How to Reset a Cisco Router or Switch to Factory Default
What if we forget the login credentials of our Cisco routers or switches and we are not able to log in to make changes in configuration? To reset the Cisco router or switch is one of the quickest ways to resolve the issue. It will make a new and blank startup configuration file, and it will show you the setup wizard for a quick configuration of the router.
But what if we want to retain the existing configuration on the router? Another solution is to perform a password recovery on the router. We will discuss how to restore our Cisco routers and switches to the factory defaults and also how to implement password recovery on them.
Factory Reset on Cisco Router or Switch IOS
The following procedure is the steps when we are going to factory reset a Cisco router.
1. In the global configuration mode, create a hostname first on the router as we will use it for verification if the router is already reset into the factory settings.
Router(config)#hostname Router 1
2. Verify the configuration by using one of the following commands.
Router 1#sh running-config Building configuration. Current configuration: 526 bytes ! version 15.1 no service timestamps log datetime msec no service timestamps debug datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname Router 1 ! !
3. Save the configuration using the ‘copy running-config startup-config’ command.
Router 1#copy running-config startup-config Router 1#write
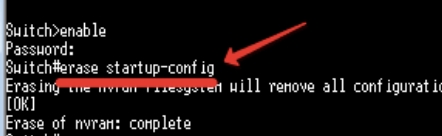
4. Resetting the Cisco router to factory default involves erasing the NVRAM.
Router 1#write erase Erasing the nvram filesystem will remove all configuration files! Continue? [confirm]y[OK] Erase of nvram: complete %SYS-7-NV_BLOCK_INIT: Initialized the geometry of nvram
5. Reload the Cisco router to complete resetting to the factory defaults, and the startup wizard or initial system configuration dialog will appear.
6. Verify if the Cisco router is reset to factory default by checking if “hostname Router 1” is disappeared and changed to default.
Router#sh running-config Building configuration. Current configuration: 584 bytes ! version 15.1 no service timestamps log datetime msec no service timestamps debug datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname Router ! !
Password Recovery on Cisco IOS
Before we proceed with password recovery, we will take a look first at the configuration register. We can use the ‘show version’ command to check the configuration register setting on our device. Configuration Register is a special 16 bits value that can be configured in Cisco routers. It is mainly used to determine how the router boots, to determine boot options, and to set console speed. The following are the most commonly used configuration register settings:
- config-register 0x2102 – boot normally (default configuration register setting)
- config-register 0x2120 – boot into ROM Monitor (ROMMON)
- config-register 0x2142 – ignore contents of NVRAM (startup-configuration)
The following procedure is the steps when we are going to recover the forgotten enable password or enable secret command configured in our Cisco router or switch.
2. Press the break sequence (ctrl-Break) while the router is initializing to break into ROMMON prompt.
3. Follow this command, confreg 0x2142, to ignore the startup-configuration and reset or reload the router.
rommon 1 > confreg 0x2142 rommon 2 > reset
4. After reboot, it will not ask you the secret password and will proceed to the setup wizard or initial system configuration dialog, as it booted up with a blank configuration.
5. The startup-configuration is still there with the full configuration, including the unknown enable secret, but the router does not use it when it boots. Enter a new enable secret in global configuration mode to overwrite the old one. This will go into the running-config.
Router(config)#enable secret cisco12345
6. In the global configuration mode, configure the configuration register back to default by entering the ‘config-register 0x2102’ router command, so the router will boot normally on the next restart.
Router(config)#config-register 0x2102
7. Save the configuration. This will merge the new enable password into the existing startup-configuration.
Router#copy running-config startup-config
8. Reboot the router using the ‘reload’ command and see that the secret password is changed to the one we configured earlier.
Download our Free CCNA Study Guide PDF for complete notes on all the CCNA 200-301 exam topics in one book.
We recommend the Cisco CCNA Gold Bootcamp as your main CCNA training course. It’s the highest rated Cisco course online with an average rating of 4.8 from over 30,000 public reviews and is the gold standard in CCNA training:
- IOS Basic Commands
- Configure an IP Address on a Switch
- Configure Descriptions
- Interface Range Command
- Power on a Cisco Device
- Half Duplex and Full Duplex
- Configure Speed and Duplex
- Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP)
- Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) overview
- show Command
- show interfaces status Command
- Interface Status Codes
- show version Command
- OSPF Overview
- Differences Between OSPF and EIGRP
- Cisco Bandwidth Command vs Clock Rate and Speed Commands
- OSPF Cost — OSPF Routing Protocol Metric Explained
- OSPF Configuration
- Designated & Backup Designated Router
- OSPF Passive Interface — Configuration and Why it is Used
- OSPF Default-Information Originate and the Default Route
- OSPF Load Balancing — Explanation and Configuration
- OSPF Summarization
- Troubleshooting OSPF and OSPF Configuration Verification
- OSPF Network Types — Point-to-Point and Broadcast
- OSPF Summary
- Cisco Three-Layer Hierarchical Model
- Collapsed Core and Three-Tier Network Architectures
- What is Spine and Leaf Network Architecture?
- What is a VLAN?
- Frame Tagging
- Configuring VLANs
- Access and Trunk Ports
- Inter-Switch Link (ISL)
- IEEE 802.1Q
- Configuring Access & Trunk Ports
- Configuring Voice VLANs
- Configuring Allowed VLANs
- Cisco Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP) Explained
- What is VTP?
- VTP Modes
- VTP Configuration
- What is STP?
- Network Bridge Explained
- How STP Works
- Electing the Root Switch in STP
- Spanning Tree Priority: Root Primary and Root Secondary
- Selecting STP Root Port
- Selecting STP Designated Port (DP)
- Spanning Tree Modes: MSTP, PVST+, and RPVST+
- What is RSTP?
- How RSTP Works
- Configuring RSTP
- Cisco HSRP and Spanning Tree Alignment Configuration
- Spanning Tree Portfast, BPDU Guard, Root Guard Configuration
- What is IPv6?
- IPv6 Address Format
- IPv6 Interface Identifier
- Differences Between IPv4 and IPv6
- Types of IPv6 Addresses
- How to Configure IPv6
- IPv6 SLAAC — Stateless Address Autoconfiguration
- IPv6 Routing — Static Routes Explained and Configured
- IPv6 Default Static Route and Summary Route
- IPv6 Routing Protocols
- Neighbor Discovery Protocol — NDP Overview
- Telnet & SSH
- Setting Up Telnet
- Setting Up SSH
- Cisco Console Port Security
- exec-timeout Command
- Encrypt Local Usernames and Passwords
- Cisco Privilege Levels — Explanation and Configuration
- What is AAA? Authentication, Authorization, & Accounting
- Configuring AAA on Cisco Devices – RADIUS and TACACS+
- Configuring a Cisco Banner: MOTD, Login, & Exec Banners
- Configure Timezone and Daylight Saving Time (DST)
- NTP (Network Time Protocol)
- Configure NTP on a Cisco Router
- What is Network Automation and Why We Need It?
- Network Programmability — Git, GitHub, CI/CD, and Python
- Data Serialization Formats — JSON, YAML, and XML
- SOAP vs REST: Comparing the Web API Services
- Model-Driven Programmability: NETCONF and RESTCONF
- Configuration Management Tools — Ansible, Chef, & Puppet
- Cisco SDN — Software Defined Networking Explained
- Cisco DNA — Digital Network Architecture Overview
- Cisco IBN — Intent-Based Networking Explained
- Cisco SD-Access (Software-Defined Access) Overview
- Cisco SD-WAN (Software-Defined WAN) Overview & Architecture
Сброс настроек Cisco до заводских настроек: пошаговое руководство
Всем привет! Сегодня столкнулся с такой проблемой – ко мне в руки попался Cisco 2960, и перед стандартной настройкой нужно выполнить сброс на заводскую конфигурацию. Никакой кнопки «reset» как на домашнем роутере нет. Поэтому все делается чуть сложнее с подключением к терминалу. Я решил написать два способа:
- Когда вы знаете пароль от привилегированного пользователя.
- Когда вы этот пароль забыли, или старый администратор забыл его сбросить.
Если возникнут какие-то трудности, то пишите свои вопросы в комментариях – постараемся разобраться вместе.
Подключение к терминалу
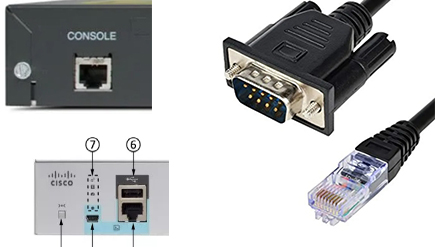
- Подключаем компьютер, или ноутбук к консольному порту через переходник. На некоторых новых моделях к подобному порту можно подключиться через USB. Или используем старый добрый COM-RJ-45.
- После подключения убедитесь, что COM-порт в диспетчере устройств определяется, и подключение есть. Иногда бывает (очень редко), что устройство не определяется – это проблема с драйверами. Заходим в свойства нашего неопределенного устройства, переходим в «Сведения», ставим «Свойства» – «ИД оборудования» и ищем по VID и PID драйвер на любом удобном сервисе (гуглим фразу «Драйвер по ID»).
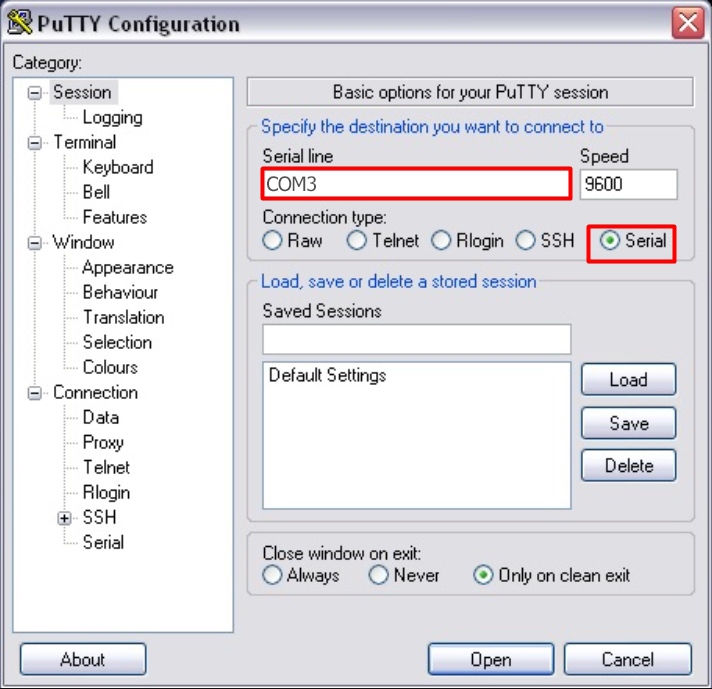
- Далее используем любую удобную терминальную программу. Я использую PuTTY, так как на мой взгляд она наиболее удобна. Запускаем программу, смотрим, чтобы был установлен нужный порт, ставим галочку «Serial» и запускаем коннект.
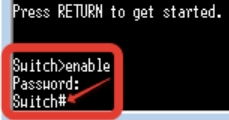
- Если вы видите, что система начала грузиться, и вы видите какие-то знакомые буковки, то значит все хорошо. Если в терминале ничего не отображается, то перезагрузите коммутатор, выдернув и снова подключив его в розетку.
Как подключиться к коммутатору я рассказал, далее я вам поведаю, как выполнить сброс, когда мы знаем и когда не знаем пароль от системы.
Я знаю пароль
ПРИМЕЧАНИЕ! Перезапустить коммутатор можно и физически, отключив его от розетки.
Я не знаю пароль
- Подключаемся к консольному порту с помощью переходника, про это я уже написал в самом начале.
- Нажимаем на кнопку «MODE», и, не отпуская, подключаем кабель питания. Ждем пока кнопка «SYST» не закончит мигать и остановится гореть зелененьким. Нужно будет подождать примерно секунд двенадцать. Отжимаем кнопку.
- Заходим через Putty в терминал.
- В этот момент система запустилась в режиме восстановления. Немного объясню саму суть сброса. По сути наша Cisco – это огромный кусок крутого железа с операционной системой. Но сброс мы делаем именно конфигурационного файла. Его можно удалить, или, например, переименовать, чтобы он остался. Вводим две команды:
flash_init (запускаем инициализацию Flash-памяти)
rename flash:config.text flash:config.old
- Последней командой, мы просто взяли конфигурационный файл, который мы используем и просто его переименовали. Таким образом, система видит, что основного файла нет, и она дальше предложит вам заново настроить устройство. Но есть и второй путь – его можно просто удалить, если он вам не нужен.
rename flash:vlan.dat flash:vlan.old
или
del flash:vlan.dat
- Делаем физическую перезагрузку – так как кнопки нет, то просто вытаскиваем кабель из розетки, ждем пару секунд и вставляем его обратно.
- На этом все, коммутатор предложит вам настроить его заново.
Видео