- Reset your Terminal state
- Reset
- Reset and Clear
- More Information
- See Also
- About
- How to reset terminal in Linux
- Methods for how to reset terminal in Linux
- Closing Thoughts
- Related Linux Tutorials:
- NEWSLETTER
- WRITE FOR US
- TAGS
- FEATURED TUTORIALS
- LATEST TUTORIALS
- Как сбросить свойства и настройки терминала?
- 7 ответов
- Ubuntu 16.04
- Сброс настроек графического интерфейса gnome-терминала по умолчанию
- Сброс оболочки
- Терминал Gnome не открывается
- Я сделал что-то для моего приглашения, я хочу, чтобы оно снова выглядело как [email protected]:~$.
- Я не хочу иметь дело с этим, просто дай мне рабочий терминал
Reset your Terminal state
After viewing a non-text file by mistake, or launching some command, it can happen the Terminal screen is unresponsive, has strange letters printed when you press keys. You can recover your Terminal in the following ways:
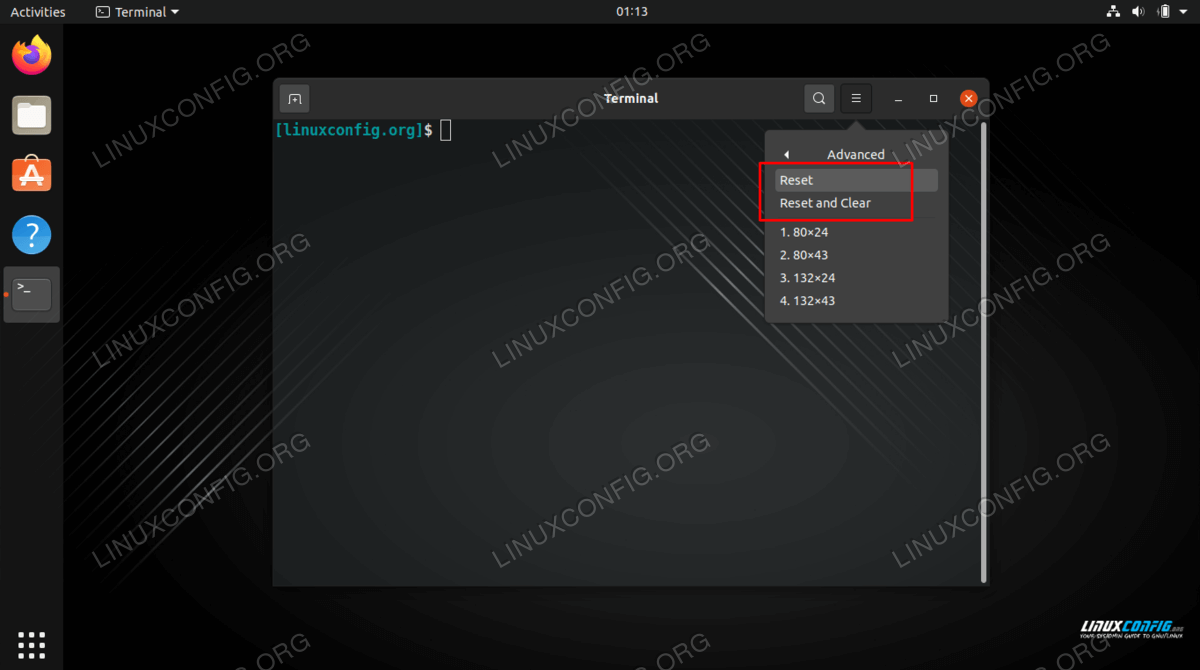
Reset
- Press the menu button in the top-right corner of the window and select Advanced ▸ Reset .
- To obtain the prompt press Enter .
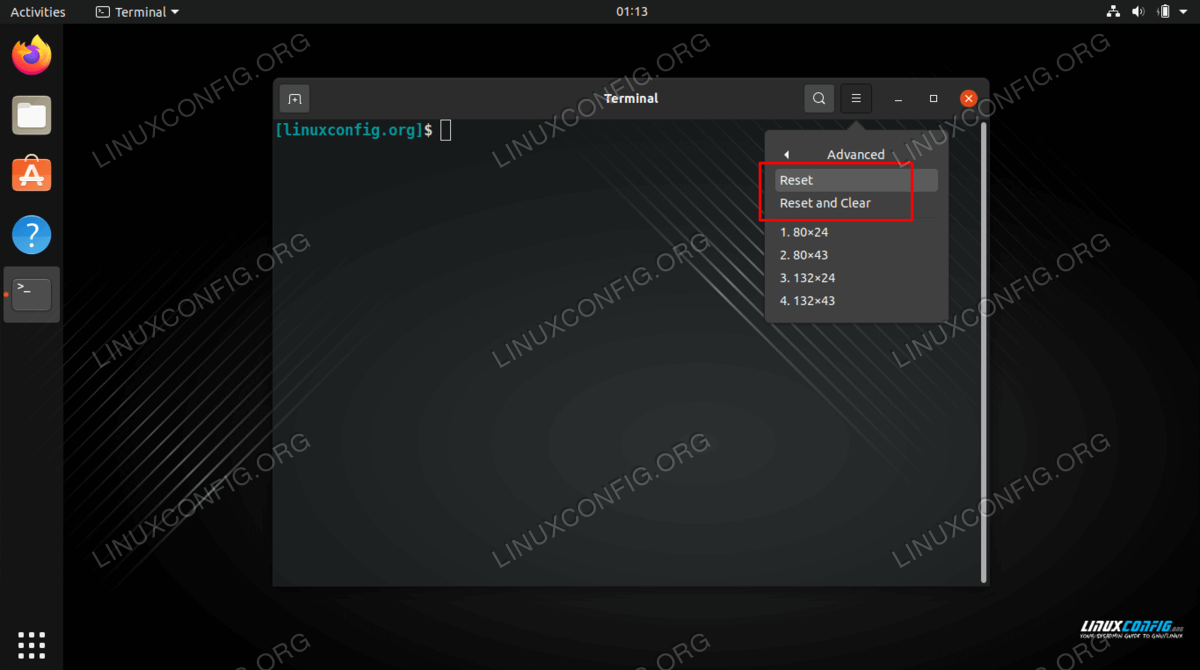
Reset and Clear
In addition to resetting your Terminal , Reset and Clear clears the visible Terminal screen space and the scrollback contents. To Reset and Clear your Terminal :
- Press the menu button in the top-right corner of the window and select Advanced ▸ Reset and Clear .
- To obtain the prompt press Enter .
Reset and Clear provides similar functionality as the terminal command reset .
More Information
See Also
About
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License and a GNU General Public License version 3 . It may be redistributed and/or modified under either license.
This work is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 3 as published by the Free Software Foundation.
This work is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with this program. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses/.
Got a comment? Spotted an error? Found the instructions unclear? Send feedback about this page.
How to reset terminal in Linux
Using the command line terminal is the most powerful way to administer a Linux system. Sometimes, though, a terminal can get hung up and become unresponsive. The terminal can also bug out if you try to read a binary file, filling your screen with strange characters.
In such cases, it is useful to reset the terminal. There are several ways to do this across all Linux systems. In this tutorial, you will see how to reset the terminal in Linux.
In this tutorial you will learn:
- How to reset terminal in Linux with commands
- How to reset terminal via GUI
- How to clear terminal history and scrollback buffer
- How to exit from a process tying up the terminal
| Category | Requirements, Conventions or Software Version Used |
|---|---|
| System | Any Linux distro |
| Software | N/A |
| Other | Privileged access to your Linux system as root or via the sudo command. |
| Conventions | # – requires given linux commands to be executed with root privileges either directly as a root user or by use of sudo command $ – requires given linux commands to be executed as a regular non-privileged user |
Methods for how to reset terminal in Linux
- The best method to reset your terminal is with the reset command. This will wipe everything that is currently in the terminal, including the scrollback buffer (in most terminal applications), and should fix issues such as a bugged terminal or one that is displaying strange characters.
$ cat /dev/null > ~/.bash_history && history -c && reset
Closing Thoughts
In this tutorial, you saw how to reset a command line terminal on a Linux system. We tried to cover every possible scenario here, including a bugged out terminal, one that displays weird characters, clearing the terminal history and scrollback buffer, and exiting from a terminal completely. Remember that your GUI may also contain a way to clear the terminal, as we showd you on GNOME.
Related Linux Tutorials:
Comments and Discussions
NEWSLETTER
Subscribe to Linux Career Newsletter to receive latest news, jobs, career advice and featured configuration tutorials.
WRITE FOR US
LinuxConfig is looking for a technical writer(s) geared towards GNU/Linux and FLOSS technologies. Your articles will feature various GNU/Linux configuration tutorials and FLOSS technologies used in combination with GNU/Linux operating system.
When writing your articles you will be expected to be able to keep up with a technological advancement regarding the above mentioned technical area of expertise. You will work independently and be able to produce at minimum 2 technical articles a month.
TAGS
FEATURED TUTORIALS
- VIM tutorial for beginners
- How to install the NVIDIA drivers on Ubuntu 20.04 Focal Fossa Linux
- Bash Scripting Tutorial for Beginners
- How to check CentOS version
- How to find my IP address on Ubuntu 20.04 Focal Fossa Linux
- Ubuntu 20.04 Remote Desktop Access from Windows 10
- Howto mount USB drive in Linux
- How to install missing ifconfig command on Debian Linux
- AMD Radeon Ubuntu 20.04 Driver Installation
- Ubuntu Static IP configuration
- How to use bash array in a shell script
- Linux IP forwarding – How to Disable/Enable
- How to install Tweak Tool on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Focal Fossa Linux
- How to enable/disable firewall on Ubuntu 18.04 Bionic Beaver Linux
- Netplan static IP on Ubuntu configuration
- How to change from default to alternative Python version on Debian Linux
- Set Kali root password and enable root login
- How to Install Adobe Acrobat Reader on Ubuntu 20.04 Focal Fossa Linux
- How to install the NVIDIA drivers on Ubuntu 18.04 Bionic Beaver Linux
- How to check NVIDIA driver version on your Linux system
- Nvidia RTX 3080 Ethereum Hashrate and Mining Overclock settings on HiveOS Linux
LATEST TUTORIALS
- Easy Steps to Update Your Raspberry Pi
- Connecting Your Raspberry Pi to Wi-Fi: A How-To
- How to install RealVNC viewer on Linux
- How to check Raspberry Pi RAM size and usage
- How to check Raspberry Pi model
- Understanding UEFI and BIOS in Relation to Linux Nvidia Driver Installation
- How to orchestrate Borg backups with Borgmatic
- How to monitor filesystem events on files and directories on Linux
- Debian USB Firmware Loader Script
- How to install and self host an Ntfy server on Linux
- How to backup your git repositories with gickup
- How to bind an SSH public key to a specific command
- Creating a Bootable USB for Windows 10 and 11 on Linux
- How to list all displays on Linux
- List of QR code generators on Linux
- How to extract text from image
- Linux EOF explained
- How to use xclip on Linux
- List of window managers on Linux
- What is zombie process on Linux
Как сбросить свойства и настройки терминала?
Я дурачился с цветами и прочим в терминале, и теперь хочу вернуться к бордово-белой конфигурации терминала по умолчанию. Какие файлы мне нужно удалить?
7 ответов
В терминале нажмите в меню «Редактировать», затем «Настройки профиля». Появится окно «Редактирование профиля». для сброса цвета убедитесь, что вы установили флажок «Использовать цвета из системной темы» на вкладке «Цвета».
Пытаться gconftool —recursive-unset /apps/gnome-terminal
Ubuntu 16.04
Эта простая команда работает в Ubuntu 16.04.
dconf reset -f /org/gnome/terminal/legacy/profiles:/ Сбросить только профиль по умолчанию
Однако, если вы хотите сбросить только профиль по умолчанию, который использует UUID b1dcc9dd-5262-4d8d-a863-c897e6d979b9 по умолчанию вы можете использовать
dconf reset -f /org/gnome/terminal/legacy/profiles:/:b1dcc9dd-5262-4d8d-a863-c897e6d979b9/ Примечание. Этот метод должен работать в Ubuntu 15.04, 15.10 и также может работать в 14.04! Но я не проверял на этих версиях
Если вы хотите сделать полный сброс настроек терминала Gnome, вы можете удалить ~/.gconf/apps/gnome-terminal каталог, который содержит их. Я бы закрыл все окна терминала на вашем рабочем столе. Затем переключитесь с GUI с помощью Ctrl + Alt + F1 и войдите в консоль.
Возможно, вам следует сначала сделать резервную копию каталога, например:
cp -a ~/.gconf/apps/gnome-terminal ~/terminal-settings.bak rm -rf ~/.gconf/apps/gnome-terminal Теперь вы можете переключиться обратно в GUI с помощью Alt + F7 или Alt + F8 и запустить терминал. Необходимо сбросить настройки системы по умолчанию.
Чтобы сбросить терминал, нужно сначала понять, какую именно часть вы хотите сбросить — хотите ли вы сбросить графические изображения? вы хотите сбросить оболочку?
Прежде всего, терминал по умолчанию в Ubuntu gnome-terminal так что для 99% новых пользователей, я полагаю, вы используете gnome-terminal , Опытные пользователи, которые используют что-то кроме gnome-terminal придется обратиться к руководствам соответствующих им эмуляторов терминала.
Сброс настроек графического интерфейса gnome-терминала по умолчанию
Для сброса gnome-terminal достаточно сделать это:
dconf reset -f /org/gnome/terminal/legacy/profiles:/ В качестве альтернативы, вы можете использовать графический инструмент под названием dconf-editor ,
ПРИМЕЧАНИЕ: несколько ответов здесь предлагают gconftool-2 , Тем не мение, GConf
. устарела как часть перехода на GNOME 3. Миграция на ее замену, GSettings и dconf, продолжается ( источник)
Сброс оболочки
Пользователи часто задают вопрос, что у них есть что-то с их оболочкой, и теперь текст в терминале выглядит иначе или они видят ошибку. Простой, быстрый и грязный способ — избавиться от старого ~/.bashrc файл и замените его на файл по умолчанию, хранящийся в /usr/share/base-files/dot.bashrc Вы можете сделать это через терминал или через графический интерфейс — не имеет значения. Через терминал, вы бы сделали cat /usr/share/base-files/dot.bashrc > ~/.bashrc и через графический интерфейс — удалить старый файл, скопировать /usr/share/base-files/dot.bashrc из файлового менеджера в вашу домашнюю папку и переименуйте в .bashrc
Терминал Gnome не открывается
Итак, вы изменили некоторые настройки и теперь gnome-terminal не работает Отлично, что теперь? К счастью, есть несколько способов обойти это.
Один, начать xterm , По умолчанию Ubuntu поставляется с двумя эмуляторами терминала. xterm является оригинальным эмулятором терминала для X11 GUI и существует с давних времен, когда динозавры Unix-систем бродили по земле. Вы можете использовать его для вызова dconf Команда, упомянутая выше, а также сбросить ваш ~/.bashrc Конфигурационный файл
Другой подход, будет использовать dconf-editor инструмент, снова упомянутый выше. Если он не установлен — используйте Software Center, чтобы получить его.
Наконец, вы всегда можете очистить и переустановить терминал. Очистка gnome-терминала означает, что любые связанные с ним файлы конфигурации будут удалены и будут установлены с нуля. Команда сделать это sudo apt-get remove —purge gnome-terminal а потом sudo apt-get install gnome-terminal , Это можно сделать через xterm или TTY ( Ctrl + Alt + F 4 )
Я сделал что-то для моего приглашения, я хочу, чтобы оно снова выглядело как [email protected]:~$.
Вот в чем дело: подсказка состоит из двух статических частей. [email protected]: а также $ , Тот, что в середине, ~ , означает ваш текущий рабочий каталог. Как и в файловом менеджере, при переходе в разные каталоги терминал отображает каталог, в котором вы сейчас работаете. Так, например:
[email protected]:~$ cd /etc xieer[email protected]:/etc$ cd /home/$USER/Desktop [email protected]:~/Desktop$ Если вы хотите увидеть ~ Опять же, все, что вам нужно сделать, это вернуться в свой домашний каталог:
[email protected]:~/Desktop$ cd [email protected]:~$ Если вы хотите навсегда избавиться от информации каталога в вашем приглашении, вам следует отредактировать ~/.bashrc файл. Добавьте эту строку:
Сохраните файл и запустите исходный код ~/.bashrc . Теперь у вас есть статическая подсказка. Большая проблема в том, что вы не увидите, где находитесь в данный момент, поэтому вам придется полагаться на команду pwd для этого и быть осторожным, чтобы не удалить ценные файлы (так что вы были предупреждены:)
Вы также можете использовать bash —posix который будет отображать этот тип приглашения:
Я не хочу иметь дело с этим, просто дай мне рабочий терминал
Это довольно просто: установить другой эмулятор терминала. Ох, и есть из чего выбирать. Лично я бы порекомендовал terminator , guake или же sakura