Disable secure boot y/n?
I have windows 10 installed. Im trying to install ubuntu. Should i turn off secure boot or leave it on? What does it do?
What machine are you using? Ubuntu has handled secure boot for 4 years, but vendors can do non-UEFI standard things which can mess things up.
Acer aspire e5-575g-53vg i think its a relatively new model so there might not be much up for it. I plan on multibooting 2 copies of windows 10, ubuntu,and steamOS. I searched google but all i could find was questions on if it was needed for older versions of ubuntu or different laptop models and noboy bothered to explain what its for either.
See ubuntuforums.org/showthread.php?t=2305965 for many specific Acer links in oldfred’s last entry #4
2 Answers 2
Secure Boot prevents from booting unsigned operational systems.
It allows to boot only systems that are signed with a key that is stored in UEFI.
Ubuntu kernels are signed and you can install Ubuntu with Secure Boot enabled, but there are some limitations if you use Secure Boot:
- You will not be able to install some 3rd party kernel modules (proprietary graphics and wireless drivers, any other custom built modules) that are not signed.
- Hibernation will not work.
Generally Secure Boot is not a very useful feature, because nowadays boot viruses are not an issue. Linux systems have other ways of protection from installing malware (root permissions).
The bottom line is that if you need unsigned modules, you do not lose much if you disable Secure Boot.
Ubuntu 16.04 — how can I disable Secure Boot?
I have Ubuntu 16.04 installed on a Dell 5470. I want to reinstall it due to some reasons. I want to boot from USB to reinstall Ubuntu. The problem is, I cannot access the BIOS and the boot menu due to Secure Boot. When I press F2 or F12 during startup the computer still boots into Ubuntu. I tried systemctl reboot —firmware-setup but I receive Cannot indicate to EFI to boot into setup mode: Operation not supported How can I boot from USB and reinstall Ubuntu?
Did you leave fast boot on in UEFI (not Windows fast start up)? If so you may not have enough time to press a key. The grub menuentry ‘System setup’ should work, if not try cold boot or remove all power, including battery if laptop, hold power switch for 10 sec or so to drain all remaining power and reboot pressing correct key to get into UEFI immediately. askubuntu.com/questions/652966/…
Thx, I have tried to remove the power, after that when I restart the PC, I press F2, and I can see that my PC can receive my input since the notice on the screen was changed from F2 to bios to prepare . . But still I cannot go into Bios /.\
3 Answers 3
There are several ways to boot into the firmware setup utility, some of which you seem to be aware of:
- Using a keypress at power-on time — Unfortunately, there’s next to no standardization as to what keypress will enter the setup tool. It’s usually Esc, Enter, or a function key (but which one varies wildly — it’s often F2, F8, or F10, but can be something else). Setting the firmware’s «fast start» feature sometimes disables this method of entry to the setup tool because that leaves USB ports uninitialized. If the computer has a PS/2 port, you may be able to work around this limitation by using a PS/2 keyboard.
- Using systemctl — The command you presented earlier, sudo systemctl reboot —firmware-setup , works on some computers; but it clearly isn’t working for you. Windows 8 and later offers a similar feature, so if you can boot into Windows, you could try it, on the off chance that it would work better.
- Using a boot manager’s reboot-to-setup feature — Some boot managers offer a feature to reboot into the setup utility. GRUB does (although it may not be active by default), as does my rEFInd boot manager (it’s active by default but can be disabled; and it will not appear if the computer lacks the necessary support), as well as gummiboot/systemd-boot (I don’t recall if it’s active by default). I’m not positive, but I suspect that this feature would work on precisely those computers on which the preceding method would work, so I wouldn’t hold out much hope of it working for you.
- Remove all other boot options — If an EFI-based computer can’t find any other boot loader, it will normally launch its setup utility. The best way to take advantage of this is usually to unplug all your hard disks (and your network cables, if your network supports network booting). Alternatively, you could delete your EFI System Partition (ESP) or delete or move all the boot loader files on it so that the firmware can’t find them. The trouble with this method is that restoring the system to its original state might not render it bootable again, since many EFIs delete their NVRAM-based references to boot options that become invalid. Thus, you might need to use Boot Repair, efibootmgr , or some other tool to re-install GRUB or re-create its NVRAM entry once you’re done.
BTW, chances are it’s not Secure Boot per se that’s preventing you from entering your firmware setup utility. (Although it could be that Dell linked Secure Boot to making it harder to enter the firmware, this type of linkage is not required of Secure Boot, and I’ve never encountered it myself.) It’s more likely that it’s the firmware’s «fast start» feature leaving the USB ports uninitialized that’s at the root of the problem. Another likely possibility is that you’re trying the wrong key or that you’re hitting it outside of the (often very narrow) window in which it will work. Ask on a Dell forum or check your documentation to learn what key to press, and try it several times, hitting it repeatedly as the computer starts up.
Disable Secure Boot in Ubuntu
In the latest releases, Ubuntu performs signature check for kernel modules before they are installed. Hence you need to load public key of kernel module into Ubuntu firmware so that it recognizes module’s signature.
Otherwise, here is the steps to disable Secure Boot in Ubuntu without reinstalling system. This is applicable especially if you have installed as VM.
Identify if secure boot is enabled or disabled on Ubuntu
The result of above command shows the status of SecureBoot if enabled or disabled.
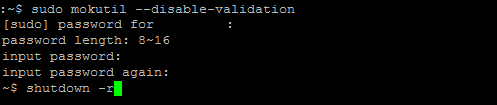
#1 Install mokutil to disable secure boot
$ sudo apt install mokutil
$ sudo mokutil –disable-validation
Note – double hypen before disable-validation
When asked for password, specify 12345678. For convenienceDo not create a complex password, as you have a trick in the following screen.
#2 Press Any key in Shim Signed Key Management
You get 10 seconds to respond and follow the screenshots to disable secure boot.
24/7/365 Technical Support, Free Site Building Tools, 4500 Website Templates, Free Shopping Cart Software, Ideal for WordPress, 45 Day Money Back Guarantee
High optimized WordPress hosting, secure firewall, HTTPS, Backup, hack-fix guarantee and many others at 30$ per month