- Что такое reverse dns lookup и как получить reverse dns
- Как получить запись reverse DNS lookup на linux?
- Top 3 ways to lookup reverse DNS on Linux
- Reverse DNS lookup in Linux
- Method 1: Check the reverse DNS using the Dig command
- Method 2: Check the reverse DNS using the Host command
- Method 3: Using the Nslookup command
- Conclusion
- What Is Reverse DNS and How Does It Work?
- What Is Reverse DNS?
- What Is Reverse DNS Lookup Used For?
- How Does Reverse DNS Lookup Work?
- How to Do a Reverse DNS?
- Reverse DNS Lookup Command
- Reverse DNS Tools
Что такое reverse dns lookup и как получить reverse dns
Что такое Reverse DNS легко понять, если вы знаете что такое DNS. Получение Reverse DNS — противоположенность DNS.
Т.е. если традиционный (прямой) DNS заключается в получении ip-адреса по хосту, то Reverse DNS (обратный, противоположенный) — это получение хоста по ip-адресу. Также Reverse DNS называют PTR-записью (pointer, указатель).
Как получить запись reverse DNS lookup на linux?
Для получения reverse DNS нужно воспользоваться одной из двух команд:
Если вам нужно только имя хоста (без дополнительной информации), то удобно будет воспользоваться командой dig с опциями -x и +short , которая вернёт одну строку — только искомый host.
-x — опция говорит включить обратный поиск DNS вместо прямого. Обратный поиск DNS (reverse dns lookup) означает, что вы хотите искать домен или имя хоста по IP-адресу.
+short — опция скрывает информацию (номер порта и адрес) о сервере, который предоставил ответ.
$ nslookup 93.125.99.10 Server: 127.0.1.1 Address: 127.0.1.1#53 Non-authoritative answer: 10.99.125.93.in-addr.arpa name = vh40.hosterby.com. Authoritative answers can be found from: 99.125.93.in-addr.arpa nameserver = ns1.tutby.com. 99.125.93.in-addr.arpa nameserver = ns2.tutby.com. ns2.tutby.com internet address = 178.124.133.100 ns1.tutby.com internet address = 93.125.30.200 $ dig +short -x 93.125.99.10 vh40.hosterby.com.
Как видно, dig вернул всего одну строку vh40.hoster.by.
Пример reverse DNS на картинке:
Хост jeka.by висит на ip 93.125.99.10. Это дешёвый shared хостинг. На этом IP висит большое количество сайтов. Для этого же ip обратным адресом является хост моего хостера vh40.hosterby.com.
Солидные ресурсы в обязательном порядке имеют собственные настроенные reverse dns. Это нужно хотя бы для того, чтобы вероятность попадания электронных писем в спам была меньше. Для этого адрес в поле From должен совпадать с доменом, указанным в reverse dns (совпадать с PTR). Это связано с тем, что спамеры часто подделывают доменные имена при отправке почты.
Для PTR записей нет конкретных технических требований. Но всё же большинство провайдеров используют следующие правила:
- Для каждого IP-адреса существует одна единственная PTR запись;
- Для серверa с несколькими IP-адресами будут прописаны несколько PTR записей, по одной на каждый IP-адрес;
- Для любого почтового сервера должна быть установлена MX-запись и A-запись – это правило является одним из самых важных;
- Для каждой PTR записи должна быть А-запись, а вот наоборот – не обязательно.
Дата добавления: 9 лет назад
Top 3 ways to lookup reverse DNS on Linux
G enerally speaking, the forward Domain Name Server or DNS can be used to detect the associated IP address for a particular domain name. In contrast, the reverse Domain Name Server or “rDNS” is the process of determining the hostname associated with a given IP address. In other words, we can say that the reverse DNS will perform a reverse IP lookup.
Reverse DNS lookup in Linux
Before starting, let’s check first how to issue a forward DNS lookup using the dig command as follows:
As you can notice, using the above command, you will be able to get the Facebook IP address.
Method 1: Check the reverse DNS using the Dig command
Typically, the dig is a shortcut for domain information groper, and it can be used to return the domain name.
- A (the IP address)
- TXT (text annotations)
- MX (mail exchanges)
- NS nameservers
Moreover, you can use some additional options just to display the answer section as following:
dig -x 157.240.195.35 +noall +answer
The Dig Command With Options
Method 2: Check the reverse DNS using the Host command
Host checks DNS, transforms domain names to IP addresses, and vice versa. If no arguments or options are given, the host will print a summary of its command-line arguments and options.
host [-aCdlnrsTwv] [-c class] [-N ndots] [-R number] [-t type] [-W wait] [-m flag] [-4] [-6] [server]
In this method, the host command will be used to return the domain name as follows:
Method 3: Using the Nslookup command
Finally, the last command that can be used to return the domain name is the nslookup command. It is a simple command that is used to query the domain name servers.
Using The Nslookup Command
Conclusion
That’s all about various ways of looking up reverse DNS from your Linux system. All the mentioned commands are Distro independent; hence you should be able to execute on any Linux system. What other method do you prefer and why? Let us know in the comments below.
What Is Reverse DNS and How Does It Work?
Home » SysAdmin » What Is Reverse DNS and How Does It Work?
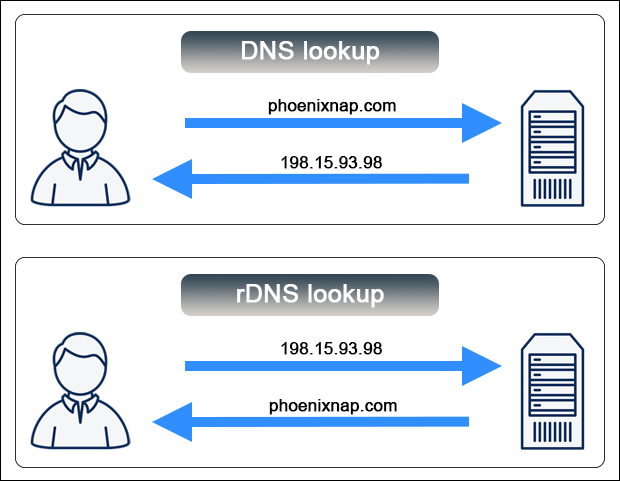
Reverse DNS (rDNS) is a process that resolves an IP address back to a domain name, the opposite of a forward DNS query.
In this article, you will learn what reverse DNS is and how it works.
What Is Reverse DNS?
Reverse DNS is a DNS lookup of a domain name from an IP address. While a regular DNS request resolves an IP address from a domain name, rDNS does the opposite, hence the name reverse.
A PTR record is used to perform reverse DNS lookups. Pointer records are configured within Address and Routing Parameter Area ( in-addr.arpa ) domains. If there is no PTR record set up, a reverse DNS lookup is unsuccessful.
Note: Learn more about PTR Record and other record types by referring to our article DNS Record Types Explained.
What Is Reverse DNS Lookup Used For?
Reverse DNS is particularly useful for those running an outgoing mail server. Besides mail servers, there are several reasons for using rDNS:
- Filtering spam emails. Most email servers use rDNS to block spam mail, rejecting messages from IP addresses without rDNS. However, rDNS is mainly used as an additional layer of protection because it isn’t reliable as some legitimate mail servers don’t have properly set up rDNS records.
- Analytics. Reverse DNS helps provide human-readable data in analytics, rather than listing logs of IP addresses.
- Tracking website visitors. IP addresses of website visitors remain in the visit logs and can help you get an idea of your website audience. Tracking website visitors is beneficial for B2B lead generation.
- Smooth network experience. Reverse DNS prevents you from encountering problems with most enterprise management systems, r-commands, SMTP servers, or network backup systems. rDNS is also one of the basic requirements for running some Internet protocols.
- Security. A reverse IP lookup can be used to find the IP address’ A records, mapping a domain name to the physical IP address of the device hosting that domain. The results help determine the virtual hosts served from a web server and identify server vulnerabilities.
Note: Read our article to fully understand what DNS is and how it works.
How Does Reverse DNS Lookup Work?
Reverse DNS works by looking up query DNS servers for a pointer record (PTR). A PTR record maps an IPv4 or IPv6 address to the canonical name for the host. If there is no PTR record on the server, it cannot resolve a reverse lookup.
PTR records store reverse DNS entries, with their IP address reversed and .in-addr.arpa appended to each record. For example, PTR stores the IP address 198.15.93.98 as 98.93.15.198.in-addr.arpa , pointing back to its designated host name.
It is advisable to have a proper reverse DNS record (PTR) set up, especially when running an SMTP/mail server.
The following image illustrates the difference between DNS and rDNS lookup:
In IPv6, PTR records store rDNS entries within the .ip6.arpa domain instead of .in-addr.arpa.
When a domain name has a valid rDNS, you can access it by entering its IP address in your browser.
How to Do a Reverse DNS?
There are several ways to perform reverse DNS lookup:
- Use the Windows command line. Perform manual rDNS lookup in Windows using the nslookup command.
- Use the Linux terminal. The dig command with -x flag allows you to perform manual rDNS lookup. Alternatively, use the host command.
- Use rDNS lookup tools. Several tools offer rDNS lookup.
Note: Follow our tutorial and set a DNS Nameserver on Ubuntu 20.04.
Reverse DNS Lookup Command
This section deals with manual reverse DNS lookup in Windows or Linux.
Reverse DNS Lookup in Windows
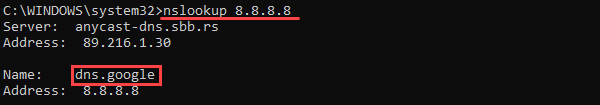
The command for reverse DNS lookup in Windows is:
The output returns the domain name for the specified IP address.
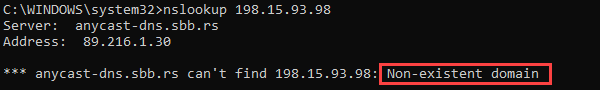
If the website doesn’t have rDNS set up, the command returns an error. For example:
Reverse DNS Lookup in Linux
There are two ways for rDNS lookup in Linux:
1. The dig command
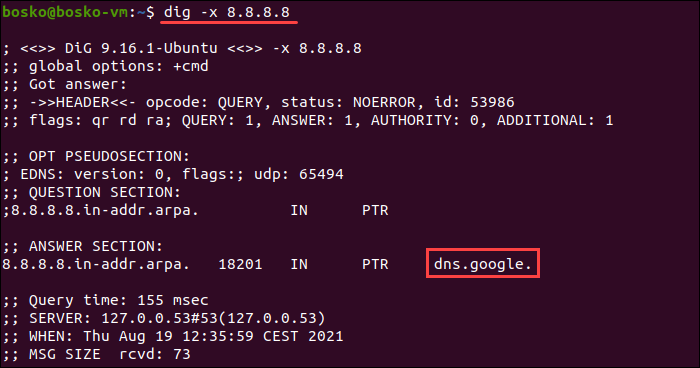
Use the dig command in Linux to perform a manual reverse DNS lookup. The syntax is:
The output displays the domain name for the specified IP address.
2. The host command
Another command for reverse DNS lookup in Linux is:
The output shows the domain name for the specified IP address.
Reverse DNS Tools
This section lists the available tools for reverse DNS lookup.
Note: Every tool listed is different in terms of capabilities and level of DNS information available, suited for individual use cases.
1. Online Tools
Online reverse DNS tools allow you to lookup a small number of addresses. Some may also provide an API for enterprise use cases.
2. Enterprise-Grade Tools
Other, enterprise-grade tools, allow you to automate and perform rDNS lookup on many IP addresses. Some of those tools are:
- https://reverseip.domaintools.com/ — Allows you to find all domains hosted on a given IP address. Lookups are free for Personal and Enterprise Members, for IPs with up to 2,000 hosted domains.
- https://reverse-ip.whoisxmlapi.com/ — A RESTful API suitable for automated solutions like scripts or programs. Provides a list of all domains associated with an IP address via API calls, and outputs results in JSON and XML formats.
- https://viewdns.info/ — A number of tools including rDNS lookup and an API that allows web developers to integrate the tools into their site. Outputs available in XML and JSON formats.
- https://toolbox.googleapps.com/apps/dig/ — A network tool that offers the same results as the Linux dig command.
- https://dnsinspect.com/ — A free web tool that checks your domain’s servers for common DNS and mail errors and generates a report with explanations how to fix them.
Note: Refer to our article on how to reduce DNS lookups to improve your website performance.
You now know what reverse DNS is and how to perform rDNS lookup in Windows, Linux, and using online tools.
Feel free to test the tools, but note that some websites don’t have rDNS set up, and the tools return an error in that case.