- How To Start / Stop / Restart / Enable / Reload The Network Service In Linux?
- What Is Network Manager?
- 1) How To Start The Network Service In Linux?
- 2) How To Stop The Network Service In Linux?
- 3) How To Restart The Network Service In Linux?
- 4) How To Reload The Network Service In Linux?
- 5) How To View The Network Service Status In Linux?
- 6) How To Enable The Network Service On Boot In Linux?
- How To start/Stop/Restart Network Service on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- Starting Network Service in Ubuntu
- Stop Network Service in Ubuntu
- Restart Network Service in Ubuntu
- Checking Status of Networking Service
- Enabling Netowrk Service in Ubuntu
- Disabling Network Service in Ubuntu
- Conclusion
- How to Start/Stop/Restart Network Service on CentOS 8 or RHEL 8
- Method1: Using NetworkManager
- Method2: Using nmcli Tool
- Restarting, Starting, Stopping, Checking the Status of the Network Service in Linux
- Network Operations
- Stop Network Service
- Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
- Fedora and CentOS
- Start Network Service
- Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
- Fedora and CentOS
- Status Network Service
- Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
- Fedora and CentOS
- Restart Network
- Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
- Fedora and CentOS
How To Start / Stop / Restart / Enable / Reload The Network Service In Linux?
systemd is a new system and service manager for Linux system, which was implemented/adapted into all the major Linux distributions over the traditional SysV init systems due to lots of issue/improvement has to be on SysVinit systems.
All the service files are available on /etc/init.d/ directory for SysVinit system.
For systemd system, the service files are available on /usr/lib/systemd/system/ directory.
If you would like to perform any kind of actions like start, stop, restart, enable, reload & status against the specific service then use the following commands.
Make sure that you should have admin privileges to run these commands except status command. It should be root or sudo permission needed to run the below commands.
What Is Network Manager?
NetworkManager is a dynamic network control and configuration system that attempts to keep network devices and connections up and active when they are available.
NetworkManager can be used to configure the following types of connections: Ethernet, wireless, mobile broadband (such as cellular 3G), and DSL and PPPoE (Point-to-Point over Ethernet).
1) How To Start The Network Service In Linux?
Use the below commands to start the networking server in Linux.
For SysVinit Systems – RHEL based systems such as Redhat, CentOS and Fedora.
# service network start or # service NetworkManager start or # /etc/init.d/network start
For systemd Systems – RHEL based systems such as Redhat, CentOS and Fedora.
# systemctl start network or # systemctl start NetworkManager or # systemctl start network.service
For systemd Systems – Debian based systems such as Debian and Ubuntu.
# systemctl start networking or # systemctl start networking.service
2) How To Stop The Network Service In Linux?
Use the below commands to stop the networking server in Linux.
For SysVinit Systems – RHEL based systems such as Redhat, CentOS and Fedora.
# service network stop or # service NetworkManager stop or # /etc/init.d/network stop
For systemd Systems – RHEL based systems such as Redhat, CentOS and Fedora.
# systemctl stop network or # systemctl stop NetworkManager or # systemctl stop network.service
For systemd Systems – Debian based systems such as Debian and Ubuntu.
# systemctl stop networking or # systemctl stop networking.service
3) How To Restart The Network Service In Linux?
Use the below commands to restart the networking server in Linux.
For SysVinit Systems – RHEL based systems such as Redhat, CentOS and Fedora.
# service network restart or # service NetworkManager restart or # /etc/init.d/network restart
For systemd Systems – RHEL based systems such as Redhat, CentOS and Fedora.
# systemctl restart network or # systemctl restart NetworkManager or # systemctl restart network.service
For systemd Systems – Debian based systems such as Debian and Ubuntu.
# systemctl restart networking or # systemctl restart networking.service
4) How To Reload The Network Service In Linux?
Use the below commands to reload the networking server in Linux.
For SysVinit Systems – RHEL based systems such as Redhat, CentOS and Fedora.
# service network reload or # service NetworkManager reload or # /etc/init.d/network reload
For systemd Systems – RHEL based systems such as Redhat, CentOS and Fedora.
# systemctl reload network or # systemctl reload NetworkManager or # systemctl reload network.service
For systemd Systems – Debian based systems such as Debian and Ubuntu.
# systemctl reload networking or # systemctl reload networking.service
5) How To View The Network Service Status In Linux?
Use the below commands to view the networking server status in Linux.
For SysVinit Systems – RHEL based systems such as Redhat, CentOS and Fedora.
# service network status or # service NetworkManager status or # /etc/init.d/network status
For systemd Systems – RHEL based systems such as Redhat, CentOS and Fedora.
# systemctl status network or # systemctl status NetworkManager or # systemctl status network.service
For systemd Systems – Debian based systems such as Debian and Ubuntu.
# systemctl status networking or # systemctl status networking.service
6) How To Enable The Network Service On Boot In Linux?
Use the below commands to enable the networking server on boot in Linux.
For SysVinit Systems – RHEL based systems such as Redhat, CentOS and Fedora.
# chkconfig network on or # chkconfig NetworkManager on
For systemd Systems – RHEL based systems such as Redhat, CentOS and Fedora.
# systemctl enable network or # systemctl enable NetworkManager or # systemctl enable network.service
For systemd Systems – Debian based systems such as Debian and Ubuntu.
# systemctl enable networking or # systemctl enable networking.service
How To start/Stop/Restart Network Service on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
If you are working on a Ubuntu Linux system, and you may be need to set IP address for a given enternet interface or you need to change network settings by modifying networking configuration file called interfaces located in the /etc/network directory using your vim text editor. or you can use cat command to dispaly the content of the current networking configuration file, type:
$ sudo vim /etc/network/interfaces
devops@devops:~$ cat /etc/network/interfaces # interfaces(5) file used by ifup(8) and ifdown(8) auto lo iface lo inet loopback auto enp0s3 iface enp0s3 inet dhcp Starting Network Service in Ubuntu
If your network service daemon is stopped, and you may be need to start it by using the following command:
$ sudo systemctl start networking.service
$ sudo /etc/init.d/networking start
Stop Network Service in Ubuntu
If you wish to stop a network service in your Ubuntu or Debian Linux, and you can type the following comand:
$ sudo systemctl stop networking.service
$ sudo /etc/init.d/networking stop
Restart Network Service in Ubuntu
If you modified networking configuration in your Ubuntu system, and you need to restart its service by using the following command:
$ sudo systemctl restart networking.service
$ sudo /etc/init.d/networking restart
Checking Status of Networking Service
If you need to check the current status of networking service in your Ubuntu system, and you can issue the following command:
$ sudo systemctl status networking.service
$ sudo /etc/init.d/networking status
devops@devops:~$ sudo systemctl status networking.service networking.service - Raise network interfaces Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/networking.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (exited) since Tue 2019-10-08 02:59:03 EDT; 18min ago Docs: man:interfaces(5) Main PID: 1158 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Tasks: 0 (limit: 1121) CGroup: /system.slice/networking.service Oct 08 02:58:59 devops systemd[1]: Starting Raise network interfaces. Oct 08 02:59:03 devops systemd[1]: Started Raise network interfaces. Enabling Netowrk Service in Ubuntu
If you want to enable your network service at system boot on your Ubuntu system, and you can run the following command:
$ sudo systemctl enable networking.service
devops@devops:~$ sudo systemctl enable networking.service Synchronizing state of networking.service with SysV service script with /lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install. Executing: /lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install enable networking Disabling Network Service in Ubuntu
If you want to diable network service at system boot, just using the following command:
$ sudo systemctl disable networking.service
Conclusion
You should know that how to start/stop/restart/enable/disalbe network service in your Ubuntu or Debian L Linux system.
How to Start/Stop/Restart Network Service on CentOS 8 or RHEL 8
This post will guide you how to start or restart network service on the latest CentOS 8 or RHEL 8 Linux. How do I start, stop or restart network service in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.
In CentOS 8 or RHEL 8 Linux, you can not find network service scripts or there is no /etc/init.d/network or systemd network service. So you can not use systemctl start network.service to start network service or using /etc/init.d/network script to start or restart networking service. How to restart network in RHEL 8 Linux. You can use the following two methods to start or restart network service in RHEL 8 or CentOS 8.
Method1: Using NetworkManager
To start network service in RHEL 8 or CentOS 8, type the following command:
$ sudo systemctl start NetworkManager.service
To stop network service in RHEL 8 or CentOS 8, type the following command:
$ sudo systemctl stop NetworkManager.service
To restart network service on your RHEL 8 or CentOS 8, type:
$ sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager.service
Method2: Using nmcli Tool
You can also use nmcli tool to configure network interface in RHEL 8 or CentOS 8. and Nmcli is a NetworkManager command line interface. You can use this tool to configure a static IP address for a network interface or restart network service. type:
$ nmcli networking off $ nmcli networking on
Note: the off will disable all NetworkManager managerd network connections. and the on will start all connections.
From the RHEL 8 release notes:
Network scripts are deprecated in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 and they are no longer provided by default. The basic installation provides a new version of the ifup and ifdown scripts which call the NetworkManager service through the nmcli tool. In Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8, to run the ifup and the ifdown scripts, NetworkManager must be running.
Restarting, Starting, Stopping, Checking the Status of the Network Service in Linux
In Linux-based operating systems, information about network operations such as network settings, network commands or network configuration is included. In Linux operating systems, as everything is a file, network settings are also kept in files. The settings can be edited with any text editor or by various tools.
Network settings are located in the following files and directories.
/ etc / sysconfig / network file / etc / sysconfig / network-scripts directory / etc / hosts /etc/resolv.conf /etc/nsswitch.conf / etc / services
Each of the settings files is used for different operations. The files in the network-scripts directory are used for network settings. Network settings are eth0, eth1, etc. according to the network card in files starting with ifcfg. kept by names.
Inside the network settings;
DEVICE - Name of the network card. ONBOOT - The state that the network is activated at startup. BOOTPROTO - How to set network settings (static, dhcp, bootp). IPADDR - IP address. NETMASK - Network mask. BROADCAST - Broadcast address. GATEWAY - Specifies the gateway address.
It also has various settings such as MAC address, Network type. When you want to get IP using DHCP , it will be sufficient to write the DEVICE, BOOTPROTO and ONBOOT settings.
Network Operations
In Linux systems, we can use the following commands to examine the Stop, Start, Restart and Status of our Network services.
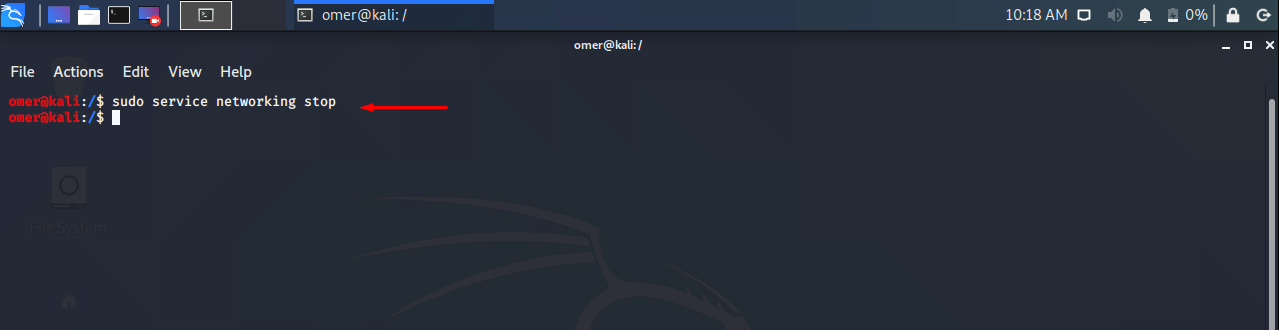
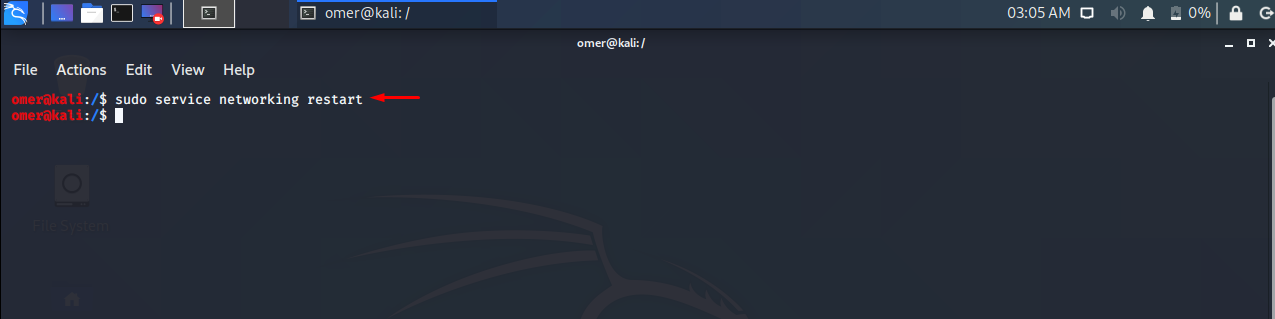
Stop Network Service
You can stop the network service as follows. Check before stopping the service. There will be a problem with your connection. We recommend that you try it in your test environment.
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali, Mint etc. We will use the networking stop command to service networking stop.
sudo service networking stop
Fedora and CentOS
Fedora and CentOS etc. We will use the networking stop command to systemctl stop network.target.
systemctl stop network.target
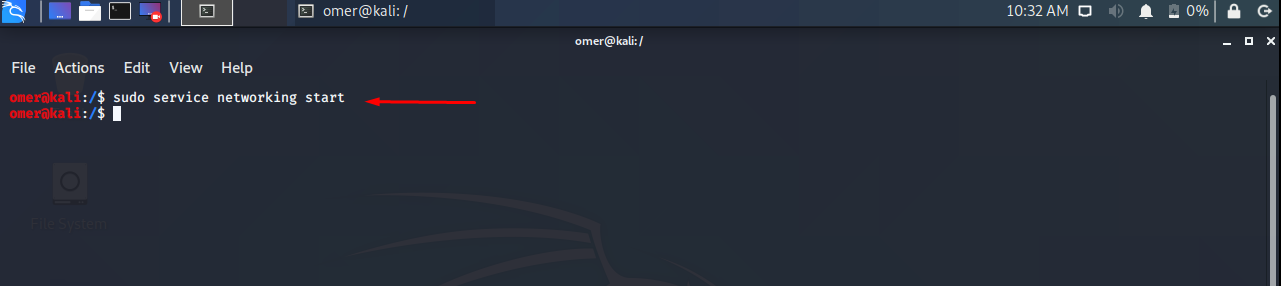
Start Network Service
You can start the network service as follows.
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali, Mint etc. We will use the networking start command to sudo service networking start.
sudo systemctl start NetworkManager-dispatcher.service
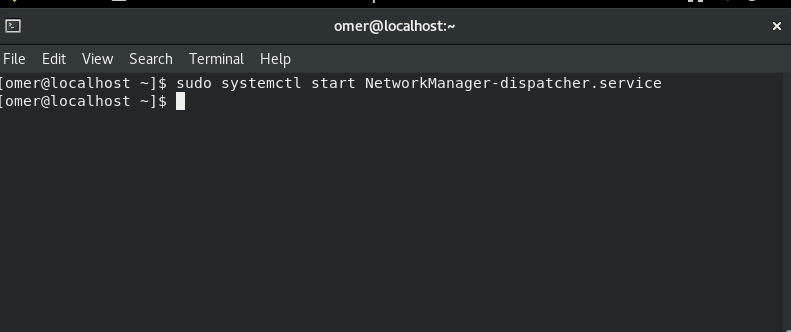
Fedora and CentOS
Fedora and CentOS etc. We will use the networking stop command to sudo systemctl start NetworkManager-dispatcher.service.
sudo systemctl start NetworkManager-dispatcher.service
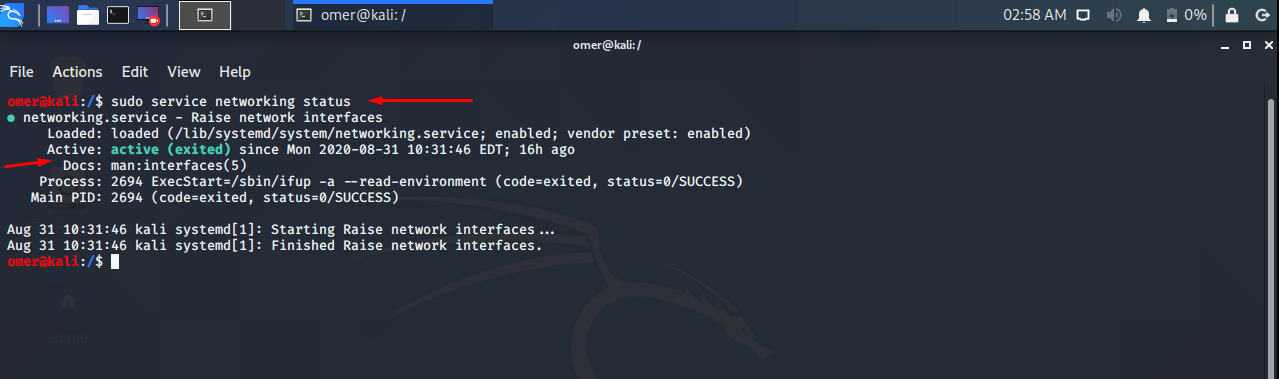
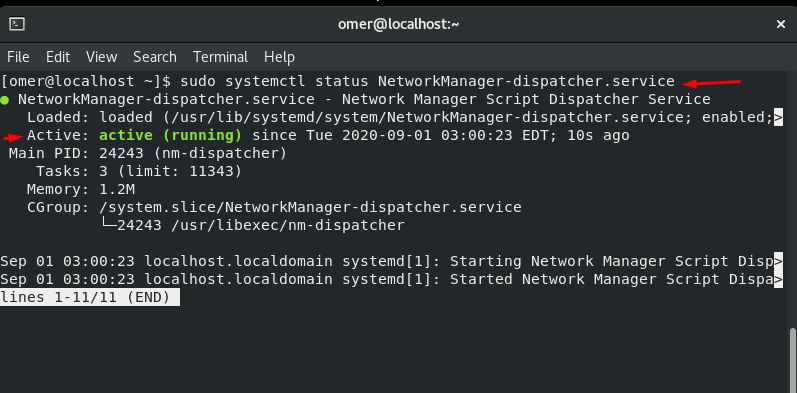
Status Network Service
You can status the network service as follows.
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali, Mint etc. We will use the networking start command to sudo service networking status.
sudo service networking status
Fedora and CentOS
Fedora and CentOS etc. We will use the networking stop command to sudo systemctl status NetworkManager-dispatcher.service.
sudo systemctl status NetworkManager-dispatcher.service
Restart Network
You can restart the network service as follows.
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali, Mint etc. We will use the networking start command to sudo service networking restart.
sudo service networking restart
Fedora and CentOS
Fedora and CentOS etc. We will use the networking stop command to sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager-dispatcher.service.
sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager-dispatcher.service