- A Practical Guide to Nmap (Network Security Scanner) in Kali Linux
- System Requirements
- Kali Linux – Working with Nmap
- How to Find Live Hosts on My Network?
- Find and Ping All Live Hosts on My Network
- Find Open Ports on Hosts
- Find Services Listening on Ports on Hosts
- Find Anonymous FTP Logins on Hosts
- Check for Vulnerabilities on Hosts
- Packages and Binaries:
A Practical Guide to Nmap (Network Security Scanner) in Kali Linux
In the second Kali Linux article, the network tool known as ‘nmap‘ will be discussed. While nmap isn’t a Kali-only tool, it is one of the most useful networks mapping tools in Kali.
Nmap, short for Network Mapper, is maintained by Gordon Lyon (more about Mr. Lyon here: http://insecure.org/fyodor/) and is used by many security professionals all over the world.
The utility works in both Linux and Windows and is a command line (CLI) driven. However, for those a little timider of the command line, there is a wonderful graphical frontend for nmap called zenmap.
It is strongly recommended that individuals learn the CLI version of nmap as it provides much more flexibility when compared to the zenmap graphical edition.
What purpose does nmap serve? Great question. Nmap allows for an administrator to quickly and thoroughly learn about the systems on a network, hence the name, Network MAPper or nmap.
Nmap has the ability to quickly locate live hosts as well as services associated with that host. Nmap’s functionality can be extended even further with the Nmap Scripting Engine, often abbreviated as NSE.
This scripting engine allows administrators to quickly create a script that can be used to determine if a newly discovered vulnerability exists on their network. Many scripts have been developed and included with most nmap installs.
A word of caution – nmap is commonly used by people with both good and bad intentions. Extreme caution should be taken to ensure that you aren’t using nmap against systems that permission has not be explicitly provided in a written/legal agreement. Please use caution when using the nmap tool.
System Requirements
- Kali Linux (nmap is available in other operating systems and functions similar to this guide).
- Another computer and permission to scan that computer with nmap – This is often easily done with software such as VirtualBox and the creation of a virtual machine.
- For a good machine to practice with, please read about Metasploitable 2
- Download for MS2 Metasploitable2
Kali Linux – Working with Nmap
The first step to working with nmap is to log into the Kali Linux machine and if desired, start a graphical session (This first article in this series installed Kali Linux with the XFCE Desktop Environment).
During the installation, the installer would have prompted the user for a ‘root‘ user password which will be needed to log in. Once logged in to the Kali Linux machine, using the command ‘startx‘ the XFCE Desktop Environment can be started – it is worth noting that nmap doesn’t require a desktop environment to run.
Once logged into XFCE, a terminal window will need to be opened. By clicking on the desktop background, a menu will appear. Navigating to a terminal can be done as follows: Applications -> System -> ‘Xterm‘ or ‘UXterm‘ or ‘Root Terminal‘.
The author is a fan of the shell program called ‘Terminator‘ but this may not show up in a default install of Kali Linux. All shell programs listed will work for the purposes of nmap.
Once a terminal has been launched, the nmap fun can begin. For this particular tutorial, a private network with a Kali machine and a Metasploitable machine was created.
This made things easier and safer since the private network range would ensure that scans remained on safe machines and prevents the vulnerable Metasploitable machine from being compromised by someone else.
How to Find Live Hosts on My Network?
In this example, both of the machines are on a private 192.168.56.0 /24 network. The Kali machine has an IP address of 192.168.56.101 and the Metasploitable machine to be scanned has an IP address of 192.168.56.102.
Let’s say though that the IP address information was unavailable. A quick nmap scan can help to determine what is live on a particular network. This scan is known as a ‘Simple List’ scan hence the -sL arguments passed to the nmap command.
Sadly, this initial scan didn’t return any live hosts. Sometimes this is a factor in the way certain Operating Systems handle port scan network traffic.
Find and Ping All Live Hosts on My Network
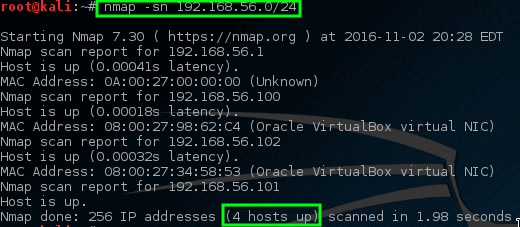
Not to worry though, there are some tricks that nmap has available to try to find these machines. This next trick will tell nmap to simply try to ping all the addresses in the 192.168.56.0/24 network.
This time nmap returns some prospective hosts for scanning! In this command, the -sn disables nmap’s default behavior of attempting to port scan a host and simply has nmap try to ping the host.
Find Open Ports on Hosts
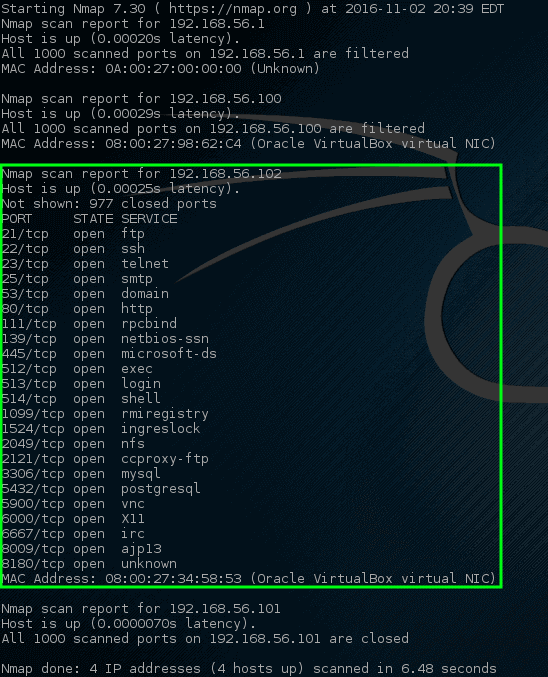
Let’s try letting nmap port scan these specific hosts and see what turns up.
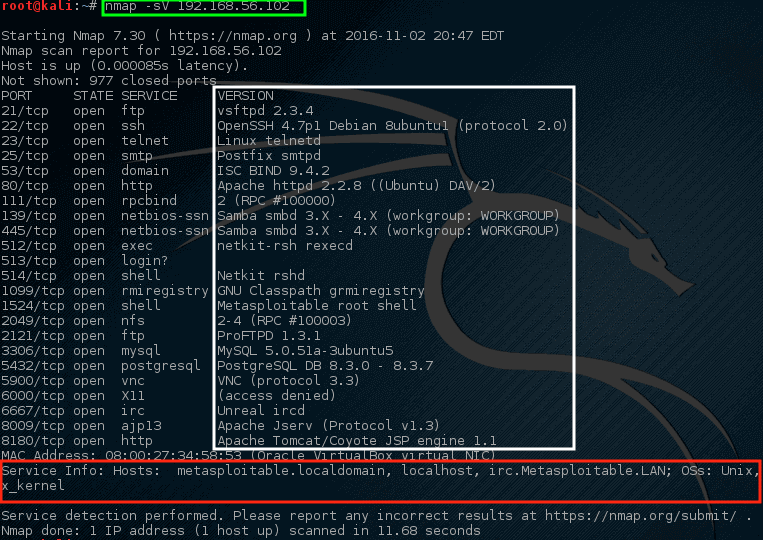
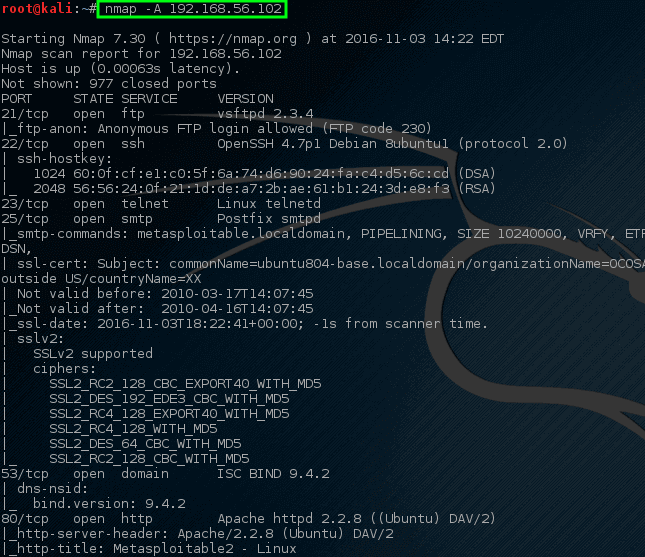
Wow! This time nmap hit a gold mine. This particular host has quite a bit of open network ports.
These ports all indicate some sort of listening service on this particular machine. Recalling from earlier, the 192.168.56.102 IP address is assigned to the metasploitable vulnerable machine hence why there are so many open ports on this host.
Having this many ports open on most machines is highly abnormal so it may be a wise idea to investigate this machine a little closer. Administrators could track down the physical machine on the network and look at the machine locally but that wouldn’t be much fun especially when nmap could do it for us much quicker!
Find Services Listening on Ports on Hosts
This next scan is a service scan and is often used to try to determine what service may be listening on a particular port on a machine.
Nmap will probe all of the open ports and attempt to banner grab information from the services running on each port.
Notice this time nmap provided some suggestions on what nmap thought might be running on this particular port (highlighted in the white box). Also, nmap also tried to determine information about the operating system running on this machine as well as its hostname (with great success too!).
Looking through this output should raise quite a few concerns for a network administrator. The very first line claims that VSftpd version 2.3.4 is running on this machine! That’s a REALLY old version of VSftpd.
Searching through ExploitDB, a serious vulnerability was found back in 2011 for this particular version (ExploitDB ID – 17491).
Find Anonymous FTP Logins on Hosts
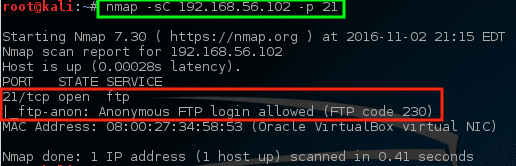
Let’s have nmap take a closer look at this particular port and see what can be determined.
With this command, nmap was instructed to run its default script (-sC) on the FTP port (-p 21) on the host. While it may or may not be an issue, nmap did find out that anonymous FTP login is allowed on this particular server.
Check for Vulnerabilities on Hosts
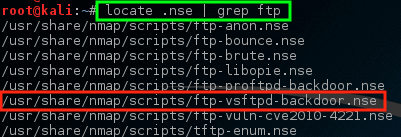
This paired with the earlier knowledge about VSftd having an old vulnerability should raise some concern though. Let’s see if nmap has any scripts that attempt to check for the VSftpd vulnerability.
Notice that nmap has an NSE script already built for the VSftpd backdoor problem! Let’s try running this script against this host and see what happens but first it may be important to know how to use the script.
# nmap --script-help=ftp-vsftd-backdoor.nse
Reading through this description, it is clear that this script can be used to attempt to see if this particular machine is vulnerable to the ExploitDB issue identified earlier.
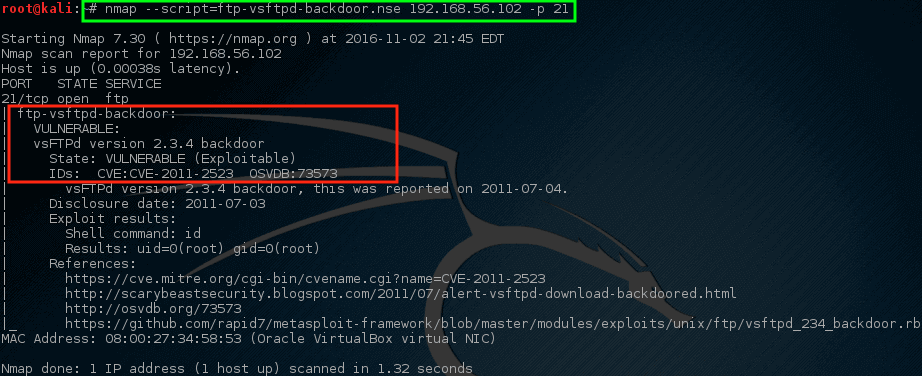
Let’s run the script and see what happens.
# nmap --script=ftp-vsftpd-backdoor.nse 192.168.56.102 -p 21
Yikes! Nmap’s script returned some dangerous news. This machine is likely a good candidate for a serious investigation. This doesn’t mean that the machine is compromised and being used for horrible/terrible things but it should bring some concerns to the network/security teams.
Nmap has the ability to be extremely selective and extremely quiet. Most of what has been done so far has attempted to keep nmap’s network traffic moderately quiet however scanning a personally owned network in this fashion can be extremely time-consuming.
Nmap has the ability to do a much more aggressive scan that will often yield much of the same information but in one command instead of several. Let’s take a look at the output of an aggressive scan (Do note – an aggressive scan can set off intrusion detection/prevention systems!).
Notice this time, with one command, nmap has returned a lot of the information it returned earlier about the open ports, services, and configurations running on this particular machine. Much of this information can be used to help determine how to protect this machine as well as to evaluate what software may be on a network.
This was just a short, shortlist of the many useful things that nmap can be used to find on a host or network segment. It is strongly urged that individuals continue to experiment with nmap in a controlled manner on a network that is owned by the individual (Do not practice by scanning other entities!).
There is an official guide on Nmap Network Scanning by author Gordon Lyon, available from Amazon.
Please feel free to post comments or questions (or even more tips/advice on nmap scans)!
Packages and Binaries:
This package contains a port scanning tool written in Go that allows you to enumerate valid ports for hosts in a fast and reliable manner. It is a really simple tool that does fast SYN/CONNECT scans on the host/list of hosts and lists all ports that return a reply. Main features are:
- Fast And Simple SYN/CONNECT probe based scanning.
- Optimized for ease of use and lightweight on resources
- Automatic handling of duplicate hosts between multiple subdomains
- NMAP Integration for service discovery
- Piped input / output support for integrating in workflows
- Multiple Output formats supported (JSON, File, Stdout)
- Multiple input support including HOST/IP/CIDR notation
Installed size: 11.44 MB
How to install: sudo apt install naabunaabu
[email protected]:~# naabu -h Naabu is a port scanning tool written in Go that allows you to enumerate open ports for hosts in a fast and reliable manner. Usage: naabu [flags] Flags: INPUT: -host string Host to scan ports for -list, -l string File containing list of hosts to scan ports -exclude-hosts, -eh string Specifies a comma-separated list of targets to be excluded from the scan (ip, cidr) -exclude-file, -ef string Specifies a newline-delimited file with targets to be excluded from the scan (ip, cidr) PORT: -port, -p string Ports to scan (80, 80,443, 100-200 -top-ports, -tp string Top Ports to scan (default top 100) -exclude-ports, -ep string Ports to exclude from scan -ports-file, -pf string File containing ports to scan for -exclude-cdn, -ec Skip full port scans for CDNs (only checks for 80,443) RATE-LIMIT: -c int General internal worker threads (default 25) -rate int Rate of port scan probe request (default 1000) OUTPUT: -o, -output string File to write output to (optional) -json Write output in JSON lines Format CONFIGURATION: -scan-all-ips Scan all the ips -scan-type, -s string Port scan type (SYN/CONNECT) (default "s") -source-ip string Source Ip -interface-list, -il List available interfaces and public ip -interface, -i string Network Interface to use for port scan -nmap Invoke nmap scan on targets (nmap must be installed) - Deprecated -nmap-cli string nmap command to run on found results (example: -nmap-cli 'nmap -sV') -r string Custom resolvers to use to resolve DNS names (comma separated or from file) OPTIMIZATION: -retries int Number of retries for the port scan probe (default 3) -timeout int Millisecond to wait before timing out (default 1000) -warm-up-time int Time in seconds between scan phases (default 2) -ping Use ping probes for verification of host -verify Validate the ports again with TCP verification DEBUG: -debug Enable debugging information -v Show Verbose output -no-color, -nc Don't Use colors in output -silent Show found ports only in output -version Show version of naabu -stats Display stats of the running scan