- How to Change or Reset Root Password in Linux
- Change or Reset Root Password as Root User
- Change or Reset Root Password as Sudo User
- Change or Reset Root Password Using GRUB Menu
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Aqsa Yasin
- How to Reset the Linux Mint Password
- How to Reset the Linux Mint Root Password
- Changing the User or Root Password Through a Command on the Terminal
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Omar Farooq
How to Change or Reset Root Password in Linux
If you have not logged in as a root user for a long time and have not saved the login information anywhere, there is a chance that you may lose access to the credentials for your system. It is not an unusual occurrence, but rather, a common issue, which most Linux users have probably encountered before. If this happens, you can easily change or reset the password via the command-line or the GUI (Graphical User Interface).
But what do you do if the root password must be modified or reset?
This article shows you how to change the root password for your Linux Mint 20 system via three different methods.
Note: To change the root password, you must have either the current root password, sudo privileges, or have physical access to the system. It is also recommended to save the new password(s) in a secure location to be accessed when needed.
In this article, we will cover how to:
- Change or reset root password as root user
- Change or reset root password as sudo user
- Change or reset root password using GRUB menu
It is worth mentioning that all the commands included in this article have been tested in the Linux Mint 20 system. These commands have been performed in the Terminal, which can be opened using the Ctrl+Alt+T key shortcut, or by clicking on the terminal icon present in the taskbar of the Linux system.
Change or Reset Root Password as Root User
If you have the current root password and want to reset it, you can do so by using the ‘passwd’ command. Perform the following steps to change or reset the root user password:
First, log in as a root user using the following command in Terminal:
When you are asked to provide the password, enter the current root password. Next, you will see the Terminal prompt changed to ‘#,’ indicating that you are now logged in as the root user.
To change the root password, type the following command in the Terminal:
You will be prompted to enter a new root password. Type the new password and hit the Enter key. Then, re-enter the password and press the Enter key to avoid any typos.
After entering the password, you will be shown a message saying that the password has been updated successfully.
Change or Reset Root Password as Sudo User
The root password can also be changed by a standard user with sudo privileges. You can change or reset the root user password by following the steps given below:
Type the following command as a sudo user in the Terminal to change the root password.
You will be asked to type a new password for the root user. Enter a new password and press Enter. Then, re-enter the password and press the Enter key to avoid any typos.
After entering the password, you will be shown a message saying that the password has been updated successfully.
Change or Reset Root Password Using GRUB Menu
If you are a root user and have forgotten the root password to your system, then you can reset the root password using the GRUB menu. GRUB is the first program that starts at system boot. However, keep in mind that physical access to your system is required to use the method described in this section.
To reset or change the root password using the GRUB menu, perform the following steps:
Restart the system and hold the Shift key or press the Esc key to enter into safe mode (recovery mode). Once you have entered safe mode, you will see the GRUB menu, as shown in the following screenshot.
Next, navigate to the Advanced options.
Then, to switch to the edit window, click ‘e’ on the keyboard.
You will see the following screen:
Scroll down the screen until you see the following line:
“linux / boot / vmlinuz-5.4.0- 26 -generic root = UUID = 35 \2d26aa-051e
-4dbe-adb2-7fbb843f6581 ro quiet splash”
Replace ‘ro‘ with ‘rw’ in the above line and, at the end of the line, append ‘init=/bin/bash’. It should now look like this:
“linux / boot / vmlinuz-5.4.0- 26 -generic root = UUID = 35 \
2d26aa-051e-4dbe-adb2-7fbb843f6581 rw quiet splash init = / bin / bash ”
Adding ‘rw’ and ‘init=/bin/bash’ in the above line basically tells the system to log in to bash with read/write privileges. Note that this configuration will only apply for the current boot, not for subsequent boots.
Now, use the F10 key or the Ctrl+X shortcut to boot up to a command prompt, as shown in the following screenshot.
In the command prompt that appears, type the following command:
You will be prompted for the root password. Input the root password and press the Enter key. Then, retype the password and press Enter to avoid any typos.
Note: You can change not only the root password but also any user’s password using this process.
After entering the password, you will then see a message stating that the new password has been updated.
Finally, use the Ctrl+Alt+Delete shortcut or type the following command at the command prompt to exit and reboot your system.
That is all you need to do to change or reset the root password of your Linux Mint 20 system without the sudo or root login. It is good practice to change the password frequently after some time, especially if you think it has been compromised.
Conclusion
In this article, we have identified three different methods to modify or reset the root password on your system. You can opt for any method, based on the privileges you have. If you have the root password or sudo privileges, you can easily reset the root password using the simple ‘passwd’ command. Otherwise, you can use the GRUB menu to change the root password, but only if you have physical access to the system.
I hope this article has helped you in changing or resetting the root password of your system.
About the author
Aqsa Yasin
I am a self-motivated information technology professional with a passion for writing. I am a technical writer and love to write for all Linux flavors and Windows.
How to Reset the Linux Mint Password
A password is a term that is used to obtain an access to something or someone. A group of characters are used to enter a level in a game or log into a computer network. You must generate a complicated password whenever you use a system. A password is the fundamental authentication of any device including computers, iPads, and other electronic devices. There are numerous methods to reset the passwords which are frequently forgotten by the users of devices or systems. If you forget your Linux password, it’s not a major deal because Linux offers several options to reset or change the password which is what we’re going to do in this article. We’ll demonstrate how to utilize the boot menu or the commands and command line interface to reset the root or the user passwords on Linux Mint.
How to Reset the Linux Mint Root Password
In this example, we’ll demonstrate one of the simplest ways to change or reset the passwords on Linux Mint. Linux offers us a variety of alternative options to reset the root or user password. The user root passwords are commonly forgotten. It commonly occurs, particularly if you haven’t logged in as the root user in a while. But don’t worry because we’ll provide you with the simplest method to reset your password again.
Let’s begin its practical implementation. First, we start the Linux Mint system and then restart it by clicking the “Start” button to open the menu. Next, we click the “Power” button at the bottom-left corner to access its choices.
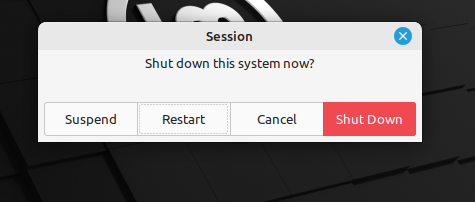
Now, after pressing the power button, a session with the “suspend,” “restart,” “cancel,” and “shutdown” buttons will appear on the screen. Since we want to restart our system, we press the restart button.
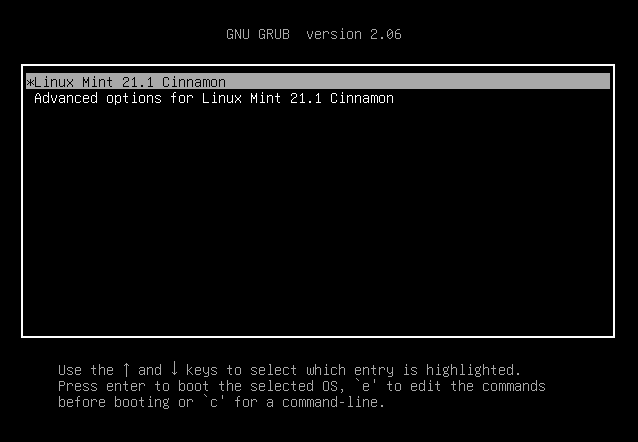
To access the “GNU GRUB” boot menu, you must now press the left “shift” button at the beginning of the boot press. You can press “ESC” on the keyboard at the GNU GRUB prompt if it cannot be enabled by holding down the shift key. The following image shows how the GRUB menu appears on the screen after holding down the shift key. Additionally, the window displays the GNU GRUB version, which is “2.06,” as well as its entries:
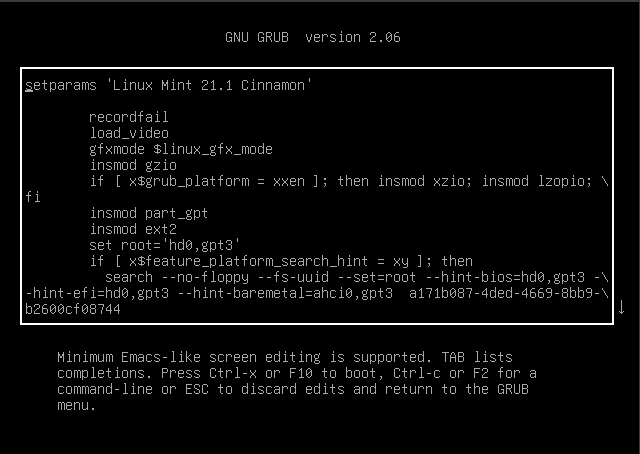
To edit the commands, hit “e” at the default option in the following step. The edit mode, which you can see in the following image, is entered when we press the “e” key from the keyboard. You may now edit the commands here.
After switching to edit mode, we use the keyboard’s arrow keys to navigate to the end of the line that begins with Linux. The following graphic demonstrates that we obtained the line that originates from Linux:
Now, we type the command at the end of this Linux line. First, we type “rw”. Then, we type “init” after a space. The term “init” refers to initialization. Simply said, init’s task is to create the processes from the scripts that are stored in the /etc/inittab configuration file which is used by the initialization system. After “init”, we type the equals symbol “=” and then the “/bin/bash”.
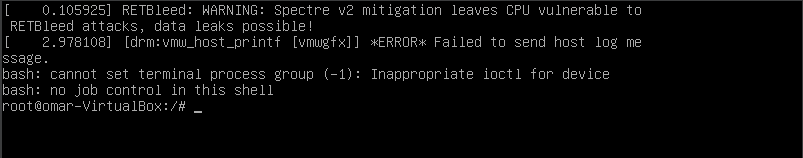
After entering the command, you must now boot your computer by pressing the “f10” key or “Ctrl-x.” After pressing the key, as shown in the following screenshot, we are now inside the root shell.
The “passwd root” command is entered to update the root password. On Linux, the “passwd” command is employed to modify the user account passwords. A common user is only able to modify their account’s password. Any user account’s password can be changed by a root.
As noted in the following illustration, the root shell now prompts you to enter your new password after you execute the previous command. For instance, if we want to use “123” as the password for our Linux system, we type “123” and then press the enter key. The shell subsequently requests us to input a new password again. We type “123” once more before hitting the enter key.
Our root password for Linux is now reset after pressing the enter key which prompt the “password updated successfully” statement to be displayed on the window as an output.
Now that we have an access to the root shell, we can also change the user password. In this section, we will do just that. But to do so, we must enter the general username for our system. In this case, the user name for our system is “Omar”. Now, we enter the password command, “passwd”, followed by the user’s name, “Omar”.
After running this command, the shell prompts you to create a new password. Enter the new password using the same instructions as in the preceding part, then hit “Enter”. The next time it prompts you to enter a new password, simply type it in again and hit “Enter”.
Now that the password is updated, the output is presented along with the “password updated successfully” message.
Changing the User or Root Password Through a Command on the Terminal
We’ll explain a different method of changing the password on Linux in this section. To change or reset the password, we use a command on the terminal. First, open the terminal. Then, input the password command, which is “passwd”, into the terminal screen.
The system prompts for the current password after running this command, so we entered it. For instance, if the current password is “123,” we must enter it and then press the enter key.
After that, we are prompted to provide a new password. We type it in here before pressing the Enter key. The new password is then required to be entered a second time.
The update of password notification will appear on the screen as seen in the image below once the new password and the password you typed again have successfully been matched.
Now that we have another user with the name “guest”, we use the sudo command in the following section to change their password. To do this, type the following commands into the “sudo” terminal, “passwd”, and “username”, which is “guest.” In our case, our other user is called “guest”. So, we type “guest” after typing “passwd”.
Therefore, when we run this command, it asks to input a new password. Here, we add the new password as we did in the previous step. After entering, it asks us to retype the password. If we do so, and the new password and the retyped password match, the password is updated.
The changed password message is now visible on the terminal.
Conclusion
We covered how to reset or modify the Linux Mint password in this article. We used two distinct approaches to password change. First, we reset the root password or modified the user passwords using the “GNU GRUB” boot menu. In the second approach, we updated the password by executing the “passwd” command in the Linux Mint terminal window. We also changed the password for another user using the sudo command.
About the author
Omar Farooq
Hello Readers, I am Omar and I have been writing technical articles from last decade. You can check out my writing pieces.