- Manual:Wireless Station Modes
- 802.11 limitations for L2 bridging
- Applicability Matrix
- Mode station
- Mode station-wds
- Mode station-pseudobridge
- Mode station-pseudobridge-clone
- Mode station-bridge
- Что такое WISP AP, CAP, CPE, HomeAP на MikroTik?
- MikroTik
- WISP на других маршрутизаторах
- «AP client router» на ASUS
- TP-Link
- Zyxel Keenetic
Manual:Wireless Station Modes
Wireless interface in any of station modes will search for acceptable access point (AP) and connect to it. The connection between station and AP will behave in slightly different way depending on type of station mode used, so correct mode must be chosen for given application and equipment. This article attempts to describe differences between available station modes.
Primary difference between station modes is in how L2 addresses are processed and forwarded across wireless link. This directly affects the ability of wireless link to be part of L2 bridged infrastructure.
If L2 bridging over wireless link is not necessary — as in case of routed or MPLS switched network, basic mode=station setup is suggested and will provide highest efficiency.
Availability of particular station mode depends on wireless-protocol that is used in wireless network. Please refer to applicability matrix for information on mode support in protocols. It is possible that connection between station and AP will be established even if particular mode is not supported for given protocol. Beware that such connection will not behave as expected with respect to L2 bridging.
802.11 limitations for L2 bridging
Historically 802.11 AP devices were supposed to be able to bridge frames between wired network segment and wireless, but station device was not supposed to do L2 bridging.
Consider the following network:
where X-to-AP and STA-to-Y are ethernet links, but AP-to-STA are connected wirelessly. According to 802.11, AP can transparently bridge traffic between X and STA, but it is not possible to bridge traffic between AP and Y, or X and Y.
802.11 standard specifies that frames between station and AP device must be transmitted in so called 3 address frame format, meaning that header of frame contains 3 MAC addresses. Frame transmitted from AP to station has the following addresses:
- destination address — address of station device, also radio receiver address
- radio transmitter address — address of AP
- source address — address of originator of particular frame
Frame transmitted from station to AP has the following addresses:
- radio receiver address — address of AP
- source address — address of station device, also radio transmitter address
- destination address
Considering that every frame must include radio transmitter and receiver address, it is clear that 3 address frame format is not suitable for transparent L2 bridging over station, because station can not send frame with source address different from its address — e.g. frame from Y, and at the same time AP can not format frame in a way that would include address of Y.
802.11 includes additional frame format, so called 4 address frame format, intended for «wireless distribution system» (WDS) — a system to interconnect APs wirelessly. In this format additional address is added, producing header that contains the following addresses:
- radio receiver address
- radio transmitter address
- destination address
- source address
This frame format includes all necessary information for transparent L2 bridging over wireless link. Unluckily 802.11 does not specify how WDS connections should be established and managed, therefore any usage of 4 address frame format (and WDS) is implementation specific.
Different station modes attempt to solve shortcomings of standard station mode to provide support for L2 bridging.
Applicability Matrix
The following matrix specifies station modes available for each wireless-protocol. Note that there are 2 columns for 802.11 protocol: 802.11 specifies availability of mode in «pure» 802.11 network (when connecting to any vendor AP) and ROS 802.11 specifies availability of mode when connecting to RouterOS AP that implements necessary proprietary extensions for mode to work.
Table applies to RouterOS v5rc11 and above:
| 802.11 | ROS 802.11 | nstreme | nv2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| station | V | V | V | V |
| station-wds | V | V | V | |
| station-pseudobridge | V | V | V | |
| station-pseudobridge-clone | V | V | V | |
| station-bridge | V | V | V |
Mode station
This is standard mode that does not support L2 bridging on station — attempts to put wireless interface in bridge will not produce expected results. On the other hand this mode can be considered the most efficient and therefore should be used if L2 bridging on station is not necessary — as in case of routed or MPLS switched network. This mode is supported for all wireless protocols.
Mode station-wds
This mode works only with RouterOS APs. As a result of negotiating connection, separate WDS interface is created on AP for given station. This interface can be thought of point-to-point connection between AP and given station — whatever is sent out WDS interface is delivered to station (and only to particular station) and whatever station sends to AP is received from WDS interface (and not subject to forwarding between AP clients), preserving L2 addresses.
This mode is supported for all wireless protocols except when 802.11 protocol is used in connection to non-RouterOS device. Mode uses 4 address frame format when used with 802.11 protocol, for other protocols (such as nstreme or nv2), protocol internal means are used.
This mode is safe to use for L2 bridging and gives most administrative control on AP by means of separate WDS interface, for example use of bridge firewall, RSTP for loop detection and avoidance, etc.
With station-wds mode, it is not possible to connect to CAPsMAN controlled CAP.
Mode station-pseudobridge
From the wireless connection point of view, this mode is the same as standard station mode. It has limited support for L2 bridging by means of some services implemented in station:
- MAC address translation for IPv4 packets — station maintains IPv4-to-MAC mapping table and replaces source MAC address with its own address when sending frame to AP (in order to be able to use 3 address frame format), and replaces destination MAC address with address from mapping table for frames received from AP. IPv4-to-MAC mappings are built also for VLAN encapsulated frames.
- single MAC address translation for the rest of protocols — station learns source MAC address from first forwarded non-IPv4 frame and uses it as default for reverse translation — this MAC address is used to replace destination MAC address for frames received from AP if IPv4-to-MAC mapping can not be performed (e.g. — non-IPv4 frame or missing mapping).
This mode is limited to complete L2 bridging of data to single device connected to station (by means of single MAC address translation) and some support for IPv4 frame bridging — bridging of non-IP protocols to more than one device will not work. Also MAC address translation limits access to station device from AP side to IPv4 based access — the rest of protocols will be translated by single MAC address translation and will not be received by station itself.
This mode is available for all protocols except nv2 and should be avoided when possible. The usage of this mode can only be justified if AP does not support better mode for L2 bridging (e.g. when non-RouterOS AP is used) or if only one end-user device must be connected to network by means of station device.
Mode station-pseudobridge-clone
This mode is the same as station-pseudobridge mode, except that it connects to AP using «cloned» MAC address — that is either address configured in station-bridge-clone-mac parameter (if configured) or source address of first forwarded frame. This essentially appears on AP as if end-user device connected to station connected to AP.
Mode station-bridge
This mode works only with RouterOS APs and provides support for transparent protocol-independent L2 bridging on the station device. RouterOS AP accepts clients in station-bridge mode when enabled using bridge-mode parameter. In this mode, the AP maintains a forwarding table with information on which MAC addresses are reachable over which station device.
This mode is MikroTik proprietary and cannot be used to connect to other brands of devices.
This mode is safe to use for L2 bridging and is the preferred mode unless there are specific reasons to use station-wds mode. With station-bridge mode, it is not possible to connect to CAPsMAN controlled CAP.
Что такое WISP AP, CAP, CPE, HomeAP на MikroTik?
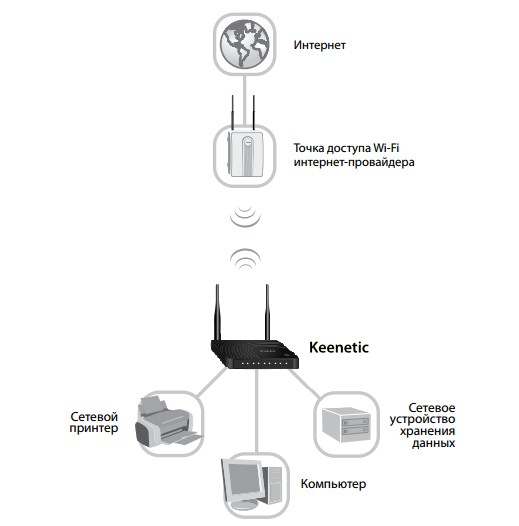
Для начала давайте разберёмся, что же такое режим WISP? Это определённый мод маршрутизатора, при котором он может принимать интернет сигнал и подключаться к сети провайдера путём радиоволн по стандартам Wi-Fi. Если раскрыть аббревиатуру, то она звучит так – «Wireless Internet Service Provider», что дословно можно перевести как «беспроводной интернет сервис провайдера».
Данная технология достаточно редкая, но появилась давно. Давайте покажу на примере. У провайдера есть большая антенна с мощным передатчиком на несколько квадратных километров. Клиент настраивает роутер и подключается к беспроводной сети. То есть в данном случае роутер принимает сигнал не через WAN порт по проводу, а именно путём Wi-Fi сигнала.
Далее при подключении он принимает сигнал и распределяет на все сегменты сети: на компьютеры, ноутбуки телефону и т.д. Интернет раздаётся как по проводам, так и по WiFi. Теперь перед настройкой роутера, именно в этом режиме сразу – скажу, что проблемой является в разных названиях модов. Компании, которые выпускают эти аппараты, по разному называют этот «мод» из-за чего клиент может запутаться. Также не все роутеры имеют данный режим и поддерживают его, поэтому перед покупкой обязательно убедитесь, что он сможет работать как повторитель WISP.
MikroTik
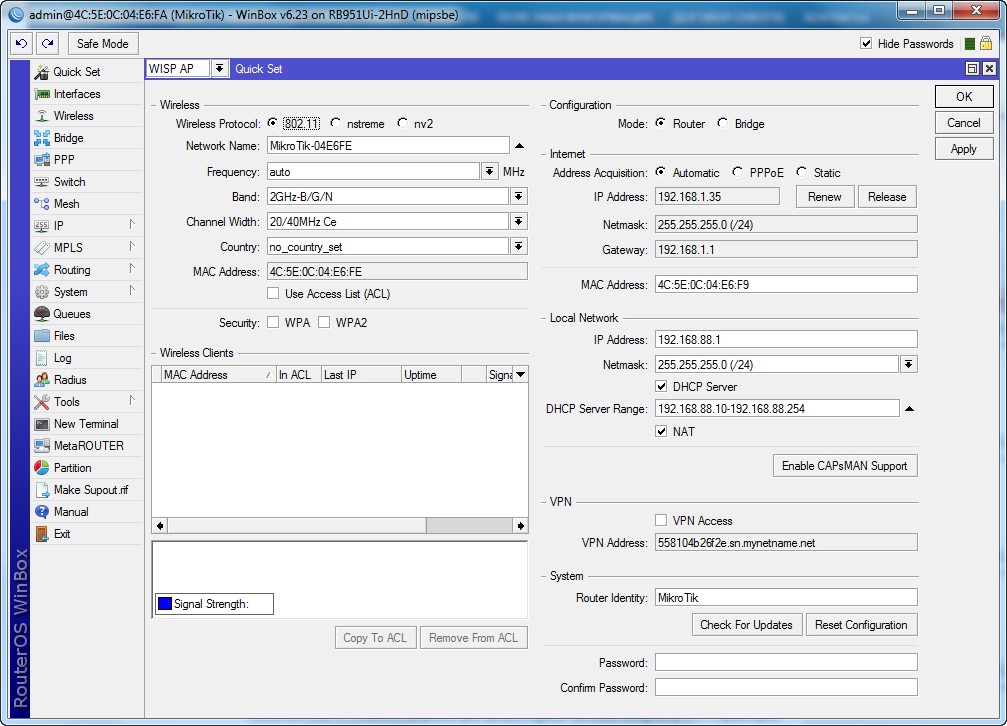
WISP AP на роутере MikroTik – что это такое? У «Микротик» данный «мод» обозначает немного другое значение. Раз вы задаетесь таким вопросом, то скорее вы уже приступили к настройке этого чудного аппарата через «Quick Set». Эта функция позволяет быстро настроит роутер без муторных, педантичных конфигураций. Можно сказать некий «Быстрый старт».
В верхней части можно выбрать несколько вариантов:
- CAP – управляемая точка доступа.
- CPE — вот данный режим и отображает реальный «WISP», кагда клиентский аппарат подключается к другой вайфай сети.
- HomeAP – обычный домашнего роутера с меньшим количеством настроек.
- PTP Bridge AP\CPE – тут все понятно – «Режим моста». Для организации нужно два аппарата, один будет работать в AP, а второй в CPE.
- WISP AP – по сути это HomeAP, но там конфигурация более детальная, для более продвинутых пользователей.
- Basic AP – пуста конфигурация для развертывания.
Для настройки заполняем конфигурацию в левом блоке «Wireless» для настройки беспроводного мода. Вписываем имя сети и пароль от неё. Чтобы появилась строка ввода пароля укажите типа шифрования как WPA2 и WPA. Тут ничего сложного нет все как на других роутерах.
Справа идут настройки IP, маски и DNS адресов. По идее эти настройки роутер должен получать от провайдера. Тогда просто ставим режим «Automatic». Если у вас статический IP с маской, то ставим «Static» и вписываем данные с листа. В разделе «Local Network» идёт настройка «айпи» адреса шлюза или нашего Микротика и диапазон локальных адресов.

WISP на других маршрутизаторах
«AP client router» на ASUS
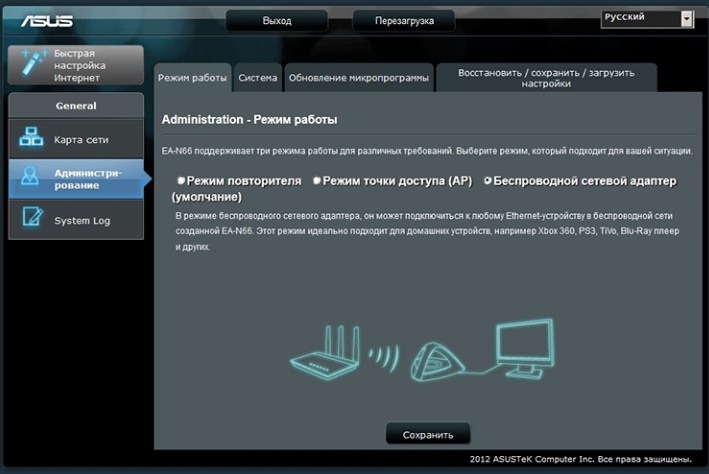
На аппаратах Асус к сожалению название не адаптивно и не понятно. Может быть это связано с переводом. Но на русской версии мод называется «Беспроводной сетевой адаптер». Для настройки вы можете использовать «Быструю настройку» – просто нажмите на волшебную палочку в левом углу окна. Или нажмите на «Режим работы» в самой верхней части на главной странице.
TP-Link
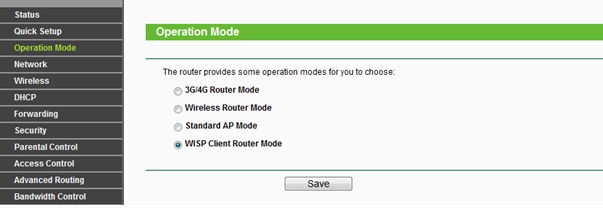
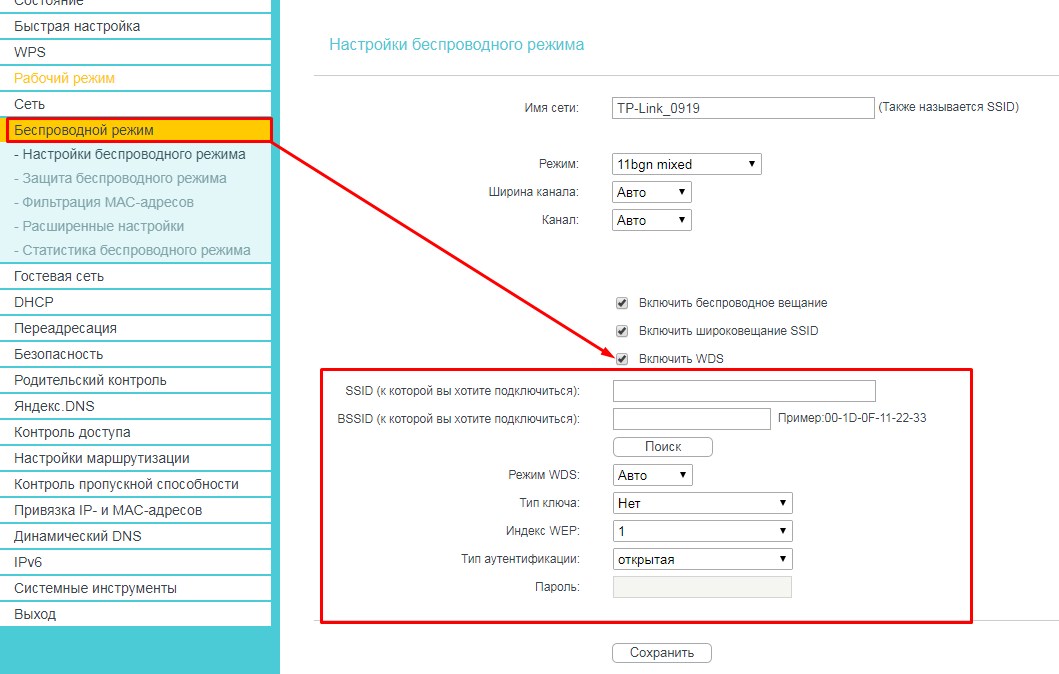
На TP-Link можно включить двумя способами. Заходим в «Operation Mode» или по-русски – «Рабочий режим». Далее выбираем наш мод. После этого переходим в «Сеть» – «WAN» и ставим динамический IP.
Второй способ – заходим в «Беспроводной режим». Теперь нажимаем «Включить WDS». Далее все просто, нужно просто подключиться к беспроводной сети провайдера. Для этого впишите данные вай-фай.
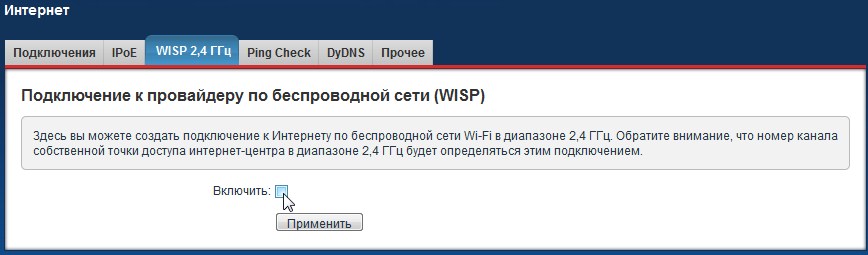
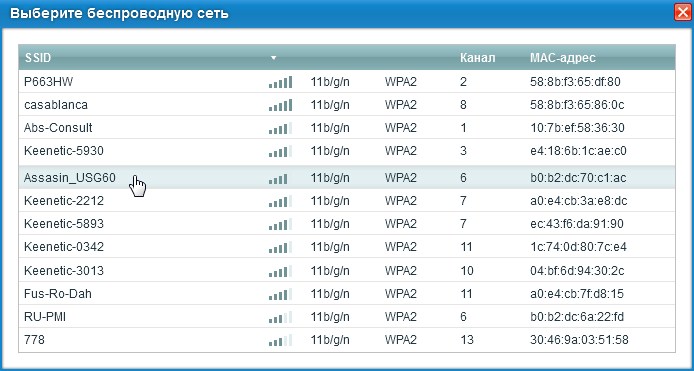
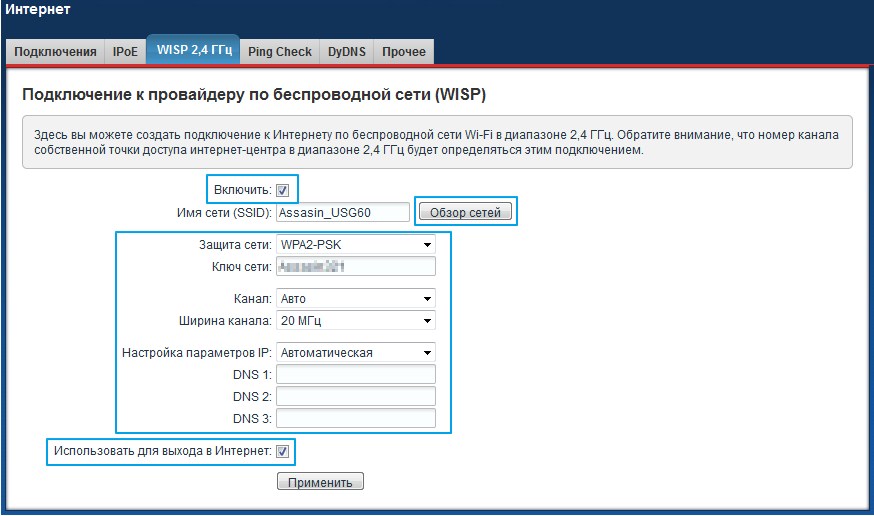
Zyxel Keenetic
- Далее вписываем пароль в поле «Ключ сети».
- Настройка IP и DNS стоит в автономном режиме, но вы всегда можете настроить вручную эти параметры. В качестве ДНС можно использовать параметры от Google: 8.8.8.8 и 8.8.4.4.