- How to Restart Network in Ubuntu
- Restart the network in Ubuntu via the command line
- 1. Restarting the Network Manager Service
- 2. nmcli
- 3. nmtui
- 4. ifup & ifdown
- Restart the network in Ubuntu graphically
- Bonus Tip: Refresh the available network list
- Wrapping Up
- Linux restart network; a step-by-step guide
- What is a network interface?
- What is a Linux network interface?
- Physical network interfaces.
- Virtual network interfaces
- How to configure the Linux network interface
- Step one:
- Step two:
- Step three:
- Step four:
- Step five:
- Step six:
- Step seven:
- Last words on Linux restart the network.
How to Restart Network in Ubuntu
Here are 6 ways you can restart the network in Ubuntu and other Linux distros. Also learn to refresh wireless network connection in Ubuntu Linux.
Restart the network in Ubuntu via the command line
If you are using the Ubuntu server edition, you are already in the terminal. If you are using the desktop edition, you can access the terminal using Ctrl + Alt + T keyboard shortcut in Ubuntu.
Now you have several commands to restart the network in Ubuntu. Some (or perhaps most) commands mentioned here should also be applicable for restarting the network in Debian and other Linux distributions.
1. Restarting the Network Manager Service
This is the easiest way to restart your network using the command line. It’s equivalent to the graphical way of doing it (restarts the Network-Manager service).
sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager.serviceThe network icon should disappear for a moment and then reappear.
2. nmcli
This is yet another tool for handling networks on a Linux machine. It is a pretty powerful tool that I find very practical. Many sysadmins prefer it since it is easy to use. This tool is a part of the NetworkManager package.
There are two steps to this method: turning the network off and then turning it back on.
sudo nmcli networking offThe network will shut down and the icon will disappear. To turn it back on:
You can check out the man page of nmcli for more options.
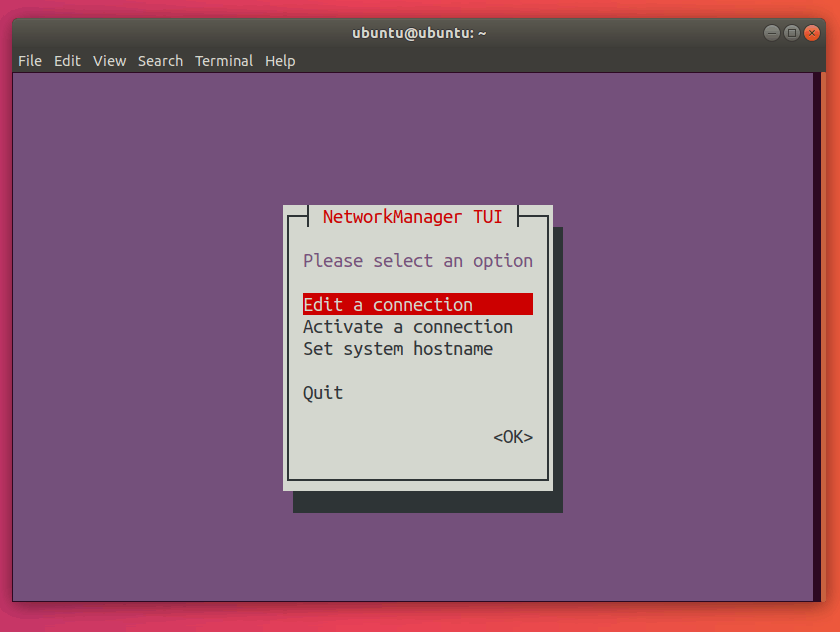
3. nmtui
This is another method often used by system administrators. It is a text menu (in a Terminal User Interface) for managing networks right in your terminal. It is also a part of the Network Manager tool.
This should open up the following menu:
Note that in nmtui, you can select another option by using the up and down arrow keys.
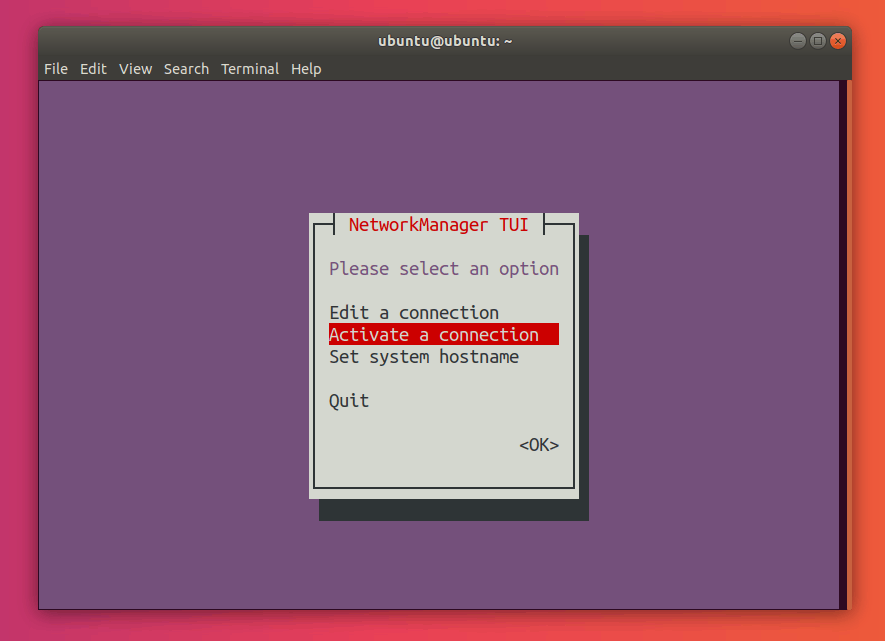
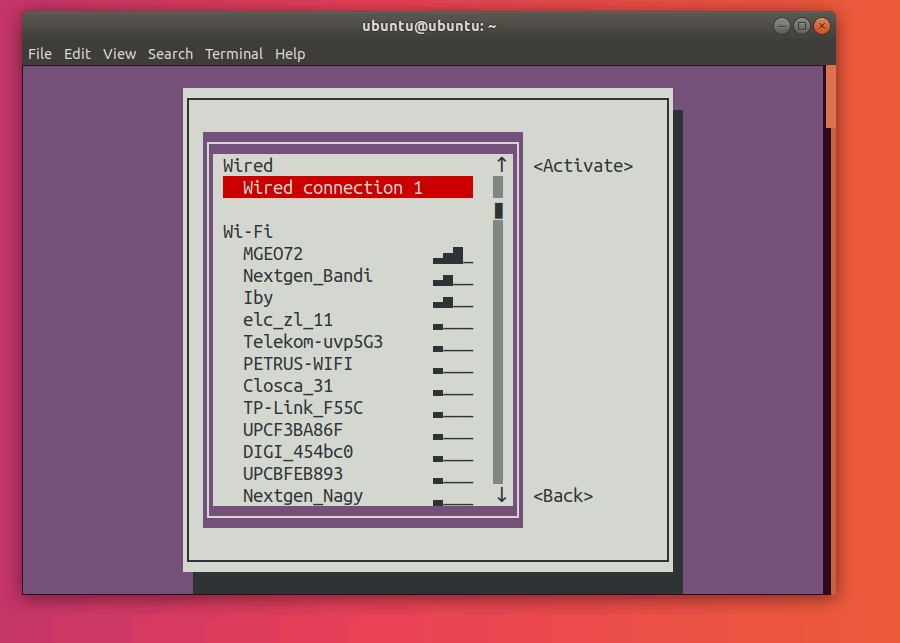
Select Activate a connection:
Press Enter. This should now open the connections menu.
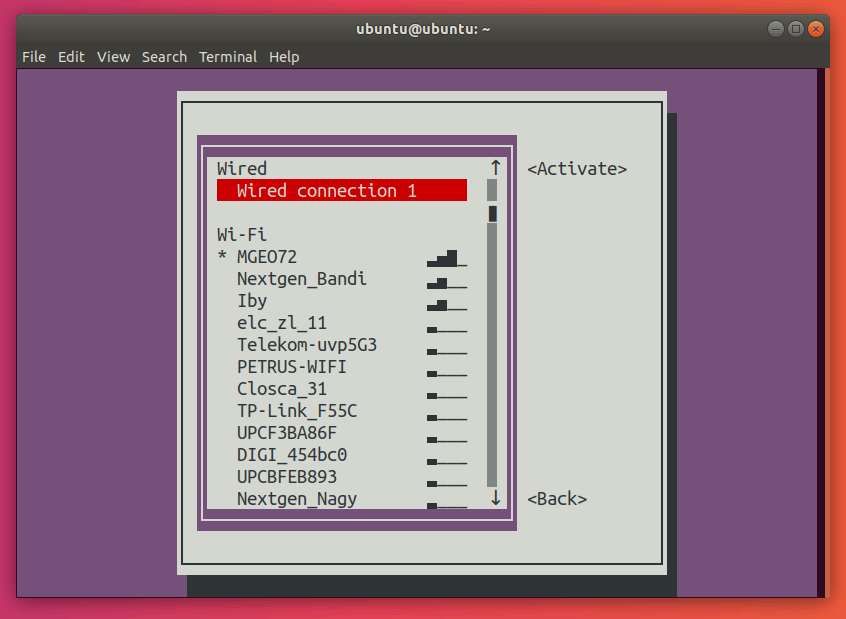
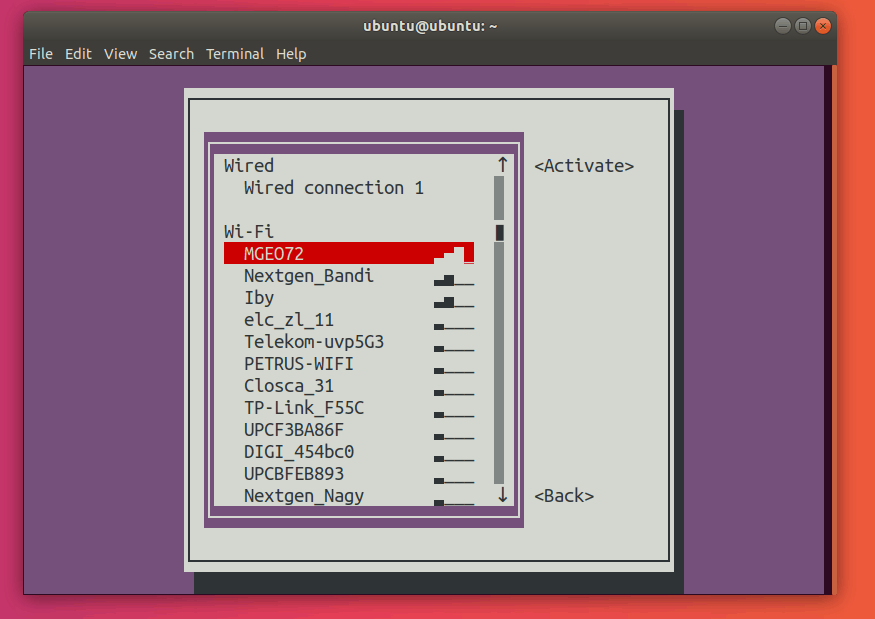
Here, go ahead and select the network with a star (*) next to it. In my case, it’s MGEO72.
Press Enter. This should deactivate your connection.
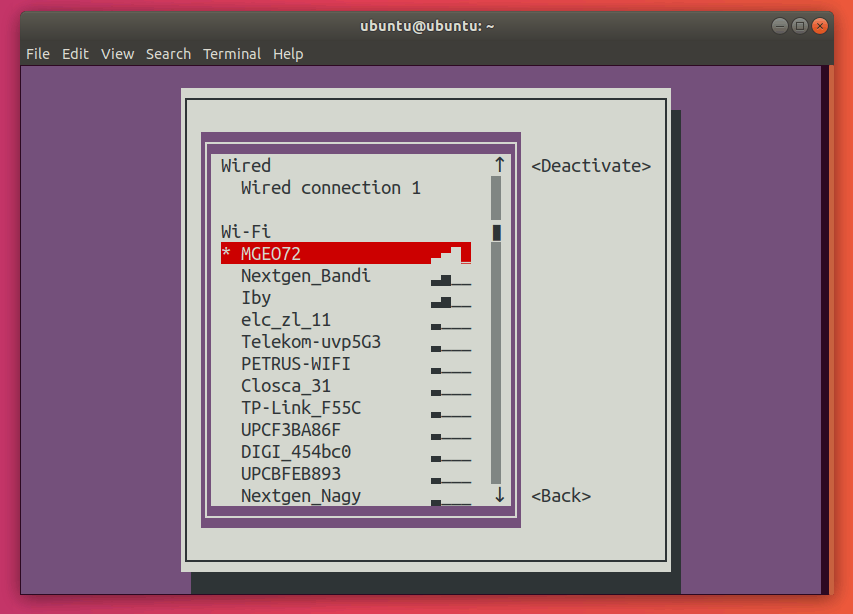
Select the connection you want to activate and press Enter. This should activate the desired connection.
Press Tab twice to select the button, and exit from the main menu. This is how you can restart a connection with nmtui.
4. ifup & ifdown
These commands handle a network interface directly, changing its state to one in which it either can or can not transmit and receive data. It’s one of the must-know networking commands in Linux.
To shut down all network interfaces, use ifdown and then use ifup to turn all network interfaces back on.
A good practice would be to combine both of these commands:
sudo ifdown -a && sudo ifup -aNote: This method will not make the network icon in your systray disappear, and yet you won’t be able to have a connection of any sort.
That’s it! You have successfully restarted your network.
Restart the network in Ubuntu graphically
This is, of course, the easiest way of restarting the network for Ubuntu desktop users. If this one doesn’t work, you can of course check the command line options mentioned in the previous section.
NM-applet is the system tray applet indicator for NetworkManager. That’s what we’re going to use to restart our network.
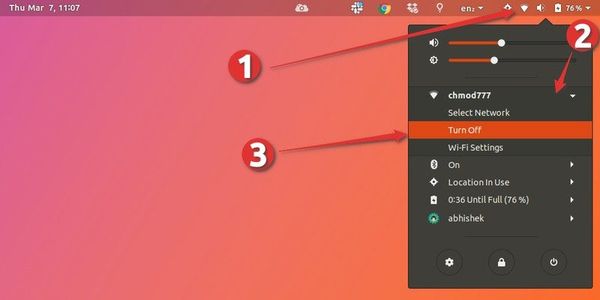
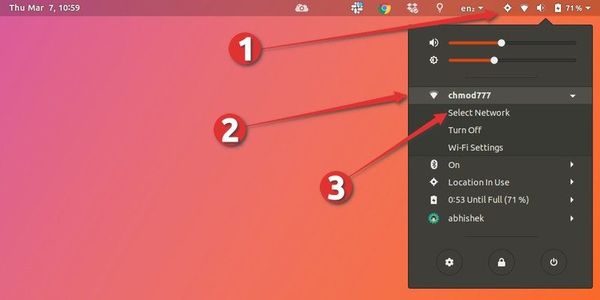
First of all, check out your top panel. You should find a network icon in your system tray (in my case, it is a Wi-Fi icon, since that’s what I use).
Go ahead and click on that icon (or the sound or battery icon). This will open up the menu. Select “Turn Off” here.
The network icon should now disappear from the top panel. This means the network has been successfully turned off.
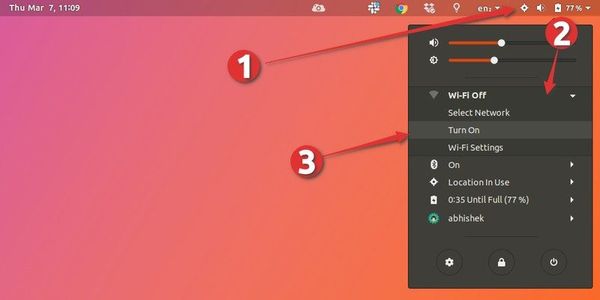
Click again on your systray to reopen the menu. Select “Turn On”.
Congratulations! You have now restarted your network.
Bonus Tip: Refresh the available network list
Suppose you are connected to a network already but you want to connect to another network. How do you refresh the WiFi to see what other networks are available? Let me show you that.
Ubuntu doesn’t have a ‘refresh wifi networks’ option directly. It’s sort of hidden.
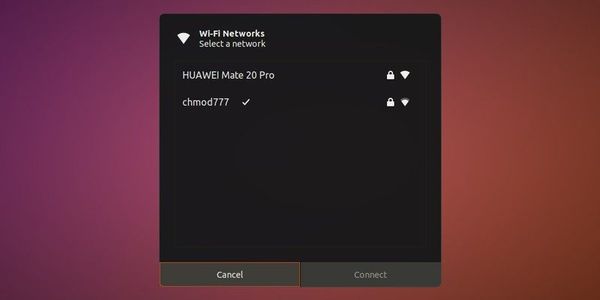
You’ll have to open the setting menu again and this time, click on “Select Network”.
Now, you won’t see the list of available wireless networks immediately. When you open the networks list, it takes around 5 seconds to refresh and show up other available wireless networks.
And here, you can select the network of your choice and click «Connect». That’s it.
Wrapping Up
Restarting your network or connection is something that every Linux user has to go through at some point in their experience. These tools can come in handy for doing the same.
But, if you’re stranded with not finding any wireless interface to connect with (no Wi-fi hardware detected), you can refer to this article.
You can also check out some of the most important networking commands in Linux:
We hope that we have helped you with plenty of methods for handling such issues!
What do you use to restart/handle your network? Is there something we missed? Leave us a comment below.
Linux restart network; a step-by-step guide
Learn how to efficiently restart network services in Linux to resolve connectivity issues, optimize performance, and ensure seamless communication within your server infrastructure — a comprehensive guide for network management and troubleshooting.
List of content you will read in this article:
Linux network interfaces are an essential part of the Linux networking stack. They let network devices communicate with one another and allow Linux computers to connect to the internet and other networks. Knowing how to configure and manage Linux network interfaces is critical for any Linux administrator or user who wants to improve network performance and security. This blog article will review the fundamentals of Linux network interfaces and discuss the Linux restart network.
We will review the most significant configuration options and give step-by-step directions for configuring a primary network interface. This post will provide the information and skills you need to handle Linux network interfaces efficiently, whether a novice or experienced user.
What is a network interface?
A network interface is a piece of software or hardware that links a device to a network. It is an endpoint that allows devices on a network to communicate with one another.
A network interface can be either a physical interface, such as an Ethernet connector, or a virtual interface established by the software. Each network interface is given a unique name, which is common in the form of ethX or wlanX for physical interfaces and virbrX or vnetX for virtual interfaces, where X is a number that distinguishes between interfaces.
What is a Linux network interface?
A network interface is a software component in Linux representing either a real or virtual network device. Each interface has a unique name and is in charge of delivering and receiving data on the network.
The kernel manages network interfaces in Linux, and their configuration may be handled via the ifconfig, ip, or nmtui commands, depending on the distribution and version of Linux. There are two types of network interfaces in Linux:
Physical network interfaces.
Depending on the distribution’s naming practice, the physical network interfaces in Linux are recognized by names such as eth0, eth1, enp0s3, or enp0s25. Typically, these interfaces are linked to the network through an Ethernet cable or a wireless adapter.
Virtual network interfaces
In contrast, software builds virtual network interfaces and does not correlate to a genuine network adapter. These interfaces provide various functions, including virtual networking, virtual private networks (VPNs), and network bridging. Tap, tun, veth, and macvlan are examples of virtual interfaces in Linux.
Linux network interfaces can be configured with extra options such as the MTU (maximum transmission unit) size, speed, duplex mode, multicast address, and fundamental setup parameters such as IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway. The ifconfig, ip, and ethtool commands can configure these settings.
Overall, Linux network interfaces are an essential part of the Linux networking stack, and their setup and administration are key for guaranteeing optimal network performance and security.
Linux restart network; step by step
To restart the network on a Linux system, you can follow these steps:
- Open a terminal window.
- Depending on the Linux distribution, you may need to be logged in as the root user or use the sudo command to execute the following commands.
- Use the following command to stop the network service:
* Alternatively, you can use the following command to restart the network service, which will stop and then start it:
systemctl restart network
This command will show you the current status of the network service. If running, it should display an output similar to this:
network. Service — LSB: Bring up/down networking
Loaded: loaded (/etc/rc.d/init.d/network; bad; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (exited) since Fri 2023-02-19 10:12:22 UTC; 5s ago
Process: 3079 ExecStop=/etc/rc.d/init.d/network stop (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 3085 ExecStart=/etc/rc.d/init.d/network start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Feb 19 10:12:22 myserver systemd[1]: Starting LSB: Bring up/down networking.
Feb 19 10:12:22 myserver network[3085]: Starting network.
Feb 19 10:12:22 myserver network[3085]: Bringing up loopback interface: [ OK ]
Feb 19 10:12:22 myserver network[3085]: Bringing up interface eth0: [ OK ]
Feb 19 10:12:22 myserver systemd[1]: Started LSB: Bring up/down networking.
🎉🎉Unlock the full potential of your online ventures with our cutting-edge Linux VPS hosting, offering blazing-fast performance, robust security, and unmatched flexibility to fuel your digital success.🎉🎉
How to configure the Linux network interface
Now that we know everything we need to know about the Linux restart network, it won’t hurt us to talk about the configuration process of the Linux Interface. To configure a network interface in Linux, you can follow these steps:
Step one:
Open a terminal window or connect to the Linux system remotely using SSH.
Step two:
Identify the name of the network interface that you want to configure. You can use the ifconfig or ip addr command to list all the available network interfaces on the system.
Step three:
Stop the network interface by executing the command sudo ifdown . This step is optional but ensures no network traffic is transmitted while you change the interface configuration.
Step four:
Set the interface’s IP address and subnet mask using the ifconfig or ip addr command. For example, to set the IP address of the interface eth0 to 192.168.1.10 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0, you can execute the following command: sudo ifconfig eth0 192.168.1.10 netmask 255.255.255.0 or sudo ip addr add 192.168.1.10/24 dev eth0.
Step five:
Set the default gateway by using the route add default gw command. For example, to set the default gateway to 192.168.1.1, execute the following command: sudo route add default gw 192.168.1.1.
Step six:
Set the DNS server by editing the /etc/resolv.conf file and add the IP addresses of the DNS servers you want to use. For example, you can add the following line to the file: nameserver 8.8.8.8.
Step seven:
Start the network interface by executing the command sudo ifup to apply the changes made in the previous steps.
Test the network connectivity by pinging a remote IP address or domain name. Note that the exact commands and configuration files may vary depending on the Linux distribution and version that you are using. It is recommended to consult the documentation for your specific distribution to ensure you use the correct commands and configuration files.
Last words on Linux restart the network.
Let’s end our article about the Linux restart network right here. It is essential to know restarting the Linux network is a must-do for every Linux administrator or user who wants to guarantee that their machine is connected to the network and communicates successfully.
Whether you’re having network connectivity problems, adding or deleting network interfaces, or changing the network settings, restarting the network is frequently the most straightforward and successful approach to execute these changes.
Understanding how to restart the Linux network allows you to guarantee that your Linux system is constantly connected to the network and communicates appropriately, even while experiencing network-related problems. You may quickly restart the Linux network and return to work by following the instructions in this post.
People also read: