- How to Reset or Change the Root Password in Linux
- Changing Your Root Password in Ubuntu
- Step 1: Open a Terminal Window
- Step 2: Change Your Root Password
- Resetting a Root Password in Ubuntu
- Step 1: Boot to Recovery Mode
- Step 2: Drop Out to Root Shell
- Step 3: Remount the File System with Write-Permissions
- Step 4: Change the Password
- Changing the Root Password in CentOS
- Step 1: Access the Command Line (Terminal)
- Step 2: Change the Password
- Reset Root Password in CentOS
- Step 1: Access Boot Menu
- Step 2: Edit Boot Options
- Step 3: Remount the Drive
- Step 4: Changing the Password
- Step 5: Restart
- Reset lost root password (Русский)
- Через sudo
- Через отладочную консоль
- Используя bash в качестве init
- При помощи LiveCD
- chroot
- Смотрите также
- Как сбросить пароль в Linux
- Когда можно использовать GRUB
- Когда нет возможности использовать GRUB
How to Reset or Change the Root Password in Linux
In Linux, root privileges (or root access) refers to a user account that has full access to all files, applications, and system functions.
Most basic Linux user accounts run with limited privileges. This keeps users from making mistakes or accidentally exposing the system to vulnerabilities.
To use protected operating system features, a Linux user has to temporarily elevate their privileges using a command like sudo . The sudo command tells the system to run a command as a superuser, or root user. When you run a function using sudo , you’ll usually have to enter your password.
Some versions of Linux will elevate your user privileges for a set amount of time around (15 minutes) before reverting. Other versions only perform a single task with elevated privileges.
It’s a good idea to change your passwords regularly and consider using enterprise password management software.
This guide will help you change your Linux root password in Ubuntu or CentOS, or reset the password.
Changing Your Root Password in Ubuntu
Step 1: Open a Terminal Window
Right-click the desktop, then left-click Open in terminal.
Alternately, you can click Menu > Applications > Accessories > Terminal.
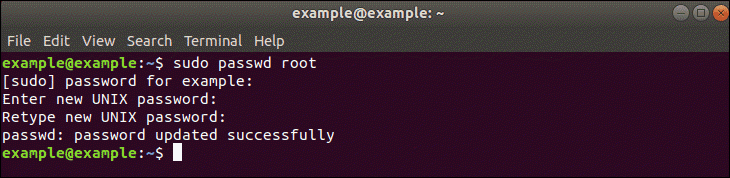
Step 2: Change Your Root Password
In the terminal window, type the following:
The system will prompt you to enter your password – this is the same password you use to log in to the system.
Next, the system will prompt you to enter a new password. Do so, and then re-enter it exactly the same when the system prompts you to retype the password. This double-entry confirms that you have typed the password correctly.
Resetting a Root Password in Ubuntu
In some situations, you may need to access an account for which you’ve lost or forgotten a password.
Step 1: Boot to Recovery Mode
Restart your system. Once you see the splash screen for the computer manufacturer, hold down the shift key. The system should come up with a black and white GRUB, or boot menu, with different Linux kernel versions displayed.
Select the second one from the top – the highest revision, followed by (recovery mode). Press Enter.
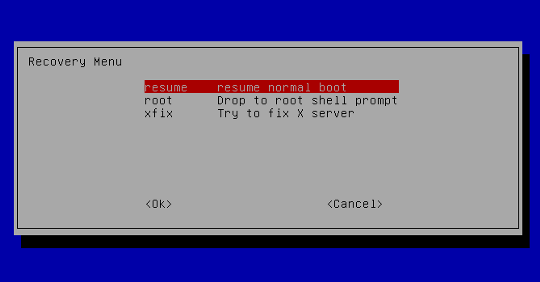
Step 2: Drop Out to Root Shell
The system should display a menu with different boot options. Use the arrow keys to navigate to the option labeled root and press Enter.
The system should respond by giving you a command-line interface with a prompt.
Step 3: Remount the File System with Write-Permissions
Right now, your system only has read-only access to your system. That means it can look at the data, but cannot make any changes. But we need write-access to change the password, so we’ll need to remount the drive with the appropriate permissions.
Press Enter. This should allow you to make changes to the data on the hard drive.
Step 4: Change the Password
Substitute the name of the user for username, then press Enter. The system asks you to type a new UNIX password and then to retype it.
Once you’ve entered and confirmed the new password, reboot the system by entering the following:
Hit Enter, and your system should restart. Don’t press any keys, let the system come up to the login screen, and test to make sure the new password works.
Note: Learn how to use the chpasswd command. Chpasswd is helpful for managing multiple passwords and making multiple changes.
Changing the Root Password in CentOS
Changing a password in CentOS is almost identical to changing it in Ubuntu.
Step 1: Access the Command Line (Terminal)
Right-click the desktop, then left-click Open in Terminal. Or, click Menu > Applications > Utilities > Terminal.
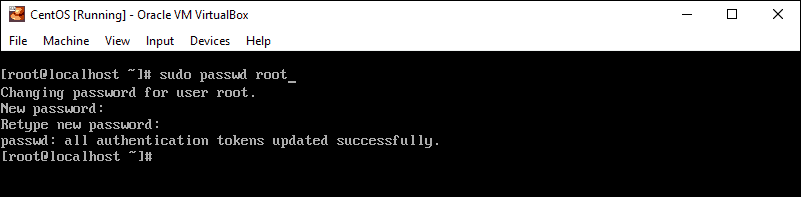
Step 2: Change the Password
At the prompt, type the following, then press Enter:
The system should prompt you to enter your existing password. Do so, then follow the prompts to enter and confirm a new root password.
Reset Root Password in CentOS
This is a similar process as in Ubuntu, with a couple of variations.
Step 1: Access Boot Menu
Restart the system, then tap the Esc key about once per second to launch the GRUB menu.
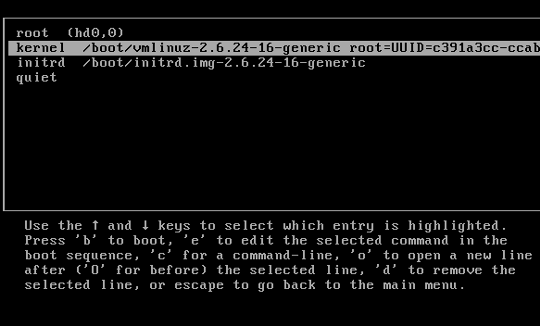
Step 2: Edit Boot Options
Use the arrows to highlight the version of Linux you boot into, then press e.
Use the arrows to highlight the line that starts with kernel or Linux.
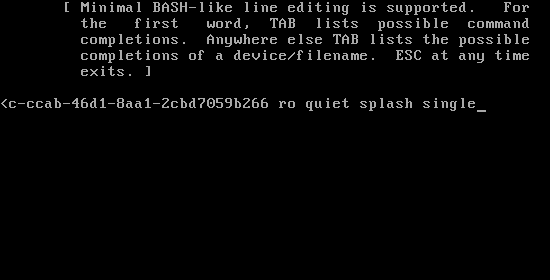
At the end of the line, add a space then type single. Press Enter, then boot into single-user mode by pressing Ctrl-X or B. (The system will display the command to use.)
Step 3: Remount the Drive
You should have a command line, and you’ll have root privileges. To enable read/write access on your hard drive, type the following:
Step 4: Changing the Password
Press Enter, and the system should prompt you to enter and confirm a new password.
Step 5: Restart
Type the following, pressing enter after each line:
Your system should restart. Confirm that your new password works by logging in.
Note: If you ever come across a Linux boot failure, be sure to save our guide on using GRUB rescue to troubleshoot it.
If you already have access to your user account, resetting or changing your password in Linux is simple.
It can be more challenging if you’ve lost or forgotten a password, but with a little creative restarting and editing, you shouldn’t find it too hard.
Sofija Simic is an experienced Technical Writer. Alongside her educational background in teaching and writing, she has had a lifelong passion for information technology. She is committed to unscrambling confusing IT concepts and streamlining intricate software installations.
In Linux, special tools were developed for managing applications. Application software for Linux typically.
The find command is a useful command-line tool in Linux. It allows you to use the terminal to search for a .
There’s a reason that tech support asks you if you’ve rebooted your Linux server. It’s cliched but true.
This guide is for users who have already configured a CentOS server and installed the Apache HTTP services.
Reset lost root password (Русский)
Состояние перевода: На этой странице представлен перевод статьи Reset lost root password. Дата последней синхронизации: 13 октября 2021. Вы можете помочь синхронизировать перевод, если в английской версии произошли изменения.
На этой странице вы сможете узнать, как сбросить забытый пароль суперпользователя. Существуют несколько способов, которые могут вам в этом помочь.
Важно: Недобросовестный пользователь может использовать указанные здесь методы для получения доступа к вашей системе. Неважно, насколько операционная система защищена от атак и как хороши ваши пароли: имея физический доступ к компьютеру, любой сможет это сделать, если вы, конечно, не выполните шифрование хранимых данных.
Через sudo
Если у вас есть установленный sudo и настроен доступ для группы wheel или для пользователя, чей пароль вы помните, вы можете сменить пароль root с помощью команды sudo passwd root .
Через отладочную консоль
- Добавьте параметр ядра systemd.debug_shell .
- Система загрузится как обычно, но запустит службу debug-shell.service , которая запустит командный интерпретатор ( /bin/sh ) на консоли tty9 . Нажмите Ctrl+Alt+F9 чтобы перейти в неё.
- Используйте команду passwd для установки нового пароля суперпользователя.
- После завершения остановите debug-shell.service .
Используя bash в качестве init
- Добавьте параметр ядра init=/bin/bash в настройках вашего загрузчика.
- Сейчас ваша корневая файловая система смонтирована только для чтения, поэтому перемонтируйте ее на чтение-запись командой mount -n -o remount,rw / .
- Используйте команду passwd для установки нового пароля суперпользователя.
- Перезагрузитесь с помощью команды reboot -f и не забудьте свой пароль снова!
Примечание: Некоторые клавиатуры не распознаются должным образом при загрузке bash из GRUB, и вы не сможете ничего ввести в консоли. В этом случае вам остается лишь использовать другой способ.
При помощи LiveCD
С загрузочным диском у вас есть два варианта: войти в сеанс chroot и использовать команду passwd , либо очистить запись с паролем в файле паролей напрямую. Вы можете использовать любой загрузочный диск на основе Linux, хотя для chroot необходимо, чтобы архитектура LiveCD совпадала с архитектурой установленной системы. Здесь мы приведем лишь способ сброса пароля при помощи chroot, так как ручное редактирование файла паролей представляет значительно больший риск.
chroot
- Загрузитесь с LiveCD и смонтируйте корневой раздел вашей основной системы.
- Используйте команду passwd —root ТОЧКА_МОНТИРОВАНИЯИМЯ_ПОЛЬЗОВАТЕЛЯ для установки нового пароля (старый пароль запрошен не будет).
- Размонтируйте корневой раздел.
- Перезагрузитесь и введите новый пароль.
Смотрите также
Как сбросить пароль в Linux
Давайте рассмотрим несколько способов сбрасывания системного пароля в Linux. Вы наверное знаете, что у пользователя root есть права на изменение пароля любого пользователя в системе. А что если вы забыли пароль от рута? Вот об этом и пойдет речь в статье.
При восстановления пароля (рута или любого другого пользователя) встречаются две различные ситуации, требующие разного подхода.
Когда можно использовать GRUB
- В окне загрузчика GRUB выделите строку с нужной версией линукса, для которого вам нужно сбросить пароль
- Нажмите ‘e’ для редактирования. Выберите строку ядра. Добавьте ‘single’ в конец строки. Нажмите ‘b’ для загрузки. Если система продолжает запрашивать пароль рута, добавьте в конец строки init=/bin/bash Снова нажмите ‘b’ для загрузки
- После этого вы либо увидите приглашение для рута, либо восстанавливающее меню, где нужно выбрать строку с рутом. Используйте passwd для того чтобы изменить пароль у любого пользователя
Когда нет возможности использовать GRUB
- Загрузитесь с live CD
- Выберите «Попробовать Ubuntu без изменений на вашем компьютере» (Try Ubuntu without any changes to your computer)