- How to go to root directory in Linux
- How to go to the root directory in Linux
- Closing Thoughts
- Related Linux Tutorials:
- How to Go to Root Directory in Linux
- How to go to root Directory
- How to go to root Directory through cd Command
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Syeda Wardah Batool
- Linux directory structure: /home and /root folders
- A brief intro to /home directory in Linux/Unix
- OK, what are user home directories for?
- The properties of /home folder?
- How about /root directory in Linux?
- Some FAQ on user home directories
- Surendra Anne
- Latest posts by Surendra Anne (see all)
How to go to root directory in Linux
The root directory on a Linux system, which is represented by the / character, is the parent path to all files on the installation’s partition. All operating systems have a root directory. If you are familiar with Windows systems, they use the C:\ path as their root directory.
You will see references to the root directory all of the time. Even when looking at the absolute path to a random file, such as /home/linuxconfig/example.txt , you can see the / at the very beginning of the file path, which indicates the root directory. From this path, we can also derive that home is directly inside of the root directory / .
The term “root directory” can sometimes also be confused with the home directory for the root user account. This is typically located at /root , and resides one directory deep within the root directory / . The /root path is treated as any typical user’s home directory, and does not serve a similar purpose to that of the root directory / .
In this tutorial, you will learn how to navigate to the root directory on a Linux system. This means both the top most directory in the file system, / , and the root user’s home directory /root . Read on to learn how.
In this tutorial you will learn:
- How to navigate to the root directory on Linux
- How to navigate to the root user’s home directory
| Category | Requirements, Conventions or Software Version Used |
|---|---|
| System | Any Linux distro |
| Software | N/A |
| Other | Privileged access to your Linux system as root or via the sudo command. |
| Conventions | # – requires given linux commands to be executed with root privileges either directly as a root user or by use of sudo command $ – requires given linux commands to be executed as a regular non-privileged user |
How to go to the root directory in Linux
You can navigate to the root directory on a Linux system by using the cd (change directory) command. As mentioned earlier, the root directory is represented with a forward slash / , so the command would be:
NOTE
The cd command is one of the most essential commands on Linux and you will be using it constantly in order to navigate to different directories via the command line on your Linux system. See our tutorial on cd command in Linux with examples for more information about the command.
To navigate to the root user’s home directory, /root , execute the following command:
If you are already logged into the root user account, then just typing the following commands would also take you to the root user directory:
Closing Thoughts
In this tutorial, we saw how to go to the root directory on a Linux system. The root directory is the top most directory in the Linux file system hierarchy, and should not be confused with the root user’s home directory. From the root directory, you can find all of the files that belong to your Linux installation’s partition, although files could possibly be buried dozens of sub directories deep.
Related Linux Tutorials:
How to Go to Root Directory in Linux
Root directory or folder in any operating system is the one containing all the folders, data, files, directories, and subdirectories. In the Linux operating system, everything that needs to support a system is stored in the root directory. Many beginners mixed the root directory with the home directory and considered them the same. Root directory is the uppermost directory in the system whereas the home directory comes under the branch of root directory.
In a file hierarchy, the root directory is mentioned at the top of the tree as it also contains programs that help to boot the system and device directory.
How to go to root Directory
Root directory is presented with a slash (/) in Linux distributions. If you want to move towards the root directory; only one command you need to follow (which will be discussed later).
Linux provides a utility to change the working directory called the “cd” command-line tool. No matter where you’re in the system, when executing a cd command with slash (/), it will change your current directory to the root directory.
The cd command is not only used to navigate towards the root directory, but also can move to the home directory or any file/folder.
This article is specifically written for how we can move towards the root directory.
How to go to root Directory through cd Command
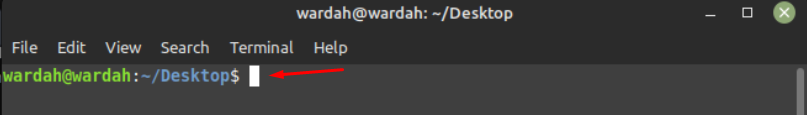
As you can see, my current working directory is desktop:
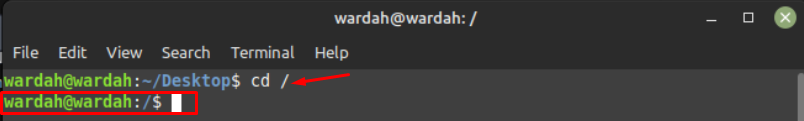
To change and move it to the root directory, the following command you need to execute:
As you can see, the “/$” sign indicates that you’re in the root directory now.
Conclusion
Root directory is the uppermost directory in the Linux system containing all the files, device data and system information in the form of directories. To move to the root directory use “cd /” command, similarly to go to the home directory you must use the similar command.
About the author
Syeda Wardah Batool
I am a Software Engineer Graduate and Self Motivated Linux writer. I also love to read latest Linux books. Moreover, in my free time, i love to read books on Personal development.
Linux directory structure: /home and /root folders
This is our 6th post on understanding first level directories in /. Knowing these folders in detail or at least what each is meant for will help you understand Linux/Unix in whole. we already covered below directories, please have a look at those to understand them. In this post we will see two more directories ie /home and /root directory. These directories are meant for similar purpose. The /root is meant for just root user and /home is for all the remaining users.
A brief intro to /home directory in Linux/Unix
The /home directory is a place where by default all user home directories are created.
OK, what are user home directories for?
These directories are a kind of personal place(Working space) for all the users other than root. There will be a separate folder for each user in /home directory. For example if you have a user called ‘Tom’, then his default home directory is /home/tom. We can change this default folder when creating user in Linux. Our Tom user can do what ever he wants in /home/tom folder where he have full rights on the files he created and owned in that folder.
The properties of /home folder?
1) A separate sub folder ie /home/ is present for each user.
2) Only user who owns this sub folder can access it’s content other than root user. So, tom user can not access Barbi user home directory content which is located at /home/barbi.
3) All his terminal properties, command history file, application setting files(~/.vimrc, ~/.ssh) etc everything is located in this folder.
4) System admins when try to implement quota for users they will implement it on /home directory. This /home directory should be mounted on a separate partition.
Each user home directory is important and frequently used directory for that user, we have alias name for it. This alias is set to ~ so that when ever user wants to navigate to his home directory, he do not have to use /home/ but just use below short cuts.
Will take you to your home directory.
When you are in your home directory even our PS1 prompt will show user’s home directory with ~.
xyz@sanne-taggle:/home$ cd xyz@sanne-taggle:~$ pwd /home/xyz
Some of the important files which are present in /home/ or /root directory are as below.
1) Bash shell related configuration files.
.bashrc
.bash_history
.bash_profile
.bash_logout
If your shell is not bash then you should see other shell configuration files.
2) Default editor configuration files.
3) You secure shell configuration files are located in ~/.ssh which contain your ssh-keys, knownhosts etc.
How about /root directory in Linux?
This is root’s home directory. Do not get confused between / and /root. Both these are meant for different purpose.
/ is the main folder where your file system resides, where as /root is root user home directory. Similar to /home/, root user saves his personal data, terminal configurations in /root directory.
Some FAQ on user home directories
Why is home directory of root is a separate folder?
Because of security reasons root’s home directory is separated from /home.
I see many users in /etc/passwd but I don’t see them in /home, why?
This can be of two reasons.
1) Either users are system defined users
2) Or users home directory resides some where else.
3) Or intentionally /home directory is not created. For this type of users / will be treated as their home directory. This is a nightmare as he can not do anything in / folder due to lack of permissions.
In our next post we will see lib folder.
Surendra Anne
Mr Surendra Anne is from Vijayawada, Andhra Pradesh, India. He is a Linux/Open source supporter who believes in Hard work, A down to earth person, Likes to share knowledge with others, Loves dogs, Likes photography. He works as Devops Engineer with Taggle systems, an IOT automatic water metering company, Sydney . You can contact him at surendra (@) linuxnix dot com.
Latest posts by Surendra Anne (see all)
- Docker: How to copy files to/from docker container — June 30, 2020
- Anisble: ERROR! unexpected parameter type in action: Fix — June 29, 2020
- FREE: JOIN OUR DEVOPS TELEGRAM GROUPS — August 2, 2019
- Review: Whizlabs Practice Tests for AWS Certified Solutions Architect Professional (CSAP) — August 27, 2018
- How to use ohai/chef-shell to get node attributes — July 19, 2018