- Среда рабочего стола для Linux какая лучше, быстрее и удобнее?
- Оконный менеджер
- Оконные менеджеры
- JWM
- i3 (i3wm)
- Среды рабочего стола, представители.
- «Отцы основатели»
- GNOME
- KDE ( KDE Plasma )
- Самые легкие и быстрые
- Xfce
- Cinnamon (Корица)
- MATE
- LXQt
- Pantheon
- Красивые
- DDE (Deepin Desktop Environment)
- Выводы, самые лучшие среды рабочего стола
- А что дальше? Какие среды рабочего стола будут?
- 8 Best Window Managers for Linux
- Is it Easy to Use a Window Manager?
- 1. bspwm
- 2. Qtile
- 3. herbstluftwm
- 4. awesome
- 5. IceWM
- 6. i3
- 7. Sway
- 8. xmonad
- Honorable Mentions
Среда рабочего стола для Linux какая лучше, быстрее и удобнее?
Среда рабочего стола или графическое окружение рабочего стола — разновидность графических интерфейсов пользователя, обеспечивает пространство, называемое рабочим столом, на котором появляются окна, пиктограммы, панели и другие элементы. Обычно поддерживаются механизмы, объединяющие разные части среды, — например, drag-n-drop, взаимодействие с браузерами, переключение окон, многие дополнительные программы, приоритеты использование памяти и много чего еще что остается «за бортом» для обычного пользователя
Назначение рабочего стола (окружения) создание интуитивного, в данном случае графического способа взаимодействия пользователя с компьютером.
Для Windows среда рабочего стола может быть только одна для каждой из поколений операционных систем, поэтому у пользователей данного вопроса не возникает. Для Linux cреда рабочего стола может быть самой разной так как сама система и графическое окружение принципиально разные программные продукты и Linux вообще может существовать без графической оболочки, а Windows нет.
Короче, по простому, это изображение с окнами, иконками, панельками сверху/снизу который вы видите на экране.
Оконный менеджер
Но, нужно помнить, есть еще понятие: «Менеджер окон Linux» или «Оконный менеджер». Он служит для управление окнами приложений, таким образом оконный менеджер понятие более узкое. А среда рабочего стола более широкое понятие. Среда рабочего стола включает в себя и менеджер окон и другие программы и библиотеки которые иногда очень тесно интегрированы с менеджерами и с сами рабочим столом с целью создать удобное, полноценное графическое окружение.
для лучшего понимания можно составить следующую формулу:
Из всего этого можно сделать вывод, что менеджер окон программа занимающее меньше места чем окружение рабочего стола и часто применяется в дистрибутивах которые направлены на экономию места и ресурсов.
Представители оконных менеджеров
i3, AWESOME WM, XMONAD, OPENBOX, DWM, GALA, KWIN, FLUXBOX, JWM и еще много и много других
Рассмотрим, например JWM или i3 (i3wm)
Оконные менеджеры
JWM
Менеджер окон для X Window System, написан на Си. Портирован на множество операционных систем FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, Minix, OpenSolaris. Используется в качестве оконного менеджера по умолчанию в Puppy Linux.
i3 (i3wm)
i3 — это тайловый (фреймовый)* оконный менеджер с открытым исходным кодом, полностью написанный с нуля для операционных систем GNU/Linux и BSD. Развитие и ответвление оконного менеджера wmii ( ссылка на страницу )
*Тайловый (фреймовый) оконный менеджер это менеджер с не перекрываемыми (не пересекающимися) окнами.
Но сегодня мы поговорим именно о среде рабочего стола или графическом окружении рабочего стола.
Среды рабочего стола, представители.
«Отцы основатели»
GNOME
Старейший дизайн рабочего стола в Linux.
KDE ( KDE Plasma )
Одно из самых мощных и настраиваемых окружений рабочего стола в Linux.
Самые легкие и быстрые
Xfce
Основана на GTK+ и использует собственный менеджер окон Xfwm.
Cinnamon (Корица)
Ответвление от GNOME. Изначально разрабатывался для Linux Mint, а сейчас используется для многих других проектов Linux (Fedora, Manjaro, Debian, Ubuntu, Calculate , Arch и др.) А еще подходит и для FreeBSD.
MATE
То же ответвление от GNOME, но на базе Gnome 2.
LXQt
На основе Qt, появился в результате слияния LXDE и Razor-qt.
Pantheon
Для дистрибутива Elementary OS. Среда рабочего стола Pantheon интегрирована с другими приложениями Elementary OS, Plank (док-панель), Epiphany (веб-браузер по умолчанию) и Code (текстовый редактор), Gala (оконный менеджер дистрибутива основанный на Mutter)
Красивые
DDE (Deepin Desktop Environment)
Для дистрибутива Linux DEEPIN, основан на Debian
Содержит оконный менеджером Gala, проигрыватель аудио Deepin, видео проигрыватель DMovie, система обмена сообщениями DTalk, инсталлятор, а также центр приложений — Deepin Store. Написан в стиле macOS, потребляет много ресурсов, был замечен в шпионаже, относится к Deepin
Выводы, самые лучшие среды рабочего стола
А что дальше? Какие среды рабочего стола будут?
А дальше все зависит от того куда повернётся и какими путями пойдет технический прогресс. Уже сейчас в связи с разработкой и уходом в массы шлемов VR, а я сейчас про Oculus Quest 2 который бьет рекорды по продажам выпускаю и еще выпустят виртуальные рабочие столы и что там будет, кто ж знает. Будет это напоминать реальный стол или комнату или еще чего то, не знаю, но думаю дизайнеры уже работают над этим. Интересные перспективы возникают с уходом от графической визуализации при переходе на нейроинтерфейсы, но там вообще «темный лес» и чего там будет вообще никто не знает.
Продолжение как всегда следует, мои маленькие, красноглазые друзья.
8 Best Window Managers for Linux
Want to organize your windows and use all the screen space you have? These window managers for Linux should come in handy!
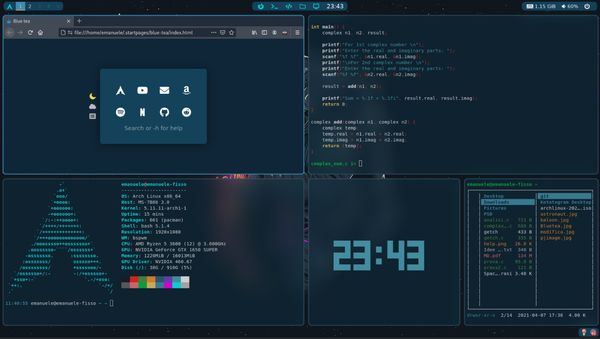
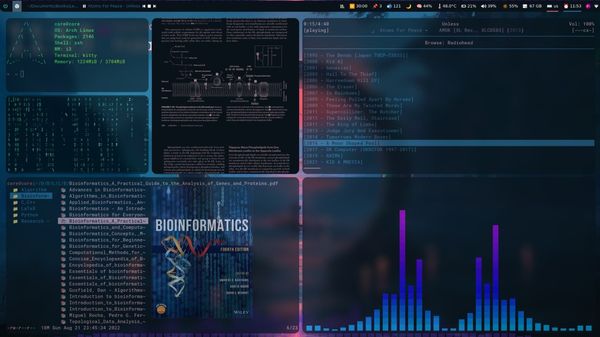
A window manager should be helpful if you dabble with multiple active windows on your system and want to make the most out of the available screen space. Sure, you can re-size and reposition your windows to organize them to some extent. However, with a window manager, you can step up your multitasking potential by organizing the windows using keyboard shortcuts, mouse and even automating some of it. With a window manager, you can improve not only the productivity but the look and feel of your desktop if you decide to put in the effort. Here’s an example of a user’s customized desktop using a window manager to organize the active windows:
Most of the options mentioned work for the Xorg display server, considering window managers on Wayland are called compositors. You can explore Arch’s documentation to learn more.
For multi-monitor setups, you might want to check for RandR and Xinerama protocol support with the window managers.
Is it Easy to Use a Window Manager?
- Some window managers provide you with room for endless customizability. If you do not know how to configure it to your liking, you may not be able to use it.
- Some window managers might need configuration even before using it. Unless you do not set it up, you cannot utilize the window manager.
- Most users prefer Arch Linux to use window managers. So, you can expect better community support for configurations/setup if you pick Arch Linux as your distro of choice. But, it is not mandatory, you can try other distributions.
- You might want to know how to switch between Xorg and Wayland to use the window manager or compositor you want.
Here, I provide the links to its documentation, and the installation commands to give you a head start.
To make things easy, you can also utilize other users’ dotfiles (configuration) to quickly modify the look and behavior of your desktop. However, you still need to know what you’re doing before you use them.
Some window managers/compositors for Wayland may not support proprietary graphics drivers, including NVIDIA. So, before installing and configuring any of the window managers, you might want to check what it supports.
1. bspwm
bspwm is a lightweight tiling window manager. The first screenshot you see in this article was made possible using bspwm.
You must install the window manager and a separate package to use the keyboard/pointer bindings. bspwm lets you manually choose how new windows get inserted or positioned or set it to automatic mode, where it follows a particular scheme to arrange the windows.
You need to configure it properly before you get to use it. Unfortunately, the documentation for it may not be easy to follow for new users trying a window manager. Arch Linux’s documentation page on bspwm should help you get started.
Install bspwm
You can easily find the package for it on the official repositories of Fedora, Ubuntu, and Arch.
For Ubuntu, type in the following command to get it installed:
sudo apt install bspwm sxhkd2. Qtile
Qtile is a customizable tiling window manager that works on X11 and Wayland.
It packs in various features and yet a simple implementation. You get a command shell to inspect and manage all aspects of the window manager.
One of the highlights of Qtile is complete remote scriptability.
Install Qtlie
You can install Qtile using pip. Once you have pip installed on Ubuntu, run these commands:
pip install xcffib pip install qtileRefer to the official documentation or its GitHub page for other Linux distributions.
3. herbstluftwm
herbstluftwm (I know, a mouthful) is a manual tiling window manager. Not as popular as other options, but a promising option for Linux users.
The key highlight of the window manager is that the configuration for the tool happens at runtime. So, you do not need to restart the window manager and yet manage to make changes live.
The documentation may not be beginner-friendly, but you can choose to explore parts of it to better understand its functioning.
Install herbstluftwm
You can find it in the official repository. To install it, run the following command:
sudo apt install herbstluftwmIn either case, feel free to explore its official website and GitHub page for more info.
4. awesome
awesome is a fast and configurable window manager. It does require a few dependencies along with the installation process to get things working, but it should not be a problem for most.
If you want to access a window manager without needing to configure much from the start, awesomewm should be a good option. It may not look pleasing if you just install and use it without configuration, but you can access most of its functions easily.
The documentation for awesome window manager is valuable enough to make the most out of it.
Install awesome
The package should be available in the repositories of all major distributions. For Ubuntu, you can type in the following command:
5. IceWM
IceWM is one of the oldest tiling window managers out there. You can find it as the default window manager with some distributions like antiX (one of the best lightweight Linux distributions).
You may not get an extensive list of functionalities with IceWM, but it has a simple approach that lets you easily use it. By default, it features an app launcher and a taskbar to keep things familiar and accessible.
Head to its official website for documentation and get started.
Install IceWM
IceWM is available in official repositories of all major distros. You can install it on Ubuntu using the following command:
6. i3
i3 is the most popular option if you are in for an insane amount of customization. Yes, it is aimed at advanced users and developers, but with its well-documented instructions, anyone can try to use it.
You can expect numerous abilities with i3 as long as you can configure them. Whether you have dual-monitor setup, or a multi-monitor setup with horizontal displays, configuration is the key here.
i3 is available in repositories for every major distribution. For Ubuntu, you can use the command below to get it installed:
To explore technical details, head to its GitHub page.
7. Sway
Sway is designed for Wayland sessions while offering compatibility with i3. In other words, the same commands are supported with Sway.
If you are using i3 and want to move to Sway on a Wayland desktop, the transition should be easy by copying the configuration to the correct file.
You should have the essential features here to organize app windows and make efficient use of desktop space.
Install Sway
Most of the popular distributions should already have the package available. For Debian-based systems, you can use the terminal to get it installed:
To explore more, check out its GitHub page.
Suggested Read 📖
8. xmonad
xmonad is a tiling window manager for X11 written and configured in Haskell language.
It aims to provide all kinds of functionalities while making it easier to automate things all the way.
You get a decent documentation to get started and start taking charge of your windows.
Install xmonad
Unlike others, it is not as simple as installing a single package (especially for Debian/Ubuntu users).
So, you may want to follow the official installation instructions and its GitHub page to proceed.
Honorable Mentions
There are various other compositors (Wayland) and window managers like ratpoison that may not be feature-rich or popular enough but can be interesting to try.
Some of those options are:
💬 What are your favorite window managers for Linux? Did we miss any of your favorites? Let us know in the comments section below.