- Run Python Scripts in Linux Command Line
- Method 1: Run it using python
- Method 2: Make Python script executable
- How to Run an Application in Linux
- How To Run an Application in Linux
- How To Run a Program Using Terminal in Linux
- How To Run Program Using Run Command In Linux
- How To Run Program using Application Menu
- How To run Program using Application Launcher Search
- How To Run Program Using Keyboard Shortcuts in Linux
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Syeda Wardah Batool
- Brilliant Ways on How to Run a Program in Linux
- Prerequisites
- Launching Programs with the Application (App) Launcher
- Launching Programs with the Applications Menu (Unity Dash)
- Using the Run Command to Launch Program
- Running Programs Using Hot Keys
- Setting Up Keyboard Shortcuts to Run Programs in Linux
- Running a Program within the Terminal
- Conclusion
Run Python Scripts in Linux Command Line
This quick tip shows how to run Python programs from the Linux command line.
If you want to do something, it is pretty much guaranteed that there is a Python script for it. So, when you have a Python script, how do you run it?
The simplest way is to use the python or python3 command in the following manner:
Some distributions have used python2 as python and have an explicit command python3 for python3. So if you want Python 3 to be guaranteed, use python3 .
Method 1: Run it using python
The easiest method to run a Python script on any Linux distribution is by invoking the python command and provide it with the name of your Python script.
This will ensure that if the file’s contents are valid, it will be executed without any problems.
Method 2: Make Python script executable
You may have encountered executing bash scripts simply by typing out their relative/absolute path in the terminal. i.e. you never had to do a bash .sh like you do with Python scripts by typing python .py
In order to achieve this, a few things should be done first.
If you might have noticed, the bash scripts that you can execute by simply typing out their relative/absolute path, they are «executable» files.
To make your Python script executable, run the following command in your terminal:
This should be it. Right? I have a file hello.py , let’s try running it.
$ cat hello.py print("Hello Linux Handbook!") $ chmod +x hello.py $ ./hello.py ./hello.py: 1: Syntax error: word unexpected (expecting ")")Uh oh. What? Syntax error? But it is a valid Python program/script.
The reason why we got this error is because by making hello.py an executable file, all we did was tell the shell that «You can execute it», but not what interpreter/program to use when it is being executed.
My shell (bash) thought that it was a bash script. And hence, we got this error.
The solution to overcome this is pretty simple. Add the following line to the first line of your Python script.
The #! syntax is used mostly in scripts (where you need an interpreter). Now, the /usr/bin/env part means that we are calling env to find the python command from $PATH and execute it for us.
This essentially starts Python for us, instead of the user needing to invoke it manually every time. And, if you don’t automate these things, are you even scripting?
Another reason to use env in shebang is to make it portable. Some systems have the Python executable interpreter stored as /usr/local/bin/python , while some might have /usr/bin/python .
Now, let’s try executing hello.py once again, but with the necessary changes made to it.
$ sed -i '1 i\#!/usr/bin/env python\n' hello.py $ cat hello.py #!/usr/bin/env python print("Hello Linux Handbook!") $ ./hello.py Hello Linux Handbook!Oh hey! It runs flawlessly now.
Now that you know how to run Python programs from the terminal, how about learning to use Linux commands from Python scripts?
How to Run an Application in Linux
Launching an application using an operating system is the basic task that anyone can perform. The working process of the Linux operating system is totally different from other operating systems like Windows OS or macOS. If you’re a Linux beginner, and want to know different ways to launch or run an application, this tutorial will show you all easy and possible ways.
How To Run an Application in Linux
Linux distribution always has several solutions to perform one operation. You will find multiple choices and can select any of them.
To run an application/program in Linux distributions can be done using command-line and GUI as well. These are the tricks we will cover in this tutorial to run a program:
(I am using Linux Mint 21 to explain these methods)
How To Run a Program Using Terminal in Linux
Most beginners might think that launching an application through GUI is easy. But when you use the command-line, it looks even easier.
To open the application through command-line, open the terminal and type the program name:
How To Run Program Using Run Command In Linux
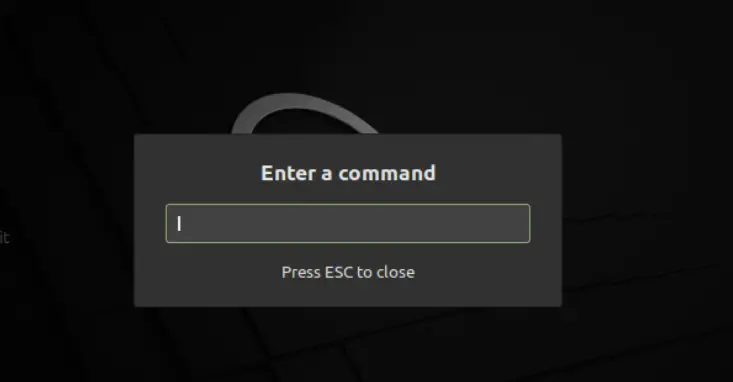
The “run command” is an alternative way to get apps quickly without using a terminal. All distributions of Linux have run commands as a built-in tool. It is quite simple, when you press “alt+f2”, a dialogue box will appear instantly with a pop-up “Enter a Command”:
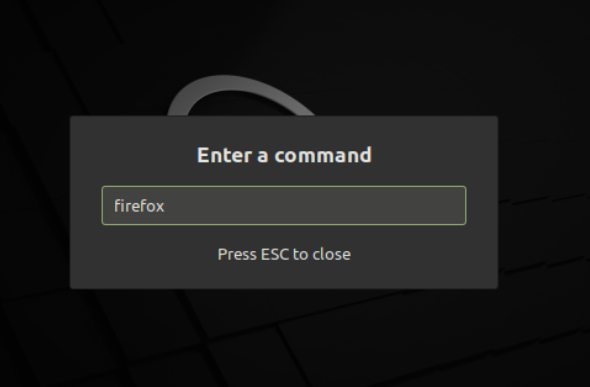
Enter a program name in the dialogue box and hit enter:
How To Run Program using Application Menu
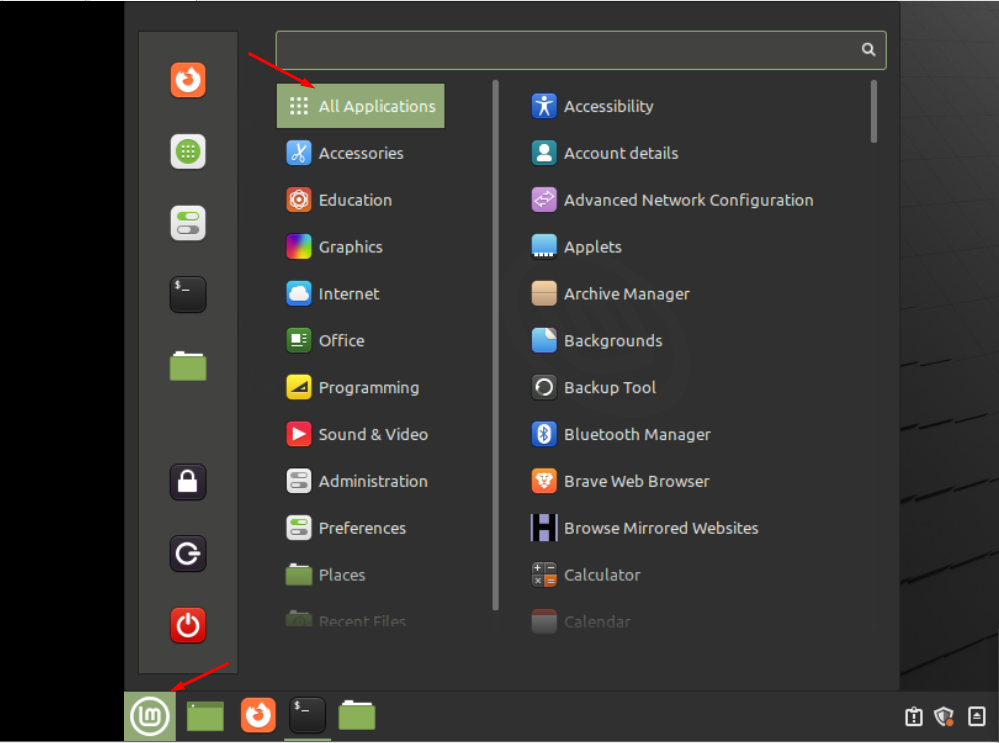
Like Windows, an application launcher is the most common way to run programs. Application launcher has a list of several icons that you can run on time. As we are working on Linux Mint, you will see the application launcher at the bottom left corner of the screen. To run the application, simply navigate to that application icon and click it:
How To run Program using Application Launcher Search
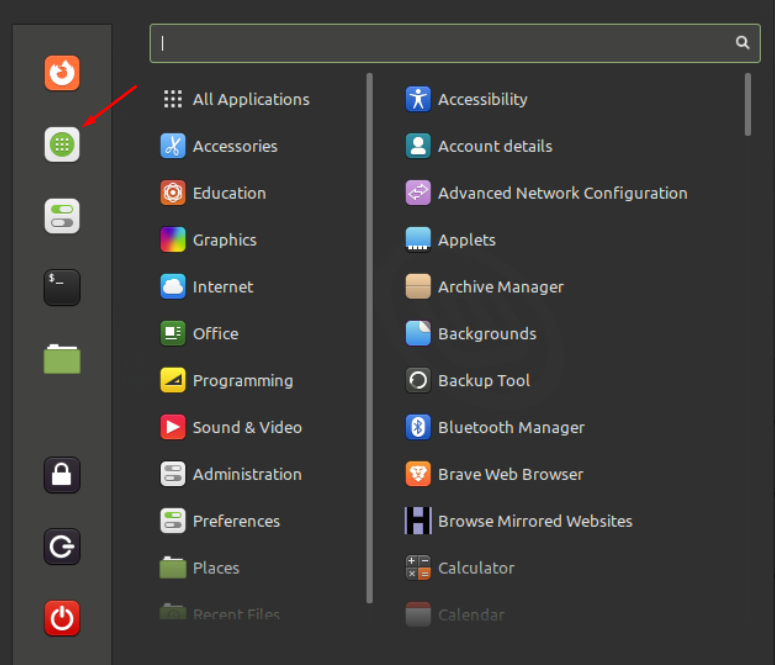
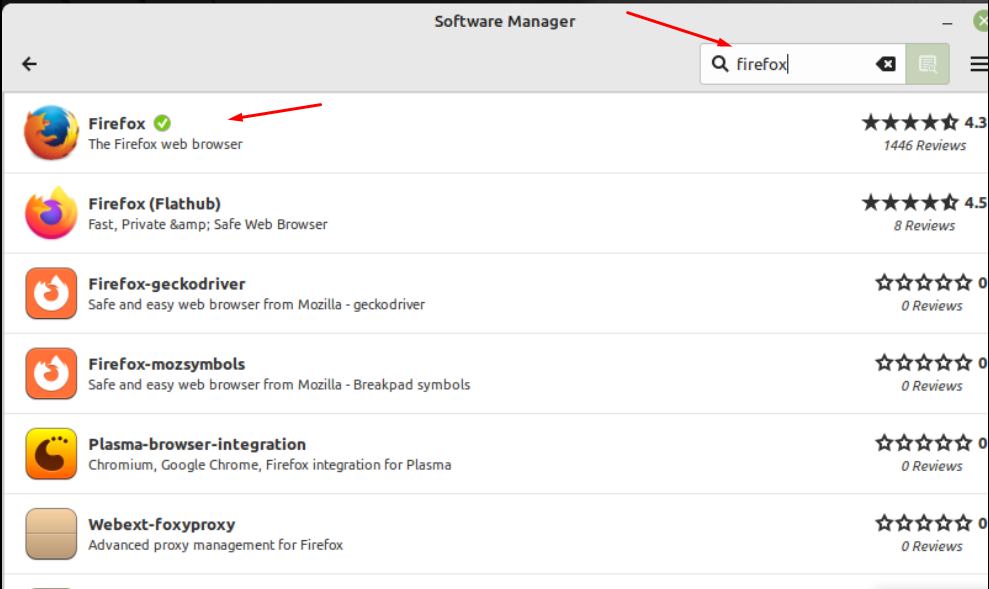
Application menu is yet another easiest way to run programs on screen. What you need to do is open the application menu by clicking its icon located at the top left corner of the screen:
It will redirect you to the Software Manager, navigate towards the search bar and type the program name with correct spelling and select it to open:
How To Run Program Using Keyboard Shortcuts in Linux
If you’re a keyboard user and don’t prefer to use a mouse, then this trick will help you. Keyboard shortcuts allow the user to run programs without using a mouse. It would be done when paying attention to the few steps we have mentioned below:
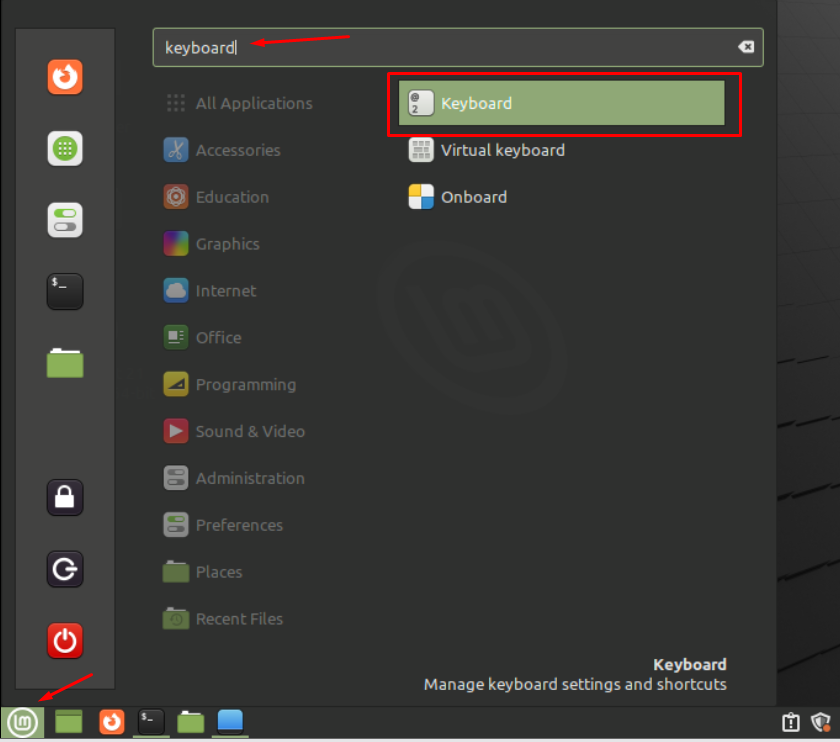
Open the application menu, type keyboard in the search bar and hit Enter:
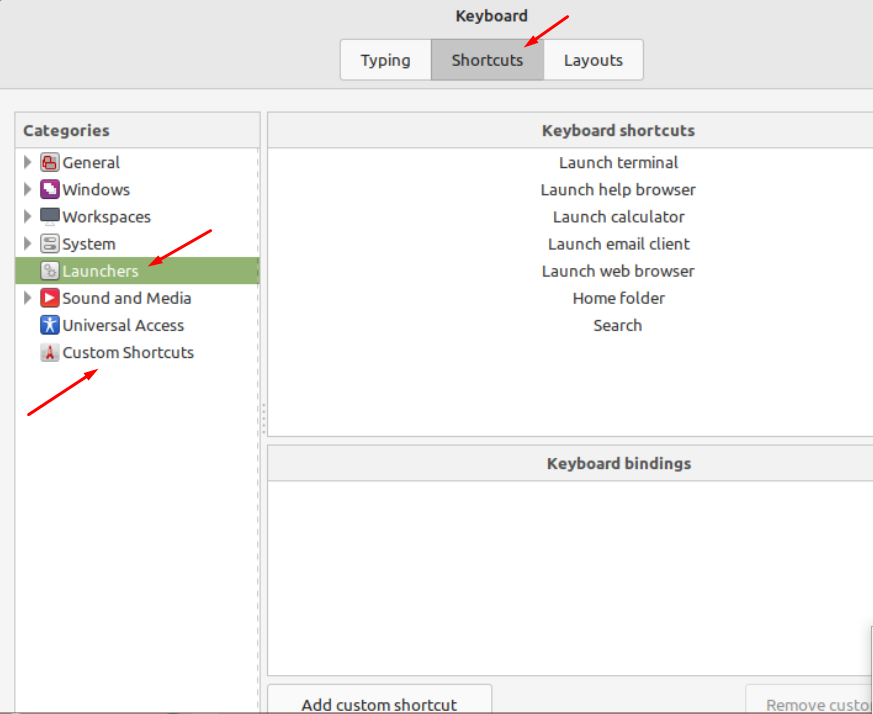
Move to the “Shortcuts” tab, select “Launchers” from the left corner and you will get “Custom Shortcuts” there, hit it and add any shortcut you want.
Conclusion
The Linux operating system provides multiple ways to the beginner. It helps them to learn each way and select their favorite one to perform the task. Similarly, this article has shown multiple tricks to run or launch a program in Linux. We have mentioned 6 easiest approaches to run or launch a program on a Linux system.
About the author
Syeda Wardah Batool
I am a Software Engineer Graduate and Self Motivated Linux writer. I also love to read latest Linux books. Moreover, in my free time, i love to read books on Personal development.
Brilliant Ways on How to Run a Program in Linux
If you are new to Linux, particularly the command line, and want to learn how to run a program in Linux, you’ve come to the right spot. Running programs in Linux is no different than how it’s done in Windows. Easy to say, right? But no worries, you’ll get to run any program in no time.
In this tutorial, you’ll learn many ways to run programs in Linux, both via GUI and a command-line environment. From a novice Linux user to a power user, you will find knowing these methods to run a program helpful.
Prerequisites
Ubuntu Desktop 15.04 or later – Ensure you have a Linux host ready to go. This tutorial uses Ubuntu 15.04 (Desktop version) with GNOME installed, but any newer distribution should work similarly.
Launching Programs with the Application (App) Launcher
There are generally multiple ways to run a program within Windows, and Linux is no different. We will start with the most common way to run a program using the Launcher.
The most common method to run programs in Linux is to use the Launcher. The Launcher is a bar similar to the Windows start menu that contains a list of icons you can click on to run programs.
In Ubuntu, the App Launcher is located on the left side of the screen, as you can see below, containing default commonly run applications. To open the program, simply click the icon representing the program.
Launching Programs with the Applications Menu (Unity Dash)
You can also run programs in Ubuntu Linux with Unity Dash. The Applications Menu or Unity Dash is a handy way to search for and run programs in GNOME. To use the Applications Menu, click on the Ubuntu button in the top left corner.
You’ll see below that the menu opens a search bar with any recently run programs.
Type in the correct name of the program you are looking for (i.e Firefox) and it will appear, then select it to launch the program.
In Ubuntu Linux v20.04+, Unity Dash has been replaced with Activities in the upper left of your screen but the process to run a program remains the same.
Using the Run Command to Launch Program
Another way to launch programs in Linux is to use the Run command. The Run command is a handy way to quickly run a program in Linux by typing the program and executing it.
To run programs via the Run command, select the Alt-F2 to open the Run Command box.
You can also hit Alt-F2 as a shortcut to the run command.
Next, type the name of the program you want to run. In this example, you’ll run the Terminal application, type terminal, select the Terminal icon and hit Enter.
You’ll see below that Linux will launch the Terminal application.
Running Programs Using Hot Keys
If you’re more of a keyboard ninja and would rather skip the mouse like we started with in the last example, you can also run programs with hotkeys. In all Linux distros, you can use the Super Key (Windows Key) + A. The Super Key will bring up all applications in alphabetical order and a text box to type in the name of a program, as shown below.
You can type the name of the program in the search box to navigate to the program or click on the program with your mouse if it appears immediately.
Setting Up Keyboard Shortcuts to Run Programs in Linux
Now that you have learned the GUI options to run programs, the remainder of this tutorial will focus on using non-GUI-based options to run programs. Let’s first begin with keyboard shortcuts. Using keyboard shortcuts can remove a lot of clicking around.
To set up keyboard shortcuts in Ubuntu:
1. Select the icon in the top left corner again and Keyboard Shortcut. The Keyboard application should show up below. When it does, click on it.
2. In the Keyboard application, click on the Shortcut tab.
In Ubuntu 20.04 and newer, selecting Keyboard Shortcut from the Activities menu brings you directly to the Shortcuts tab.
3. Click on the + icon to create a new keyboard shortcut. Ubuntu will direct you to the Custom Shortcuts section.
4. Next, enter a descriptive Name for the shortcut key and provide the Command (program) to execute and click Apply.
When Ubuntu creates the shortcut, you’ll see that the Name shows up under Custom Shortcuts but it’s disabled.
5. Now, click on the Disabled text as shown above and press the desired keyboard shortcut such as Ctrl+T. Once you type your desired shortcut, it will show up, as shown below.
6. Finally, launch the application by pressing the keyboard shortcut!
Running a Program within the Terminal
Although if you’re a newcomer to Linux, chances are you’ll be running programs with the GUI but if you need to use the command line for any reason, the Terminal makes it easy to do so. The Terminal is a command-line application that allows you to manage all facets of Linux with the keyboard.
To run programs in the Terminal, open the App Launcher (or Activities) in the upper left corner and run the Terminal application as shown below.
When the Terminal opens, as shown below, simply type the name of the program and press Enter.
Running programs in the Terminal will not work for all programs. Some programs may not be in the PATH.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you’ve learned many different methods to run programs in Linux. Using both GUI-based and command-line-based methods, you should now know how to launch programs wherever you are within Linux.
Try installing programs in Linux such as the tutorial to install a common program such as Docker for practice and then run it using a shortcut, command line, or GUI Interface. Which way will you use most often to run your favorite programs?
Hate ads? Want to support the writer? Get many of our tutorials packaged as an ATA Guidebook.