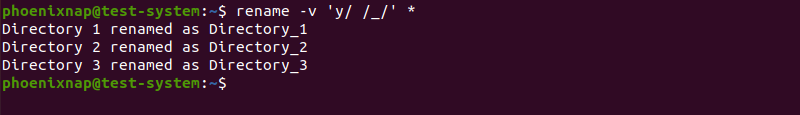
The rename command can also translate file names by using the y argument instead of the s argument. In this case, it translates one string of characters into another, character-for-character.
The command above translates every a character into d, every b into e, and every c into f.
In the example below, we translated blank spaces in directory names to underscores (_).
Renaming Directories With the find Command
In case you are not sure where the directory you want to rename is located, using the find command with the mv command lets you search for it and rename it when it’s found:
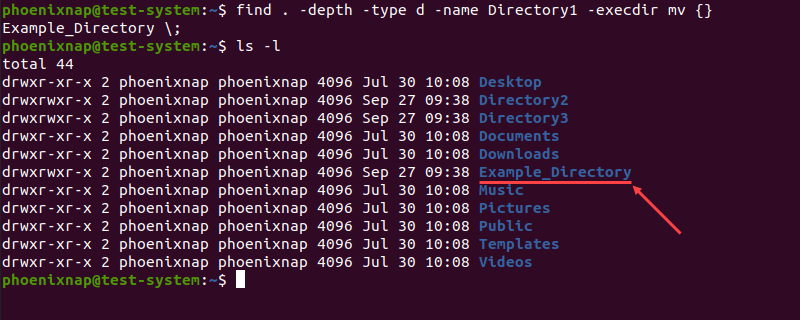
find . -depth -type d -name [current directory name] -execdir mv <> [new directory name] \;In the example above, -execdir executes the mv command once the find command locates the directory.
For instance, the command below finds and renames Directory1 into Example_Directory:
find . -depth -type d -name Directory1 -execdir mv <> Example_Directory \;Renaming Directories With Bash Scripts
Using bash scripts is another way of renaming multiple directories at the same time. Unlike the rename command, bash scripts allow you to save a template for future use.
Start by creating the script with a text editor, such as Nano:
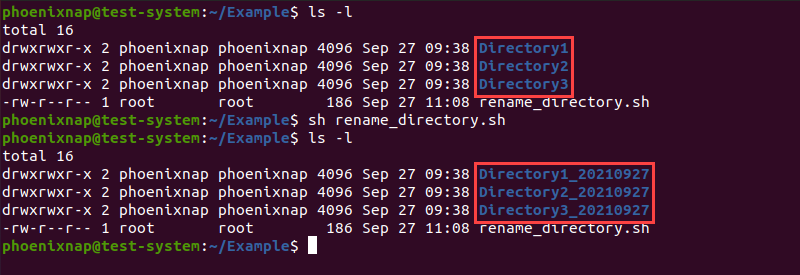
sudo nano rename_directories.shThe following example is a bash script that searches for directories and appends the current date to their name:
#!/bin/bash #Searches for directories and renames them according to the specified pattern for d in * do if [ -d "$d" ] then mv -- "$d" "_$(date +%Y%m%d)" fi done - The first line instructs the script to go through all files and directories in the current location.
- Lines 2 and 3 check for directories.
- Lines 4 and 5 append the current date to the name of any directory found.
Press Ctrl+X, type Y, and press Enter to close and save the script.
As an example, let’s use the script above to change the names of Directory1, Directory2, and Directory3, located in the Example directory.
Start by moving in to the Example directory:
Learn more about Linux cd command in our guide on how to change and move to different categories.
Next, execute the script by using the sh command:
Using the ls command allows us to verify the name change:
After reading this article, you should know how to rename directories in Linux using commands and bash scripts.
Learn more about using Linux commands in our Linux Commands All Users Should Know .