- How do I force Linux to reacquire a new IP address from the DHCP server?
- How to Release old IP or force Renew DHCP lease IP in Linux
- What is DHCP
- How to Release old IP or force Renew DHCP Lease IP in Linux
- Solution 1: Restart Network Manager
- Solution 2: Using nmcli command
- Solution 3: Restart systemd-networkd
- Примеры команд Linux. Команда «ip»
How do I force Linux to reacquire a new IP address from the DHCP server?
Where interface is the device you want to get a new address for.
The -r flag forces dhclient to first release any leases you have, you can then use this command to request a new lease:
-r Tell dhclient to release the current lease it has from the server. This is not required by the DHCP protocol, but some ISPs require their clients to notify the server if they wish to release an assigned IP address. After this command my Debian failed to get a new IP, but after a reboot I was assigned to a new one, so it work’s!
@EricNord — You can still do this via SSH. Use the ‘at’ command to schedule a one-time command, 1 minute in the future or less, disconnect your SSH session then reconnect. You could even automate it, and reconnect to the same host via Multicast DNS (assuming you have that running, most home networks do)
Either of the following should get it to renew.
/etc/init.d/networking restart I wouldn’t recommend running either over an SSH connection, although you’ll probably get away with the first one if it doesn’t come back with a new ip address.
SSH connections will tolerate a few seconds of «disconnect» provided that you get the connection back up in a few seconds at the same IP address. Under these conditions, I have never lost a connection during /etc/init.d/networking restart , even when it was taking more than 5 seconds to come back up.
Worst case you reconnect. If you’re trying to automate this, see mDNS and ‘at’ command, and use a wrapper script to orchestrate the change and the reconnect.
Would comment p.campbell, but I have only 1 reputation and therefore cannot, first I review installed interfaces:
release IP from selected interface (e.g. eth0, eth1, enp1s0, sit0, wlan0. ):
sudo dhclient -r *interface* request new IP from DHCP server (alert on error):
sudo dhclient -1 *interface* Ubuntu 16.04 LTS confirmed
If you’re using the dhcpcd tool then:
dhcpcd -k interface dhcpcd -n interface The first says to release and deconfigure the interface, and the second says to reload configuration and rebind the interface again.
If the MAC address of the interface isn’t changed, the DHCP server may assign it the same address when renewing. Therefore, a simple release and renew with dhclient may not acquire a new address. Change the MAC address and acquire a new IP address with the following commands. Don’t forget to write the original down if you need to revert back to it at a later time.
ifconfig down ifconfig hw ether ifconfig up This was so helpful, thank you! No number of dhclient -r or ifconfig down gave me a new IP address on my work network, until I changed the MAC address to something random using that command.
In systems where NetworkManager is on, running.
. gets you a connection list, and running.
nmcli con down id 'Connection Name' nmcli con up id 'Connection Name' takes the connection down and back up
How to Release old IP or force Renew DHCP lease IP in Linux
In this article, we will see how to release old IP or force renew DHCP lease IP in Linux. Dynamically allocated IP is an IP leased out from a DHCP server for a particular amount of time over a network. If you are using a lease IP then you always have to renew your ip before the lease period expires. Usually, when a lease reaches 50% of its validity time period, the DHCP client unicasts a DHCP Request message to the DHCP server to request lease renewal. The same can be forced manually through a dhcp client tool in Linux Systems.
What is DHCP
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol is a network management protocol used on Internet Protocol networks for automatically assigning IP addresses and other communication parameters to devices connected to the network using a client–server architecture.
How to Release old IP or force Renew DHCP Lease IP in Linux
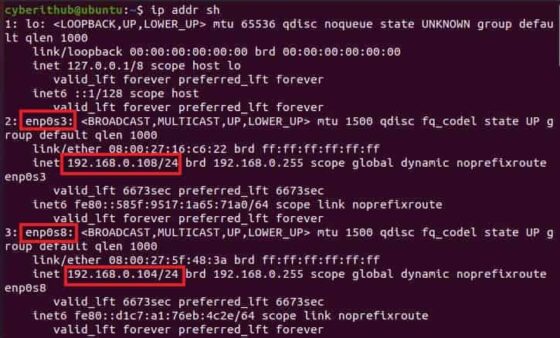
If you have any DHCP lease IP allocated to an interface which you want to release due to certain reasons then you always have the option to release it by using DHCP client tool called dhclient. For example, in my case I have two interfaces attached to my system — enp0s3 and enp0s8 .
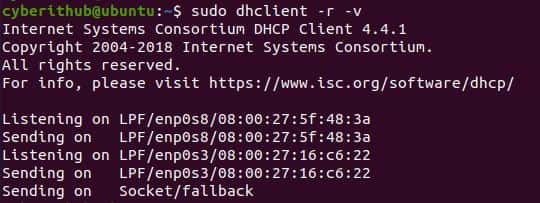
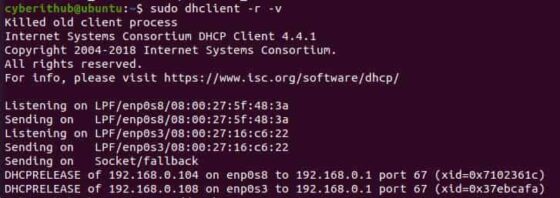
To release the IP attached to both the above interfaces, we need to use sudo dhclient -r -v command. But sometimes what happens is that the IP does not get released as you can see below.
Please don’t ever try to release the IP over SSH connection as it will disconnect you from the host system and you may not be able to reconnect unless a new IP is assigned which is known to you.
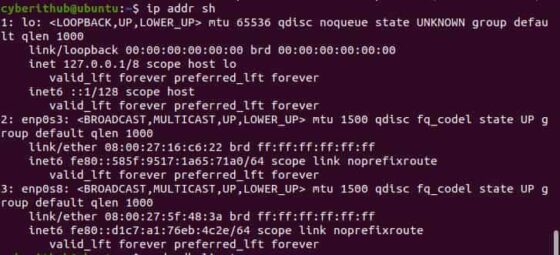
If we try to check again the IP got released or not using ip addr sh command then we can notice that nothing happened. The assigned IP did not got released.
If you try to release IP from specific interface by choosing the interface using sudo dhclient -r -v enp0s3 command then also you can notice that the IP did not got released. This is a very common scenario faced by lot of folks hence I purposefully chosen this one while trying to explain how to release the DHCP lease IP so that you will understand what needs to be done here.
Sometimes even if you try to kill the dhclient process using kill -9 command then you will notice that it is getting started every time you kill this process and the IP is not getting changed. To check the process ID of currently running dhclient program, you can use ps -ef | grep dhclient command as shown below.
In my case process ID(PID) is 2167 , so to kill this one we are using kill -9 2167 command as shown below.
Now if I try to check the process again, I can see that a new dhclient command is launched with process ID(PID) 2169 . So now you must be wondering how did this happen.
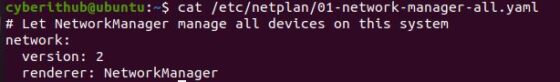
Well, this happened because the network interfaces are currently controlled by Network Manager. You can verify this on Debian/Ubuntu systems by checking one of the below netplan configuration file depending on Ubuntu installation you are currently having.
Please note if you are using RHEL/CentOS based systems, then you need to check /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-
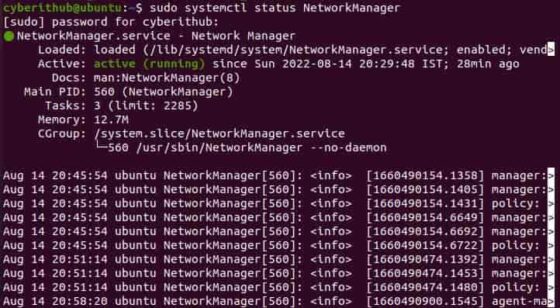
You can check the running status of Network Manager by using sudo systemctl status NetworkManager command as shown below.
If you are also facing problems like above, then you can try below solutions that works for you.
Solution 1: Restart Network Manager
First solution you can try is that you can restart Network Manager by running sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager command as shown below.
Solution 2: Using nmcli command
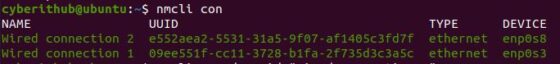
If the first solution does not work then next you can try restarting your connection using nmcli command. Here you need to first check the current connection using nmcli con command as shown below.
Then first take down the connection for the interface where you need to renew the IP. In our case, let’s say we want to renew the IP of enp0s3 interface, then we need to run nmcli con down id «Wired Connection 1» command after releasing the IP as shown below.
Then bring up the connection using nmcli con up id «Wired connection 1» command as shown below.
Solution 3: Restart systemd-networkd
If second solution also did not worked out, then you can try restarting systemd-networkd once by using sudo systemctl restart systemd-networkd command as shown below.
After applying above solution, you can see that you will be able to release the IP as shown below.
You can verify the same by checking the status of ip assigned to network interfaces using ip addr sh command as shown below. From the output, you can see that none of the IP is assigned to both the interfaces — enp0s3 and enp0s8 . This confirms that IP release was successful.
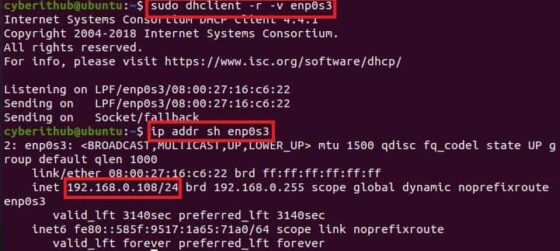
Once the IP is released, you will be able to get the new ip by running sudo dhclient -v command as shown below.
Примеры команд Linux. Команда «ip»
Команда «ip» используется для настройки параметров сетевого интерфейса и назначения ему адреса в ОС Linux. Эта команда заменяет старую добрую и устаревшую команду «ifconfig» в современных дистрибутивах Linux. В статье описываются её различные способы применения.
Как использовать команду IP
Примеры объектов (OBJECT) приведены ниже. Их можно использовать в полной или сокращённой форме.
ip OBJECT help ip OBJECT h ip a help ip r helpВнимание: Приведённые ниже команды необходимо выполнять с осторожностью, по ошибке есть риск потерять связь с сервером. Будьте внимательны при работе с удалённым сеансом по протоколу ssh.
Пример вывода команды
Отображение IP-адреса с помощью команды «ip»
### Only show TCP/IP IPv4 ## ip -4 a ### Only show TCP/IP IPv6 ### ip -6 a### Only show eth0 interface ### ip a show eth0 ip a list eth0 ip a show dev eth0 ### Only show running interfaces ### ip link ls upПример вывода команды
Назначить IP-адрес интерфейсу
Чтобы добавить адреса IPv4/IPv6 используется синтаксис:
ip a add 192.168.1.200/255.255.255.0 dev eth0 ip a add 192.168.1.200/24 dev eth0 Добавление широковещательного адреса на интерфейс
По умолчанию команда «ip» не добавляет широковещательных адресов, если они явно не заданы. Для назначения широковещательного адреса используется следующий синтаксис:
ip addr add brd dev ip addr add broadcast dev ip addr add broadcast 172.20.10.255 dev dummu0Удалить / Удалить IP-адрес с интерфейса
Для удаления IPv4/IPv6-адреса из интерфейса используется синтаксис:
ip a del 192.168.1.200/24 dev eth0 Сбросить IP-адрес с интерфейса
Можно удалить IPv4/IPv6-адреса последовательно, как описано выше. Но есть еще один способ – использовать команду «flush». С помощью неё можно удалить ip-адрес в соответствии с заданным условием. Например, вы можете удалить все IP-адреса из частной сети 192.168.2.0/24, используя следующую команду:
2: eth0 inet 192.168.2.201/24 scope global secondary eth0 2: eth0 inet 192.168.2.200/24 scope global eth0 *** Round 1, deleting 2 addresses *** *** Flush is complete after 1 round *** ip -4 addr flush label "ppp*"ip -4 addr flush label "eth*" Изменяем статус интерфейса UP/DOWN
Как изменить txqueuelen устройства?
Вы можете установить длину очереди передачи устройства с помощью команды «ifconfig» или команды «ip» следующим образом:
ip link set txqueuelen dev
ip link set txqueuelen 10000 dev eth0 ip a list eth0Как изменить MTU устройства?
Для гигабитных сетей можно установить максимальный размер передачи (MTU) с целью повышения производительности сети.
Синтаксис:
ip link set mtu 9000 dev eth0 ip a list eth0 2: eth0: mtu 9000 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000 link/ether 00:08:9b:c4:30:30 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 192.168.1.10/24 brd 192.168.1.255 scope global eth1 inet6 fe80::208:9bff:fec4:3030/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft foreverПосмотреть ip-адреса соседних устройств
74.xx.yy.zz dev eth1 lladdr 00:30:48:yy:zz:ww REACHABLE 10.10.29.66 dev eth0 lladdr 00:30:48:c6:0a:d8 REACHABLE 74.ww.yyy.xxx dev eth1 lladdr 00:1a:30:yy:zz:ww REACHABLE 10.10.29.68 dev eth0 lladdr 00:30:48:33:bc:32 REACHABLE 74.fff.uu.cc dev eth1 lladdr 00:30:48:yy:zz:ww STALE 74.rr.ww.fff dev eth1 lladdr 00:30:48:yy:zz:ww DELAY 10.10.29.65 dev eth0 lladdr 00:1a:30:38:a8:00 REACHABLE 10.10.29.74 dev eth0 lladdr 00:30:48:8e:31:ac REACHABLE STALE — означает действительную, но недоступную запись.
DELAY — означает, что ядро всё еще ожидает проверки из устаревшей записи.
REACHABLE — означает действительную запись до истечения таймаута.
Добавить новую ARP- запись
ip neigh add lladdr dev nud
ip neigh add 192.168.1.5 lladdr 00:1a:30:38:a8:00 dev eth0 nud perm ip neigh del dev ip neigh del 192.168.1.5 dev eth1ip neigh chg 192.168.1.100 dev eth1 nud reachable IP route: команды отображения и изменения таблицы маршрутизации
ip r ip r list ip route list ip r list [options] ip route В качестве примера отобразим маршрутизацию для 192.168.1.0/24:
ip route add via ip route add dev ## Add default route using ip ## ip route add default dev ip route add default via
ip route add 192.168.1.0/24 via 192.168.1.254 ip route add 192.168.1.0/24 dev eth0 ip route del 192.168.1.0/24 dev eth0 Изменить MAC-адрес в Linux
MAC-адрес – это физический идентификатор, назначаемый каждому интерфейсу. Его можно изменить следующим образом:
Вывод сервера будет примерно таким. Он будет содержать параметры (mac — адреса всех ваших интерфейсов):
Настройка цветного вывода
Можно сделать вывод команды ip цветным и удобным для восприятия, для этого добавляем опцию: «-c» .
Также для удобства можно создать постоянный псевдоним, тогда вывод команды можно будет запускать более простой командой.
alias ip='ip -c' alias ipc='ip -c' # run it # ipc route ip link Примеры алиасов
Посмотреть IP-адреса всех сетевых интерфейсов
$ sudo ip -br -c addr show $ sudo ip -br -c link showПример вывода
Устаревшие и новые заменяющие их команды в Linux:
Оформите заявку на сайте, мы свяжемся с вами в ближайшее время и ответим на все интересующие вопросы.