- How to Run a Program from the Command Line on Linux
- Running a Program From the Terminal
- Running a Program Outside the $PATH Variable
- Adding a Directory to your $PATH Variable
- Installing and Uninstalling a Program in the Terminal
- Expert Q&A
- Tips
- You Might Also Like
- How to Run an Application in Linux
- How To Run an Application in Linux
- How To Run a Program Using Terminal in Linux
- How To Run Program Using Run Command In Linux
- How To Run Program using Application Menu
- How To run Program using Application Launcher Search
- How To Run Program Using Keyboard Shortcuts in Linux
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Syeda Wardah Batool
- How to start an application from the terminal?
- 4 Answers 4
How to Run a Program from the Command Line on Linux
This article was co-authored by wikiHow staff writer, Travis Boylls. Travis Boylls is a Technology Writer and Editor for wikiHow. Travis has experience writing technology-related articles, providing software customer service, and in graphic design. He specializes in Windows, macOS, Android, iOS, and Linux platforms. He studied graphic design at Pikes Peak Community College.
The wikiHow Tech Team also followed the article’s instructions and verified that they work.
This article has been viewed 278,083 times.
Most Linux distributions have a graphical user interface that allows you to open programs by just clicking on the program’s icon in the Apps menu. However, there are situations where you may want to run a program from the Terminal. The Terminal is a powerful tool that allows you to run programs and manage your Linux system using keyboard commands. This wikiHow teaches you how to run a program from the Terminal in Linux.
Running a Program From the Terminal
Press Ctrl + Alt + T to open the Terminal. You can open the Terminal using the keyboard shortcut on most Linux distributions. The keyboard shortcut is Ctrl + Alt + T. You can also click the Terminal icon in your Apps menu. It generally has an icon that resembles a black screen with a white text cursor.
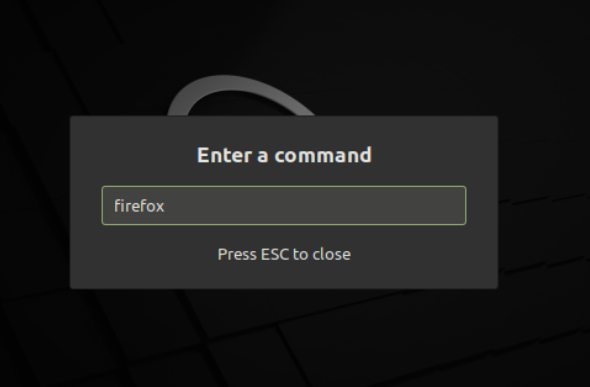
- For example, if you want to run Firefox from the Terminal, you would simply type firefox and press Enter.
- Type -h or —help after the program name to display the help menu for that program. Many programs have additional command modifiers you can use to launch the program in a specific way. For example, you can launch a website in a web browser by typing the web browser name followed by the web address and press Enter to launch that website in the web browser (i.e. firefox www.wikihow.com .
- If you receive a message that says you don’t have permission to run a program or access is denied, type sudo before the program name and press Enter. The «sudo» command allows regular users to run Terminal commands with administrative privileges or root access.
- If you want to run a C or C++ program from the Terminal, you will first need to complie the program before you can launch it from the Terminal.
Running a Program Outside the $PATH Variable
Press Ctrl + Alt + T to open the Terminal. You can open the Terminal using the keyboard shortcut on most Linux distributions. The keyboard shortcut is Ctrl + Alt + T. You can also click the Terminal icon in your Apps menu. It generally has an icon that resembles a black screen with a white text cursor.
Type cd followed by a space and the location the program file is saved to. If the program launch file is saved to a location that is not in your $PATH variable, then you will need to navigate to that location inside the Terminal. You can do so using the «cd» command. For example, if you have folder for Python programs saved in your «Documents» folder, you can navigate to it in the Terminal by typing cd ~/Documents/Python or something similar, and then press Enter.
Type chmod a+x [filename] and press ↵ Enter . Replace «filename» with the actual launch file of the program. The «chmod a+x» command tells Linux the file is an executable file. [1] X Research source
Type «./» followed by the launch filename and press ↵ Enter . This launches the program. For example, if you have a Python file called «Helloworld.py», you would type ./helloworld.py to launch the file. [2] X Research source
Adding a Directory to your $PATH Variable
Press Ctrl + Alt + T to open the Terminal. If you cannot run a program by simply typing the program’s name, you may need to add the directory that the program is installed in to your $PATH variable. You can do this from the Terminal as well. Use the keyboard shortcut to open the Terminal if you haven’t already done so.
- For example, if you have a program installed in the «bin» directory of your «Home» folder, you would type export PATH=$PATH:$Home/bin and press Enter. This will temporarily add the «$Home/bin» directory to your $PATH variable.
- You can see which directories are currently added to your $PATH variable by typing the command echo $PATH and pressing Enter.
Type nano ~/.bashrc and press ↵ Enter . This opens the «.bashrc» file in a text editor that is based in the Terminal. You can use this file to permanently add the directory to your $PATH variable.
Add the «export PATH» command to the file. To do so, scroll down to the bottom of the file using the mouse wheel and type export PATH=$PATH:[path/to/program] at the bottom. Replace «[path/to/program]» with the actual directory tree the program is installed in. [3] X Research source
Press Y and press ↵ Enter . This confirms that you want to save and exit the text editor. You will be returned to the standard command prompt in the Terminal.
Type source ~/.bashrc and press ↵ Enter . This loads the updated $PATH variable into your current session. [4] X Research source
Type the name of the program and press ↵ Enter . With the program’s directory now added to your $PATH variable, you should be able to launch the program by simply typing the program name and pressing Enter.
Installing and Uninstalling a Program in the Terminal
Press Ctrl + Alt + T to open the Terminal. In addition to launching programs from within the Terminal, you can also install and uninstall programs from within the Terminal. Use the keyboard shortcut to open the Terminal if you haven’t already done so.
Type sudo apt install [app_name] and press ↵ Enter (Debian). Replace «[app_name]» with the actual name of the program you want to install. This command works in Debian-based Linux distributions, such as Ubuntu, and Mint.
Type sudo apt remove [app_name] and press ↵ Enter (Debian). Replace «[app_name]» with the name of the app you want to uninstall. This command works in Debian-based Linux distributions, such as Ubuntu, and Mint.
Type sudo dnf install [app_name] and press ↵ Enter (Red Hat). Replace «[app_name]» with the actual name of the program you want to install. This command works for Red Hat Linux distributions such as RHEL, Fedora, and CentOS.
Type sudo dnf remove [app_name] and press ↵ Enter (Red Hat). Replace «[app_name]» with the name of the app you want to uninstall. This command works for Red Hat Linux distributions such as RHEL, Fedora, and CentOS. [5] X Research source
Type the name of the program and press ↵ Enter . Once the program is installed, you can launch the program by simply typing the program’s name and pressing Enter in the Terminal.
Expert Q&A

Tips
You Might Also Like
How to Change 4-Digit User Codes on Schlage Locks
How to Delay a Batch File: Timeout, Pause, Ping, Choice & Sleep
How to Factory Reset a Schlage Lock & Restore the Default Programming Code
Learn to Write Pseudocode: What It Is and Why You Need It
How to Start Coding: The Beginner’s Guide to Programming
3 Ways to Download GitHub Directories and Repositories
How to Run an Application in Linux
Launching an application using an operating system is the basic task that anyone can perform. The working process of the Linux operating system is totally different from other operating systems like Windows OS or macOS. If you’re a Linux beginner, and want to know different ways to launch or run an application, this tutorial will show you all easy and possible ways.
How To Run an Application in Linux
Linux distribution always has several solutions to perform one operation. You will find multiple choices and can select any of them.
To run an application/program in Linux distributions can be done using command-line and GUI as well. These are the tricks we will cover in this tutorial to run a program:
(I am using Linux Mint 21 to explain these methods)
How To Run a Program Using Terminal in Linux
Most beginners might think that launching an application through GUI is easy. But when you use the command-line, it looks even easier.
To open the application through command-line, open the terminal and type the program name:
How To Run Program Using Run Command In Linux
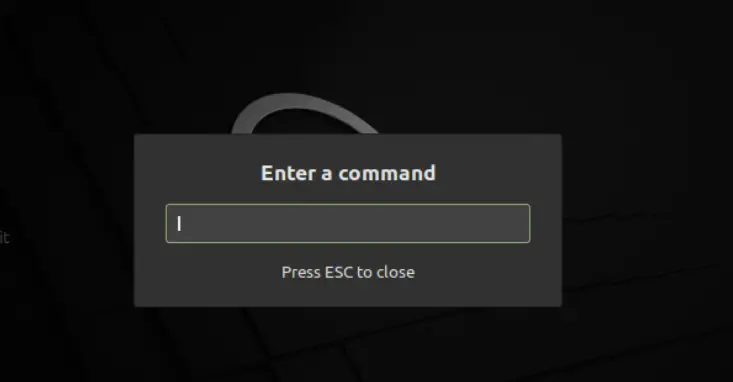
The “run command” is an alternative way to get apps quickly without using a terminal. All distributions of Linux have run commands as a built-in tool. It is quite simple, when you press “alt+f2”, a dialogue box will appear instantly with a pop-up “Enter a Command”:
Enter a program name in the dialogue box and hit enter:
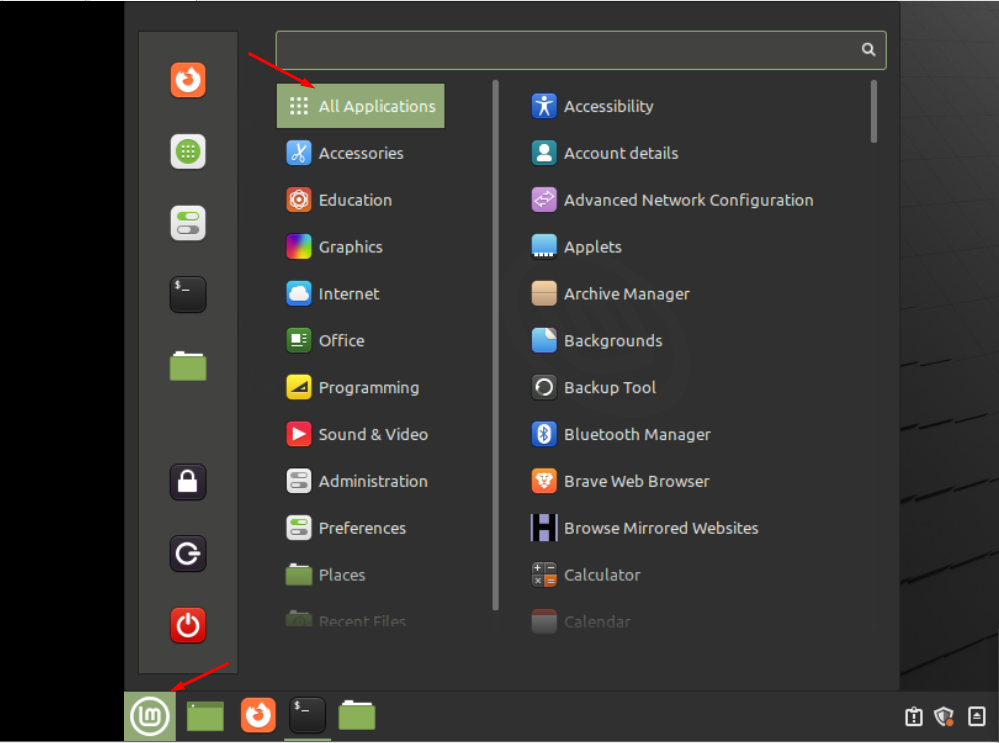
How To Run Program using Application Menu
Like Windows, an application launcher is the most common way to run programs. Application launcher has a list of several icons that you can run on time. As we are working on Linux Mint, you will see the application launcher at the bottom left corner of the screen. To run the application, simply navigate to that application icon and click it:
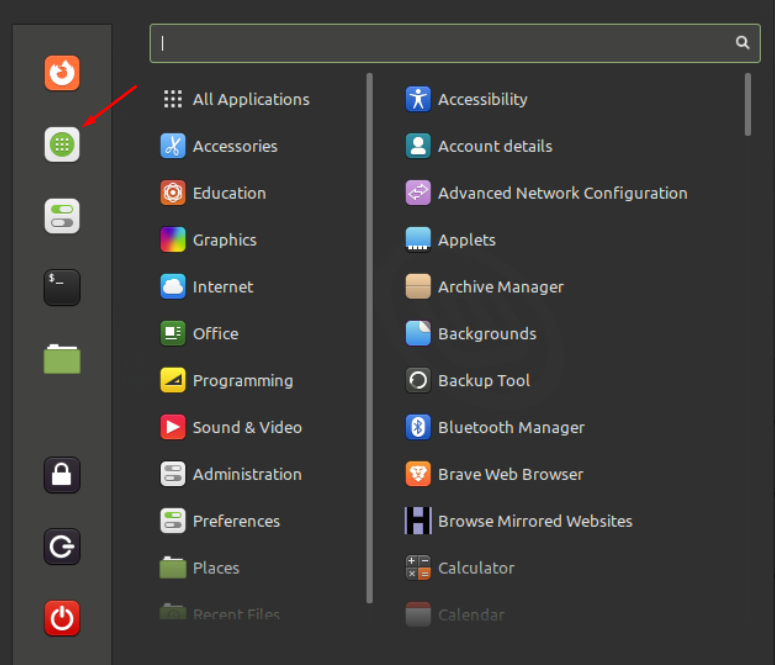
How To run Program using Application Launcher Search
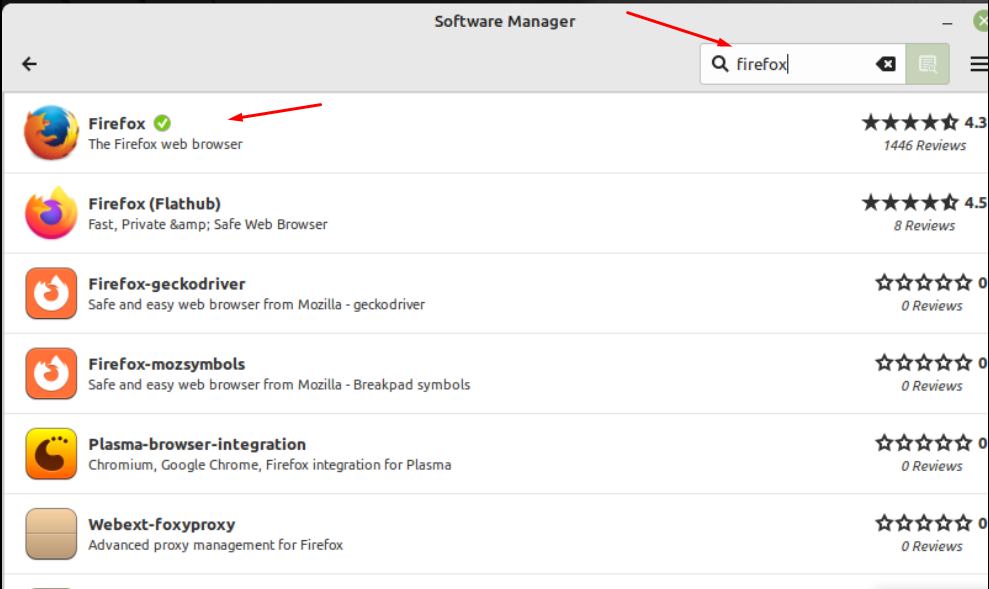
Application menu is yet another easiest way to run programs on screen. What you need to do is open the application menu by clicking its icon located at the top left corner of the screen:
It will redirect you to the Software Manager, navigate towards the search bar and type the program name with correct spelling and select it to open:
How To Run Program Using Keyboard Shortcuts in Linux
If you’re a keyboard user and don’t prefer to use a mouse, then this trick will help you. Keyboard shortcuts allow the user to run programs without using a mouse. It would be done when paying attention to the few steps we have mentioned below:
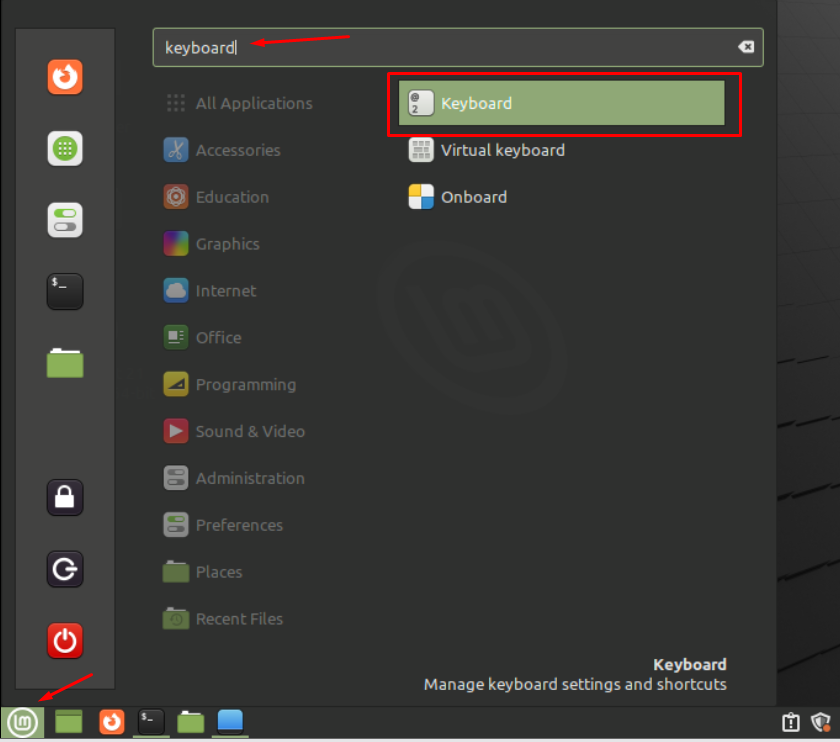
Open the application menu, type keyboard in the search bar and hit Enter:
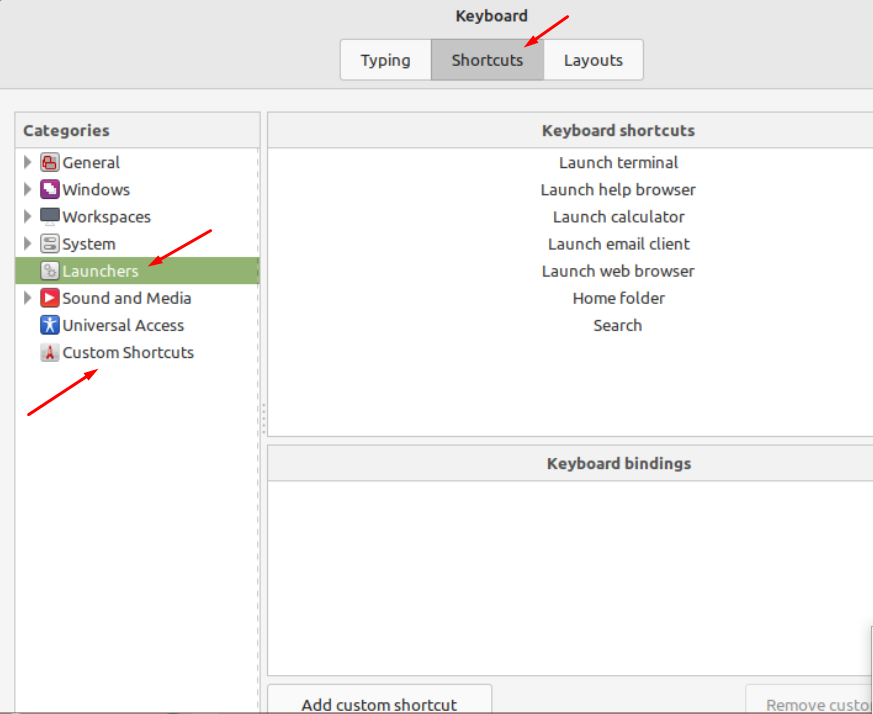
Move to the “Shortcuts” tab, select “Launchers” from the left corner and you will get “Custom Shortcuts” there, hit it and add any shortcut you want.
Conclusion
The Linux operating system provides multiple ways to the beginner. It helps them to learn each way and select their favorite one to perform the task. Similarly, this article has shown multiple tricks to run or launch a program in Linux. We have mentioned 6 easiest approaches to run or launch a program on a Linux system.
About the author
Syeda Wardah Batool
I am a Software Engineer Graduate and Self Motivated Linux writer. I also love to read latest Linux books. Moreover, in my free time, i love to read books on Personal development.
How to start an application from the terminal?
I’m getting started on the Ubuntu terminal. How can I start an application (for example, CompizConfig Settings Manager ) from the terminal? Which command do I have to use?
4 Answers 4
to run Compiz Config Settings Manager you have to type ccsm
Options: -h, --help show this help message and exit -p PLUGIN, --plugin=PLUGIN Directly jump to the page of PLUGIN -c CATEGORY, --category=CATEGORY Directly jump to CATEGORY -v, --version Version I believe after you’ve installed compizconfig-settings-manager
You can try and gradually you start remembering Therefore first you must understand the concept. Linux terminal is the way to interact with the overall Linux system that is underneath the Graphical environment.
To find out what the command line name of an application is, you would need to check the files which get placed into the GUI menu. This is actually not very obvious any more and I can’t point you to the answer directly.
If you open the system-monitor gui application, or run top in a shell, you will see the most active processes at any one time. Doing this whilst interacting with CCSM should help you to identify it’s process name. On the command line, you can use tab completion (try typing c-c-tab-tab then s-tab and you’ll see what I mean.
One small detail, if you run ccsm from the command line, the shell you are running will be suspended whilst that GUI program is running. You will see some output as it runs, then when you quit, the prompt will come back. An alternative it to type ccsm & which will allow the gui to run in the background in parallel with your shell.