- How to Start, Stop & Restart Services in Ubuntu and Other Linux Distributions
- Method 1: Managing services in Linux with systemd
- 1. List all services
- 2. Start a service
- 3. Stop a service
- 4. Restart a service
- 5. Check the status of a service
- Method 2: Managing services in Linux with init
- 1. List all services
- 2. Start a service
- 3. Stop a service
- 4. Restart a service
- 5. Check the status of a service
- Как запустить, остановить и перезапустить сервисы в Linux
- Базовый синтаксис команды systemctl
- Как проверить, работает ли служба в Linux
- Как перезапустить сервис
- Как перезагрузить конфигурационные файлы сервиса
- Как запустить сервис
- Как остановить сервис
- Как включить сервис при загрузке
- Как отключить сервис при загрузке
- How to Restart Services in Linux
- Community Q&A
- You Might Also Like
- How to Restart Service in Linux
How to Start, Stop & Restart Services in Ubuntu and Other Linux Distributions
Services are essential background processes that are usually run while booting up and shut down with the OS.
If you are a sysadmin, you’ll deal with the service regularly.
If you are a normal desktop user, you may come across the need to restart a service like setting up Barrier for sharing mouse and keyboard between computers. or when you are using ufw to setup firewall.
Today I will show you two different ways you can manage services. You’ll learn to start, stop and restart services in Ubuntu or any other Linux distribution.
Ubuntu and many other distributions these days use systemd instead of the good old init.
In systemd, you manage sevices with systemctl command.
In init, you manage service with service command.
You’ll notice that even though your Linux system uses systemd, it is still able to use the service command (intended to be used with init system). This is because service command is actually redirect to systemctl. It’s sort of backward compatibility introduced by systemd because sysadmins were habitual of using the service command.
I’ll show both systemctl and service command in this tutorial.
I am Ubuntu 18.04 here, but the process (no pun intended) is the same for other versions.
Method 1: Managing services in Linux with systemd
I am starting with systemd because of the obvious reason of its widespread adoption.
1. List all services
In order to manage the services, you first need to know what services are available on your system.
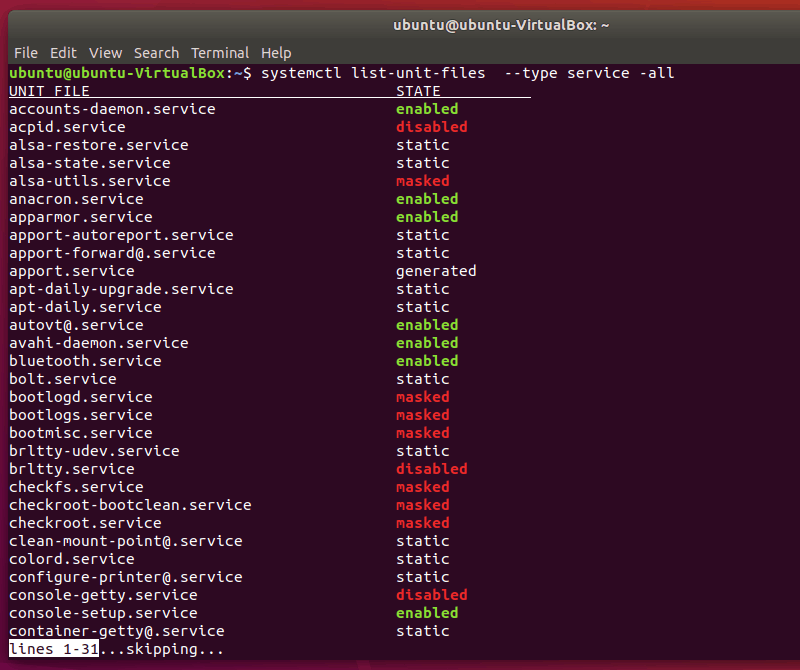
You can use the systemd command to list all the services on your Linux system:
systemctl list-unit-files --type service -allThis command will output the state of all services. The value of a service’s state can be enabled, disabled, masked (inactive until mask is unset), static and generated.
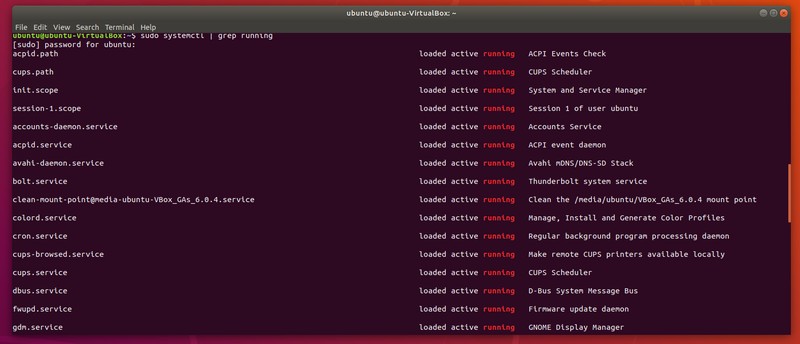
Combine it with the grep command and you can display just the running services:
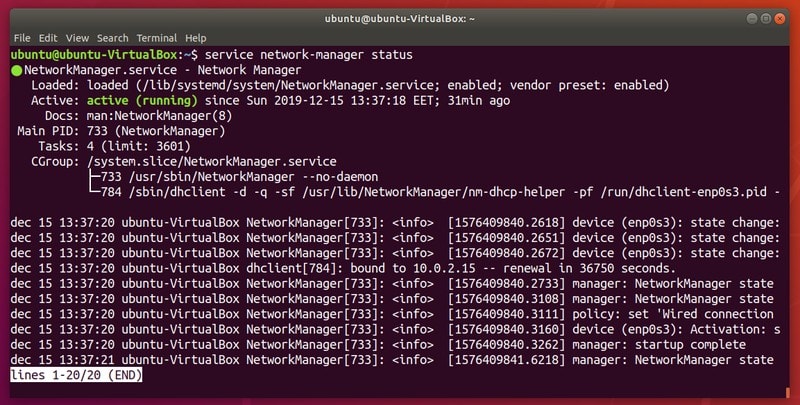
sudo systemctl | grep runningNow that you know how to reference all different services, you can start actively managing them.
Note: name> in the commands should be replaced by the name of the service you wish to manage (e.g. network-manager, ufw etc.).
2. Start a service
To start a service in Linux, you just need to use its name like this:
3. Stop a service
To stop a systemd service, you can use the stop option of systemctl command:
4. Restart a service
To restart a service in Linux with systemd, you can use:
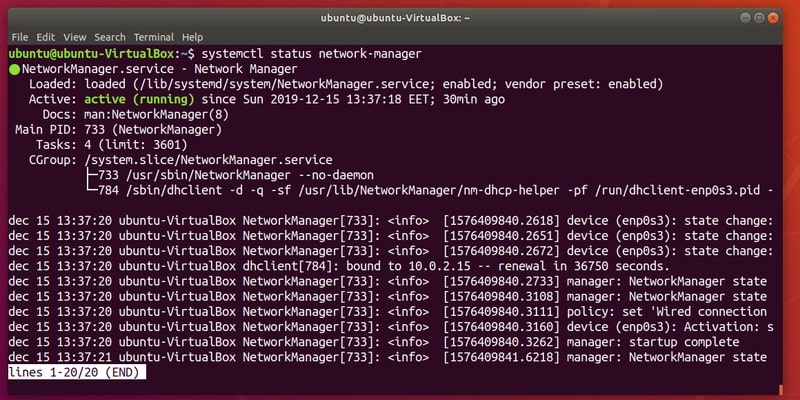
5. Check the status of a service
You can confirm that you have successfully executed a certain action by printing the service status:
This will output information in the following manner:
That was systemd. Let’s switch to init now.
Method 2: Managing services in Linux with init
The commands in init are also as simple as system.
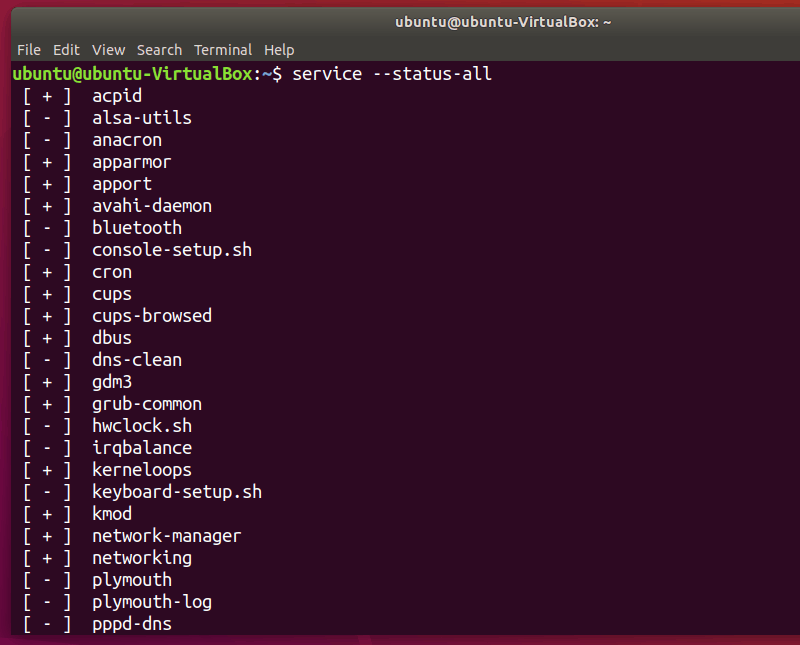
1. List all services
To list all the Linux services, use
The services preceded by [ – ] are disabled and those with [ + ] are enabled.
2. Start a service
To start a service in Ubuntu and other distributions, use this command:
3. Stop a service
Stopping a service is equally easy.
4. Restart a service
If you want to restart a service, the command is:
5. Check the status of a service
Furthermore, to check if your intended result was achieved, you can output the service status:
This will output information in the following manner:
This will, most importantly, tell you if a certain service is active (running) or not.
Wrapping Up
Today I detailed two very simple methods of managing services on Ubuntu or any other Linux system. I hope this article was helpful to you.
Which method do you prefer? Let us know in the comment section below!
Как запустить, остановить и перезапустить сервисы в Linux
Linux обеспечивает детальный контроль над системными службами через systemd с помощью команды systemctl. Службы могут быть включены, выключены, перезапущены, перезагружены или даже включены или отключены при загрузке. Если вы используете Debian, CentOSили Ubuntu, ваша система, вероятно, использует systemd.
Это руководство покажет вам, как использовать основные команды для запуска, остановки и перезапуска служб в Linux.
Базовый синтаксис команды systemctl
Основной синтаксис для использования команды systemctl:
systemctl [command] [service_name]
Как правило, вам нужно запускать это как суперпользователь поэтому команды будут начинаться с sudo.
Как проверить, работает ли служба в Linux
Чтобы проверить, активна ли служба или нет, выполните следующую команду:
sudo systemctl status SERVICE_NAME
Замените SERVICE_NAME на нужный сервис.
В нашем случае мы будем брать за пример веб-сервер Apache.
Интересный факт: в Ubuntu и других дистрибутивах на основе Debian служба Apache называется apache2. В CentOS и других дистрибутивах RedHat служба Apache называется httpd или httpd.service
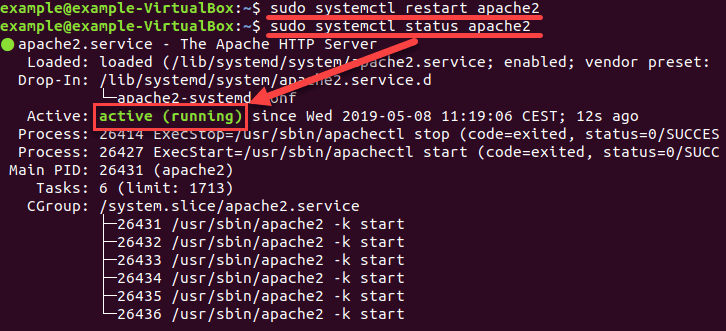
sudo systemctl status apache2
Так мы проверили состояние Apache. Выходные данные показывают, что служба активна (работает), как на рисунке ниже:

Как перезапустить сервис
Чтобы остановить и перезапустить службу в Linux, используйте команду:
sudo systemctl restart SERVICE_NAME
Где SERVICE_NAME — имя вашего сервиса.
После выполнения команды ваш сервис должен снова заработать. Вы можете проверить состояние с помощью команды status
Для перезапуска нашего сервера Apache используем:
sudo systemctl restart apache2
Как перезагрузить конфигурационные файлы сервиса
Чтобы служба перезагрузила свои файлы конфигурации, введите в терминале следующую команду:
sudo systemctl reload SERVICE_NAME
После перезагрузки проверьте ее состояние командой status для подтверждения.
В нашем примере мы перезагрузили Apache, используя:
sudo systemctl reload apache2
Как запустить сервис
Чтобы запустить службу в Linux вручную, введите в терминале следующее:
sudo systemctl start SERVICE_NAME
Например, команда для запуска службы Apache:
sudo systemctl start apache2
Как остановить сервис
Чтобы остановить активную службу в Linux, используйте следующую команду:
sudo systemctl stop SERVICE_NAME
Для нашего апача используем команду
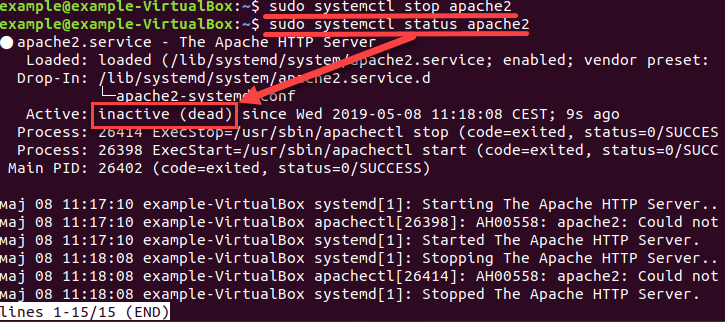
sudo systemctl stop apache2
Проверьте, остановился ли сервис с помощью команды status . Вывод должен показать, что сервис неактивен — inactive (dead)
Как включить сервис при загрузке
Чтобы настроить службу для запуска при загрузке системы, используйте команду:
sudo systemctl enable SERVICE_NAME
Чтобы включить Apache при загрузке системы, выполните команду:
sudo systemctl enable apache2
Как отключить сервис при загрузке
Вы можете запретить запуск службы при загрузке с помощью команды:
sudo systemctl disable SERVICE_NAME
sudo systemctl disable apache2
How to Restart Services in Linux
This article was co-authored by wikiHow staff writer, Jack Lloyd. Jack Lloyd is a Technology Writer and Editor for wikiHow. He has over two years of experience writing and editing technology-related articles. He is technology enthusiast and an English teacher.
The wikiHow Tech Team also followed the article’s instructions and verified that they work.
This article has been viewed 469,101 times.
This wikiHow teaches you how to force a currently running service to restart in Linux. You can do this with just a few simple commands regardless of your Linux type.
- Since Linux distributions vary in appearance from release to release, you may have to look for the «Terminal» or command line app inside of a folder in the Menu.
- You may find the «Terminal» app on the desktop or in the toolbar at the bottom of the screen instead of in the Menu.
- Some Linux distributions have a command line bar at the top or bottom of the screen.
Find the command name of the service that you want to restart. You’ll typically find the name of the service (e.g., «Apache») on the left side of the screen, while the command name (e.g., «httpd» or «apache2», depending on your Linux distribution) will appear on the right side.
- For example, to restart Apache on Ubuntu Linux, you would type sudo systemctl restart apache2 into Terminal.
- If the service doesn’t restart after doing this, try typing in sudo systemctl stop service , pressing ↵ Enter , and then entering sudo systemctl start service .
Community Q&A
It means both, actually. If you’re talking about hard drives and storage, SSHD is correct for solid state hybrid drive. If you’re talking about Linux, the Secure Shell Daemon is also correct.
Thanks! We’re glad this was helpful.
Thank you for your feedback.
As a small thank you, we’d like to offer you a $30 gift card (valid at GoNift.com). Use it to try out great new products and services nationwide without paying full price—wine, food delivery, clothing and more. Enjoy! Claim Your Gift If wikiHow has helped you, please consider a small contribution to support us in helping more readers like you. We’re committed to providing the world with free how-to resources, and even $1 helps us in our mission. Support wikiHow
Thanks! We’re glad this was helpful.
Thank you for your feedback.
As a small thank you, we’d like to offer you a $30 gift card (valid at GoNift.com). Use it to try out great new products and services nationwide without paying full price—wine, food delivery, clothing and more. Enjoy! Claim Your Gift If wikiHow has helped you, please consider a small contribution to support us in helping more readers like you. We’re committed to providing the world with free how-to resources, and even $1 helps us in our mission. Support wikiHow
Thanks! We’re glad this was helpful.
Thank you for your feedback.
As a small thank you, we’d like to offer you a $30 gift card (valid at GoNift.com). Use it to try out great new products and services nationwide without paying full price—wine, food delivery, clothing and more. Enjoy! Claim Your Gift If wikiHow has helped you, please consider a small contribution to support us in helping more readers like you. We’re committed to providing the world with free how-to resources, and even $1 helps us in our mission. Support wikiHow
To see a comprehensive list of all current services in all directories on your computer, enter ps -A into Terminal.
Don’t stop services at random while trying this out. Some of the services listed are necessary to keep your system stable and running happily.
You Might Also Like
Simple Ways to Format a Linux Hard Disk to Windows
Can Linux Run .exe Files? How to Run Windows Software on Linux
How to Open Linux Firewall Ports: Ubuntu, Debian, & More
How to Run an INSTALL.sh Script on Linux in 4 Easy Steps
Use Ping in Linux: Tutorial, Examples, & Interpreting Results
How to Delete Read-Only Files in Linux
How to Restart Service in Linux
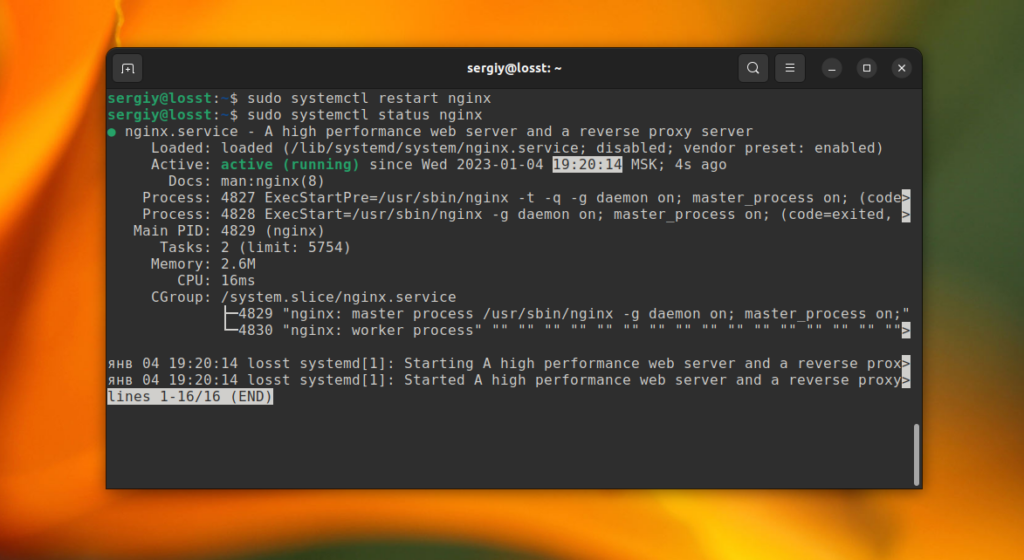
You can use the restart command to restart Systemd services. This command stops the service and then starts it back. Or it just starts the service if it is not running. For example, you can restart the Nginx web server using this command:
sudo systemctl restart nginx
If everything is okay, the command will output nothing. But if an error occurs while the process is stopped or started, an error message will be displayed.
When you want to restart the service only if it is running use the try-restart command:
sudo systemctl try-restart nginx
The Systemd initialization system supports not only services restarting, when the services are entirely stopped but also soft reloading. In this case, the service continues working without downtime and only updates its configuration from configuration files. You can use this reloading by entering the reload command:
sudo systemctl reload nginx
This method is not supported by all services. If you don’t know whether a specific service supports reloading but still want to restart it, use the reload-or-restart command. For example:
sudo systemctl reload-or-restart nginx
This command will use soft reloading if it is supported. But if it is not, the service will be restarted in the usual way. You can read more about service management in Linux in this article.
Found a mistake in the text? Let me know about that. Highlight the text with the mistake and press Ctrl+Enter.