- How to correctly add a path to PATH?
- 12 Answers 12
- The simple stuff
- Where to put it
- Potential complications in some system scripts
- Notes on shells other than bash
- How to Add a Directory to PATH in Linux
- Adding a directory to PATH in Linux
- Making the changes to PATH permanent
- 💡See the path in a simplified view
- Bonus tip: The directories take precedence in PATH
- Was it clear enough?
- Переменная PATH в Linux
- Переменная PATH в Linux
- Выводы
How to correctly add a path to PATH?
I’m wondering where a new path has to be added to the PATH environment variable. I know this can be accomplished by editing .bashrc (for example), but it’s not clear how to do this. This way:
If there are already some paths added, e.g. PATH=$PATH:$HOME/.local/bin:$HOME/bin , another can be added by separating with a : e.g. PATH=$PATH:$HOME/.local/bin:$HOME/bin:/home/ec2-user/pear/bin .
12 Answers 12
The simple stuff
depending on whether you want to add ~/opt/bin at the end (to be searched after all other directories, in case there is a program by the same name in multiple directories) or at the beginning (to be searched before all other directories).
You can add multiple entries at the same time. PATH=$PATH:~/opt/bin:~/opt/node/bin or variations on the ordering work just fine. Don’t put export at the beginning of the line as it has additional complications (see below under “Notes on shells other than bash”).
If your PATH gets built by many different components, you might end up with duplicate entries. See How to add home directory path to be discovered by Unix which command? and Remove duplicate $PATH entries with awk command to avoid adding duplicates or remove them.
Some distributions automatically put ~/bin in your PATH if it exists, by the way.
Where to put it
Put the line to modify PATH in ~/.profile , or in ~/.bash_profile or if that’s what you have. (If your login shell is zsh and not bash, put it in ~/.zprofile instead.)
The profile file is read by login shells, so it will only take effect the next time you log in. (Some systems configure terminals to read a login shell; in that case you can start a new terminal window, but the setting will take effect only for programs started via a terminal, and how to set PATH for all programs depends on the system.)
Note that ~/.bash_rc is not read by any program, and ~/.bashrc is the configuration file of interactive instances of bash. You should not define environment variables in ~/.bashrc . The right place to define environment variables such as PATH is ~/.profile (or ~/.bash_profile if you don’t care about shells other than bash). See What’s the difference between them and which one should I use?
Don’t put it in /etc/environment or ~/.pam_environment : these are not shell files, you can’t use substitutions like $PATH in there. In these files, you can only override a variable, not add to it.
Potential complications in some system scripts
You don’t need export if the variable is already in the environment: any change of the value of the variable is reflected in the environment.¹ PATH is pretty much always in the environment; all unix systems set it very early on (usually in the very first process, in fact).
At login time, you can rely on PATH being already in the environment, and already containing some system directories. If you’re writing a script that may be executed early while setting up some kind of virtual environment, you may need to ensure that PATH is non-empty and exported: if PATH is still unset, then something like PATH=$PATH:/some/directory would set PATH to :/some/directory , and the empty component at the beginning means the current directory (like .:/some/directory ).
if [ -z "$" ]; then export PATH=/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin; fi Notes on shells other than bash
In bash, ksh and zsh, export is special syntax, and both PATH=~/opt/bin:$PATH and export PATH=~/opt/bin:$PATH do the right thing even. In other Bourne/POSIX-style shells such as dash (which is /bin/sh on many systems), export is parsed as an ordinary command, which implies two differences:
- ~ is only parsed at the beginning of a word, except in assignments (see How to add home directory path to be discovered by Unix which command? for details);
- $PATH outside double quotes breaks if PATH contains whitespace or \[*? .
So in shells like dash, export PATH=~/opt/bin:$PATH sets PATH to the literal string ~/opt/bin/: followed by the value of PATH up to the first space. PATH=~/opt/bin:$PATH (a bare assignment) doesn’t require quotes and does the right thing. If you want to use export in a portable script, you need to write export PATH=»$HOME/opt/bin:$PATH» , or PATH=~/opt/bin:$PATH; export PATH (or PATH=$HOME/opt/bin:$PATH; export PATH for portability to even the Bourne shell that didn’t accept export var=value and didn’t do tilde expansion).
¹ This wasn’t true in Bourne shells (as in the actual Bourne shell, not modern POSIX-style shells), but you’re highly unlikely to encounter such old shells these days.
How to Add a Directory to PATH in Linux
Learn all the essential steps about adding a directory to the PATH in Linux and making those changes permanently.
The PATH variable in Linux stores the path to the directories where it should look for executables when you run a command.
[email protected]:~$ echo $PATH /usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games:/snap/binAs you can see, the PATH consists of several directories (like /usr/local/sbin, /usr/bin and more) separated by a colon (:). If you want to run some executables as commands from anywhere in the system, you should add their location in the PATH variable. This is common while setting up a development environment. For example, imagine you downloaded and installed Java and Maven. To make your programs work properly, you’ll need to specify the location of the binaries of Maven and Java in the PATH. This quick tutorial is about setting up PATH in Linux. Apart from the steps, I’ll also mention things you should be careful about while dealing with PATH.
Adding a directory to PATH in Linux
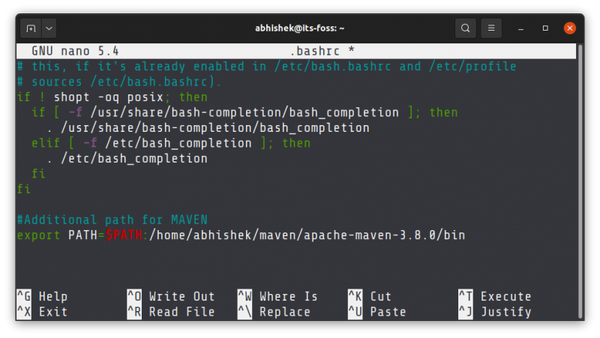
export PATH=$PATH:your_directoryWhere your_directory is the absolute path to the concerned directory. Let’s say you download and extract Maven to the home directory and you want to add its bin directory to the PATH. Let’s assume that the absolute path of this bin directory is /home/abhishek/maven/apache-maven-3.8.0/bin. Here’s what you should be doing: export PATH=$PATH:/home/abhishek/maven/apache-maven-3.8.0/bin
export PATH=$PATH:/home/abhishek/maven/apache-maven-3.8.0/bin- The $ before a variable name means you are referring to its value. PATH is the variable name, $PATH is the value of the variable PATH.
- You should not use $ with PATH on the left side of =
- There must not be any spaces before and after =
- Don’t forget to include the : after $PATH because the directories in the PATH are separated by a colon.
- There must not be a space before and after the colon (:).
Once you have set the PATH with the new value, please check that the PATH has been correctly updated.
[email protected]:~$ echo $PATH /usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games:/snap/bin:/home/abhishek/maven/apache-maven-3.8.0/binYou may want to run the command or script for which you modified the PATH. This will tell you for sure if the PATH is correctly set now.
Making the changes to PATH permanent
You added the desired directory to the PATH variable, but the change is temporary. If you exit the terminal, exit the session or log out from the system, the PATH will revert, and the changes will be lost.
If you want to make the changes to the PATH variable permanent for yourself, you can add it to the .bashrc file in your home directory, assuming you are using the Bash shell.
You can use a text editor like Nano or Vim for this task.
If you want the modified PATH variable to be available for everyone on the Linux system, you can add the export to the /etc/profile file. This is suitable when you are a sysadmin and have a configured system with a custom path.
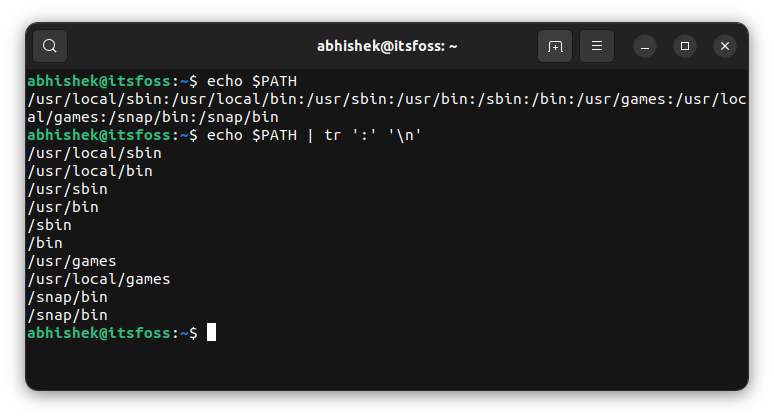
💡See the path in a simplified view
Reading the PATH variable values and figuring out the directories could be complicated for some people. You can use the tr command to format its output to make it more easily readable.
Bonus tip: The directories take precedence in PATH
There are several directories in the PATH variable. When you run an executable file/command, your system looks into the directories in the same order as they are mentioned in the PATH variable.
If /usr/local/sbin comes before /usr/bin, the executable is searched first in /usr/local/sbin. If the executable is found, the search ends and the executable is executed.
This is why you’ll find some examples where the additional directory is added before everything else in PATH:
export PATH=your_directory:$PATHIf you think that your additional directory should be searched before everything else you should add it before the $PATH; otherwise, add it after $PATH.
Was it clear enough?
I highly suggest reading up on the concept of absolute and relative paths in Linux. It will give you a better understanding of the topic.
I have tried to explain things with the necessary details but not going too deep into details. Does it make the topic clear, or are you more confused than before? If you still have doubts, please let me know in the comments.
Переменная PATH в Linux
Когда вы запускаете программу из терминала или скрипта, то обычно пишете только имя файла программы. Однако, ОС Linux спроектирована так, что исполняемые и связанные с ними файлы программ распределяются по различным специализированным каталогам. Например, библиотеки устанавливаются в /lib или /usr/lib, конфигурационные файлы в /etc, а исполняемые файлы в /sbin/, /usr/bin или /bin.
Таких местоположений несколько. Откуда операционная система знает где искать требуемую программу или её компонент? Всё просто — для этого используется переменная PATH. Эта переменная позволяет существенно сократить длину набираемых команд в терминале или в скрипте, освобождая от необходимости каждый раз указывать полные пути к требуемым файлам. В этой статье мы разберёмся зачем нужна переменная PATH Linux, а также как добавить к её значению имена своих пользовательских каталогов.
Переменная PATH в Linux
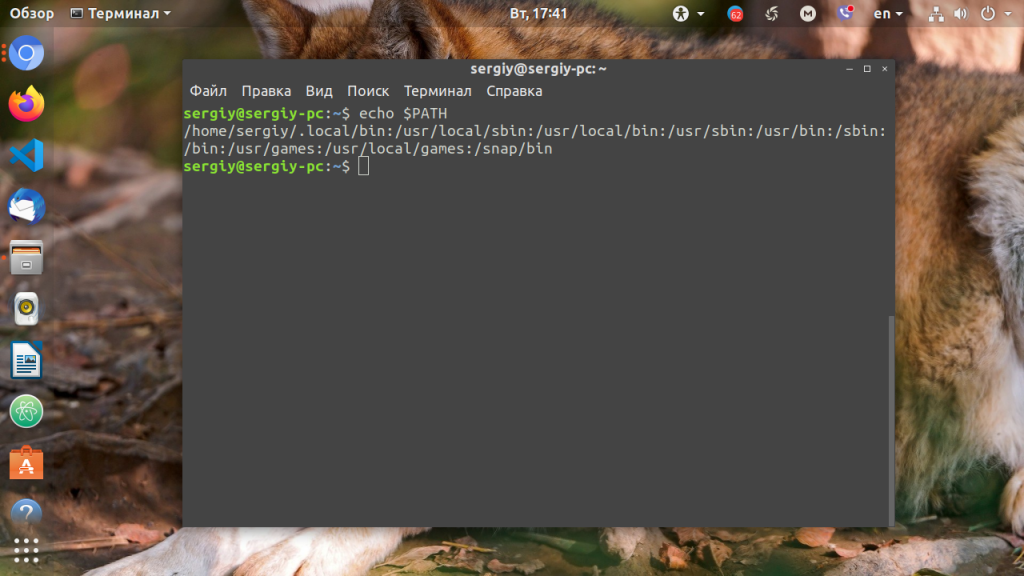
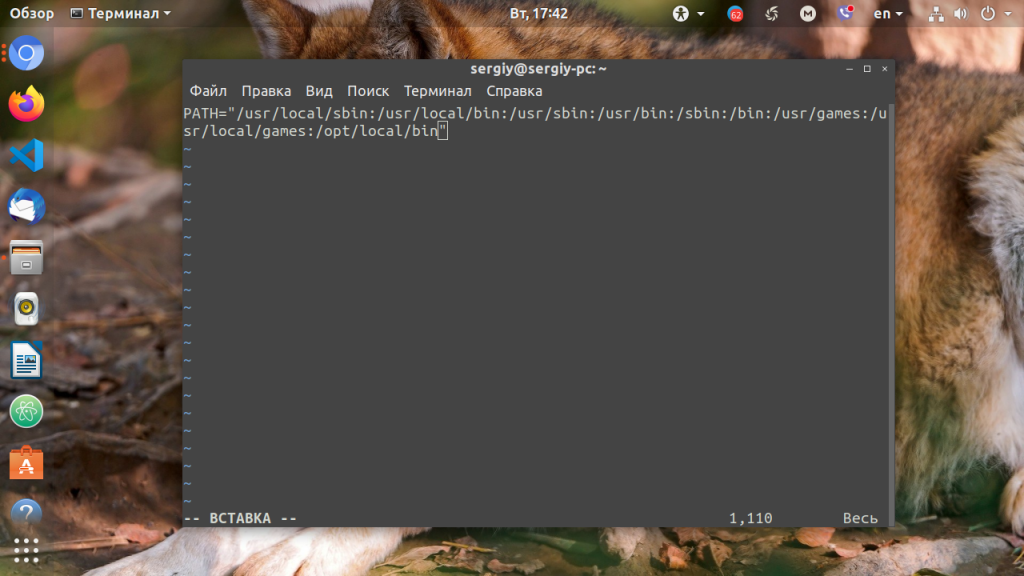
Для того, чтобы посмотреть содержимое переменной PATH в Linux, выполните в терминале команду:
На экране появится перечень папок, разделённых двоеточием. Алгоритм поиска пути к требуемой программе при её запуске довольно прост. Сначала ОС ищет исполняемый файл с заданным именем в текущей папке. Если находит, запускает на выполнение, если нет, проверяет каталоги, перечисленные в переменной PATH, в установленном там порядке. Таким образом, добавив свои папки к содержимому этой переменной, вы добавляете новые места размещения исполняемых и связанных с ними файлов.
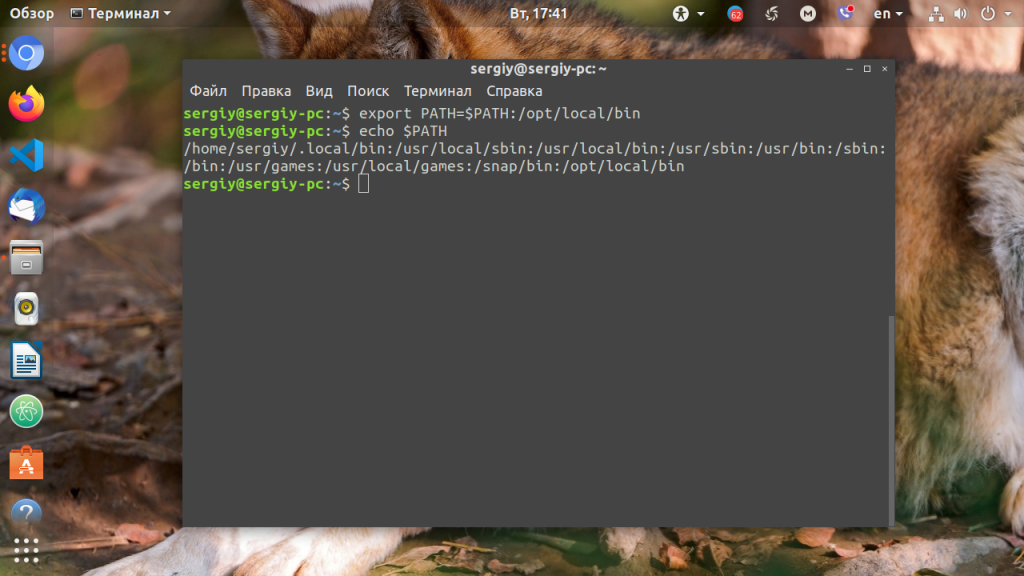
Для того, чтобы добавить новый путь к переменной PATH, можно воспользоваться командой export. Например, давайте добавим к значению переменной PATH папку/opt/local/bin. Для того, чтобы не перезаписать имеющееся значение переменной PATH новым, нужно именно добавить (дописать) это новое значение к уже имеющемуся, не забыв о разделителе-двоеточии:
Теперь мы можем убедиться, что в переменной PATH содержится также и имя этой, добавленной нами, папки:
Вы уже знаете как в Linux добавить имя требуемой папки в переменную PATH, но есть одна проблема — после перезагрузки компьютера или открытия нового сеанса терминала все изменения пропадут, ваша переменная PATH будет иметь то же значение, что и раньше. Для того, чтобы этого не произошло, нужно закрепить новое текущее значение переменной PATH в конфигурационном системном файле.
В ОС Ubuntu значение переменной PATH содержится в файле /etc/environment, в некоторых других дистрибутивах её также можно найти и в файле /etc/profile. Вы можете открыть файл /etc/environment и вручную дописать туда нужное значение:
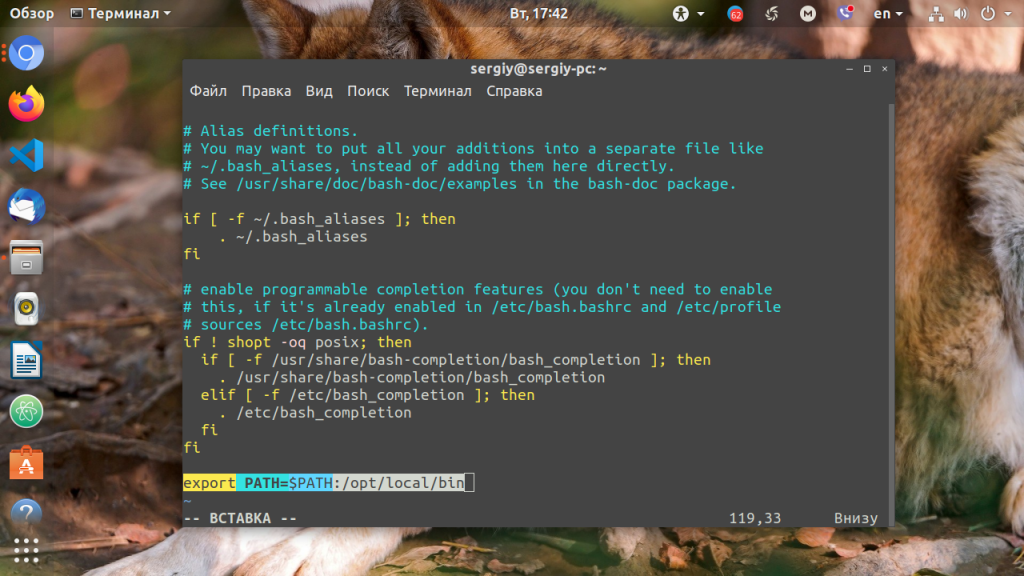
Можно поступить и иначе. Содержимое файла .bashrc выполняется при каждом запуске оболочки Bash. Если добавить в конец файла команду export, то для каждой загружаемой оболочки будет автоматически выполняться добавление имени требуемой папки в переменную PATH, но только для текущего пользователя:
Выводы
В этой статье мы рассмотрели вопрос о том, зачем нужна переменная окружения PATH в Linux и как добавлять к её значению новые пути поиска исполняемых и связанных с ними файлов. Как видите, всё делается достаточно просто. Таким образом вы можете добавить столько папок для поиска и хранения исполняемых файлов, сколько вам требуется.
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.