- Tools to Access The Linux File System from Windows
- Differences between Windows and Linux file systems
- Read-Only Access to Linux Filesystem from Windows
- Read & Write Access to Linux Filesystem from Windows
- Как открыть диск Linux в Windows — подключение разделов ext4, ext3, ext2
- Ext2 File System Driver (Ext2Fsd) — самый простой способ открыть раздел ext4/ext3/ext2 в Windows
- Доступ к разделам Linux средствами Подсистемы Windows для Linux (WSL)
- Другие способы
- A Deep Dive Into How WSL Allows Windows to Access Linux Files
- Let’s jump in!
- How does this story fit in with WSL 2?
- What would you like to see next?
Tools to Access The Linux File System from Windows
One of the most popular problems with dual-booting Linux and Windows operating systems is the ability to access Windows files from within Linux but the inability of the reverse; this is due to the way Linux and Windows file systems are set up.
The point of today’s articles is to recommend the most reliable tools that you can install to easily access your Linux files from within your Windows installation. But first, you should know how the file system in Windows and Linux differ.
Differences between Windows and Linux file systems
- The Linux filesystem is case-sensitive so you can have file names like fossmint.html and Fossmint.html in the same directory. This can’t happen on Windows because the file system is not case-sensitive as sees both file names as the same.
- Windows file systems are in the FAT (FAT12, FAT16, and FAT32) and NTFS formats while Linux file systems are in Ext2, Ext3, Ext4, JFS, XFS, etc.
- Windows disks are partitioned and given letters e.g. C: for local disk and E: for a removable disk. In Linux, everything is under the root directory denoted by / and all devices are treated as files. E.g. /dev/cdrom for removable media.
- Linux doesn’t lock access to files as often as Windows and thus allows files to be deleted in situations wherein they wouldn’t be if the user was on Windows. For example, on Windows, you can’t delete a video file that was previously running a VLC without quitting the app. On Linux, you might even be able to delete the file while it’s still running in VLC.
So the most important home point is that while Linux has native support for Windows file systems i.e. NTFS and FAT, we need a 3rd party application to access Linux files from Windows.
These are the best tools available for free.
Read-Only Access to Linux Filesystem from Windows
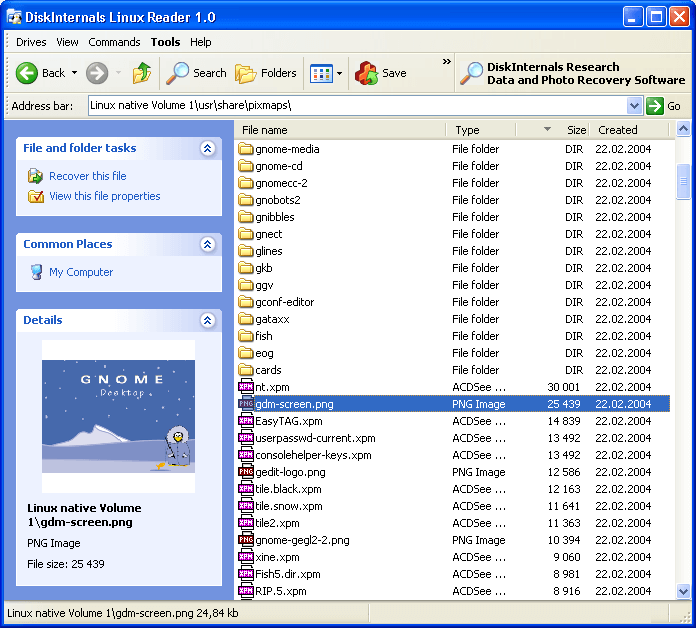
DiskInternals Linux Reader allows users safe and quick read-only access to Ext2, Ext3, and Ext4 Linux files using a UI similar to that of the default Windows Explorer to view and extract files. It is free software but offers a pro version with extra features.
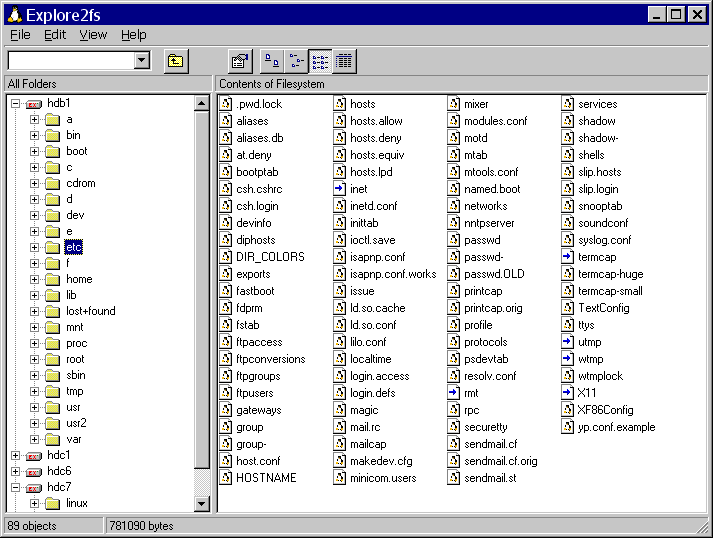
Explore2fs is a GUI drag& drop file explorer for Ex2 and Ex3 file systems. It runs on all Windows versions to allow users to read files but without the ability to make any changes.
Read & Write Access to Linux Filesystem from Windows
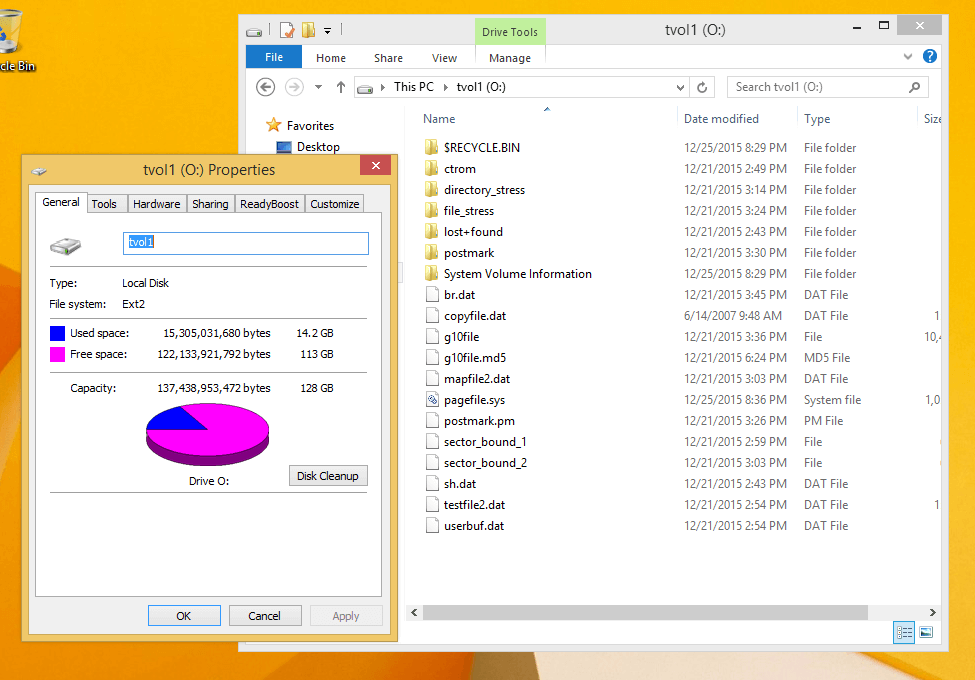
EX2 Installable File System for Windows is a freeware that provides Windows users will full read and write access to Linux Ext2 volumes by installing a pure kernel mode file system driver which extends the Windows file system to include the Ext2 file system.
With EX2 IFS, you can view Linux partitions in the disk management application and assign drive letters to them. Mind you, Ext2 Volume manager and Ext2 IFS need to be run with Compatibility mode enabled on Windows 8 and later.
Ext2Fsd is an open-source Linux Ext2 and Ext3 file system driver for all Windows versions with the option to access files in both read-only and read & write modes. However, Ext4 file systems load in read-only mode by default due to Ext2Fsd limited support.
Experts advise that accessing files from other operating systems is best done in read-only mode in other to avoid unfixable mistakes or data corruption. While the odds of such happening are slim in my opinion, always be careful when working with files. I’m not worried because it’s not the same as playing around in sever directories.
I hope this article is useful to you in getting on with your daily tasks. Do you already use any of the software on the list? Or do you have notable mentions to suggest? Add yours in the section below.
Как открыть диск Linux в Windows — подключение разделов ext4, ext3, ext2
В случае, если вам потребовался доступ из Windows к данным на разделе диска с файловой системой Linux — ext4/ext3/ext2, встроенными средствами системы сделать это не получится. Однако, возможности есть, причем реализовать это можно встроенными средствами системы или с помощью сторонних инструментов.
В этой инструкции подробно о способах подключить раздел диска в файловой системе Linux в Windows 11 и Windows 10 для доступа к данным на этом разделе как для чтения, так и для записи.
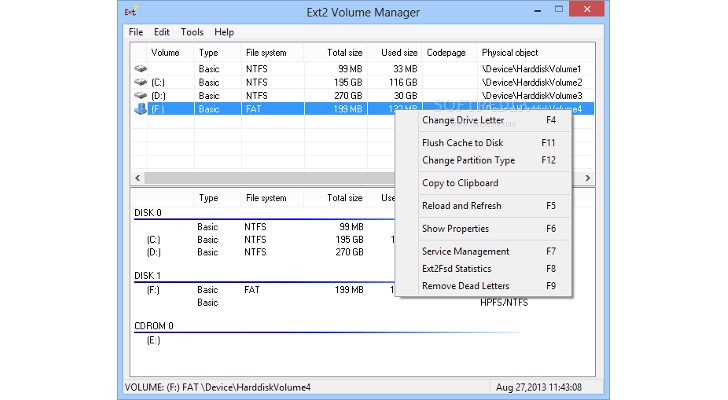
Ext2 File System Driver (Ext2Fsd) — самый простой способ открыть раздел ext4/ext3/ext2 в Windows
Ext2 File System Driver или Ext2Fsd — сторонний и полностью бесплатный драйвер для подключения разделов Linux во всех версиях Windows начиная с XP. Несмотря на название, поддерживаются не только разделы не только с файловой системой ext2, но и более новые ext4 и ext3.
Порядок использования Ext2 File System Driver для доступа к дискам Linux будет следующим:
- Загрузите установщик Ext2Fsd с сайта https://sourceforge.net/projects/ext2fsd/
- Установите драйвер, в параметрах установки как правило не требуется ничего изменять.
- По завершении установки вам будет предложено запустить Ext2 Volume Manager (менеджер томов), запустите его.
- Нажмите правой кнопкой мыши по разделу Linux ext4, ext3, ext2 и выберите пункт «Assign Drive Letter» — назначить букву диска.
- Для раздела будет автоматически назначена буква диска, и вы увидите раздел в Проводнике Windows с возможностью чтения и записи файлов на нём.
В дальнейшем вы тем же способом сможете удалить букву диска с раздела (опция «Change letter» — «Remove»).
Доступ к разделам Linux средствами Подсистемы Windows для Linux (WSL)
Подсистема Windows для Linux (WSL) также может быть использована для подключения дисков Linux в Windows таким образом, чтобы доступ к ним был возможен из проводника. Шаги будут следующими:
- Запустите командную строку, Терминал или PowerShell от имени администратора и по порядку введите команды
wsl --install wsl --set-default-version 2 dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:VirtualMachinePlatform /all /norestart wsl --install -d Ubuntu
sudo mkdir -p /mnt/ext-drives/
для создания папки, к которой будут монтироваться диски.
В консоли Windows (командная строка, терминал, Powershell) введите команду
wmic diskdrive list brief
В консоли Ubuntu введите команду lsblk — это отобразит список подключенных дисков, разделов на них и их размер. В следующей команде используем имя нужного раздела для монтирования:
sudo mount /dev/sdИМЯ /mnt/ext-drives/

В дальнейшем для отключения диска от WSL можно использовать ту же команду, которая использовалась на 5-м шаге, заменив mount на unmount.
Другие способы
Есть и другие программы (драйверы) для доступа к разделам Linux из Windows, но не полностью бесплатные. Среди них:
- DiskInternals Linux Reader — в бесплатной версии доступно только чтение данных с разделов.
- Paragon Linux File Systems for Windows — бесплатная работа в течение пробной версии, затем необходимо приобретать лицензию.
А вдруг и это будет интересно:
- Лучшие бесплатные программы для Windows
- Запуск драйвера для этого устройства заблокирован Код 48 — варианты решения
- Не работают Ctrl+C и Ctrl+V — варианты решения
- Интерфейс не поддерживается при открытии файлов в Windows 11 и Windows 10 — варианты решения
- RustDesk — удобная работа с удаленными рабочими столами
- Unable to load library dbdata.dll — как исправить?
- Windows 11
- Windows 10
- Android
- Загрузочная флешка
- Лечение вирусов
- Восстановление данных
- Установка с флешки
- Настройка роутера
- Всё про Windows
- В контакте
- Одноклассники
A Deep Dive Into How WSL Allows Windows to Access Linux Files
Three months ago, we announced that the Windows Subsystem for Linux will be able to access Linux files from Windows in the blog post: What’s new for WSL in Windows 10 version 1903, and in today’s post we will be showing you how we made these changes possible.
Let’s jump in!
We’re continuing our whiteboard series of deep dives (you can find the full list here) with a new video where Sven Groot and Craig Loewen explain the full architecture behind this new feature. You can expect to learn about how WSL currently accesses Linux files, how we’ve added a 9P file server into the init process of each Linux distro, and how Windows interacts with that 9P file server to interact with Linux files inside of your distro. So, grab a coffee and a snack, sit down, relax, and enjoy this look behind the scenes of WSL!
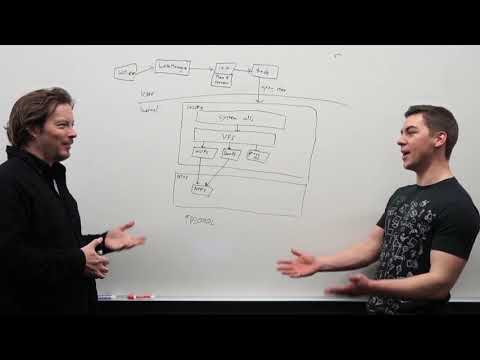
How does this story fit in with WSL 2?
We don’t explicitly mention WSL 2 in the video above as at the time of filming we were still finalizing the details behind WSL 2, and ultimately there are very little changes to our explanation of how Linux files are accessed from Windows with the new architecture. The only difference from the explanation in the video, is where the Linux files themselves are stored. In WSL 1, these Linux files are stored in the Windows drive (which uses the NT file system), while in WSL 2 these Linux files are stored in a virtual hard disk which uses the EXT4 file system. Every other detail on how the files are accessed remains the same.
What would you like to see next?
If you have more questions about how we use a 9P file server, accessing Linux files, or just about WSL in general you can find a list of our team members on twitter here! Please feel free to reach out to ask us any questions, and give suggestions on any other deep dives that you’d be interested in seeing.