- How to mount a hard disk as read-only from the terminal
- Исправление Read-Only File System в Linux
- Ошибки файловой системы и опция remount-ro
- Read-only файловая система в виртуальных машинах
- How to Fix Read Only File System Error on Ubuntu
- How to Fix Read Only File System Error on Ubuntu
- read-only file system for Ubuntu
- The read-only file system cannot be removed using rm.
- Filesystem Access Rights
- Symptom
- Potential Causes
- Precautions
- Solution
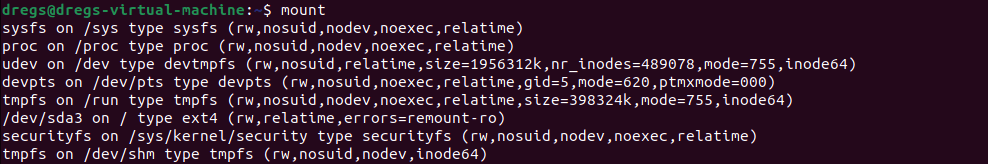
- Display Mounted File Systems
- Как исправить read only file system в Linux
- Ошибка read only file system в Linux
How to mount a hard disk as read-only from the terminal
You do not mount /dev/sda , that refers to the entire disk. You mount /dev/sda1 or whatever partition you want.
Make a mount point, call it anything you like.
sudo mount -o ro /dev/sda1 /media/2tb When your done, you should unmount the disk
When mounting the filesystem read-only, some trouble may happen. The system may try to write into the device anyway and fail.
For that reason the noload flag may be used, to notify to the system that the disk is blocked.
The best solution I found was:
sudo mount -o ro,noload /dev/sda1 /media/2tb The manual of mount(8) explains this options as follows:
-r , —read-only
Mount the filesystem read-only. A synonym is -o ro .
Note that, depending on the filesystem type, state and kernel behavior, the system may still write to the device. For example, Ext3 or ext4 will replay its journal if the filesystem is dirty. To prevent this kind of write access, you may want to mount ext3 or ext4 filesystem with ro,noload mount options or set the block device to read-only mode, see command blockdev(8) .
[…]
norecovery / noload
Don’t load the journal on mounting. Note that if the filesystem was not unmounted cleanly, skipping the journal replay will lead to the filesystem containing inconsistencies that can lead to any number of problems.
Yes, when I was trying to mount a single disk from an old RAID 1 array, I was able to mount it only with nolaod option — sudo mount -o ro,noload /dev/md0 /mnt/disk1 once I have rebuilt the array with sudo mdadm —assemble —readonly /dev/md0 /dev/sda
I am plugging a USB connected drive into Ubuntu 12.04 and the system is mounting it automatically. In Terminal, if I just say mount it shows me the current info. I want to remount it read-only.
Extrapolated from man mount(8) :
sudo mount -o remount,ro /dev/sdb4 /media/HP_TOOLS Seemed to work nicely. Had to do it for each automounted partition.
Step 1: After connecting the disk to the machine, give the command below to see what it shows the disk as.
It will show the disk as /dev/sda or /dev/sdb with a partion table.
Disk /dev/sdb: 7.5 GiB, 8053063680 bytes, 15728640 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disklabel type: dos Disk identifier: 0x0e0e8e70 Device Boot Start End Sectors Size Id Type /dev/sdb1 * 0 2902111 2902112 1.4G 0 Empty /dev/sdb2 2888004 2892739 4736 2.3M ef EFI (FAT-12/16/32) Step 2: Execute the command below to see where it is mounted. For example,
$ sudo df -HT Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on udev devtmpfs 4.2G 0 4.2G 0% /dev tmpfs tmpfs 829M 10M 819M 2% /run /dev/mapper/ubuntu--vg-root ext4 484G 149G 311G 33% / tmpfs tmpfs 4.2G 20M 4.2G 1% /dev/shm tmpfs tmpfs 5.3M 4.1k 5.3M 1% /run/lock tmpfs tmpfs 4.2G 0 4.2G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/sda1 ext2 495M 111M 359M 24% /boot /dev/sdb1 iso9660 1.5G 1.5G 0 100% /media/username/Ubuntu Step 3: Finally execute the command below to remount it as an ro only.
sudo mount -o remount,ro /dev/sdb1 /media/username/Ubuntu Исправление Read-Only File System в Linux
21.10.2022
itpro
CentOS, Linux, Ubuntu
Один комментарий
В некоторый случаях файловая система в Linux может перейти в состояние read-only, при котором вы можете только читать данные с диска, а при попытке записи любых изменение или создании нового файла появдляется ошибка Read-only file system.
Ошибки файловой системы и опция remount-ro
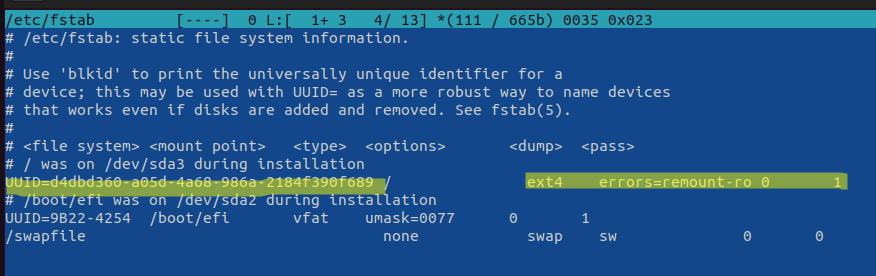
Проверьте параметры монтирования дисков при загрузке Linux. Настройки монтирования файловых систем при загрузке задаются в файле /etc/fstab.
Обратите что в fstab есть строка монтирования корневой директории вида:
UUID=aaaaaaaaa-aaaa-aaaa-aaaa-aaaaaaaaa / ext4 errors=remount-ro 0 1
Параметр errors=remount-ro означает, что данная директория будет смонтирована в режиме чтения, если на файловой системе устройства обнаружены проблемы. В этом случае нужно выполнить проверку диска с помощью FSCK.
Обычные файловые системы такие как EXT4/BTRFS/XFS можно монтировать как в режиме записи, так и только для чтения (в отличии от файловых систем ISO или SquashFS, которые доступны только для чтения).
В случае обнаружения ошибок на диске вы можете использовать одну из трех опций errors=[continue|remount-ro|panic]
- continue – игнорировать ошибки,
- remount-ro – перемонтировать диск в режиме только для чтения
- panic – остановить загрузку системы
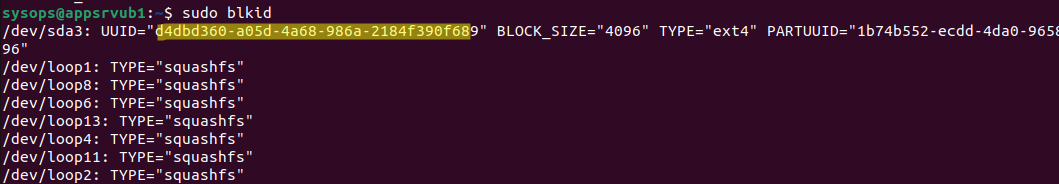
Вы можете вывести соответствие между UUID диска и именем устройства:
В данном примере вы получили, что вашему UUID соответствует устройство /dev/sda3.
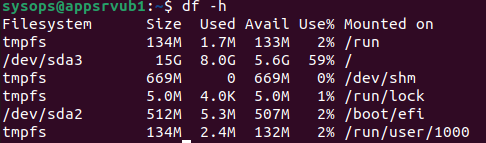
Также можно имена устройства и точки монтирования с помощью команды:
Т.к. в данном примере ошибки обнаружены в корневой директории которая является точкой монтирования, вы сможете выполнить ее проверку только загрузившись с LiveCD. Для исправления ошибок файловой системы используется команда:
$ sudo fsck –y UUID=aaaaaaaaa-aaaa-aaaa-aaaa-aaaaaaaaa
Если вы не можете прямо сейчас выполнить проверку диска, и вы хотите немедленно вывести файловую систему из режима read-only, нужно выполниться команду:
Read-only файловая система в виртуальных машинах
Файловая система раздела Linux на виртуальной машине можете перейти в read-only в случае недоступность системы хранения данных (СХД). Самый простой способ восстановить работу ОС – выполнить сброс виртуальной машины (фактически перезапуск с параметрами по умолчанию).
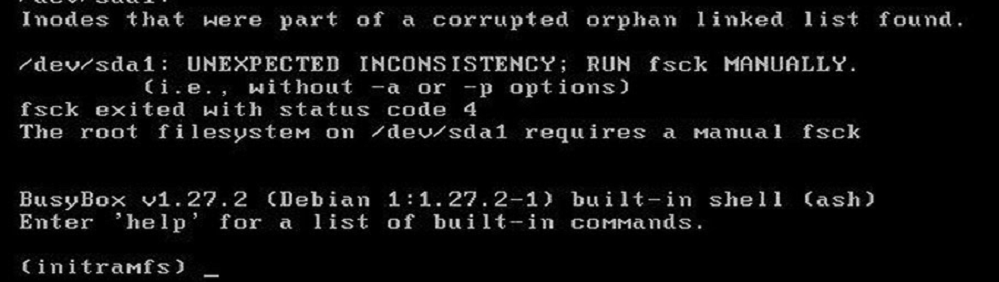
Может оказаться, что ВМ с Linux вообще не загружается и вам доступна только командная строка initramfs с предупреждениями:
UNEXPECTED INCONSISTENCY: RUN fsck MANUALLY. Fsck exitrd with code 4. The root file system of /dev/sdx requires a manual fsck.
Initramfs это начальная файловая система в оперативной памяти, которая основана на tmpfs, которая содержит утилиты и скрипты, необходимые для работы с дисками, файловыми системами и тд. После запуска initramfs отобразится проблемная ситуация.
Если же ошибок нет – просто вводим exit. Иначе выполняем проверку диска:
Здесь указан том (в данной случае /dev/sda1), для которого требуется выполнить ручную проверку. С помощью следующей команды можно проверить все подключенные файловые системы:
После этого перезагрузите ВМ.

How to Fix Read Only File System Error on Ubuntu
The “Read-only file system…” error is a file system-related error. This could happen in many circumstances for various causes. In this article, we will discuss how to fix read only file system error on Ubuntu.
A filesystem is a grouping of data (files and directories) kept on a storage device in Linux. The filesystem is used by your operating system to report the physical location and positioning of the files. The files would appear as invisible or random bits without the filesystem.
Each file system also has its own permissions, which control which users or groups can read and write files. The “Read-only file system” problem on Ubuntu will be fixed with this guide.
How to Fix Read Only File System Error on Ubuntu
read-only file system for Ubuntu
By default, Ubuntu has a read-only file system. It implies that the user cannot change or remove files from the system. It helps to safeguard system data and folders and stop unintentional removals. Linux distribution Ubuntu uses the read-only ShrinkFS file system.
This file system saves disk space. It can be used to keep executables, configuration files, and other information that shouldn’t be changed by the user. Linux distribution Ubuntu comes included with a read-only file system. The “Btrfs” file system aims to increase performance and dependability.
The read-only file system cannot be removed using rm.
An error warning will appear if you attempt to delete a read-only file system while the machine is running. It is thus because you cannot delete the file system, which is a component of the computer’s main operating system.
A read-only file system cannot be removed, and any attempts to rename or relocate it will fail with a read-only file system error message. It’s because the Rm command cannot alter a read-only file system’s permissions. Use the Remove-Item cmdlet to correctly remove a read-only file system.
Filesystem Access Rights
Linux is an OS that supports multiple users. Linux uses several security mechanisms to regulate which user has access to which area of the system. File permissions and ownership are one such functionality. It establishes the file’s owner and who has access to read, write, and execute the files.
Linux filesystems follow a similar principle. User permissions secure each filesystem by dictating who is permitted to carry out certain actions on the filesystem.
Because the target filesystem is a read-only filesystem, as the error says, it is rejecting write requests. If it’s intentional, you’ll need the system administrator’s written consent if you want to proceed. If that isn’t the case, then adhere to this advice.
Symptom
On a Linux system, the notification Read-only file system appears when you delete or change a file.
Potential Causes
These are some of the potential reasons:
- After that, the file system enters read-only mode.
- The mounted file system is read-only.
- The hardware is broken, for instance, the disk has damaged sectors, or the RAID controller card is broken.
Precautions
- Data loss could occur when file systems are repaired. Back up your files first.
- Check for a hardware defect if your problem doesn’t fit into one of the following categories.
Solution
The filesystem’s permissions need to be fixed to resolve this problem. Several tools are available, depending on the type of filesystem.
These actions are usually best carried out from a live Ubuntu session. No other program will interfere with the process in this manner. As an alternative, you can start Ubuntu from a different installation. With that said, you may want to consider setting up Ubuntu on a USB drive.
Display Mounted File Systems
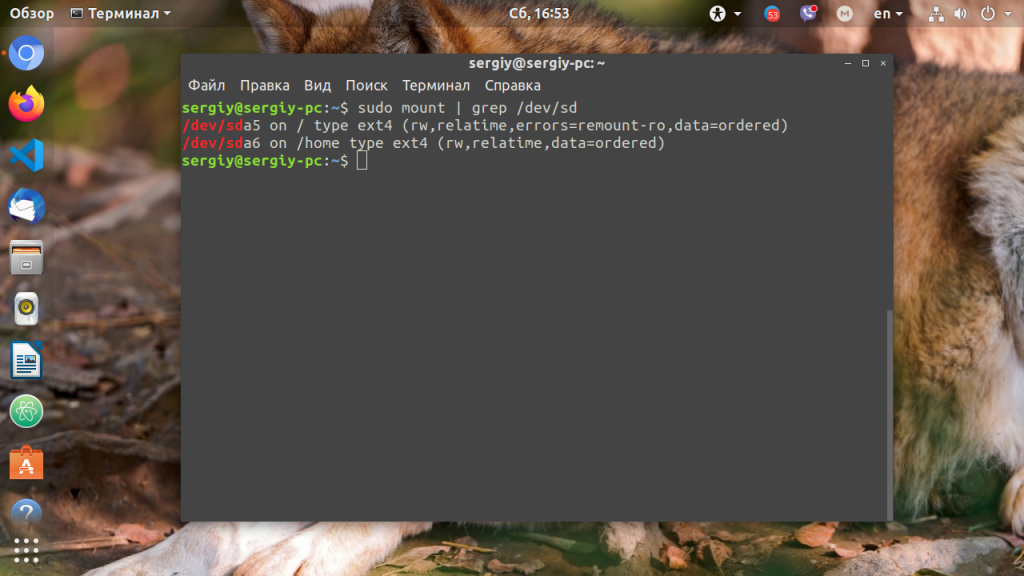
We shall first list the file systems that are already mounted. The mounted file systems can be listed using the mount command. Even though the output may be lengthy, only look for the lines about the root path and home path.
The third line from the bottom is the line we are interested in when looking at this screenshot.
Как исправить read only file system в Linux
Ошибка read only file system может возникнуть при загрузке с LiveCD диска или в режиме восстановления вашего дистрибутива. Она означает, что файловая система в которую вы пытаетесь вести запись примонтирована только для чтения. Этому может быть несколько причин. Есть файловые системы, которые доступны только для чтения это файловая система оптических дисков — ISO, а также файловая система образов SquashFS.
С такими файловыми системами вы сделать ничего не сможете. Для изменения данных в них, надо распаковать образ, изменить данные и запаковать его обратно. Но что касается обычных файловых систем, таких как EXT4, BTRFS, XFS, то их можно монтировать и для чтения и для записи.
Ошибка read only file system в Linux
В этой небольшой статье мы рассмотрим как исправить read only file system Linux перемонтировав файловую систему для записи. Первым делом надо определиться с точкой монтирования, для которой надо разрешить запись. Попытаемся создать файл в корневом каталоге:
Ошибка, файловая система корневого каталога доступна только для чтения. Чтобы посмотреть все точки монтирования доступные в системе выполните в терминале:
В данном случае, корневая файловая система и есть точкой монтирования. Но у вас, например, возникнут проблемы с созданием файла в домашней папке, то надо будет уже перемонтировать /home. Смотрите внимательно. Когда точка монтирования выбрана, осталось её примонтировать с правами на запись:
sudo mount -o remount,rw /home
После этого вы сможете создать файл без каких-либо проблем. После завершения работы, во избежание повреждения данных при перезагрузке, желательно перемонтировать файловую систему обратно в режим только для чтения:
Теперь вы знаете что означает эта ошибка и как с ею справится. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.